An RF scanner is a crucial tool for modern automotive repair, streamlining diagnostics and parts management. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers expert insights and resources to help you understand and utilize RF scanners effectively. By using the right scanner, automotive professionals can greatly improve efficiency and accuracy.
Contents
- 1. What Is an RF Scanner?
- 1.1. Other Names for RF Scanners
- 1.2. Purpose of RF Scanners
- 2. Why Use an RF Scanner?
- 2.1. RF vs. RFID: Key Differences
- 3. Industries Using RF Scanning
- 4. Components of an RF Scanning System
- 4.1. How RF Scanning Works
- 4.2. Types of Labels Read by RF Scanners
- 5. RF Scanning in Warehousing
- 5.1. Receiving Goods
- 5.2. Order Picking
- 5.3. Quality Control
- 5.4. Equipment Tracking
- 5.5. Order Confirmation
- 5.6. Storage Utilization
- 5.7. Inventory Management
- 6. How to Use an RF Scanner
- 6.1. Receiving Goods with an RF Scanner
- 6.2. Picking Orders with an RF Scanner
- 7. Benefits of RF Scanners
- 7.1. Better Storage Utilization
- 7.2. Reduced Errors
- 7.3. Lower Costs
- 7.4. Better Inventory Control
- 7.5. Improved Productivity
- 8. Types of RF Scanners
- 8.1. Types by Technological Sophistication
- 8.1.1. Laser RF Scanners
- 8.1.2. Image Scanners
- 8.1.3. Mobile Computers
- 8.2. Types by Form
- 8.2.1. Handheld RF Scanners
- 8.2.2. Wearable RF Scanners
- 8.2.3. Presentation RF Scanners
- 8.2.4. Encounter RF Scanners
- 8.2.5. Fixed-Mount RF Scanners
- 8.2.6. Vehicle-Mount RF Scanners
- 9. RF Scanner Costs
- 10. How to Choose an RF Scanner
- 10.1. Budget
- 10.2. Desired Capabilities
- 10.3. Number of Items Handled
- 10.4. Scanning Frequency
- 10.5. Scanning Range
- 10.6. Type of Scanned Items
- 10.7. Scanning Environment
- 11. Frequently Asked Questions About RF Scanners
- 11.1. How Does Barcode Size Impact Scanning Distance?
- 11.2. Are All Barcode Scanners the Same?
- 11.3. What Are “Rugged” Barcode Scanners?
- 12. Streamline Your Auto Repair Process with Advanced Scanner Technology
- 12.1. Benefits of Consulting with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 12.2. Ready to Get Started?
1. What Is an RF Scanner?
An RF scanner, often called a barcode scanner or RF terminal, is a handheld device used to automatically enter data about physical items into computer systems. This allows for efficient logging, tracking, and management of items.
1.1. Other Names for RF Scanners
RF scanners are also known by various names, including:
- RF terminals
- Barcode scanners
- Handheld barcode readers
- Data collection terminals
1.2. Purpose of RF Scanners
RF scanners bridge the gap between warehouse management systems (WMS) and human workers, automating the process of directing workers to their next tasks. According to a study by the University of Michigan’s Transportation Research Institute in 2022, automating data entry reduces errors by up to 60%.
 Wireless RF scanner scanning a barcode with a red laser beam
Wireless RF scanner scanning a barcode with a red laser beam
2. Why Use an RF Scanner?
Using RF scanners offers numerous benefits, particularly in automotive repair environments. Here are some key advantages:
- Versatility: RF scanning can be used for various operations, including picking, put-away, stock replenishment, and shipping and receiving.
- Paperless Option: Reducing paper usage saves time and reduces waste, aligning with sustainability efforts.
- More Accurate Picking: RF scanning systems automatically update in regular intervals, ensuring greater accuracy in stock levels and item movements.
- Reduced Errors: Immediate display of scan results allows for quick error detection.
- Custom Implementation Flexibility: RF scanning can be used alone or in concert with other technologies like RFID scanning and voice-picking.
