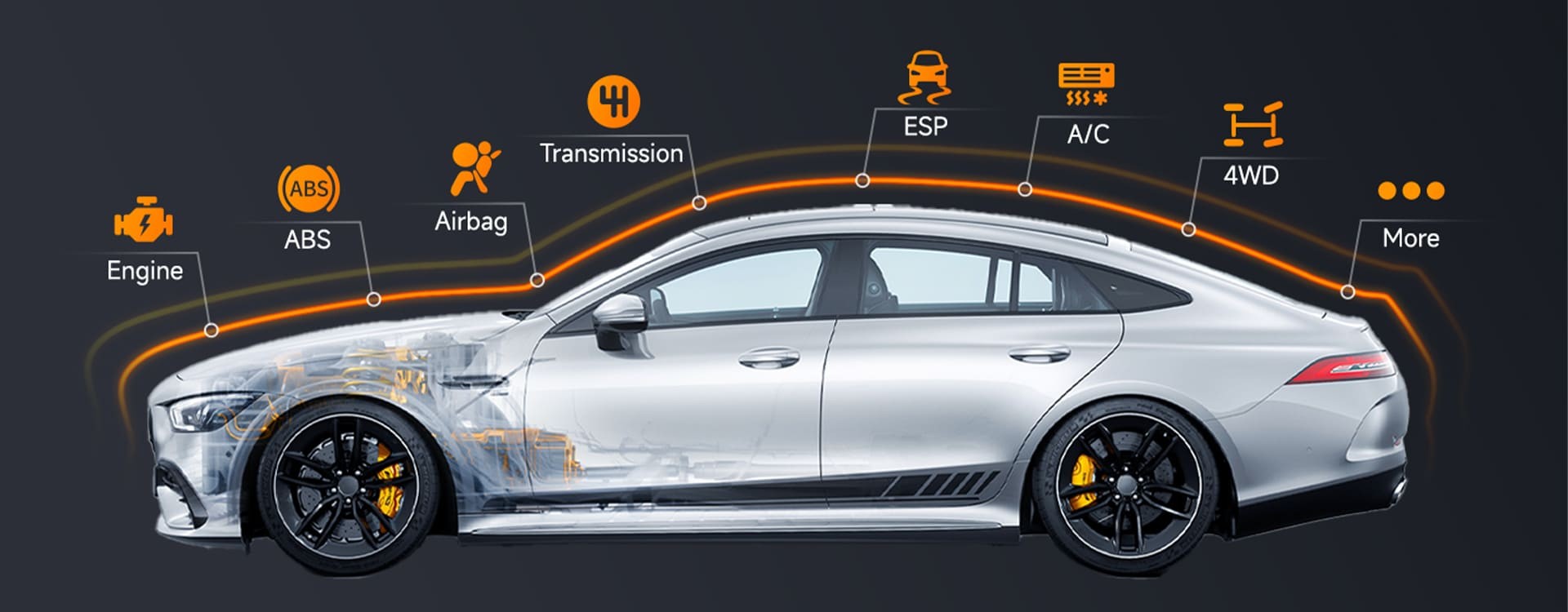
An Obd2 Airbag Scanner is a vital tool for diagnosing and resolving issues within your vehicle’s supplemental restraint system (SRS). This specialized scanner goes beyond basic engine diagnostics, offering comprehensive insights into your airbag system’s health and ensuring your safety on the road. At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide the tools and knowledge you need to maintain your vehicle’s safety systems effectively. An airbag diagnostic tool, SRS scan tool, and auto diagnostic scanner are crucial for thorough vehicle maintenance.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Need for an OBD2 Airbag Scanner
- 1.1 Why Can’t Standard OBD2 Scanners Read Airbag Codes?
