Obd Port Finder is an essential tool for accessing your vehicle’s diagnostic data, and at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we simplify this process. Understanding how to locate and utilize your OBD II connector empowers you to efficiently monitor and maintain your vehicle’s health. Explore diagnostic port locations, automotive diagnostic tools, and vehicle data retrieval with us.
Contents
- 1. What is an OBD Port Finder and Why Do You Need One?
- 1.1. Understanding the Importance of the OBD II Port
- 1.2. Common Reasons for Using an OBD Port Finder
- 1.3. The Evolution from OBD I to OBD II
- 1.4. Intended Search queries for “OBD Port Finder”
- 2. Where to Find Your OBD Port: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2.1. Common OBD Port Locations by Vehicle Type
- 2.2. Step-by-Step Guide to Locating Your OBD Port
- 2.3. Using Online OBD Port Finder Tools
- 2.4. Troubleshooting Common Issues When Finding the OBD Port
- 3. The OBD II Connector and Pinout: What You Need to Know
- 3.1. Understanding the OBD II Pinout
- 3.2. Key Pin Functions and Their Importance
- 3.3. How the OBD II Connector Facilitates Vehicle Diagnostics
- 3.4. Common Issues with the OBD II Connector and How to Resolve Them
- 4. Why the OBD Port is Essential for Modern Vehicle Maintenance
- 4.1. Accessing Real-Time Vehicle Data
- 4.2. Diagnosing and Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.3. Ensuring Compliance with Emissions Standards
- 4.4. Enhancing Vehicle Performance and Fuel Efficiency
- 5. How to Use the OBD Port Effectively for Vehicle Diagnostics
- 5.1. Choosing the Right OBD II Scanner or Code Reader
- 5.2. Connecting the Scanner to the OBD Port
- 5.3. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 5.4. Utilizing Live Data for In-Depth Analysis
- 5.5. Safety Precautions When Using the OBD Port
- 6. Advanced OBD II Applications and Tools
- 6.1. Performance Monitoring and Tuning
- 6.2. Data Logging for Advanced Diagnostics
- 6.3. ECU Programming and Reprogramming
- 6.4. The AutoPi CAN-FD Pro: Taking Vehicle Diagnostics to the Next Level
- 7. Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for Your OBD Port Needs
- 7.1. Comprehensive OBD Port Database
- 7.2. Expert Advice and Guidance
- 7.3. High-Quality OBD II Tools and Equipment
- 7.4. Up-to-Date Information and Resources
- 7.5. Contact Us for Personalized Assistance
- 8. FAQ: Your Questions About OBD Ports Answered
- 9. Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Your OBD Port
1. What is an OBD Port Finder and Why Do You Need One?
An OBD port finder is a tool or guide that helps you locate the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) port in your vehicle. This port is essential for accessing your car’s computer system, allowing you to diagnose issues, read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and monitor various performance parameters.
The OBD II port, standardized since 1996, is a crucial access point for mechanics and vehicle owners alike. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD II systems monitor nearly everything that can affect emissions, ensuring vehicles meet environmental standards. Using an OBD port finder can save you time and frustration by quickly pinpointing the port’s location.
1.1. Understanding the Importance of the OBD II Port
The OBD II port serves as the gateway to your vehicle’s central computer, providing access to a wealth of information about its operation. This data includes:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These codes indicate specific issues or malfunctions within the vehicle’s systems, such as the engine, transmission, or emissions control system.
- Live Data: Real-time information about various engine parameters, including engine speed (RPM), coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim levels.
- Freeze Frame Data: A snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a DTC was triggered, providing valuable context for diagnosing intermittent issues.
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): A unique identifier for your vehicle, which can be used to retrieve vehicle-specific information and specifications.
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), technicians who utilize OBD II data effectively can diagnose and repair vehicles more quickly and accurately, reducing repair times and improving customer satisfaction.