2.1. RF vs. RFID: Key Differences
While the terms RF and RFID are often used interchangeably, they have key differences:
| Feature | RF | RFID |
|---|---|---|
| Stands For | Radio Frequency | Radio Frequency Identification |
| Scanning Range | Requires Line-of-Sight | Doesn’t Need Physical Contact or Line-of-Sight |
| Basics | Reads Barcode Labels with Lasers | Identifies Tags Attached to Items Using Radio Waves |
| Scanning Efficiency | Scans One Item at a Time | Scans Many Items Simultaneously |
| Expense | Cheaper | More Expensive |
| Information Capacity | Less Information Conveyed | More Information Conveyed |
| Security | Less Secure | More Secure |
| Power Source | None | Battery-Powered or Passive |
| Interference | Less Prone to Outside Interference | Prone to Interference (e.g., from Metals and Liquids) |
3. Industries Using RF Scanning
RF scanning isn’t limited to warehouses; it is used across various industries:
- Retail and grocery (Point-of-Sale transactions)
- Sales and marketing (Customer loyalty programs)
- Healthcare (Patient admission and medication verification)
- Manufacturing (Inventory management and asset tracking)
- Logistics and parcel delivery (Item scanning and fleet management)
- Food (Tracking from farm to table)
- Utilities (Meter readings)
- Education (Asset tracking and staff communication)
- E-commerce (Order fulfillment)
- Military (Weapons and equipment tracking)
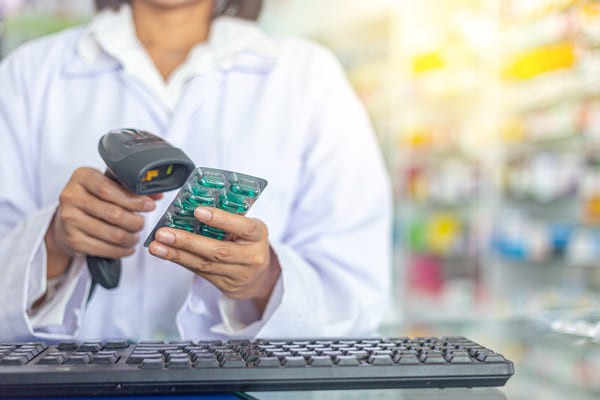 Pharmacist using a handheld RF scanner to scan a package of pills
Pharmacist using a handheld RF scanner to scan a package of pills
4. Components of an RF Scanning System
An effective RF scanning system includes:
- Barcodes or Labels: Attached to goods with embedded information.
- Mobile RF Scanner Device: Links workers to the warehouse management system.
- Wireless Network Connection: Radio frequency, Wi-Fi, 3G, 4G, or 5G systems for data transfer.
- Wireless Access Point: Receives the radio signal from the scanner.
- Server and Database: Digitally holds inventory, orders, and shipping data.
- Warehouse Management System (WMS): Software system acting as the warehouse’s brain, managing inventory and locations.
4.1. How RF Scanning Works
RF scanners use a light source to illuminate the barcode with red light. The scanner’s sensor detects the reflected light, generating an analog signal sent to a decoder. The decoder:
- Receives the analog signal
- Interprets and validates the signal
- Converts the signal to text and sends it to the computer system
The WMS compares the received data to its database to verify the item’s identity and determine the next steps.
 RF scanner projecting a red laser light into the sky
RF scanner projecting a red laser light into the sky
4.2. Types of Labels Read by RF Scanners
- One-Dimensional Scanners: Read basic barcodes like UPCs.
- Two-Dimensional Scanners (Image Scanners): Read basic barcodes and 2D barcodes, including QR codes.
5. RF Scanning in Warehousing
In warehousing, RF scanning is used for:
5.1. Receiving Goods
Workers scan each item as it’s offloaded, and the WMS compares the scanned data to what’s on file.
