Obd2 Scanner Srs tools are essential for diagnosing and maintaining your vehicle’s safety systems, including airbags. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive resources to help you understand how these scanners work, their benefits, and how to choose the right one for your needs. Explore our detailed guides and product comparisons to ensure your car’s SRS is always in top condition. Key takeaways include SRS diagnostics, diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and automotive safety.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Scanner SRS
- 2. Why You Need an OBD2 Scanner for SRS Diagnostics
- 3. Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner SRS Tool
- 4. Top OBD2 Scanner SRS Recommendations
- 5. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner SRS Tool
- 6. Interpreting SRS Codes: A Comprehensive Guide
- 7. Common SRS Problems and How to Fix Them
- 8. Advanced SRS Diagnostic Techniques
- 9. Maintaining Your OBD2 Scanner SRS Tool
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Scanner SRS
Table of Contents
- Understanding the OBD2 Scanner SRS
- Why You Need an OBD2 Scanner for SRS Diagnostics
- Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner SRS Tool
- Top OBD2 Scanner SRS Recommendations
- How to Use an OBD2 Scanner SRS Tool
- Interpreting SRS Codes: A Comprehensive Guide
- Common SRS Problems and How to Fix Them
- Advanced SRS Diagnostic Techniques
- Maintaining Your OBD2 Scanner SRS Tool
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Scanner SRS
- CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
1. Understanding the OBD2 Scanner SRS
What is an OBD2 scanner SRS?
An OBD2 scanner SRS, or Supplemental Restraint System scanner, is a specialized tool used to diagnose issues within a vehicle’s airbag system. According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), malfunctioning airbags can significantly increase the risk of injury in a car accident. These scanners go beyond basic engine diagnostics, delving into the complex network of sensors and modules that control airbag deployment. The scanner interfaces with the vehicle’s computer to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the SRS, helping technicians pinpoint problems like faulty sensors, wiring issues, or module failures. By providing detailed information about the SRS, these scanners enable mechanics and car owners to ensure the airbag system is functioning correctly, enhancing vehicle safety.
What are the key components of an SRS?
The Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) comprises several critical components working together to protect vehicle occupants during a collision. These components include:
- Airbags: Inflatable cushions designed to protect occupants from hitting the interior of the vehicle.
- Sensors: Detect impact and send signals to the airbag control module.
- Control Module (ECU): Processes sensor data and triggers airbag deployment.
- Seat Belts: Restrain occupants and work in conjunction with airbags to minimize injury.
- Crash Sensors: Located in various parts of the vehicle to detect collisions from different angles.
- Wiring Harness: Connects all components, ensuring proper communication.
- Diagnostic System: Monitors the system for faults and alerts the driver via the airbag warning light.
A study published in the journal “Accident Analysis & Prevention” highlights the importance of regular SRS maintenance to ensure all components function correctly. The control module, often considered the brain of the SRS, continuously monitors the sensors and deployment circuits for any malfunctions. When a problem is detected, the control module stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and illuminates the airbag warning light on the dashboard. This warning light indicates that the SRS may not function as intended in a collision, necessitating immediate diagnostic and repair.
What is the role of an OBD2 port in SRS diagnostics?
The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port serves as the gateway for accessing a vehicle’s computer system, including the Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). According to SAE International, the OBD2 port is standardized across all vehicles manufactured after 1996 in the United States, ensuring compatibility with diagnostic tools. When an OBD2 scanner SRS tool is connected to this port, it can communicate with the vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU) to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the SRS. This allows technicians and car owners to identify issues such as faulty airbag sensors, wiring problems, or malfunctions within the airbag control module.
The OBD2 port’s ability to provide real-time data and diagnostic information makes it an indispensable tool for maintaining vehicle safety. Furthermore, it enables the clearing of fault codes after repairs, ensuring the airbag warning light is turned off and the SRS is functioning correctly. The OBD2 standard promotes consistency in diagnostic procedures, making it easier for mechanics to service a wide range of vehicle makes and models, ultimately contributing to improved vehicle safety and reliability. The address of CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States. Please contact Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit the website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information.