1.2. Common Reasons for Using an OBD Port Finder
There are several reasons why you might need an OBD port finder:
- First-Time Use: If you’re new to vehicle diagnostics or have recently purchased a new car, you may not know the exact location of the OBD port.
- Vehicle Model Variations: Although the OBD II port is standardized, its location can vary depending on the make, model, and year of the vehicle.
- Hidden or Obscured Ports: In some vehicles, the OBD port may be hidden behind a panel or obscured by other components.
- Using Diagnostic Tools: To connect diagnostic tools, such as scan tools, code readers, or performance monitors, you need to access the OBD port.
1.3. The Evolution from OBD I to OBD II
The transition from OBD I to OBD II marked a significant advancement in vehicle diagnostics. OBD I systems were manufacturer-specific, meaning each automaker used different connectors, protocols, and diagnostic codes. This lack of standardization made it difficult for technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles from different manufacturers.
In contrast, OBD II systems are standardized across all vehicles sold in the United States since 1996. This standardization includes:
- A Universal Connector: All OBD II-compliant vehicles use the same 16-pin Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC).
- Standardized Diagnostic Codes: DTCs are standardized, allowing technicians to use the same code definitions across different makes and models.
- Common Communication Protocols: OBD II systems use a set of standardized communication protocols, enabling diagnostic tools to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
According to a report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the standardization of OBD II has greatly simplified vehicle diagnostics, making it easier for technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles from different manufacturers.
1.4. Intended Search queries for “OBD Port Finder”
- “Where is my OBD port located?” Users want to quickly find the OBD port in their specific vehicle model.
- “OBD2 port location guide” Users are looking for a comprehensive guide to help them locate the OBD2 port.
- “How to find OBD port in car” Users seek instructions on how to locate the OBD port in their car.
- “OBD port finder tool” Users are interested in using a tool to help them locate the OBD port.
- “Vehicle diagnostic port location” Users want to know where the diagnostic port is located for vehicle maintenance.
 Illustration of typical obd2 port locations in a common vehicle
Illustration of typical obd2 port locations in a common vehicle
2. Where to Find Your OBD Port: A Comprehensive Guide
The OBD II port is typically located inside the passenger compartment, but its exact placement can vary depending on the vehicle’s make, model, and year. Here are some common locations to check:
- Under the Dashboard: This is the most common location, usually on the driver’s side, near the steering column.
- Near the Center Console: In some vehicles, the OBD port may be located in the center console area, often near the gear shifter or parking brake.
- Behind a Panel: Some manufacturers conceal the OBD port behind a small panel or access door, which may require a screwdriver or other tool to remove.
- In the Glove Compartment: Although less common, a few vehicles have the OBD port located inside the glove compartment.
If you’re having trouble locating the OBD port, consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or use an online OBD port finder tool. These resources can provide specific information about your vehicle’s OBD port location.
2.1. Common OBD Port Locations by Vehicle Type
The location of the OBD II port can differ based on the type of vehicle. Here’s a breakdown of common locations:
- Sedans and Hatchbacks: Typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- SUVs and Trucks: Often located under the dashboard but can also be found near the center console.
- Vans: May be located under the dashboard or in the glove compartment.
- European Vehicles: Frequently placed in the center console or behind a panel.
According to research by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), knowing the common locations for different vehicle types can significantly reduce the time spent searching for the OBD II port.
2.2. Step-by-Step Guide to Locating Your OBD Port
Follow these steps to find your OBD II port:
- Consult Your Owner’s Manual: The owner’s manual is the best resource for finding the exact location of the OBD II port in your vehicle.
- Check Under the Dashboard: Look under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the steering column. Use a flashlight to illuminate the area.
- Inspect the Center Console: Check the center console area, near the gear shifter or parking brake.
- Look for a Panel or Access Door: Some vehicles conceal the OBD II port behind a small panel or access door.
- Check the Glove Compartment: Although less common, a few vehicles have the OBD II port located inside the glove compartment.