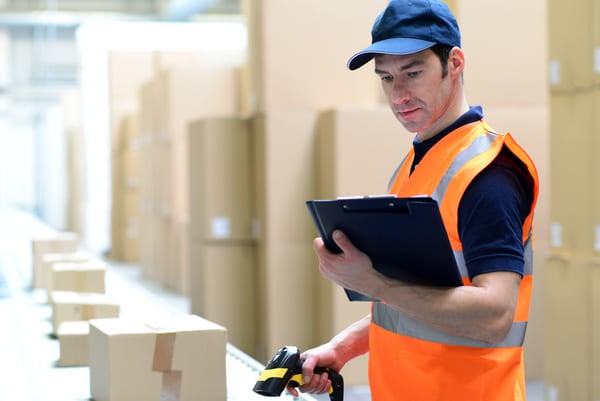 Warehouse worker in an orange safety vest scanning a box with an RF scanner while looking at a clipboard
Warehouse worker in an orange safety vest scanning a box with an RF scanner while looking at a clipboard
5.2. Order Picking
RF scanners reduce errors by directing workers to the correct aisle, communicating the quantity to pick, and indicating where each item should be sent.
5.3. Quality Control
Workers scan items to quickly identify defective products, check expiration dates, and ensure timely shipment.
5.4. Equipment Tracking
Barcodes and scanners monitor equipment use and maintenance, quickly identifying parts needed for repairs.
![]() Hand holding an RF scanner pointed at a forklift
Hand holding an RF scanner pointed at a forklift
5.5. Order Confirmation
The scanner/WMS sends confirmation notifications to suppliers upon scanning incoming shipment barcodes.
5.6. Storage Utilization
RF scanners track inventory to provide data on warehouse storage space utilization, improving storage density.
 Warehouse aisle lined with pallet racking, pallets, and boxes
Warehouse aisle lined with pallet racking, pallets, and boxes
5.7. Inventory Management
RF units help maintain a digital log of what’s in the facility and its location, making inventory management more efficient and accurate.
6. How to Use an RF Scanner
Using an RF scanner involves understanding its buttons and functions. The process may vary between models but generally includes:
- Replacing the battery
- Powering the unit on
- Moving between screens
- Scrolling up, down, and side-to-side
- Scanning and entering data manually
- Displaying options using function keys
- Selecting options
- Correcting mistakes
6.1. Receiving Goods with an RF Scanner
- Get the bill of lading and packing list from the delivery driver.
- Log into the scanner (enter username and password, if prompted).
- Select the correct activity: “Receiving.”
- Scan the “transfer order” barcode on the packing list.
- Scan the item’s barcode.
- Confirm receipt of the correct quantity when prompted by the scanner.
- Use a marker to cross through the barcode on the received box.
- Continue scanning until all items are received.
- Update the statuses of any missing shipments in the scanner.
6.2. Picking Orders with an RF Scanner
- Prepare the scanner with a freshly charged battery.
- Turn the scanner on and sign in with your username and password.
- Choose the “outbound” warehousing process.
- Choose the “picking” warehousing process.
- Move to the aisle containing the specific section of shelving where the first item to be picked is.
- Scan the barcode attached to the shelving.
- Scan the barcode attached to the item.
- Enter the quantity picked into the scanner.
- Place the item in the storage container indicated by the scanner.
- Scan the barcode attached to the storage container.
- Move to the next item to pick as indicated by the scanner.
- Complete the previous steps until all picks are made.
7. Benefits of RF Scanners
7.1. Better Storage Utilization
RF scanners enable warehouse operators to track stored goods, making informed decisions about space allocation and adopting storage models like “random storage.”
 Empty warehouse with rows of unused pallet racking
Empty warehouse with rows of unused pallet racking
7.2. Reduced Errors
Replacing pen-and-paper systems with RF scanning reduces manual data entry, minimizing errors. Critical information is held digitally in the WMS and updated with each scan.
