OBD car systems are vital for modern vehicle diagnostics, providing access to crucial data about a car’s health and performance, and CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to simplify that process. By understanding OBD systems, you can streamline maintenance, troubleshoot issues effectively, and potentially save money on repairs. Dive in to explore the evolution, standards, and practical applications of OBD technology and find the tools and resources you need at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN. Discover how scan tools and diagnostic information empower informed car care.
Contents
- 1. What Is an OBD Car and How Does It Work?
- 1.1. Breaking Down the OBD System: Key Components and Functions
- 1.2. The Evolution of OBD: From Basic Monitoring to Comprehensive Diagnostics
- 1.3. OBD-II: The Standard for Modern Vehicle Diagnostics
- 2. What Are the Benefits of Using an OBD Car System?
- 2.1. Proactive Maintenance: Catching Problems Early
- 2.2. Accurate Diagnostics: Pinpointing the Source of Problems
- 2.3. Cost Savings: Avoiding Expensive Repairs
- 2.4. Improved Fuel Efficiency: Optimizing Engine Performance
- 2.5. Reduced Emissions: Contributing to a Cleaner Environment
- 3. What Are the Key Components of an OBD Car System?
- 3.1. Sensors: Monitoring Vital Parameters
- 3.2. Engine Control Unit (ECU): The Brain of the System
- 3.3. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Identifying Problems
- 3.4. Data Link Connector (DLC): Accessing the System
- 4. What Are the Different Types of OBD Scanners Available?
- 4.1. Basic OBD Scanners: Reading and Clearing Codes
- 4.2. Enhanced OBD Scanners: Live Data and Advanced Functions
- 4.3. Wireless OBD Adapters: Smartphone Connectivity
- 4.4. Professional Scan Tools: Comprehensive Diagnostic Capabilities
- 4.5. Comparison of OBD Scanner Types
- 5. How to Choose the Right OBD Scanner for Your Needs?
- 5.1. Determine Your Diagnostic Needs
- 5.2. Consider Compatibility with Your Vehicle
- 5.3. Evaluate Features and Functions
- 5.4. Read Reviews and Compare Brands
- 5.5. Set a Budget
- 6. What Are Common OBD Car Codes and What Do They Mean?
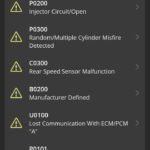
- 6.1. P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 6.2. P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- 6.3. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 6.4. P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
- 6.5. P0505: Idle Air Control System Malfunction
- 6.6. Interpreting OBD Codes: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 7. Where Can You Find More Information and Resources About OBD Car Systems?
- 7.1. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN: Your Comprehensive Resource for Automotive Tools and Information
- 7.2. Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE): Standards and Publications
- 7.3. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Regulations and Compliance
- 7.4. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Global Standards for Automotive Technology
- 7.5. Automotive Repair Manuals: Detailed Diagnostic and Repair Procedures
- 8. What Are the Future Trends in OBD Car Technology?
- 8.1. Enhanced Data Logging and Analytics
- 8.2. Wireless Connectivity and Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 8.3. Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
- 8.4. Cybersecurity Enhancements
- 8.5. Standardization and Interoperability
- 9. How Can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Help You with Your OBD Car Needs?
- 9.1. Wide Selection of OBD Scanners and Diagnostic Tools
- 9.2. Expert Advice and Technical Support
- 9.3. Detailed Product Reviews and Comparisons
- 9.4. Informative Articles and Guides
- 9.5. Contact Us for Personalized Assistance
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD Car Systems
- 10.1. What Type of OBD Scanner Is Right for My Car?
- 10.2. Where Can I Purchase a Reliable OBD Car Scanner?
- 10.3. What Does the Check Engine Light Indicate?
- 10.4. How Can I Interpret OBD Codes?
- 10.5. Can I Fix OBD-Related Issues Myself?
- 10.6. How Often Should I Scan My Car’s OBD System?
- 10.7. What Is the Difference Between OBD-I and OBD-II?
- 10.8. Can an OBD Scanner Improve My Car’s Performance?
- 10.9. Are Wireless OBD Adapters Safe to Use?
- 10.10. Where Can I Find a Professional Mechanic to Diagnose OBD Issues?
1. What Is an OBD Car and How Does It Work?
An OBD (On-Board Diagnostics) car utilizes an electronic system that monitors various vehicle components and reports diagnostic information, enabling mechanics and car owners to identify issues and maintain optimal performance. This system, initially designed to monitor emissions, has evolved into a comprehensive tool for assessing engine, transmission, and other vital system health, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). This evolution is essential for understanding how modern vehicles communicate their status and needs.