2.3. Using Online OBD Port Finder Tools
Several online tools can help you locate your OBD II port. These tools typically require you to enter your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Once you provide this information, the tool will display the most likely location of the OBD II port in your vehicle.
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive OBD port lookup tool to help you quickly identify the port’s location.
2.4. Troubleshooting Common Issues When Finding the OBD Port
Sometimes, finding the OBD II port can be challenging. Here are some common issues and how to troubleshoot them:
- Port Hidden by Wires or Cables: Gently move any wires or cables that may be obstructing your view of the OBD II port.
- Port Covered by a Panel: Use a screwdriver or other tool to remove the panel covering the OBD II port.
- Port Located in an Unusual Spot: Consult your owner’s manual or an online OBD port finder tool for specific information about your vehicle.
3. The OBD II Connector and Pinout: What You Need to Know
The OBD II connector is a 16-pin Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC) that provides access to the vehicle’s computer system. Each pin in the connector has a specific function, allowing diagnostic tools to communicate with various vehicle systems.
3.1. Understanding the OBD II Pinout
The OBD II connector has a standardized pinout, meaning each pin is assigned a specific function. Here’s a breakdown of the most important pins:
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground
- Pin 5: Signal Ground
- Pin 6: CAN High (J-2284)
- Pin 7: ISO 9141-2 K Line
- Pin 10: SAE J1850 Bus (-)
- Pin 14: CAN Low (J-2284)
- Pin 15: ISO 9141-2 L Line
- Pin 16: Battery Power
According to the SAE, understanding the OBD II pinout is essential for developing and using diagnostic tools.
3.2. Key Pin Functions and Their Importance
Here’s a closer look at some of the key pin functions and their importance:
- Ground Pins (4 and 5): Provide a common ground for the diagnostic tool and the vehicle’s computer system, ensuring accurate data transmission.
- CAN Bus Pins (6 and 14): Allow communication with the vehicle’s Controller Area Network (CAN) bus, which is used to transmit data between various electronic control units (ECUs).
- ISO 9141-2 K and L Lines (7 and 15): Used for communication with older vehicles that do not support CAN bus.
- Battery Power (16): Provides power to the diagnostic tool.
3.3. How the OBD II Connector Facilitates Vehicle Diagnostics
The OBD II connector serves as a standardized interface between the vehicle’s computer system and diagnostic tools. This standardization allows technicians to use a single diagnostic tool to diagnose and repair vehicles from different manufacturers. The connector provides access to a wealth of information about the vehicle’s operation, including diagnostic trouble codes, live data, and freeze frame data. This information can be used to identify and diagnose a wide range of vehicle issues.
3.4. Common Issues with the OBD II Connector and How to Resolve Them
Here are some common issues with the OBD II connector and how to resolve them:
- Damaged Pins: Inspect the connector for any bent or broken pins. If you find any damaged pins, you may need to replace the connector.
- Corrosion: Clean the connector with a contact cleaner to remove any corrosion.
- Loose Connection: Ensure the connector is securely plugged into the OBD II port.
- Faulty Wiring: Check the wiring connected to the OBD II connector for any damage or loose connections.