7.3. Lower Costs
RF scanning offers long-term cost savings by:
- Reducing the number of workers doing manual tasks
- Eliminating redundant administrative tasks
- Reducing costs associated with inventory and shipping mistakes
- Reducing seasonal labor costs
- Verifying inventory levels remotely
- Training workers faster
- Reducing overtime pay
- Lowering capital investment compared to other systems
- Capturing additional revenues by adjusting for market price fluctuations
7.4. Better Inventory Control
RF scanning makes inventory management easier and more accurate by:
- Providing instant knowledge of product locations and quantities
- Recording all product movements
- Enabling product traceability back to the manufacturer
- Potentially eliminating the need for manual inventory counts
- Automatically updating and checking for errors
7.5. Improved Productivity
Automating inventory tracking with RF scanning dramatically improves productivity by:
- Handling more orders and shipments
- Eliminating guesswork in item placement
- Tracking employee productivity
- Automatically assigning tasks to workers by zones
- Improving mobility with wireless technologies
8. Types of RF Scanners
RF scanners can be categorized by technology and form.
8.1. Types by Technological Sophistication
8.1.1. Laser RF Scanners
Laser scanners use light from a laser beam to read barcode information. They are suitable for handling consumer goods with frequent price changes.
 Wireless RF scanner scanning a barcode with a red laser beam
Wireless RF scanner scanning a barcode with a red laser beam
Advantages of Laser RF Scanners
- Cheapest type of RF scanner
- Simple to operate
- Scan distances up to 24 inches
- Can be powered by a cord or battery
Disadvantages of Laser RF Scanners
- Can only read 1D barcodes
- Can have difficulty reading damaged barcodes
- More susceptible to damage
8.1.2. Image Scanners
Image scanners use a digital camera to capture an image of a barcode and can scan both 1D and 2D barcodes.
 Worker using an RF scanner to scan a smartphone screen
Worker using an RF scanner to scan a smartphone screen
Advantages of Image Scanners
- Work with more barcode types
- Can scan barcodes on computer and smartphone screens
- Can read barcodes from any angle
- Work on smaller barcodes
- More durable than laser scanners
- Can read damaged barcodes better
Disadvantages of Image Scanners
- More expensive than 1D laser scanners
8.1.3. Mobile Computers
Mobile computers combine barcode scanning capabilities with computer processing power.
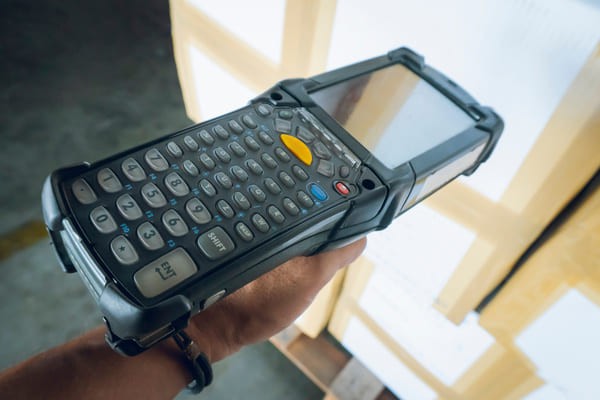 Closeup of a mobile computer scanning a box barcode
Closeup of a mobile computer scanning a box barcode
Advantages of Mobile Computers
- Most powerful of all RF scanners
- Can scan a large variety of barcodes and labels
- Captures digital images and allows instant updates
- Compatible with wireless technologies like Wi-Fi, 3G, and 4G networks
- Can save scanned data offline
- Can be ruggedized
Disadvantages of Mobile Computers
- More expensive than basic barcode scanners
- Potential vulnerability to security threats when uploading data to the cloud
8.2. Types by Form
8.2.1. Handheld RF Scanners
These are the most common type due to their ease of use.