1.1. Breaking Down the OBD System: Key Components and Functions
The OBD system comprises several key components working together to monitor and report on a vehicle’s health:
- Sensors: These devices monitor various parameters such as engine speed, oxygen levels, and coolant temperature, as noted by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE).
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The brain of the system, the ECU processes sensor data to identify deviations from normal operating conditions, according to a study by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): When the ECU detects a problem, it generates a DTC, a standardized code that indicates the nature and location of the fault, as detailed by the EPA.
- Data Link Connector (DLC): This standardized port allows technicians and car owners to access the OBD system using scan tools to retrieve DTCs and other data.
1.2. The Evolution of OBD: From Basic Monitoring to Comprehensive Diagnostics
The evolution of OBD systems can be broadly divided into two main phases:
- OBD-I: Early systems were manufacturer-specific and lacked standardization, making diagnostics complex and requiring specialized tools for each make and model.
- OBD-II: Introduced in the mid-1990s, OBD-II brought standardization to diagnostic systems, using a universal connector and a standardized set of DTCs, according to the California Air Resources Board (CARB).
1.3. OBD-II: The Standard for Modern Vehicle Diagnostics
OBD-II is characterized by several key features:
- Standardized Connector: A 16-pin DLC, typically located under the dashboard, allows for easy access to the system.
- Standardized DTCs: A common set of codes ensures that any OBD-II scanner can interpret and display diagnostic information, as noted by the SAE.
- Comprehensive Monitoring: OBD-II systems monitor a wide range of engine and emissions-related parameters, providing detailed insights into vehicle performance.
2. What Are the Benefits of Using an OBD Car System?
Using an OBD car system offers numerous benefits for vehicle owners and technicians, including proactive maintenance, accurate diagnostics, and potential cost savings. These benefits make OBD systems an indispensable tool in modern automotive care.
2.1. Proactive Maintenance: Catching Problems Early
OBD systems allow for proactive maintenance by identifying potential issues before they escalate into major problems. By regularly monitoring DTCs and vehicle data, owners can address minor issues promptly, preventing costly repairs down the line, states the EPA.
2.2. Accurate Diagnostics: Pinpointing the Source of Problems
OBD systems provide accurate diagnostics by pinpointing the source of problems. DTCs help technicians quickly identify the faulty component or system, reducing diagnostic time and improving repair accuracy. The SAE has detailed information on standardized DTCs and their meanings.
2.3. Cost Savings: Avoiding Expensive Repairs
By identifying and addressing issues early, OBD systems can save vehicle owners money on expensive repairs. Regular monitoring and maintenance can prevent major breakdowns, extending the life of the vehicle and reducing overall ownership costs. The ISO provides standards for OBD system functionality and data reporting.
2.4. Improved Fuel Efficiency: Optimizing Engine Performance
OBD systems monitor engine performance, helping to optimize fuel efficiency. By identifying issues that can reduce fuel economy, such as faulty oxygen sensors or malfunctioning fuel injectors, owners can take corrective action to improve gas mileage, according to research from CARB.
2.5. Reduced Emissions: Contributing to a Cleaner Environment
OBD systems play a crucial role in reducing vehicle emissions. By monitoring emissions-related components, such as catalytic converters and oxygen sensors, OBD systems ensure that vehicles meet environmental standards, contributing to a cleaner environment, as noted by the EPA.
3. What Are the Key Components of an OBD Car System?
Understanding the key components of an OBD car system is essential for effective diagnostics and maintenance. These components work together to monitor vehicle performance, detect issues, and report diagnostic information.
3.1. Sensors: Monitoring Vital Parameters
Sensors are the foundation of the OBD system, monitoring various parameters such as:
- Engine Speed: Measures the rotational speed of the engine crankshaft.
- Oxygen Levels: Monitors the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
- Coolant Temperature: Tracks the temperature of the engine coolant.
- Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP): Measures the pressure in the intake manifold.
- Mass Airflow (MAF): Measures the amount of air entering the engine.
These sensors provide critical data to the ECU, allowing it to assess engine performance and detect potential issues, as outlined by the SAE.
3.2. Engine Control Unit (ECU): The Brain of the System
The ECU, also known as the engine control module (ECM), is the central processing unit of the OBD system. It receives data from sensors, analyzes the information, and makes adjustments to engine operation. The ECU also stores DTCs when it detects a problem. According to research from the ISO, the ECU uses sophisticated algorithms to interpret sensor data and make real-time decisions to optimize engine performance and emissions.
