The OBD2 port in your car is your gateway to understanding its health and performance through onboard diagnostics. This port, a standardized feature in most vehicles since 1996, allows technicians and car owners alike to access critical data using diagnostic tools. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides resources to help you effectively locate and utilize your OBD2 port, empowering you to maintain your vehicle in optimal condition. By understanding how to use this port, you can unlock valuable insights into your vehicle’s engine, emission system, and overall performance.
Contents
- 1. What Exactly Is An OBD2 Port?
- 1.1. History and Evolution of OBD Systems
- 1.2. Key Functions of the OBD2 Port
- 1.3. Standardized Connector and Protocol
- 1.4. Benefits of Using an OBD2 Port
- 2. Locating The OBD2 Port In Your Vehicle
- 2.1. Common Locations
- 2.2. Using Your Vehicle’s Manual
- 2.3. Online OBD2 Port Finders
- 2.4. Visual Inspection Tips
- 2.5. What To Do If You Still Can’t Find It
- 3. Understanding The OBD2 Connector And Pinout
- 3.1. Standardized 16-Pin Configuration
- 3.2. Key Pin Assignments
- 3.3. Communication Protocols
- 3.4. Pinout Diagrams and Resources
- 3.5. Common Misconceptions About Pinouts
- 4. Importance of the OBD2 Port
- 4.1. Vehicle Diagnostics
- 4.2. Emissions Monitoring
- 4.3. Performance Tuning
- 4.4. Data Logging
- 4.5. Safety Implications
- 4.6. Benefits for Mechanics
- 5. Using The OBD2 Port: A Step-By-Step Guide
- 5.1. Gather Necessary Tools
- 5.2. Locate the OBD2 Port
- 5.3. Plug in the OBD2 Scanner
- 5.4. Turn on the Ignition
- 5.5. Follow Scanner Instructions
- 5.6. Record and Interpret Data
- 5.7. Clear Codes (Optional)
- 5.8. Safety Precautions
- 6. Advanced OBD2 Applications
- 6.1. Performance Monitoring
- 6.2. Custom Gauges and Displays
- 6.3. Data Logging and Analysis
- 6.4. Remote Vehicle Monitoring
- 6.5. Integration with Mobile Apps
- 7. Taking Vehicle Diagnostics to the Next Level with Advanced Tools
- 7.1. Enhanced Data Access
- 7.2. Comprehensive Vehicle Monitoring
- 7.3. Upgrade for OBD2 Projects
- 8. Common Problems And Troubleshooting
- 8.1. Scanner Won’t Connect
- 8.2. Inaccurate Readings
- 8.3. Check Engine Light Won’t Turn Off
- 8.4. Communication Errors
- 8.5. When to Seek Professional Help
- 9. FAQs About OBD2 Ports
- 9.1. What if I can’t find the OBD2 location?
- 9.2. Are all OBD2 ports the same?
- 9.3. How many OBD2 ports does a car have?
- 9.4. Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my car?
- 9.5. Is it safe to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time?
- 9.6. Can the OBD2 port be used to track my car?
- 9.7. How often should I scan my car’s OBD2 port?
- 9.8. What does it mean when the check engine light comes on?
- 9.9. Can I damage my car by using the OBD2 port?
- 9.10. Where can I find more information about OBD2?
- 10. Conclusion
1. What Exactly Is An OBD2 Port?
An OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port is a standardized interface in vehicles that provides access to the car’s computer system for diagnostic purposes. It’s essentially a socket that allows mechanics and vehicle owners to connect diagnostic tools or scanners to read error codes, monitor vehicle parameters, and assess the overall health of the car. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 was mandated in all cars and light trucks sold in the United States starting in 1996 to standardize emissions testing and provide better diagnostics.
1.1. History and Evolution of OBD Systems
The journey to OBD2 began with the introduction of On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) systems in the late 1960s. These early systems were relatively basic, primarily focused on monitoring emissions-related components. As technology advanced, so did the complexity of OBD systems.
- OBD-I: The first generation of on-board diagnostics, implemented in the late 1980s, varied widely between manufacturers, lacking standardization in diagnostic codes and data reporting.
- OBD-1.5: An interim solution used by some manufacturers in the mid-1990s, bridging the gap between OBD-I and the fully standardized OBD2.
- OBD2: Introduced in 1996, OBD2 brought standardization to diagnostic protocols, connectors, and fault codes, making it easier to diagnose and repair vehicles across different makes and models. This standardization was largely driven by environmental regulations aimed at reducing vehicle emissions.