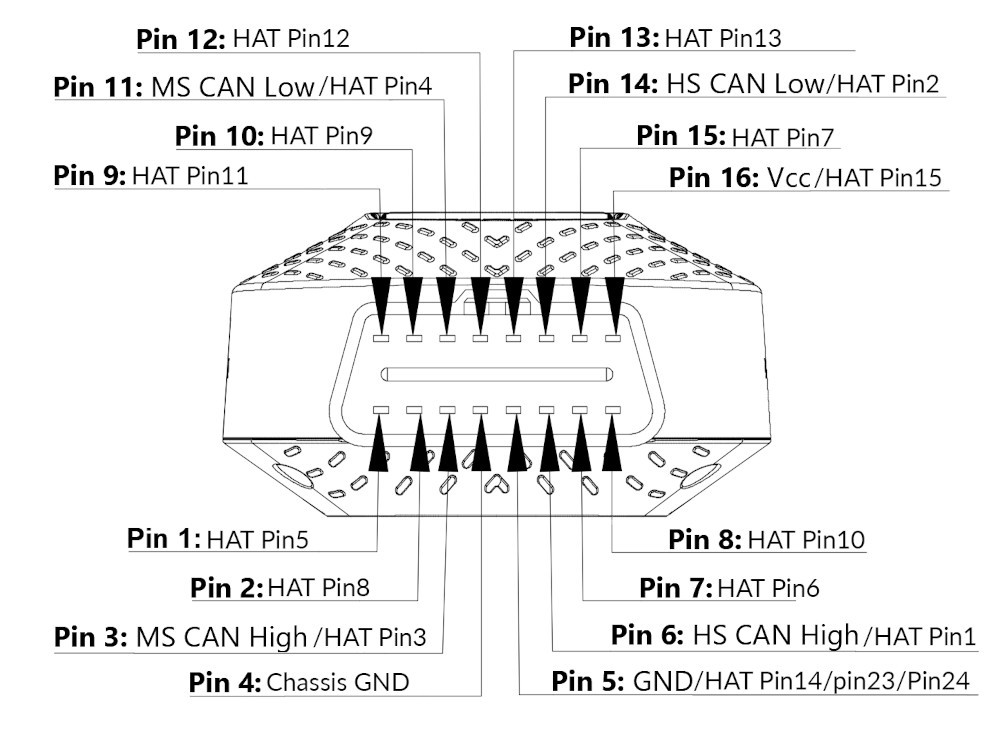 OBD2 connector pinouts from autopi device
OBD2 connector pinouts from autopi device
4. Why the OBD Port is Essential for Modern Vehicle Maintenance
The OBD port is indispensable for modern vehicle maintenance because it provides access to critical diagnostic data. This data enables technicians and vehicle owners to identify and address issues before they escalate into more significant problems.
4.1. Accessing Real-Time Vehicle Data
The OBD II port allows you to access real-time data about your vehicle’s operation. This data includes:
- Engine Speed (RPM): The number of revolutions per minute the engine is turning.
- Coolant Temperature: The temperature of the engine coolant.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: The amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
- Fuel Trim Levels: Adjustments to the amount of fuel being injected into the engine.
This real-time data can be used to monitor your vehicle’s performance and identify any potential issues.
4.2. Diagnosing and Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
The OBD II port allows you to diagnose and clear DTCs. These codes indicate specific issues or malfunctions within the vehicle’s systems. By reading the DTCs, you can identify the source of the problem and take steps to repair it. Once the problem is resolved, you can clear the DTCs to turn off the check engine light.
According to the EPA, the OBD II system is designed to monitor nearly everything that can affect emissions. This means that DTCs can indicate a wide range of issues, from minor problems like a loose gas cap to more serious problems like a faulty oxygen sensor or catalytic converter.
4.3. Ensuring Compliance with Emissions Standards
The OBD II port plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance with emissions standards. The OBD II system monitors various components and systems that affect emissions, such as the oxygen sensors, catalytic converter, and evaporative emissions control system. If the OBD II system detects a problem that could cause the vehicle to exceed emissions standards, it will set a DTC and illuminate the check engine light.
By addressing these issues promptly, you can ensure that your vehicle complies with emissions standards and avoid costly fines or penalties.
4.4. Enhancing Vehicle Performance and Fuel Efficiency
The OBD II port can also be used to enhance vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. By monitoring real-time data and diagnosing DTCs, you can identify and address issues that may be affecting your vehicle’s performance or fuel economy. For example, a faulty oxygen sensor can cause the engine to run rich, which can reduce fuel efficiency and increase emissions. By replacing the faulty oxygen sensor, you can restore your vehicle’s performance and fuel economy.