3.3. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Identifying Problems
DTCs are standardized codes used to identify specific problems within the vehicle. When the ECU detects a fault, it generates a DTC, which can be retrieved using a scan tool. DTCs are categorized into several types:
- P Codes: Powertrain codes, related to the engine and transmission.
- B Codes: Body codes, related to systems such as airbags and power windows.
- C Codes: Chassis codes, related to systems such as ABS and suspension.
- U Codes: Network codes, related to communication between different ECUs.
Each DTC provides specific information about the nature and location of the fault, helping technicians diagnose and repair the problem efficiently, as detailed by the EPA.
3.4. Data Link Connector (DLC): Accessing the System
The DLC is a standardized 16-pin connector that provides access to the OBD system. Located typically under the dashboard, the DLC allows technicians and car owners to connect scan tools and retrieve diagnostic information. The DLC is a key component of the OBD-II standard, ensuring compatibility between vehicles and diagnostic equipment, according to CARB.
4. What Are the Different Types of OBD Scanners Available?
OBD scanners are essential tools for accessing and interpreting data from a vehicle’s OBD system. Various types of scanners are available, each with its own features and capabilities.
4.1. Basic OBD Scanners: Reading and Clearing Codes
Basic OBD scanners are designed to read and clear DTCs. These scanners are typically inexpensive and easy to use, making them suitable for car owners who want to perform basic diagnostics. They can display DTCs, provide brief descriptions of the codes, and allow users to clear the codes after addressing the issue. The SAE provides standards for basic OBD scanner functionality.
4.2. Enhanced OBD Scanners: Live Data and Advanced Functions
Enhanced OBD scanners offer more advanced features, such as the ability to display live data from sensors, perform component tests, and access manufacturer-specific codes. These scanners are typically used by professional technicians and offer more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities. Enhanced scanners can provide real-time information about engine performance, helping technicians pinpoint intermittent problems and diagnose complex issues, according to the ISO.
4.3. Wireless OBD Adapters: Smartphone Connectivity
Wireless OBD adapters connect to the DLC and transmit data to a smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. These adapters, combined with OBD scanner apps, allow users to monitor vehicle performance and diagnose problems using their mobile devices. Wireless OBD adapters offer convenience and portability, making them a popular choice for car enthusiasts and DIY mechanics. CARB has information on the compatibility of wireless OBD adapters with various vehicle models.
4.4. Professional Scan Tools: Comprehensive Diagnostic Capabilities
Professional scan tools are high-end diagnostic devices used by automotive technicians in repair shops and dealerships. These tools offer comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including advanced coding, programming, and bi-directional control. Professional scan tools can perform a wide range of functions, such as resetting service lights, programming new keys, and calibrating sensors. The EPA requires professional scan tools to meet specific standards for emissions-related diagnostics.
4.5. Comparison of OBD Scanner Types
| Feature | Basic OBD Scanners | Enhanced OBD Scanners | Wireless OBD Adapters | Professional Scan Tools |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Read and Clear DTCs | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Live Data Display | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Component Tests | No | Yes | Limited | Yes |
| Manufacturer-Specific Codes | No | Yes | Limited | Yes |
| Advanced Coding/Programming | No | No | No | Yes |
| Price Range | $20-$100 | $100-$500 | $30-$200 | $500-$5000+ |
5. How to Choose the Right OBD Scanner for Your Needs?
Choosing the right OBD scanner depends on your specific needs and budget. Consider the following factors when selecting an OBD scanner:
5.1. Determine Your Diagnostic Needs
Assess your diagnostic needs based on your experience level and the types of repairs you typically perform. If you are a car owner looking to perform basic diagnostics, a basic OBD scanner or wireless adapter may be sufficient. If you are a professional technician, you will need a more comprehensive scan tool with advanced capabilities, advises the SAE.
5.2. Consider Compatibility with Your Vehicle
Ensure that the OBD scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Some scanners may not support all vehicles, especially older models. Check the scanner’s compatibility list before making a purchase. CARB provides information on OBD scanner compatibility with California vehicles.
5.3. Evaluate Features and Functions
Evaluate the features and functions offered by the OBD scanner. Consider whether you need live data display, component tests, or manufacturer-specific codes. Choose a scanner that offers the features you need to perform the types of diagnostics you typically perform, the ISO suggests.
5.4. Read Reviews and Compare Brands
Read reviews and compare brands to get an idea of the scanner’s reliability and performance. Look for scanners with positive reviews and a good reputation. Consider brands that are known for producing high-quality diagnostic equipment.