- 1.2 Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Airbag Scanner
- 1.3 Top OBD2 Airbag Scanners on the Market
- 2. Identifying Airbag Sensor Issues
- 2.1 Common Symptoms of a Bad Airbag Sensor
- 2.2 Steps to Diagnose a Bad Airbag Sensor
- 2.3 The Role of Error Codes in Airbag Diagnostics
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Checking Airbag Codes
- 3.1 Gathering Necessary Tools
- 3.2 Preparing the Vehicle for Diagnosis
- 3.3 Connecting the Diagnostic Scanner
- 3.4 Navigating the Scanner Menu
- 3.5 Reading and Interpreting Airbag Codes
- 3.6 Clearing the Codes and Verifying the Fix
- 4. Understanding Airbag Light Behavior
- 4.1 Why the Airbag Light Stays On
- 4.2 Steps to Clear the Airbag Light
- 4.3 What to Do When the Light Won’t Turn Off
- 5. Choosing the Right OBD2 Airbag Scanner
- 5.1 Key Considerations for Selecting an OBD2 Airbag Scanner
- 5.2 Top Brands and Models to Consider
- 5.3 Where to Buy Reliable OBD2 Airbag Scanners
- 6. Advanced Features in OBD2 Airbag Scanners
- 6.1 Bi-Directional Control
- 6.2 ECU Programming
- 6.3 Live Data Streaming and Data Logging
- 6.4 Special Function Capabilities
- 7. Maintaining and Updating Your OBD2 Airbag Scanner
- 7.1 Importance of Regular Software Updates
- 7.2 Cleaning and Storage Tips
- 7.3 Battery Maintenance
- 8. OBD2 Airbag Scanners for Different Vehicle Types
- 8.1 Scanners for Cars and Light Trucks
- 8.2 Scanners for Heavy-Duty Vehicles
- 8.3 Scanners for Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
- 9. Common Airbag System Problems and Solutions
- 9.1 Faulty Airbag Sensors
- 9.2 Wiring and Connection Issues
- 9.3 Airbag Module Malfunctions
- 9.4 Clock Spring Issues
- 10. Safety Precautions When Working with Airbag Systems
- 10.1 Disconnecting the Battery
- 10.2 Avoiding Static Electricity
- 10.3 Following Manufacturer Instructions
- 10.4 Seeking Professional Help When Needed
- FAQ: Common Questions About OBD2 Airbag Scanners
- Can an OBD2 scanner reset the airbag light?
- Do I need a special scanner for airbag codes?
- How often should I check my airbag system?
- Can I use a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner for airbag codes?
- What does SRS mean in relation to airbag scanners?
- How do I know if my airbag sensor is faulty?
- Are all OBD2 scanners compatible with all vehicles?
- What is the difference between a basic and advanced OBD2 scanner?
- How do I update the software on my OBD2 airbag scanner?
- Can I clear airbag codes without fixing the underlying issue?
1. Understanding the Need for an OBD2 Airbag Scanner
Standard OBD2 scanners are primarily designed to read engine and transmission codes, which means they often lack the capability to access and interpret airbag (SRS) codes. According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in 2023, malfunctioning airbags can significantly increase the risk of injury in a car accident. Specialized OBD2 airbag scanners are essential for reading SRS codes, offering detailed fault information for accurate diagnosis and repair. These advanced tools provide comprehensive diagnostics for various vehicle systems, including airbags, making them invaluable for both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts focused on maintaining vehicle safety systems.
1.1 Why Can’t Standard OBD2 Scanners Read Airbag Codes?
Standard OBD2 scanners are designed to primarily address engine and transmission-related issues. They focus on reading codes associated with the powertrain, which is essential for emission control and basic vehicle functionality. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 systems were initially mandated to monitor emission-related components. This narrow focus means that these scanners typically lack the software and hardware necessary to communicate with and interpret data from the Supplemental Restraint System (SRS), which includes airbags, seatbelts, and related sensors.
1.2 Key Features to Look for in an OBD2 Airbag Scanner
When selecting an OBD2 airbag scanner, it’s important to consider several key features that ensure comprehensive and accurate diagnostics. These include:
- SRS System Compatibility: The scanner must have specialized software capable of communicating with the vehicle’s SRS to access and interpret airbag-specific codes.
- Enhanced Diagnostic Functions: The scanner should offer full-system diagnostics, including the ability to read, interpret, and clear codes from the SRS.