 Keywords about the OBD2 connector and why its important as a gateway
Keywords about the OBD2 connector and why its important as a gateway
5. How to Use the OBD Port Effectively for Vehicle Diagnostics
Using the OBD II port effectively requires the right tools and knowledge. Here are some tips for using the OBD II port for vehicle diagnostics:
5.1. Choosing the Right OBD II Scanner or Code Reader
There are many different OBD II scanners and code readers available on the market, ranging from basic code readers to advanced scan tools. When choosing an OBD II scanner or code reader, consider the following factors:
- Features: Determine what features you need. Do you need to read and clear DTCs, view live data, perform advanced diagnostics, or program ECUs?
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner or code reader is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner or code reader that is easy to use and has a clear, intuitive interface.
- Price: Set a budget and choose a scanner or code reader that fits your needs and your budget.
5.2. Connecting the Scanner to the OBD Port
Connecting the scanner to the OBD II port is typically straightforward. Simply plug the scanner’s connector into the OBD II port. Make sure the connector is securely plugged in and that the scanner is powered on.
5.3. Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DTCs are five-digit codes that indicate specific issues or malfunctions within the vehicle’s systems. The first character of the DTC indicates the system that is affected:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission, etc.)
- B: Body (airbags, lights, etc.)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension, etc.)
- U: Network (communication systems)
The remaining four characters of the DTC provide more specific information about the nature of the problem. You can use an online DTC lookup tool or consult a repair manual to interpret the DTC and identify the source of the problem.
5.4. Utilizing Live Data for In-Depth Analysis
Live data provides real-time information about your vehicle’s operation. This data can be used to monitor your vehicle’s performance and identify any potential issues. For example, you can use live data to monitor the engine’s coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim levels.
By analyzing live data, you can gain a deeper understanding of your vehicle’s operation and identify subtle issues that may not trigger a DTC.
5.5. Safety Precautions When Using the OBD Port
When using the OBD II port, it’s important to take certain safety precautions:
- Do not use the OBD II port while driving.
- Disconnect the scanner before starting or stopping the engine.
- Do not attempt to repair any components or systems unless you are qualified to do so.
- Consult a professional technician if you are unsure about any aspect of the diagnostic or repair process.
6. Advanced OBD II Applications and Tools
Beyond basic diagnostics, the OBD II port can be used for a variety of advanced applications, including performance monitoring, data logging, and ECU programming.
6.1. Performance Monitoring and Tuning
The OBD II port can be used to monitor your vehicle’s performance and make adjustments to improve its performance. For example, you can use a performance monitor to track your vehicle’s horsepower, torque, and acceleration. You can also use the OBD II port to adjust various engine parameters, such as fuel injection timing and ignition timing.
However, it’s important to note that making changes to your vehicle’s ECU can void your warranty and may not be legal in all areas.
6.2. Data Logging for Advanced Diagnostics
Data logging involves recording real-time data from the OBD II port over a period of time. This data can be used to analyze your vehicle’s performance under different conditions and identify any potential issues. For example, you can use data logging to track your vehicle’s fuel economy over a long period of time or to monitor the performance of your engine during a race.
6.3. ECU Programming and Reprogramming
ECU programming and reprogramming involve modifying the software that controls your vehicle’s engine and other systems. This can be used to improve your vehicle’s performance, fuel economy, or emissions. However, it’s important to note that ECU programming and reprogramming can be complex and may require specialized tools and knowledge.
6.4. The AutoPi CAN-FD Pro: Taking Vehicle Diagnostics to the Next Level
The AutoPi CAN-FD Pro is an advanced diagnostic tool that connects to your vehicle’s OBD II port and provides faster, more detailed insights into your vehicle’s performance. It works with your OBD II port to give you faster, more detailed insights into your vehicle’s performance. The AutoPi device helps you keep track of important car systems, like the engine and emissions. If you want deeper insights into how your car is really doing, the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro is the perfect upgrade to your OBD II projects.