5.5. Set a Budget
Set a budget for your OBD scanner and choose a scanner that offers the best value for your money. Basic scanners are typically inexpensive, while professional scan tools can be quite costly. Consider your diagnostic needs and choose a scanner that fits your budget.
6. What Are Common OBD Car Codes and What Do They Mean?
Understanding common OBD car codes is essential for diagnosing and repairing vehicle issues. Here are some of the most common OBD codes and their meanings:
6.1. P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the engine is running lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture. Possible causes include vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, and malfunctioning fuel injectors, according to the EPA.
6.2. P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
This code indicates that the engine is misfiring, meaning one or more cylinders are not firing properly. Possible causes include faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, and fuel injectors, as outlined by the SAE.
6.3. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning properly. Possible causes include a faulty catalytic converter, faulty oxygen sensors, and exhaust leaks, the ISO states.
6.4. P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
This code indicates that there is a small leak in the evaporative emission control system, which is designed to prevent fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. Possible causes include a loose gas cap, a cracked fuel tank, and faulty vapor recovery components, notes CARB.
6.5. P0505: Idle Air Control System Malfunction
This code indicates that there is a problem with the idle air control system, which is designed to maintain a steady idle speed. Possible causes include a faulty idle air control valve, vacuum leaks, and throttle body issues, the EPA advises.
6.6. Interpreting OBD Codes: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Retrieve the Code: Use an OBD scanner to retrieve the DTC from the vehicle’s ECU.
- Research the Code: Consult a reliable source, such as a repair manual or online database, to determine the meaning of the code.
- Identify Possible Causes: Based on the code definition, identify the possible causes of the problem.
- Inspect and Test Components: Inspect and test the components that are likely to be causing the problem.
- Repair or Replace Faulty Components: Repair or replace any faulty components as needed.
- Clear the Code: After completing the repairs, clear the DTC from the vehicle’s ECU and retest the system to ensure that the problem has been resolved.
7. Where Can You Find More Information and Resources About OBD Car Systems?
Finding reliable information and resources about OBD car systems is essential for both vehicle owners and technicians. Here are some sources to consider:
7.1. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN: Your Comprehensive Resource for Automotive Tools and Information
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wealth of information and resources about OBD car systems, including detailed guides, product reviews, and expert advice. Our website is dedicated to providing accurate and up-to-date information to help you diagnose and repair vehicle issues effectively.
7.2. Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE): Standards and Publications
The SAE is a leading authority on automotive technology and standards. Their website offers a wealth of information on OBD systems, including technical papers, standards documents, and educational resources. The SAE is a valuable resource for both vehicle owners and technicians seeking in-depth knowledge about OBD technology.
7.3. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Regulations and Compliance
The EPA is responsible for regulating vehicle emissions and ensuring compliance with environmental standards. Their website provides information on OBD regulations, emissions testing, and vehicle maintenance. The EPA is a valuable resource for understanding the environmental impact of OBD systems.
7.4. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Global Standards for Automotive Technology
The ISO develops and publishes international standards for automotive technology, including OBD systems. Their website provides access to standards documents and technical information related to OBD technology. The ISO is a valuable resource for understanding the global standards that govern OBD systems.
7.5. Automotive Repair Manuals: Detailed Diagnostic and Repair Procedures
Automotive repair manuals provide detailed diagnostic and repair procedures for specific vehicle makes and models. These manuals typically include information on OBD systems, DTCs, and component testing. Repair manuals are a valuable resource for technicians and car owners who want to perform their own repairs.
8. What Are the Future Trends in OBD Car Technology?
OBD car technology is constantly evolving to meet the demands of modern vehicles. Here are some of the future trends in OBD technology:
8.1. Enhanced Data Logging and Analytics
Future OBD systems will offer enhanced data logging and analytics capabilities, allowing technicians to monitor vehicle performance over time and identify potential issues before they become major problems. Advanced data analytics will help technicians diagnose complex issues more efficiently and accurately, states the SAE.
8.2. Wireless Connectivity and Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Wireless connectivity and cloud-based diagnostics will become more prevalent in future OBD systems. These technologies will allow technicians to access diagnostic information remotely, perform remote diagnostics, and receive real-time updates and alerts. Wireless connectivity will also enable vehicle owners to monitor their vehicle’s health using their smartphones or tablets, the ISO advises.
8.3. Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
OBD systems will increasingly integrate with ADAS, such as adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and automatic emergency braking. This integration will allow OBD systems to monitor the performance of ADAS components and diagnose issues that could affect their functionality, the EPA notes.