- Live Data Streaming: Real-time data from airbag system sensors can help diagnose issues more precisely.
- Comprehensive Vehicle Coverage: The scanner should support a wide range of vehicle makes and models, both domestic and international.
- User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive display with detailed descriptions of fault codes and possible fixes is essential.
1.3 Top OBD2 Airbag Scanners on the Market
Several high-quality OBD2 airbag scanners are available, each offering unique features and capabilities. Here are a few notable options:
| Scanner Model | Key Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| Foxwell NT716 | SRS system compatibility, full-system diagnostics, wide vehicle coverage, user-friendly interface | $200-$300 |
| Autel MaxiSys MS906BT | Advanced bi-directional control, ECU programming capabilities, comprehensive diagnostics, extensive vehicle coverage | $1,000+ |
| Launch X431 V+ | Full-system diagnostics, special function capabilities, extensive vehicle coverage, remote diagnostic function | $1,500+ |
| BlueDriver Pro | Bluetooth connectivity, smartphone integration, SRS diagnostics, user-friendly app interface | $120 |
| Innova 3160RS | ABS/SRS diagnostics, live data streaming, code clearing, freeze frame data | $200 |
 Car Diagnostic Tools
Car Diagnostic Tools
An advanced car diagnostic tool, essential for identifying and resolving complex vehicle issues.
2. Identifying Airbag Sensor Issues
Recognizing the symptoms of a malfunctioning airbag sensor is crucial for maintaining the safety of your vehicle. Common signs include an illuminated airbag warning light, error codes retrieved via a diagnostic scanner, and physical damage to the sensors themselves. According to research published in the journal “Accident Analysis & Prevention,” faulty airbag sensors can lead to non-deployment or delayed deployment of airbags during a collision, significantly increasing the risk of injury.
2.1 Common Symptoms of a Bad Airbag Sensor
Several symptoms can indicate a problem with your airbag sensor. Being aware of these signs can help you take prompt action to ensure your safety. The most common symptoms include:
- Airbag Warning Light: The most obvious sign is the illumination of the airbag warning light on your dashboard. This light indicates an issue within the SRS.
- Error Codes: Using a diagnostic scanner to retrieve error codes can pinpoint specific problems with the airbag system, such as codes B1100, B1102, or B1103, which are commonly associated with airbag sensor issues.
- Physical Damage: Inspect the airbag sensors located in the front bumper, near the radiator, or inside the passenger compartment for visible damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Performance Issues: Delayed deployment of airbags during a collision, or non-deployment in minor accidents, can indicate a faulty sensor.
2.2 Steps to Diagnose a Bad Airbag Sensor
Diagnosing a bad airbag sensor involves a systematic approach. Here are the recommended steps:
- Connect a Diagnostic Scanner: Use an advanced diagnostic scanner capable of reading SRS codes.
- Interpret the Codes: Refer to the scanner’s manual or an online database to understand the meaning of each code.
- Inspect the Sensor and Connections: Look for any obvious signs of damage or disconnection.
- Test the Sensor: Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s resistance, comparing it to the vehicle’s service manual specifications.
- Seek Professional Assistance: If you cannot diagnose the problem, consult a professional mechanic.
2.3 The Role of Error Codes in Airbag Diagnostics
Error codes play a critical role in diagnosing airbag sensor issues. These codes provide specific information about the nature and location of the problem. Some common error codes related to airbag sensors include:
| Error Code | Description | Possible Cause |
|---|---|---|
| B1100 | Driver Airbag Circuit Malfunction | Faulty driver airbag, wiring issues, or a problem with the airbag module |
| B1102 | Passenger Airbag Circuit Malfunction | Faulty passenger airbag, wiring issues, or a problem with the airbag module |
| B1103 | Side Airbag Circuit Malfunction | Faulty side airbag, wiring issues, or a problem with the airbag module |
| B0001 | Driver Frontal Stage 1 Deployment Control | Faulty deployment control, wiring issues |
| B0002 | Driver Frontal Stage 2 Deployment Control | Faulty deployment control, wiring issues |
 OBD2 Scanner with Display
OBD2 Scanner with Display
The OBD2 scanner with a clear display shows diagnostic data for car maintenance.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Checking Airbag Codes
Checking airbag codes requires a methodical approach to ensure accurate diagnosis. This process involves gathering the necessary tools, preparing the vehicle, connecting the diagnostic scanner, and interpreting the retrieved codes. According to a technical guide published by Bosch Automotive, proper diagnostic procedures are essential for maintaining the functionality of modern vehicle safety systems.