 The new CAN-FD AutoPi TMU Device
The new CAN-FD AutoPi TMU Device
7. Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for Your OBD Port Needs
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is your go-to resource for all things OBD II. We provide comprehensive information, tools, and resources to help you locate, understand, and utilize your vehicle’s OBD II port.
7.1. Comprehensive OBD Port Database
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN features a comprehensive database of OBD II port locations for a wide range of vehicles. Simply enter your vehicle’s make, model, and year, and we’ll show you the exact location of the OBD II port.
7.2. Expert Advice and Guidance
Our team of experienced automotive technicians is available to provide expert advice and guidance on all aspects of OBD II diagnostics. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional technician, we can help you get the most out of your OBD II port.
7.3. High-Quality OBD II Tools and Equipment
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wide selection of high-quality OBD II tools and equipment, including scanners, code readers, and performance monitors. We only carry products from trusted brands that are known for their reliability and accuracy.
7.4. Up-to-Date Information and Resources
We are constantly updating our website with the latest information and resources on OBD II diagnostics. We also provide access to a library of repair manuals, technical articles, and other resources to help you stay informed about the latest automotive technologies.
7.5. Contact Us for Personalized Assistance
If you have any questions or need assistance with locating your OBD II port or using OBD II tools, please don’t hesitate to contact us. Our team is available to provide personalized assistance and help you find the right solutions for your needs. You can reach us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information.
8. FAQ: Your Questions About OBD Ports Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD ports:
8.1. What if I can’t find the OBD2 location?
Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or search online for your specific vehicle’s diagnostic connector location.
8.2. Are all OBD2 ports the same?
Yes, all OBD2 ports and connectors follow the same standardization.
8.3. How many OBD2 ports does a car have?
Typically, a standard passenger car has one OBD2 port.
8.4. What does OBD port stand for?
OBD stands for On-Board Diagnostics. It’s a system that monitors a vehicle’s performance and identifies potential issues.
8.5. Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my car?
Most OBD2 scanners are universally compatible with vehicles manufactured after 1996. However, it’s always best to check the scanner’s compatibility list to ensure it works with your specific make and model.
8.6. Is it safe to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in?
Leaving an OBD2 scanner plugged in can drain the battery over time, especially if the vehicle is not used regularly. It’s generally recommended to unplug the scanner when not in use.
8.7. Can an OBD2 scanner improve my car’s performance?
An OBD2 scanner itself cannot improve your car’s performance. However, it can help you identify issues that may be affecting performance, such as faulty sensors or engine problems.
8.8. What should I do if my OBD port isn’t working?
Check the fuses related to the OBD port and ensure the port is clean and free from debris. If the port still isn’t working, there may be an issue with the vehicle’s computer system, requiring professional diagnosis.
8.9. Are there different types of OBD2 protocols?
Yes, there are several OBD2 protocols, including CAN (Controller Area Network), ISO 9141-2, SAE J1850 VPW, and SAE J1850 PWM. Most modern vehicles use the CAN protocol.
8.10. Where can I find more information about OBD2 codes?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive resources and information about OBD2 codes. You can also consult your vehicle’s repair manual or seek advice from a qualified technician.
9. Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Your OBD Port
The OBD II port is a powerful tool that can help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. By understanding how to locate, use, and interpret the data from your OBD II port, you can save time, money, and frustration.
At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing you with the information, tools, and resources you need to get the most out of your OBD II port. Explore our website today to learn more about OBD II diagnostics and how it can benefit you.
Don’t let vehicle diagnostics intimidate you. With the right tools and knowledge, you can harness the power of your OBD II port and keep your vehicle running at its best.
For expert advice and guidance on all aspects of OBD II diagnostics, contact us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information. Let CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in vehicle maintenance and diagnostics.