1.2. Key Functions of the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port serves several crucial functions:
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): When a problem occurs in a vehicle, the car’s computer stores a DTC, which can be read using an OBD2 scanner. These codes provide valuable information about the nature and location of the problem.
- Monitoring Vehicle Parameters: The OBD2 port allows real-time monitoring of various vehicle parameters, such as engine speed, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim. This data can be used to diagnose performance issues and identify potential problems before they become severe.
- Clearing Trouble Codes: Once a problem has been identified and repaired, the OBD2 port can be used to clear the stored DTCs, turning off the check engine light.
- Emissions Testing: OBD2 plays a critical role in emissions testing, allowing technicians to quickly and accurately assess a vehicle’s compliance with emissions standards.
1.3. Standardized Connector and Protocol
One of the key features of OBD2 is its standardized connector, a 16-pin Data Link Connector (DLC). This connector is typically located within easy reach of the driver, usually under the dashboard. The standardization of the connector and communication protocols ensures that any OBD2-compliant scanner can be used to diagnose any OBD2-compliant vehicle, regardless of make or model.
1.4. Benefits of Using an OBD2 Port
Using the OBD2 port offers numerous benefits for both mechanics and car owners:
- Early Problem Detection: By regularly scanning your vehicle’s OBD2 port, you can identify potential problems early on, before they lead to costly repairs or breakdowns.
- Cost Savings: Diagnosing and repairing issues early can prevent more extensive damage and save you money in the long run.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Monitoring vehicle parameters through the OBD2 port can help you identify and address issues that may be affecting your fuel economy.
- Informed Decision-Making: Access to real-time vehicle data empowers you to make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs.
- DIY Diagnostics: With the availability of affordable OBD2 scanners, car owners can perform basic diagnostics themselves, saving time and money on professional mechanic fees.
2. Locating The OBD2 Port In Your Vehicle
Finding the OBD2 port in your car is generally straightforward, but its exact location can vary depending on the make and model. In most vehicles, the OBD2 port is located inside the passenger compartment. It is often found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
2.1. Common Locations
Here are some typical locations where you might find the OBD2 port:
- Under the Dashboard: This is the most common location. Look for a 16-pin connector, often black or white, under the steering wheel column or in the vicinity of the pedals.
- Near the Center Console: In some vehicles, the OBD2 port may be located near the center console, often concealed behind a small panel or in a storage compartment.
- Inside the Glove Box: Although less common, some manufacturers place the OBD2 port inside the glove box.
- Behind an Ashtray or Coin Holder: In older vehicles, the OBD2 port might be hidden behind a removable ashtray or coin holder.
2.2. Using Your Vehicle’s Manual
The most reliable way to find the OBD2 port is to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual. The manual will typically provide a diagram or description of the port’s location.
2.3. Online OBD2 Port Finders
If you can’t find the OBD2 port using the above methods, there are online OBD2 port finders available. These tools allow you to enter your vehicle’s make, model, and year to locate the port. These tools can be invaluable for quickly identifying the port’s location.
2.4. Visual Inspection Tips
If you prefer a hands-on approach, here are some tips for visually inspecting your vehicle to find the OBD2 port:
- Look for the Standardized Connector: The OBD2 port is a 16-pin connector with a trapezoidal shape.
- Check Common Areas: Focus your search on the areas mentioned above, such as under the dashboard and near the center console.
- Use a Flashlight: A flashlight can help you see into dark or hard-to-reach areas.
- Feel Around: If you can’t see the port, try feeling around under the dashboard for the connector.
2.5. What To Do If You Still Can’t Find It
If you’ve exhausted all of the above methods and still can’t find the OBD2 port, consider the following:
- Consult a Mechanic: A professional mechanic will be able to quickly locate the OBD2 port for you.
- Check Online Forums: Online forums dedicated to your vehicle’s make and model may have information about the port’s location.
- Contact the Manufacturer: As a last resort, you can contact the vehicle manufacturer for assistance.
 Illustration depicting the common locations of the OBD2 port under the dashboard in a vehicle
Illustration depicting the common locations of the OBD2 port under the dashboard in a vehicle
3. Understanding The OBD2 Connector And Pinout
The OBD2 connector is a standardized 16-pin Data Link Connector (DLC) that serves as the interface between a vehicle’s computer system and diagnostic tools. Understanding the pinout of the OBD2 connector is essential for advanced diagnostics and custom applications.
3.1. Standardized 16-Pin Configuration
The OBD2 connector features a standardized 16-pin configuration, with each pin assigned a specific function. This standardization ensures compatibility between different vehicles and diagnostic tools.