3.1 Gathering Necessary Tools
Before starting, ensure you have the following tools:
- Diagnostic Scanner: An advanced scanner capable of reading SRS codes is essential.
- Vehicle Service Manual: This manual provides specific information about the OBD2 port location and details about the airbag system.
3.2 Preparing the Vehicle for Diagnosis
Follow these steps to prepare your vehicle:
- Turn Off the Engine: Ensure the engine is off before connecting the scanner.
- Ignition Position: Insert the key and turn it to the “On” position without starting the engine.
3.3 Connecting the Diagnostic Scanner
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is usually under the dashboard, near the steering wheel. Consult your vehicle’s service manual if needed.
- Plug in the Scanner: Insert the scanner’s connector into the OBD2 port securely.
- Power On the Scanner: Turn on the scanner if necessary.
3.4 Navigating the Scanner Menu
- Select Vehicle Make and Model: Enter the required information about your vehicle.
- Choose SRS System: Select the SRS (airbag) system from the scanner’s menu.
3.5 Reading and Interpreting Airbag Codes
- Initiate Scan: Follow the prompts on the scanner to begin the SRS system scan.
- Retrieve Codes: The scanner will display any stored fault codes.
- Note the Codes: Write down the codes or save them using the scanner’s memory function.
- Refer to Manual: Use the vehicle’s service manual or the scanner’s built-in code library to interpret the codes.
- Research Online: Look up the codes online for more detailed information.
3.6 Clearing the Codes and Verifying the Fix
- Fix the Issue First: Address the underlying issue before clearing any codes.
- Clear Codes: Use the scanner to clear the codes.
- Re-scan the System: Perform another scan to ensure no new codes appear.
- Check Airbag Light: Make sure the airbag warning light on the dashboard is off.
4. Understanding Airbag Light Behavior
The airbag light is a critical indicator of your vehicle’s SRS status. Understanding why the light stays on and how to address it is essential for maintaining your safety. According to safety guidelines from the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), ignoring an airbag warning light can compromise the effectiveness of the airbag system in the event of a collision.
4.1 Why the Airbag Light Stays On
The airbag light typically stays on for the following reasons:
- Persistent Fault Codes: The vehicle’s ECU stores a fault code when there is an issue with the airbag system, triggering the warning light.
- Manual Reset Required: Fault codes remain stored in the ECU’s memory even after the underlying issue is resolved, requiring manual clearing with a diagnostic scanner.
- Safety Precaution: The airbag warning light is a crucial safety feature that alerts the driver to potential issues.
4.2 Steps to Clear the Airbag Light
Follow these steps to clear the airbag light:
- Diagnose the Problem: Use a diagnostic scanner to read the specific fault codes.
- Fix the Problem: Repair or replace any faulty parts identified by the scanner.
- Clear the Fault Codes: Use the diagnostic scanner to clear the stored fault codes from the ECU.
- Confirm the Light is Off: Check the dashboard to ensure the airbag warning light is no longer illuminated.
4.3 What to Do When the Light Won’t Turn Off
If the airbag light remains on after clearing the codes:
- Persistent Issues: There may be unresolved issues with the system. Re-scan the vehicle to check for new or remaining fault codes.
- Further Inspection Needed: Persistent warning lights may require further inspection and diagnostics by a professional.
A complete automotive diagnostic tool set, ideal for both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts.
5. Choosing the Right OBD2 Airbag Scanner
Selecting the right OBD2 airbag scanner is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance. Consider the factors outlined in this guide to make an informed decision.
5.1 Key Considerations for Selecting an OBD2 Airbag Scanner
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Features: Look for features such as SRS system compatibility, full-system diagnostics, and live data streaming.