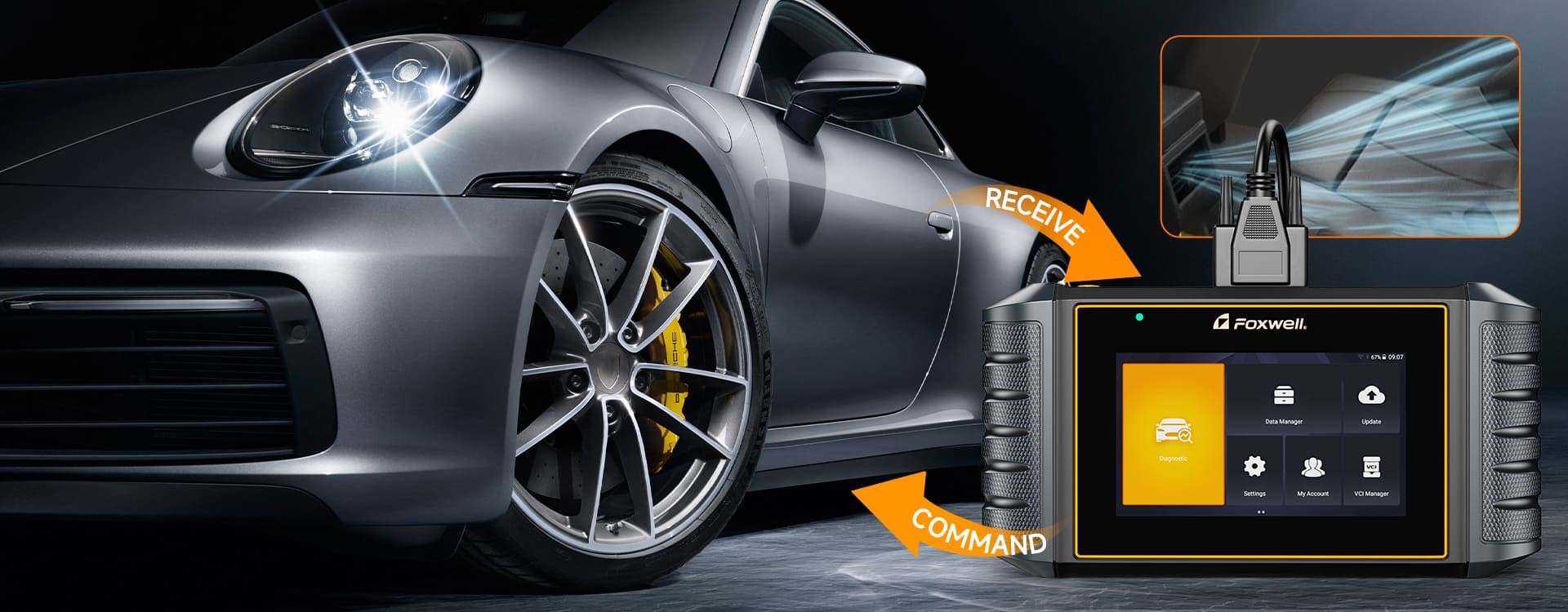 OBD2 Scanner
OBD2 Scanner
2. Why You Need an OBD2 Scanner for SRS Diagnostics
How does an OBD2 scanner enhance vehicle safety?
An OBD2 scanner enhances vehicle safety by providing critical insights into the functionality of essential safety systems, including the Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). Research from the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) indicates that properly functioning airbags and seatbelts significantly reduce the risk of serious injury in a collision. By connecting to the vehicle’s OBD2 port, the scanner can read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the SRS, which alert the driver and technician to potential issues such as malfunctioning sensors, wiring problems, or a faulty airbag control module.
Early detection of these issues allows for timely repairs, ensuring that safety features like airbags deploy correctly in the event of a crash. Regular use of an OBD2 scanner can also help identify underlying problems before they escalate into more serious safety risks. Moreover, these scanners can clear fault codes after repairs, confirming that the system is functioning correctly and the airbag warning light is turned off. By facilitating proactive maintenance and immediate attention to safety-related problems, OBD2 scanners play a vital role in enhancing overall vehicle safety and protecting occupants.
What are the benefits of diagnosing SRS issues early?
Diagnosing SRS issues early offers several critical benefits, primarily focused on enhancing vehicle safety and reducing potential risks. According to a study by the National Safety Council, a properly functioning Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) significantly reduces the severity of injuries in the event of a collision. Early diagnosis allows for timely repairs, ensuring that airbags and seatbelts deploy correctly, which can be life-saving. By identifying and addressing problems such as faulty sensors, wiring issues, or a malfunctioning control module before they lead to system failure, drivers can avoid the increased risk of injury.
Additionally, early diagnosis can prevent more costly repairs down the line. Small issues, if left unattended, can escalate and cause further damage to the SRS, leading to extensive and expensive repairs. Furthermore, diagnosing SRS issues early can help maintain the vehicle’s resale value. A vehicle with a fully functional safety system is more attractive to potential buyers. Overall, early diagnosis of SRS issues is a proactive approach that enhances safety, saves money, and protects the vehicle’s value. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is located at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States. For more information, contact Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit the website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN.
How does it save time and money on repairs?