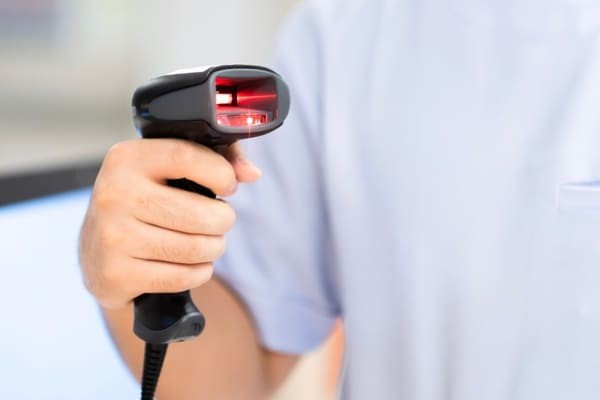 Person holding a handheld RF scanner with a red light projecting out
Person holding a handheld RF scanner with a red light projecting out
8.2.2. Wearable RF Scanners
Wearable scanners are valued for their lightweight, ergonomic design.
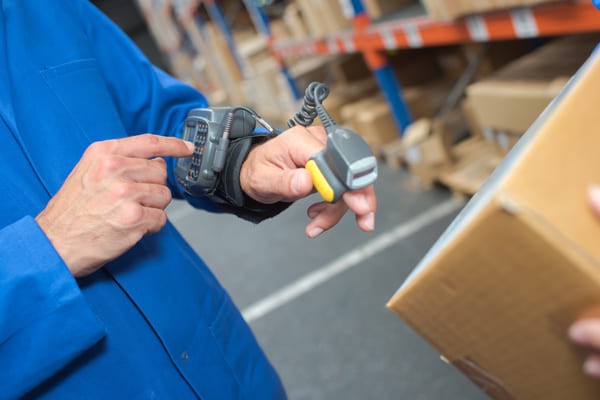 Warehouse worker pressing buttons on a wearable RF scanner
Warehouse worker pressing buttons on a wearable RF scanner
8.2.3. Presentation RF Scanners
Stationary scanners that scan items placed in front of them.
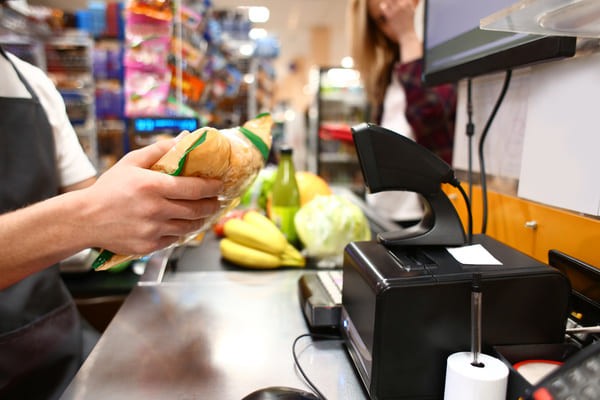 Grocery store worker ringing up an item using a presentation RF scanner
Grocery store worker ringing up an item using a presentation RF scanner
8.2.4. Encounter RF Scanners
Mounted scanners designed to scan items swiped across the reader.
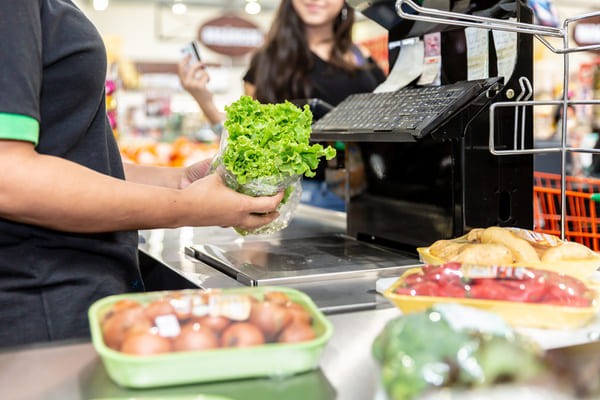 Grocery store worker scanning produce using an RF scanner
Grocery store worker scanning produce using an RF scanner
8.2.5. Fixed-Mount RF Scanners
Designed to scan items automatically at high speeds, often integrated into conveyor systems.
 Box moving down a conveyor belt with a laser beam surrounding it
Box moving down a conveyor belt with a laser beam surrounding it
8.2.6. Vehicle-Mount RF Scanners
Mounted on vehicles like forklifts, allowing workers to scan items directly from their vehicle.