3.2. Key Pin Assignments
Here’s a quick overview of some of the key pin assignments:
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 6: CAN High (J-2284)
- Pin 7: K-Line ISO 9141-2
- Pin 10: SAE J1850 Bus (-)
- Pin 14: CAN Low (J-2284)
- Pin 15: L-Line ISO 9141-2
- Pin 16: Battery Power
3.3. Communication Protocols
The OBD2 connector supports several communication protocols, including:
- SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width Modulation): Used primarily by General Motors.
- SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used primarily by Ford.
- ISO 9141-2: Used primarily by European and Asian manufacturers.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): The most modern and widely used protocol, mandated for all vehicles sold in the United States since 2008.
3.4. Pinout Diagrams and Resources
Numerous online resources provide detailed pinout diagrams for the OBD2 connector. These diagrams can be helpful for understanding the function of each pin and for troubleshooting communication issues.
3.5. Common Misconceptions About Pinouts
It’s important to note that not all pins are used in every vehicle. The specific pins used will depend on the vehicle’s make, model, and communication protocol. Additionally, some pins may be reserved for manufacturer-specific functions.
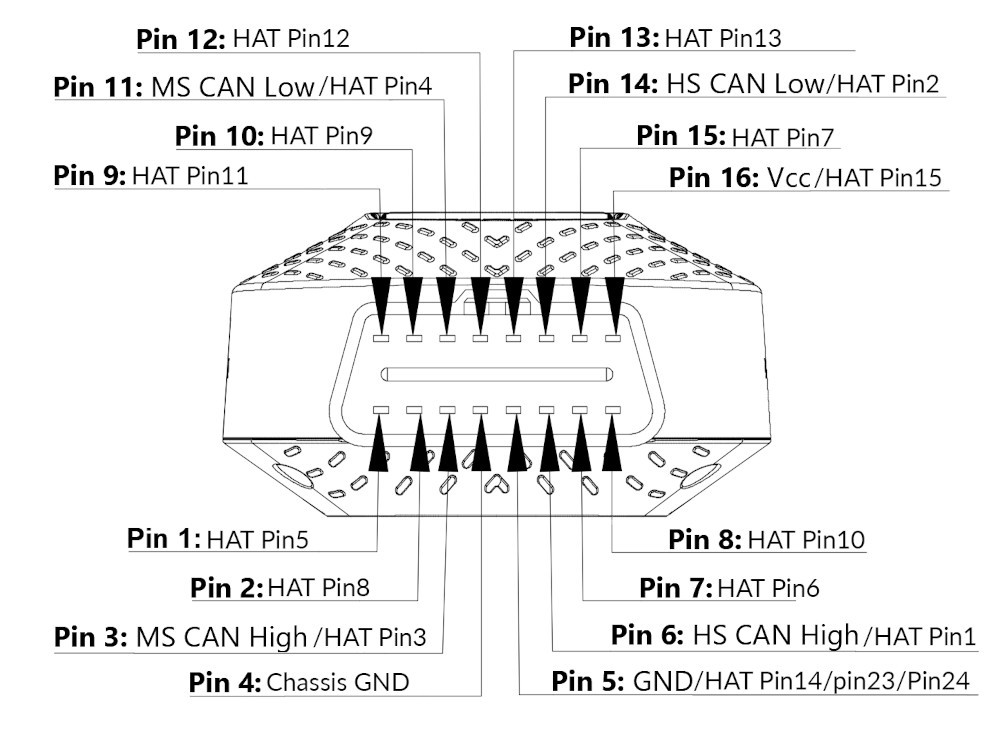 Detailed illustration of the OBD2 connector pinouts from an AutoPi device, showcasing the function of each pin
Detailed illustration of the OBD2 connector pinouts from an AutoPi device, showcasing the function of each pin
4. Importance of the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port is a critical component of modern vehicles, providing access to a wealth of diagnostic information. Its importance stems from its ability to help mechanics and vehicle owners identify and address problems quickly and efficiently.
4.1. Vehicle Diagnostics
The primary function of the OBD2 port is to facilitate vehicle diagnostics. By connecting a compatible scanner to the port, technicians can read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), monitor vehicle parameters, and assess the overall health of the car.
4.2. Emissions Monitoring
OBD2 plays a vital role in emissions monitoring. The system continuously monitors emissions-related components and systems, alerting the driver to any potential problems that could affect emissions levels. This helps ensure that vehicles comply with environmental regulations.
4.3. Performance Tuning
The OBD2 port can also be used for performance tuning. By accessing and modifying certain parameters, tuners can optimize engine performance, improve fuel economy, and enhance the overall driving experience.