Using an OBD2 scanner for SRS diagnostics can save both time and money on vehicle repairs by quickly identifying the root cause of problems. According to a report by AAA, diagnosing automotive issues can account for a significant portion of repair costs. By using an OBD2 scanner, technicians and car owners can bypass the often lengthy and expensive process of manual troubleshooting. The scanner provides specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that pinpoint the exact issue within the Supplemental Restraint System (SRS), such as a faulty sensor or wiring problem.
This precision allows for targeted repairs, avoiding unnecessary replacements of functioning components. Moreover, early detection of minor issues can prevent them from escalating into major, more costly problems. For example, a simple wiring issue can be fixed quickly if caught early, preventing damage to the airbag control module. Additionally, having a clear understanding of the problem enables car owners to seek accurate estimates from repair shops, avoiding inflated bills for unnecessary services. In summary, an OBD2 scanner streamlines the diagnostic process, reduces labor costs, and ensures that repairs are focused and efficient, ultimately saving both time and money.
3. Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Scanner SRS Tool
What is SRS system compatibility?
SRS (Supplemental Restraint System) compatibility refers to an OBD2 scanner’s ability to effectively communicate with and diagnose a vehicle’s airbag system. According to research published in the “Journal of Automotive Engineering,” the complexity of modern vehicle systems requires diagnostic tools to have specific software and firmware to access and interpret SRS data accurately. A scanner with good SRS compatibility can read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the airbag system, view live data from sensors, and perform necessary system resets.
Key aspects of SRS compatibility include:
- Coverage of vehicle makes and models: The scanner should support a wide range of vehicle brands and models to ensure versatility.
- Access to SRS-specific codes: It must be able to read manufacturer-specific codes beyond generic OBD2 codes.
- Firmware updates: Regular updates are essential to keep the scanner compatible with new vehicle models and system changes.
- Bi-directional control: This feature allows the scanner to send commands to the SRS for testing and diagnostics.
Ensuring that an OBD2 scanner has robust SRS compatibility is crucial for accurate and efficient diagnostics, leading to safer and more reliable vehicle maintenance.
What are enhanced diagnostic functions?
Enhanced diagnostic functions in an OBD2 scanner SRS refer to advanced capabilities that go beyond basic code reading and clearing. These functions provide more detailed and comprehensive insights into the vehicle’s Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) highlights the importance of these advanced features for accurate and efficient diagnostics.
Key enhanced diagnostic functions include:
- Live Data Streaming: Allows technicians to view real-time data from SRS sensors, such as airbag deployment status, sensor readings, and voltage levels. This helps in identifying intermittent issues and verifying sensor functionality.
- Bi-Directional Control: Enables the scanner to send commands to the SRS components to test their functionality. For example, it can trigger airbag deployment simulations to check the system’s response.
- Actuation Tests: Allows specific components like sensors and solenoids to be activated for testing purposes.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions when a fault code is triggered, providing valuable context for diagnosing the issue.
- Advanced Code Definitions: Provides detailed descriptions of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), including possible causes and troubleshooting steps.
These enhanced diagnostic functions empower technicians to perform in-depth analysis, identify the root causes of SRS problems, and implement effective repairs, ultimately enhancing vehicle safety and reliability. For any assistance, visit CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States or contact Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880.
What is comprehensive vehicle coverage?
Comprehensive vehicle coverage refers to an OBD2 scanner’s ability to support a wide range of vehicle makes, models, and years. According to a report by Consumer Reports, the versatility of a diagnostic tool is a key factor for both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts. A scanner with comprehensive coverage ensures that it can be used across different brands and types of vehicles, both domestic and international, making it a valuable investment.
Key aspects of comprehensive vehicle coverage include:
- Broad vehicle compatibility: The scanner should support a wide range of vehicle manufacturers, including major brands like Ford, GM, Toyota, Honda, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and more.
- Extensive model year support: It should be compatible with vehicles from older model years as well as the latest models.
- Regular updates: The scanner should receive frequent software updates to add support for new vehicles and system changes.