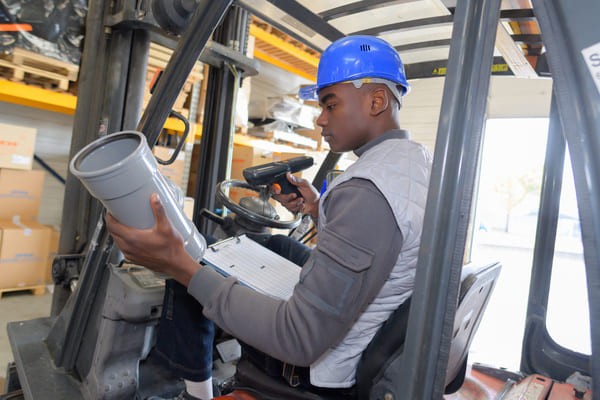 Forklift operator using an RF scanner to scan an item in a loading dock
Forklift operator using an RF scanner to scan an item in a loading dock
9. RF Scanner Costs
RF scanner prices vary widely. Basic handheld 1D laser scanners can be found for around $13.98, while new handheld 2D image scanners cost around $29. Mobile computers range from $600 to over $2,500 for ruggedized models.
10. How to Choose an RF Scanner
Choosing the right RF scanner involves considering:
10.1. Budget
Determine what you can afford and balance it with the capabilities you need.
 Person typing on a calculator on a desk
Person typing on a calculator on a desk
10.2. Desired Capabilities
Assess the sophistication you need based on your specific requirements.
10.3. Number of Items Handled
Simpler scanners may suffice for small warehouses, while larger operations may benefit from a network of mobile computers.
10.4. Scanning Frequency
Consider battery life for long scanning periods and whether wired power is an option.
10.5. Scanning Range
Determine whether workers need wireless options for mobility.
10.6. Type of Scanned Items
Ensure the scanner is compatible with the labels or tags you use.
10.7. Scanning Environment
Consider durability based on the work environment and potential exposure to harsh conditions.
For expert advice on selecting the right RF scanning system for your automotive repair needs, contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or call +1 (641) 206-8880.
11. Frequently Asked Questions About RF Scanners
11.1. How Does Barcode Size Impact Scanning Distance?
Larger barcodes are needed for greater scanning distances to ensure readability.
 Group of barcodes
Group of barcodes
11.2. Are All Barcode Scanners the Same?
No, different scanners read different types of barcodes. Laser scanners read 1D barcodes, while 2D scanners read both 1D and 2D barcodes.
11.3. What Are “Rugged” Barcode Scanners?
Rugged scanners are designed to withstand harsh conditions and are sealed to guard against drops, extreme temperatures, water, shock, and dust.
12. Streamline Your Auto Repair Process with Advanced Scanner Technology
Navigating the world of RF scanners can be complex, but CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to assist. Do you want to improve your auto repair operations? Our team provides personalized guidance to find the perfect tools for your unique needs.
Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert assistance:
- Address: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
12.1. Benefits of Consulting with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- Expert Guidance: Our experienced professionals provide tailored advice to match your specific requirements.
- Wide Selection: We offer an extensive range of RF scanners and automotive tools to fit any budget.
- Latest Technology: Stay updated with the latest innovations in scanning technology.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Learn how to streamline your auto repair processes and maximize productivity.
- Reliable Support: We are committed to providing ongoing support and answering any questions you may have.
12.2. Ready to Get Started?
Don’t delay optimizing your auto repair process! Reach out to us via WhatsApp, visit our website, or come see us in person at our location. We are committed to improving the accuracy and speed of your auto repair operations with the best RF scanner solutions. Get the tools you need to thrive in today’s competitive market by contacting CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN now!
Take Action Now:
- Send us a message on WhatsApp
- Explore our website for more information
- Visit us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN – Your trusted partner for superior automotive tools and expert advice.