4.4. Data Logging
The OBD2 port allows for data logging, which involves recording vehicle parameters over time. This data can be used to analyze vehicle performance, identify trends, and troubleshoot intermittent problems.
4.5. Safety Implications
Early detection and repair of vehicle problems can have significant safety implications. By identifying and addressing issues such as brake problems, faulty sensors, and engine malfunctions, the OBD2 port helps ensure that vehicles are safe to operate.
4.6. Benefits for Mechanics
For mechanics, the OBD2 port is an invaluable tool. It allows them to quickly and accurately diagnose vehicle problems, saving time and money. Additionally, the standardized nature of the OBD2 system makes it easier to work on a wide range of vehicles.
 Infographic highlighting keywords related to the OBD2 connector and its importance as a vehicle gateway
Infographic highlighting keywords related to the OBD2 connector and its importance as a vehicle gateway
5. Using The OBD2 Port: A Step-By-Step Guide
Using the OBD2 port is a relatively simple process that can be done by anyone with a compatible scanner. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
5.1. Gather Necessary Tools
Before you begin, make sure you have the following tools:
- OBD2 Scanner: You’ll need an OBD2 scanner to read data from the port. These scanners range from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools.
- Vehicle’s Key: You’ll need the vehicle’s key to turn on the ignition.
- Vehicle’s Manual (Optional): The vehicle’s manual can be helpful for locating the OBD2 port and understanding diagnostic codes.
5.2. Locate the OBD2 Port
Follow the steps outlined earlier in this article to locate the OBD2 port in your vehicle.
5.3. Plug in the OBD2 Scanner
With the ignition off, plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. Make sure the connection is secure.
5.4. Turn on the Ignition
Turn the ignition to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
5.5. Follow Scanner Instructions
Follow the instructions provided with your OBD2 scanner to read diagnostic codes, monitor vehicle parameters, or perform other functions.
5.6. Record and Interpret Data
Record any diagnostic codes or data displayed by the scanner. Use online resources or your vehicle’s manual to interpret the data and identify potential problems.
5.7. Clear Codes (Optional)
If you’ve identified and repaired a problem, you can use the OBD2 scanner to clear the diagnostic codes and turn off the check engine light.
5.8. Safety Precautions
When using the OBD2 port, it’s important to take the following safety precautions:
- Do not operate the vehicle while using the scanner.
- Follow the scanner manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
- If you’re not comfortable performing diagnostics yourself, consult a professional mechanic.
6. Advanced OBD2 Applications
Beyond basic diagnostics, the OBD2 port can be used for a variety of advanced applications:
6.1. Performance Monitoring
Advanced OBD2 scanners can provide real-time data on engine performance, allowing you to monitor parameters such as horsepower, torque, and fuel efficiency.
6.2. Custom Gauges and Displays
The OBD2 port can be used to create custom gauges and displays that show real-time vehicle data. These displays can be mounted on the dashboard or integrated into the vehicle’s infotainment system.
6.3. Data Logging and Analysis
Advanced data logging applications allow you to record vehicle parameters over time and analyze the data to identify trends and patterns. This can be useful for diagnosing intermittent problems and optimizing vehicle performance.
6.4. Remote Vehicle Monitoring
Some devices allow you to remotely monitor your vehicle’s performance and location using the OBD2 port. This can be useful for fleet management, theft prevention, and monitoring teenage drivers.
6.5. Integration with Mobile Apps
Many mobile apps can connect to the OBD2 port via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, providing access to diagnostic data, performance monitoring, and other advanced features.
7. Taking Vehicle Diagnostics to the Next Level with Advanced Tools
While your car’s OBD2 port provides essential information, advanced tools like the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro can take your vehicle diagnostics to a new level, offering faster and more detailed insights into your vehicle’s performance.
7.1. Enhanced Data Access
The AutoPi CAN-FD Pro works with your OBD2 port to provide faster, more detailed access to your vehicle’s data. This allows you to monitor critical systems, such as the engine and emissions, with greater precision.
7.2. Comprehensive Vehicle Monitoring
With the AutoPi device, you can keep track of important car systems, ensuring that you are always aware of your vehicle’s performance and health. This comprehensive monitoring can help you identify potential issues before they become major problems.
7.3. Upgrade for OBD2 Projects
If you are looking to enhance your OBD2 projects, the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro is the perfect upgrade. It provides deeper insights into your car’s performance, allowing you to optimize its efficiency and longevity.
By leveraging advanced tools like the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro, you can unlock the full potential of your vehicle’s OBD2 port and gain a deeper understanding of its performance.