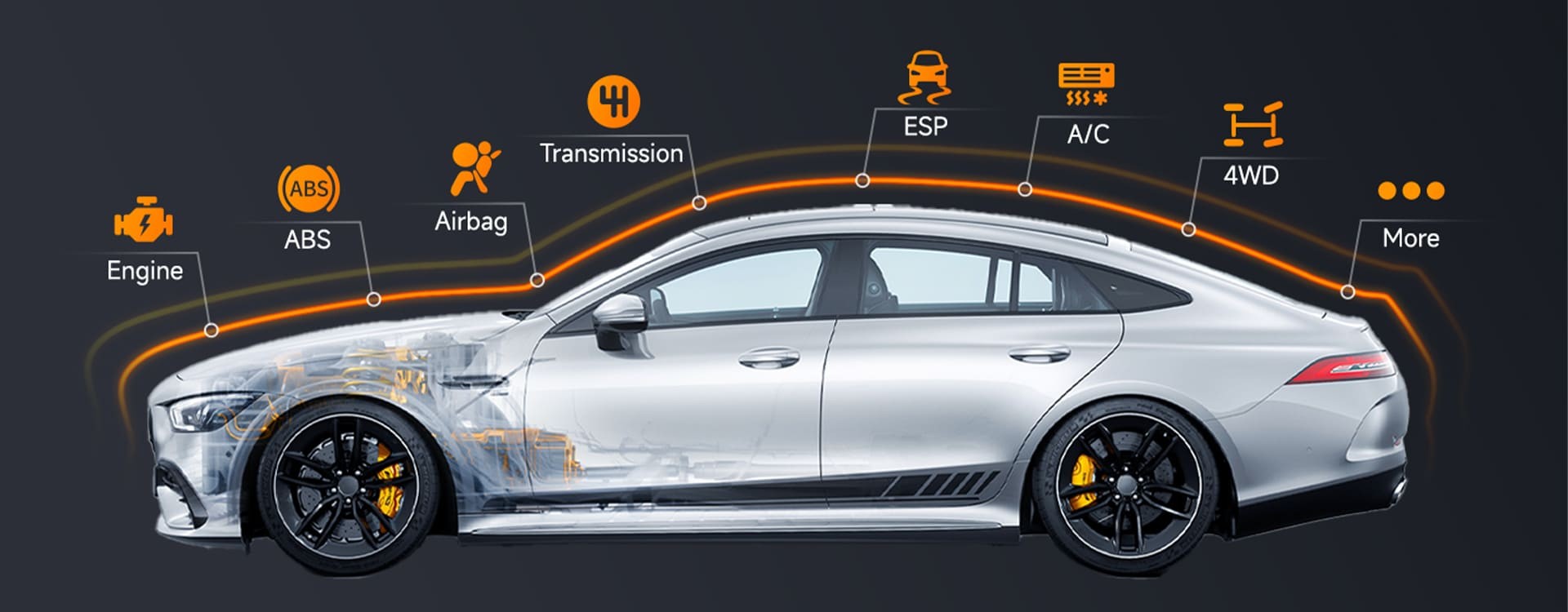
- Coverage of various systems: It should be able to diagnose not only the SRS but also other critical systems like the engine, transmission, ABS, and more.
Having an OBD2 scanner with comprehensive vehicle coverage ensures that you can diagnose and repair a variety of vehicles, making it a versatile and cost-effective tool for automotive maintenance.
 OBD2 Scanner Functions
OBD2 Scanner Functions
4. Top OBD2 Scanner SRS Recommendations
What are the best OBD2 scanners for SRS diagnostics?
Selecting the best OBD2 scanner for SRS diagnostics depends on specific needs and budget considerations. According to a survey by “Professional Tool & Equipment News” (PTEN), professional mechanics prioritize scanners with comprehensive vehicle coverage, advanced diagnostic functions, and reliable performance. For DIY enthusiasts, ease of use and affordability are often key factors.
Here are some top OBD2 scanner recommendations for SRS diagnostics:
- Snap-on Solus Edge: Known for its extensive vehicle coverage and advanced diagnostic capabilities, including bi-directional control and live data streaming.
- Autel MaxiSys MS906BT: A versatile scanner with comprehensive SRS coverage, wireless connectivity, and a user-friendly interface.
- Launch X431 V+: Offers wide vehicle coverage and advanced functions like ECU coding and programming, making it suitable for professional use.
- Foxwell NT630 Plus: A cost-effective option that provides reliable SRS diagnostics, including code reading, clearing, and live data viewing.
- Innova 3160g: An easy-to-use scanner with SRS diagnostics, ABS functions, and the ability to read and clear engine codes.
These scanners offer a range of features and capabilities, ensuring that both professional technicians and DIY users can find a suitable tool for diagnosing and repairing SRS issues.
What are the key features of each recommended scanner?
Each recommended OBD2 scanner for SRS diagnostics offers a unique set of features tailored to different user needs and budgets.
- Snap-on Solus Edge:
- Comprehensive Vehicle Coverage: Supports a wide range of domestic, Asian, and European vehicles.
- Advanced Diagnostic Functions: Includes bi-directional control, live data streaming, and detailed code definitions.
- User-Friendly Interface: Features a large color display and intuitive navigation.