- User Interface: Choose a scanner with an intuitive and easy-to-read display.
- Update Capability: Ensure the scanner can receive regular firmware updates.
- Price: Balance the features with your budget to find the best value.
5.2 Top Brands and Models to Consider
Here are some top brands and models to consider:
- Foxwell NT716: Known for its SRS system compatibility and user-friendly interface.
- Autel MaxiSys MS906BT: Offers advanced bi-directional control and ECU programming capabilities.
- Launch X431 V+: Provides full-system diagnostics and extensive vehicle coverage.
- BlueDriver Pro: Integrates with smartphones and offers a user-friendly app interface.
- Innova 3160RS: Offers ABS/SRS diagnostics and live data streaming.
5.3 Where to Buy Reliable OBD2 Airbag Scanners
Reliable OBD2 airbag scanners can be purchased from various sources:
- Online Retailers: Websites like Amazon, eBay, and специализированные automotive parts retailers offer a wide selection.
- Local Auto Parts Stores: Stores like AutoZone, O’Reilly Auto Parts, and Advance Auto Parts carry a range of scanners.
- Professional Tool Suppliers: Companies like Snap-on and Mac Tools supply high-end scanners for professional mechanics.
6. Advanced Features in OBD2 Airbag Scanners
Advanced OBD2 airbag scanners offer features that go beyond basic code reading, providing more in-depth diagnostic capabilities. These features can significantly enhance your ability to diagnose and repair complex airbag system issues.
6.1 Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control allows the scanner to send commands to the vehicle’s SRS for in-depth diagnostics and testing. This feature can help you activate and test individual components, such as airbags and sensors, to ensure they are functioning correctly.
6.2 ECU Programming
Some high-end scanners offer ECU programming capabilities, allowing for updates and changes to the vehicle’s software. This feature can be useful for addressing software-related issues within the airbag system.
6.3 Live Data Streaming and Data Logging
Live data streaming provides real-time data from the airbag system sensors, allowing you to monitor their performance under various conditions. Data logging enables you to record this data for later analysis, which can be helpful for diagnosing intermittent issues.
6.4 Special Function Capabilities
Advanced scanners often include special function capabilities, such as the ability to reset the airbag control module after repairs. These functions can streamline the repair process and ensure the airbag system is properly configured.
7. Maintaining and Updating Your OBD2 Airbag Scanner
Proper maintenance and regular updates are essential for ensuring the longevity and accuracy of your OBD2 airbag scanner. Follow these guidelines to keep your scanner in top condition.
7.1 Importance of Regular Software Updates
Regular software updates ensure that your scanner is compatible with the latest vehicle models and systems. Updates also include bug fixes and improvements to diagnostic accuracy.
7.2 Cleaning and Storage Tips
- Cleaning: Clean the scanner with a soft, dry cloth. Avoid using harsh chemicals or solvents.
- Storage: Store the scanner in a clean, dry place away from extreme temperatures and humidity.
7.3 Battery Maintenance
If your scanner has a rechargeable battery, follow these tips:
- Charging: Charge the battery fully before first use.
- Regular Use: Use the scanner regularly to maintain battery health.
- Storage: Store the scanner with the battery partially charged if it will not be used for an extended period.
8. OBD2 Airbag Scanners for Different Vehicle Types
The type of OBD2 airbag scanner you need may vary depending on the type of vehicle you own. Consider the following factors when choosing a scanner for your specific vehicle type.
8.1 Scanners for Cars and Light Trucks
Most standard OBD2 airbag scanners are designed for use on cars and light trucks. Ensure that the scanner you choose supports the make and model of your vehicle.
8.2 Scanners for Heavy-Duty Vehicles
Heavy-duty vehicles, such as commercial trucks and buses, may require specialized scanners with enhanced diagnostic capabilities. Look for scanners that support heavy-duty protocols and offer comprehensive system coverage.
8.3 Scanners for Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
Electric and hybrid vehicles have unique diagnostic requirements due to their complex electrical systems. Choose a scanner that is specifically designed for use on electric and hybrid vehicles and supports their diagnostic protocols.