8.4. Cybersecurity Enhancements
As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity will become an increasingly important concern. Future OBD systems will incorporate enhanced cybersecurity measures to protect against hacking and unauthorized access. Cybersecurity enhancements will help ensure the safety and security of vehicle data and prevent malicious attacks, CARB explains.
8.5. Standardization and Interoperability
Efforts to further standardize OBD systems and improve interoperability will continue in the future. Standardization will make it easier for technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles from different manufacturers, while interoperability will allow different diagnostic tools and systems to communicate with each other seamlessly.
9. How Can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Help You with Your OBD Car Needs?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is your one-stop resource for all your OBD car needs. We offer a wide range of products, services, and information to help you diagnose and repair vehicle issues effectively.
9.1. Wide Selection of OBD Scanners and Diagnostic Tools
We offer a wide selection of OBD scanners and diagnostic tools from leading brands. Whether you are a car owner looking for a basic scanner or a professional technician in need of a comprehensive scan tool, we have the products you need to get the job done.
9.2. Expert Advice and Technical Support
Our team of experienced automotive technicians is available to provide expert advice and technical support. We can help you choose the right OBD scanner for your needs, troubleshoot diagnostic issues, and provide guidance on repair procedures.
9.3. Detailed Product Reviews and Comparisons
We provide detailed product reviews and comparisons to help you make informed purchasing decisions. Our reviews are based on hands-on testing and analysis, so you can be confident that you are getting accurate and unbiased information.
9.4. Informative Articles and Guides
Our website features a wealth of informative articles and guides on OBD car systems, DTCs, and diagnostic procedures. We provide easy-to-understand explanations of complex topics, helping you learn about OBD technology and improve your diagnostic skills.
9.5. Contact Us for Personalized Assistance
If you have any questions or need personalized assistance, please don’t hesitate to contact us. You can reach us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. You can also visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD Car Systems
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD car systems:
10.1. What Type of OBD Scanner Is Right for My Car?
The right type of OBD scanner depends on your vehicle’s make, model, and year, as well as your diagnostic needs. Basic OBD scanners are suitable for car owners who want to perform basic diagnostics, while enhanced scanners and professional scan tools are better suited for professional technicians.
10.2. Where Can I Purchase a Reliable OBD Car Scanner?
You can purchase reliable OBD car scanners from automotive parts stores, online retailers, and diagnostic equipment suppliers. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wide selection of high-quality OBD scanners from leading brands.
10.3. What Does the Check Engine Light Indicate?
The check engine light indicates that there is a problem with the vehicle’s engine or emissions system. The light may come on for a variety of reasons, ranging from minor issues such as a loose gas cap to more serious problems such as a faulty catalytic converter.
10.4. How Can I Interpret OBD Codes?
You can interpret OBD codes by consulting a reliable source, such as a repair manual or online database. These resources provide definitions and possible causes for each code.
10.5. Can I Fix OBD-Related Issues Myself?
Whether you can fix OBD-related issues yourself depends on your mechanical skills and the complexity of the problem. Some issues, such as a loose gas cap, are easy to fix, while others may require specialized tools and knowledge.
10.6. How Often Should I Scan My Car’s OBD System?
You should scan your car’s OBD system whenever the check engine light comes on, or if you notice any unusual symptoms such as decreased fuel efficiency or rough running. Regular scanning can help you identify potential issues before they become major problems.
10.7. What Is the Difference Between OBD-I and OBD-II?
OBD-I is an early version of the OBD system that was not standardized, while OBD-II is a standardized system that has been in use since the mid-1990s. OBD-II offers a universal connector and a standardized set of DTCs, making diagnostics easier and more efficient.
10.8. Can an OBD Scanner Improve My Car’s Performance?
An OBD scanner cannot directly improve your car’s performance, but it can help you identify issues that may be affecting performance, such as a faulty oxygen sensor or malfunctioning fuel injector. By addressing these issues, you can improve your car’s performance and fuel efficiency.
10.9. Are Wireless OBD Adapters Safe to Use?
Yes, wireless OBD adapters are generally safe to use, but it is important to choose a reputable brand and ensure that the adapter is compatible with your vehicle. Some low-quality adapters may pose a security risk or drain your vehicle’s battery.
10.10. Where Can I Find a Professional Mechanic to Diagnose OBD Issues?
You can find a professional mechanic to diagnose OBD issues by searching online directories, asking for recommendations from friends or family, or checking with your local Better Business Bureau. Look for mechanics who are certified by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE).
Are you ready to take control of your car’s health? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 to explore our wide range of OBD scanners and diagnostic tools. Our expert team is here to help you find the perfect solution for your needs and provide the support you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Visit CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN now and start your journey to informed car care.