- Autel MaxiSys MS906BT:
- Wireless Connectivity: Bluetooth connectivity for convenient use around the vehicle.
- Extensive SRS Coverage: Supports SRS diagnostics for numerous vehicle makes and models.
- User-Friendly Interface: Android-based operating system with easy-to-navigate menus.
- Launch X431 V+:
- Advanced Functions: Offers ECU coding, programming, and actuation tests.
- Wide Vehicle Coverage: Supports a broad range of vehicles, including heavy-duty trucks.
- Remote Diagnostics: Allows for remote diagnostic assistance from other technicians.
- Foxwell NT630 Plus:
- Cost-Effective: Provides reliable SRS diagnostics at an affordable price.
- User-Friendly Interface: Simple and intuitive interface for easy navigation.
- Special Functions: Includes ABS and SRS diagnostics, as well as oil service reset.
- Innova 3160g:
- Easy to Use: Designed for DIY users with a straightforward interface.
- Comprehensive Diagnostics: Reads and clears SRS, ABS, and engine codes.
- All-in-One Display: Shows over 20 pieces of information on a single screen.
These features make each scanner a valuable tool for diagnosing and repairing SRS issues, catering to both professional technicians and DIY enthusiasts. Remember CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is available at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, contact Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit the website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN.
How to choose the right scanner for your needs?
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner for your needs involves considering several factors, including your budget, technical expertise, and the types of vehicles you’ll be working on.
- Assess Your Needs: Determine whether you need the scanner for professional use or DIY maintenance. Professional technicians typically require scanners with comprehensive vehicle coverage, advanced diagnostic functions, and regular updates. DIY users may prioritize ease of use, affordability, and basic SRS diagnostic capabilities.
- Set a Budget: OBD2 scanners range in price from under $100 to several thousand dollars. Set a budget based on your needs and research scanners within that price range.
- Check Vehicle Coverage: Ensure the scanner supports the makes, models, and years of the vehicles you’ll be working on.
- Consider Features: Evaluate the features that are important to you, such as bi-directional control, live data streaming, wireless connectivity, and user-friendliness.
- Read Reviews: Look for reviews from other users to get an idea of the scanner’s performance, reliability, and ease of use.
- Check for Updates: Ensure the scanner receives regular software updates to stay compatible with new vehicles and system changes.
- Warranty and Support: Check the warranty and customer support offered by the manufacturer.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose an OBD2 scanner that meets your needs and provides reliable SRS diagnostics.
5. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner SRS Tool
What are the steps for connecting and using an OBD2 scanner?
Connecting and using an OBD2 scanner involves several straightforward steps to ensure accurate diagnostics.
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Consult your vehicle’s manual if you have trouble finding it.
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the vehicle’s ignition is turned off before connecting the scanner.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. Ensure it is securely connected.
- Turn On the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine. This powers up the vehicle’s electrical systems.
- Power On the Scanner: If necessary, turn on the scanner. Some models power on automatically when connected.
- Select Vehicle Information: Enter the required information about your vehicle, such as make, model, and year.
- Navigate the Menu: Use the scanner’s menu to select the SRS (airbag) system. This option may be labeled differently depending on the scanner (e.g., Airbag, Safety Restraint System).
- Read Codes: Follow the prompts to initiate a scan of the SRS system and retrieve any stored fault codes.
- Interpret Codes: Refer to the scanner’s manual or an online database to interpret the codes and understand the issues.
- Clear Codes (if necessary): After addressing the underlying issue, use the scanner to clear the fault codes.
- Verify the Fix: Perform another scan to ensure no new codes appear and that the airbag warning light is off.
What are the common errors to avoid when using a scanner?
When using an OBD2 scanner, avoiding common errors is essential for accurate diagnostics and preventing potential issues.
- Incorrect Vehicle Information: Ensure you enter the correct vehicle make, model, and year. Incorrect information can lead to inaccurate diagnostic results.
- Poor Connection: Make sure the scanner is securely connected to the OBD2 port. A loose connection can result in communication errors and incomplete scans.
- Ignoring Warning Lights: Pay attention to any warning lights or messages on the scanner’s display. These can indicate connection problems or other issues.
- Clearing Codes Without Fixing the Problem: Never clear fault codes without addressing the underlying issue. The airbag warning light will likely reappear, and the problem will persist.
- Using Outdated Software: Keep your scanner’s software up to date to ensure compatibility with new vehicles and system changes.
- Misinterpreting Codes: Refer to the scanner’s manual or a reliable online database to accurately interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Overlooking Physical Damage: Inspect the OBD2 port and scanner cable for any physical damage that could affect the connection.