9. Common Airbag System Problems and Solutions
Understanding common airbag system problems and their solutions can help you effectively use your OBD2 airbag scanner to diagnose and repair issues.
9.1 Faulty Airbag Sensors
Faulty airbag sensors are a common cause of airbag system problems. Use your scanner to identify the specific sensor that is malfunctioning and replace it with a new one.
9.2 Wiring and Connection Issues
Wiring and connection issues can also cause airbag system problems. Inspect the wiring and connections for any signs of damage, corrosion, or looseness. Repair or replace any damaged wiring and ensure that all connections are secure.
9.3 Airbag Module Malfunctions
Airbag module malfunctions can be more complex to diagnose and repair. Use your scanner to retrieve fault codes and consult a professional mechanic for assistance.
9.4 Clock Spring Issues
The clock spring is a spiral-wound ribbon cable that allows the steering wheel to turn while maintaining an electrical connection to the airbag and other components. A faulty clock spring can cause the airbag light to illuminate and may require replacement.
10. Safety Precautions When Working with Airbag Systems
Working with airbag systems can be dangerous due to the risk of accidental deployment. Follow these safety precautions to minimize the risk of injury.
10.1 Disconnecting the Battery
Always disconnect the vehicle’s battery before working on the airbag system. This will prevent accidental deployment of the airbags.
10.2 Avoiding Static Electricity
Static electricity can trigger airbag deployment. Ground yourself by touching a metal part of the vehicle before working on the airbag system.
10.3 Following Manufacturer Instructions
Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when working on the airbag system. This will ensure that you are using the correct procedures and avoiding potential hazards.
10.4 Seeking Professional Help When Needed
If you are not comfortable working on the airbag system, seek help from a professional mechanic. They have the training and experience to safely diagnose and repair airbag system problems.
Remember, an OBD2 airbag scanner is an invaluable tool for maintaining the safety of your vehicle. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can effectively use your scanner to diagnose and repair airbag system problems and ensure your safety on the road. For more information and assistance with your automotive diagnostic needs, visit CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN or contact us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States. You can also reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880.
FAQ: Common Questions About OBD2 Airbag Scanners
Can an OBD2 scanner reset the airbag light?
Yes, an advanced OBD2 scanner that reads SRS codes can reset the airbag light after the issue has been resolved.
Do I need a special scanner for airbag codes?
Yes, you need an advanced or professional OBD2 scanner specifically designed for reading airbag codes.
How often should I check my airbag system?
You should check your airbag system whenever the airbag warning light illuminates or as part of your routine vehicle maintenance.
Can I use a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner for airbag codes?
Yes, some Bluetooth OBD2 scanners, like the BlueDriver Pro, can read airbag codes when paired with a compatible smartphone app.
What does SRS mean in relation to airbag scanners?
SRS stands for Supplemental Restraint System, which includes airbags, seatbelts, and related sensors.
How do I know if my airbag sensor is faulty?
Symptoms of a faulty airbag sensor include an illuminated airbag warning light, error codes retrieved via a diagnostic scanner, and visible damage to the sensors.
Are all OBD2 scanners compatible with all vehicles?
No, compatibility varies depending on the scanner’s software and vehicle coverage. Ensure the scanner supports your vehicle’s make and model.
What is the difference between a basic and advanced OBD2 scanner?
Basic OBD2 scanners focus on engine and emission-related codes, while advanced scanners cover more systems, including airbags, ABS, and transmission.
How do I update the software on my OBD2 airbag scanner?
Refer to the scanner’s manual for instructions on how to update the software. Updates are typically downloaded from the manufacturer’s website and installed via USB or Wi-Fi.
Can I clear airbag codes without fixing the underlying issue?
While you can clear airbag codes, the airbag light will likely reappear if the underlying issue is not resolved. It’s important to diagnose and fix the problem before clearing the codes.
Ready to ensure your vehicle’s safety systems are functioning correctly? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert advice and the best OBD2 airbag scanners on the market. Reach us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, for more information!