 Image of the new CAN-FD AutoPi TMU Device, showcasing its advanced capabilities for vehicle diagnostics
Image of the new CAN-FD AutoPi TMU Device, showcasing its advanced capabilities for vehicle diagnostics
8. Common Problems And Troubleshooting
While the OBD2 system is generally reliable, problems can sometimes occur. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips:
8.1. Scanner Won’t Connect
If your scanner won’t connect to the OBD2 port, try the following:
- Check the connection: Make sure the scanner is securely plugged into the port.
- Check the ignition: Make sure the ignition is turned to the “on” position.
- Check the scanner’s power: Make sure the scanner is powered on and has sufficient battery life.
- Try a different scanner: If possible, try a different scanner to rule out a problem with the scanner itself.
- Check the OBD2 port fuse: The OBD2 port is typically protected by a fuse. Check the fuse box to see if the fuse has blown.
8.2. Inaccurate Readings
If you’re getting inaccurate readings from the OBD2 port, try the following:
- Check the scanner’s calibration: Some scanners require calibration to ensure accurate readings.
- Check the vehicle’s sensors: Faulty sensors can cause inaccurate readings.
- Check for wiring problems: Damaged or corroded wiring can also cause inaccurate readings.
8.3. Check Engine Light Won’t Turn Off
If the check engine light won’t turn off after you’ve cleared the codes, try the following:
- Make sure the problem is fixed: The check engine light will only stay off if the underlying problem has been resolved.
- Drive the vehicle: Some vehicles require a certain number of drive cycles before the check engine light will turn off.
- Check for pending codes: The scanner may be showing pending codes that haven’t yet triggered the check engine light.
8.4. Communication Errors
If you’re getting communication errors, try the following:
- Check the scanner’s compatibility: Make sure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s communication protocol.
- Check the wiring: Damaged or corroded wiring can cause communication errors.
- Check the vehicle’s computer: In rare cases, the vehicle’s computer may be faulty.
8.5. When to Seek Professional Help
If you’re unable to resolve the problem yourself, it’s best to seek professional help from a qualified mechanic.
9. FAQs About OBD2 Ports
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD2 ports:
9.1. What if I can’t find the OBD2 location?
Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual or search online for your specific vehicle’s diagnostic connector location. You can also consult our documentation at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for guidance.
9.2. Are all OBD2 ports the same?
Yes, all OBD2 ports and connectors follow the same standardization.
9.3. How many OBD2 ports does a car have?
Typically, a standard passenger car has one OBD2 port.
9.4. Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my car?
Yes, all OBD2 scanners should be compatible with any OBD2-compliant vehicle. However, some scanners may offer more advanced features or be better suited for specific makes and models.
9.5. Is it safe to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time?
It is generally not recommended to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time, as it can drain the vehicle’s battery.
9.6. Can the OBD2 port be used to track my car?
Yes, some devices can use the OBD2 port to track your car’s location. However, it’s important to be aware of the privacy implications of such devices.
9.7. How often should I scan my car’s OBD2 port?
It’s a good idea to scan your car’s OBD2 port periodically, especially if you notice any unusual symptoms or if the check engine light comes on.
9.8. What does it mean when the check engine light comes on?
The check engine light can indicate a wide range of problems, from minor issues to serious malfunctions. It’s important to scan the OBD2 port to determine the cause of the light.
9.9. Can I damage my car by using the OBD2 port?
No, using the OBD2 port correctly will not damage your car. However, it’s important to follow the scanner manufacturer’s instructions carefully and avoid making any unauthorized modifications to the vehicle’s computer system.
9.10. Where can I find more information about OBD2?
You can find more information about OBD2 on websites like CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, as well as in your vehicle’s owner’s manual.
10. Conclusion
The OBD2 port is an essential tool for modern vehicle diagnostics and maintenance. By understanding its location, function, and capabilities, you can take control of your vehicle’s health and ensure that it runs smoothly and efficiently. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a first-time car owner, the OBD2 port offers a wealth of information that can help you keep your vehicle in top condition. At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing you with the resources and tools you need to make the most of your OBD2 port and keep your vehicle running its best. By exploring our range of OBD2 tools and automotive data loggers, you can leverage the power of advanced diagnostics today.
If you’re looking for detailed information about specific auto parts or diagnostic tools, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is your go-to resource. We offer comprehensive specifications, comparisons, and user reviews to help you make informed decisions.
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s health? Contact us today via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert advice and top-quality auto parts and tools. Our address is 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States. Let CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