By avoiding these common errors, you can ensure accurate and reliable SRS diagnostics, leading to effective vehicle maintenance and enhanced safety. For prompt assistance, contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit the website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN.
How to interpret the data from the OBD2 scanner?
Interpreting data from an OBD2 scanner requires understanding diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and their meanings.
- Understanding DTCs: Diagnostic trouble codes are alphanumeric codes that indicate specific issues within the vehicle’s systems. For SRS diagnostics, codes typically start with “B” (Body).
- Referencing the Manual: Consult the scanner’s manual or a reliable online database to find detailed descriptions of the DTCs.
- Identifying the Problem: The DTC description will provide information about the nature of the problem, such as a faulty sensor, wiring issue, or module malfunction.
- Analyzing Freeze Frame Data: Some scanners provide freeze frame data, which captures the vehicle’s operating conditions when the DTC was triggered. This can offer valuable context for diagnosing intermittent issues.
- Viewing Live Data: Use the scanner to view live data from SRS sensors and components. This can help you verify sensor functionality and identify any abnormalities.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Based on the DTC description and live data, follow the recommended troubleshooting steps to diagnose the root cause of the problem.
- Verifying the Fix: After addressing the issue, clear the DTCs and perform another scan to ensure the problem is resolved and no new codes appear.
6. Interpreting SRS Codes: A Comprehensive Guide
What are the common SRS codes and their meanings?
Understanding common SRS (Supplemental Restraint System) codes and their meanings is crucial for accurate diagnostics and effective repairs. Here are some common SRS codes and their interpretations:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| B0001 | Driver Airbag Deployment Control | Short to ground, open circuit, faulty airbag module |
| B0002 | Passenger Airbag Deployment Control | Short to ground, open circuit, faulty airbag module |
| B1001 | Airbag Warning Lamp Circuit Failure | Faulty airbag module, wiring issue, blown fuse |
| B1317 | Battery Voltage High | Overcharging, faulty voltage regulator |
| B1318 | Battery Voltage Low | Low battery, faulty alternator |
| B1481 | Driver Side Impact Sensor Fault | Faulty sensor, wiring issue, corrosion |
| B1482 | Passenger Side Impact Sensor Fault | Faulty sensor, wiring issue, corrosion |
| B1650 | Occupant Classification System Malfunction | Faulty sensor, wiring issue, incorrect occupant classification |
| B1990 | Airbag Deployment Circuit Open | Open circuit in airbag wiring, faulty clock spring |
| B2224 | Internal Control Module Failure | Faulty airbag module, internal circuit failure |
These codes provide a starting point for diagnosing SRS issues. Always refer to the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online database for detailed information and troubleshooting steps.
How to diagnose issues based on specific SRS codes?
Diagnosing issues based on specific SRS codes involves a systematic approach to identify the root cause of the problem.
- Record the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve and record the specific SRS code.
- Research the Code: Consult the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online database to understand the code’s meaning, possible causes, and troubleshooting steps.
- Inspect Wiring and Connections: Check the wiring and connections related to the affected component. Look for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Test the Component: Use a multimeter or other diagnostic tools to test the functionality of the component. Compare the readings to the specifications in the service manual.
- Check Power and Ground: Verify that the component is receiving proper power and ground. Use a multimeter to check voltage and continuity.
- Consult Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs): Check for any TSBs related to the code or component. TSBs may provide additional information or updated troubleshooting procedures.
- Replace the Component (if necessary): If the component is faulty, replace it with a new or refurbished part.
- Clear the Code: After addressing the issue, use the OBD2 scanner to clear the fault code.
- Verify the Fix: Perform another scan to ensure the code does not reappear and that the SRS system is functioning correctly.
What tools are needed for effective SRS code diagnosis?
Effective SRS code diagnosis requires a combination of diagnostic tools and equipment to accurately identify and resolve issues within the airbag system.
- OBD2 Scanner: An advanced OBD2 scanner capable of reading and clearing SRS codes is essential for retrieving diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and accessing live data.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is used to test voltage, continuity, and resistance in circuits and components.
- Wiring Diagram: A wiring diagram for the vehicle’s SRS is necessary for tracing circuits and identifying wiring issues.
- Service Manual: The vehicle’s service manual provides detailed information about the SRS, including component locations, specifications, and troubleshooting procedures.
- Scan Tool with Oscilloscope: A scan tool with oscilloscope capabilities can be used to analyze sensor signals and identify intermittent problems.
- Airbag Tester: An airbag tester is a specialized tool used to safely deploy airbags for testing purposes.
- Connector Test Kit: A connector test kit includes various connectors and adapters for testing wiring connections.
- Protective Gear: Always wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, when working on the SRS.
Having these tools and equipment on hand ensures that you can effectively diagnose and repair SRS issues, leading to safer and more reliable vehicle maintenance. For more information visit CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States. You can also contact us through Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit the website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN.
7. Common SRS Problems and How to Fix Them
What are the most frequent SRS issues encountered?
Several common SRS (Supplemental Restraint System) issues are frequently encountered in vehicles. Understanding these problems can help technicians and car owners diagnose and address them effectively.
- Faulty Airbag Sensors: Airbag sensors can fail due to physical damage, corrosion, or electrical issues, triggering the airbag warning light.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt the communication between SRS components, leading to system malfunctions.
- Clock Spring Issues: The clock spring, located in the steering column, can break or wear out, causing airbag and horn malfunctions.
- Faulty Airbag Module: The airbag control module (ECU) can fail due to internal circuit problems or software glitches, preventing proper airbag deployment.
- Seat Belt Pretensioner Problems: Seat belt pretensioners may fail to activate properly in a collision due to mechanical or electrical issues.
- Occupant Classification System (OCS) Malfunctions: The OCS, which detects the presence and weight of the occupant, can malfunction, leading to incorrect airbag deployment.
- Low Battery Voltage: Low battery voltage can cause SRS malfunctions and trigger the airbag warning light.
How to troubleshoot and resolve airbag sensor failures?
Troubleshooting and resolving airbag sensor failures involves a systematic approach to identify and address the root cause of the problem.
- Scan for Codes: Use an OBD2 scanner to retrieve the specific SRS code related to the airbag sensor.
- Inspect the Sensor: Visually inspect the sensor for any signs of physical damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Check Wiring: Check the wiring and connectors leading to the sensor for damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Use a wiring diagram to trace the circuit.
- Test the Sensor: Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s resistance and voltage. Compare the readings to the specifications in the service manual.
- Replace the Sensor: If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new or refurbished part.
- Clear the Code: After replacing the sensor, use the OBD2 scanner to clear the fault code.
- Verify the Fix: Perform another scan to ensure the code does not reappear and that the SRS system is functioning correctly.
What are the steps for fixing wiring and connector issues?
Fixing wiring and connector issues in the SRS requires careful inspection, repair, and verification to ensure proper system functionality.
- Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Visually inspect the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Clean Connectors: Clean corroded connectors with a wire brush or electrical contact cleaner.
- Repair Damaged Wires: Repair damaged wires by splicing in new sections or using heat-shrink tubing to insulate the repair.
- Secure Connections: Ensure all connectors are securely connected and properly latched.
- Use Dielectric Grease: Apply dielectric grease to the connectors to prevent corrosion and improve electrical contact.
- Test Continuity: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the wiring and connectors.
- Replace Damaged Components: Replace any damaged wiring or connectors that cannot be repaired.
- Verify the Fix: After repairing the wiring and connectors, use an OBD2 scanner to clear any fault codes and perform another scan to ensure the SRS system is functioning correctly.
8. Advanced SRS Diagnostic Techniques
What is the role of live data streaming in SRS diagnostics?
Live data streaming plays a crucial role in SRS (Supplemental Restraint System) diagnostics by providing real-time information about the system’s performance.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Live data streaming allows technicians to monitor the real-time values of various SRS sensors and components, such as airbag deployment status, sensor readings, and voltage levels.
- Identifying Intermittent Issues: By observing live data, technicians can identify intermittent problems that may not trigger fault codes, such as a sensor that occasionally malfunctions.
- Verifying Sensor Functionality: Live data can be used to verify that sensors are functioning correctly and providing accurate readings.
- Analyzing System Response: Technicians can analyze the system’s response to various inputs and conditions, such as changes in vehicle speed or impact forces.
- Diagnosing Complex Problems: Live data streaming can help diagnose complex problems that involve multiple components or systems.
What are bi-directional control and actuation tests?
Bi-directional control and actuation tests are advanced diagnostic functions that allow technicians to interact with the SRS (Supplemental Restraint System) components to test their functionality.
- Bi-Directional Control: Bi-directional control enables the technician to send commands to the SRS components to test their response. For example, a technician can use bi-directional control to simulate airbag deployment and verify that the system responds correctly.
- Actuation Tests: Actuation tests allow specific components to be activated for testing purposes. For example, a technician can activate the seat belt pretensioners to ensure they are functioning properly.
- Comprehensive Diagnostics: Bi-directional control and actuation tests provide a more comprehensive diagnostic approach by allowing technicians to directly interact with and test the SRS components.
- Pinpointing Problems: These functions can help pinpoint the exact cause of SRS problems by isolating and testing individual components.
- Verifying Repairs: Bi-directional control and actuation tests can be used to verify that repairs have been successful and that the SRS is functioning correctly.
How can you use an oscilloscope for SRS diagnostics?
Using an oscilloscope for SRS (Supplemental Restraint System) diagnostics can provide valuable insights into the performance of sensors and circuits.
- Analyzing Sensor Signals: An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the signals from SRS sensors, such as airbag sensors and impact sensors.
- Identifying Signal Problems: Technicians can use an oscilloscope to identify signal problems, such as signal distortion, noise, or dropouts.
- Verifying Signal Integrity: An oscilloscope can be used to verify the integrity of the signals in the SRS circuits.
- Diagnosing Intermittent Problems: An oscilloscope can help diagnose intermittent problems by capturing and analyzing transient signals.
- Testing Circuit Components: An oscilloscope can be used to test the performance of circuit components, such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes.
9. Maintaining Your OBD2 Scanner SRS Tool
How to keep your scanner software up to date?
Keeping your OBD2 scanner’s software up to date is crucial for maintaining its compatibility with new vehicles and ensuring accurate diagnostics.
- Check for Updates Regularly: Check the scanner manufacturer’s website or software application for updates regularly.
- Download and Install Updates: Download and install any available updates following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Connect to the Internet: Ensure your scanner is connected to the internet during the update process.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Follow the update instructions carefully to avoid errors or damage to the scanner.
- Backup Data: Back up any important data or settings before installing updates.
- Register Your Scanner: Register your scanner with the manufacturer to receive notifications about new updates.
What are the best practices for storing and handling the scanner?
Proper storage and handling of your OBD2 scanner can help prolong its lifespan and ensure reliable performance.
- Store in a Safe Place: Store the scanner in a safe, dry place away from extreme temperatures, moisture, and direct sunlight.
- Use a Protective Case: Use a protective case or pouch to protect the scanner from physical damage.
- Handle with Care: Handle the scanner with care and avoid dropping or mishandling it.
- Keep Clean: Keep the scanner clean by wiping it down with a soft, dry cloth.
- Protect the Cable: Protect the scanner cable from damage by avoiding sharp bends or strains.
- Disconnect Properly: Disconnect the scanner from the vehicle’s OBD2 port properly by pulling on the connector, not the cable.
How to troubleshoot common scanner issues?
Troubleshooting common OBD2 scanner issues can help you resolve problems and ensure the scanner is functioning correctly.
- Connection Problems: Check the connection between the scanner and the vehicle’s OBD2 port. Ensure the connector is securely plugged in and the port is clean.
- Power Issues: Check the scanner’s power source. Ensure the battery is charged or the scanner is properly connected to a power outlet.
- Software Issues: Check for software updates. Install any available updates to resolve software glitches or compatibility problems.
- Communication Errors: Check the vehicle’s compatibility with the scanner. Ensure the scanner supports the vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Display Problems: Check the scanner’s display settings. Adjust the brightness or contrast if the display is dim or difficult to read.
- User Manual: Consult the scanner’s user manual for troubleshooting tips and solutions to common problems.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Scanner SRS
Can a standard OBD2 scanner read SRS codes?
No, a standard OBD2 scanner typically cannot read SRS (Supplemental Restraint System) codes. SRS diagnostics require a specialized scanner capable of accessing and interpreting the codes specific to the airbag system.
What type of OBD2 scanner do I need for SRS diagnostics?
You need an advanced or professional OBD2 scanner that includes SRS diagnostic capabilities. These scanners are equipped with the necessary software and hardware to communicate with the vehicle’s airbag system and retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
Why can’t all OBD2 scanners read SRS codes?
Basic OBD2 scanners focus on engine and emission-related codes, while advanced scanners cover more systems, including the SRS. SRS diagnostics require specialized software and hardware that are not included in basic OBD2 scanners.
How do I know if my airbag sensor is bad?
Common signs of a bad airbag sensor include the airbag warning light being illuminated on the dashboard, diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to airbag sensor failures, and a failure of the airbags to deploy in a collision.
Can I clear SRS codes myself?
Yes, you can clear SRS codes yourself using an OBD2 scanner that supports SRS diagnostics. However, it’s important to address the underlying issue before clearing the codes to ensure the SRS system is functioning correctly.
Will an airbag light clear itself?
No, an airbag light typically won’t clear itself. The light will remain on until the fault code is cleared using an OBD2 scanner after the underlying issue has been resolved.
How often should I check my SRS system?
It’s recommended to check your SRS system whenever the airbag warning light is illuminated or as part of your regular vehicle maintenance schedule. Regular checks can help identify potential problems before they