Ob2 Scanner Codes are diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that your vehicle’s onboard computer system uses to report issues. Understanding these codes is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance and can save you time and money. At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we help you decipher these codes and provide the tools and knowledge you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly, so you can easily find the right auto parts, compare repair tool prices and features, and access reliable information. With this information, you can avoid the uncertainty of product durability and effectiveness, read user reviews, and locate reputable suppliers with the best prices.
Contents
- 1. What Exactly Are OB2 Scanner Codes?
- 2. What Are the Primary Categories of OB2 Codes?
- 2.1. Powertrain Codes
- 2.2. Body Codes
- 2.3. Chassis Codes
- 2.4. Network Communication Codes
- 3. How to Interpret OB2 Code Structure?
- 4. What Tools Are Needed to Read OB2 Codes?
- 4.1. Basic OB2 Code Readers
- 4.2. Advanced Diagnostic Scanners
- 4.3. Smartphone-Based Scanners
- 5. How to Use an OB2 Scanner to Retrieve Codes?
- 6. Where Can I Find a Comprehensive OB2 Code List?
- 6.1. Online Databases
- 6.2. Repair Manuals
- 6.3. Smartphone Apps
- 7. How to Diagnose Common OB2 Codes?
- 7.1. P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- 7.2. P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 7.3. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 8. What Are Some Common Mistakes When Diagnosing OB2 Codes?
- 8.1. Replacing Parts Without Proper Diagnosis
- 8.2. Ignoring Related Symptoms
- 8.3. Using Inexpensive Code Readers for Complex Problems
- 8.4. Neglecting Basic Maintenance
- 9. How Can I Clear OB2 Codes?
- 9.1. Using an OB2 Scanner to Clear Codes
- 9.2. Disconnecting the Battery
- 10. What Role Do Oxygen Sensors Play in OB2 Codes?
- 10.1. How Oxygen Sensors Work
- 10.2. Common OB2 Codes Related to Oxygen Sensors
- 10.3. Diagnosing Oxygen Sensor Problems
- 11. What Is Freeze Frame Data and How to Use It?
- 11.1. What Information Does Freeze Frame Data Include?
- 11.2. How to Access Freeze Frame Data
- 11.3. Interpreting Freeze Frame Data
- 12. How Can I Prevent OB2 Codes From Occurring?
- 12.1. Regular Maintenance
- 12.2. Using High-Quality Parts and Fluids
- 12.3. Addressing Minor Issues Promptly
- 12.4. Driving Habits
- 13. Where Can I Get Professional Help with OB2 Codes?
- 13.1. Local Mechanics
- 13.2. Dealership Service Centers
- 13.3. Online Diagnostic Services
- 14. How Can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Help with OB2 Codes?
- 14.1. Comprehensive Product Listings
- 14.2. User Reviews and Ratings
- 14.3. Expert Advice and Guides
- 14.4. Contact Us for Personalized Assistance
- 15. What Are Some Advanced OB2 Diagnostic Techniques?
- 15.1. Performing a Compression Test
- 15.2. Performing a Leak-Down Test
- 15.3. Using an Oscilloscope
- 16. How Do Aftermarket Performance Parts Affect OB2 Codes?
- 16.1. Common Issues with Aftermarket Parts
- 16.2. Tuning the Engine Control Module (ECM)
- 16.3. Using High-Quality Aftermarket Parts
- 17. How to Stay Updated on the Latest OB2 Code Information?
- 17.1. Subscribing to Industry Publications
- 17.2. Attending Training Seminars
- 17.3. Following Online Forums and Communities
- 18. What Are the Legal Implications of Ignoring OB2 Codes?
- 18.1. Emissions Testing
- 18.2. Fines and Penalties
- 18.3. Environmental Impact
- 19. How Do Electric and Hybrid Vehicles Use OB2 Codes?
- 19.1. Unique Codes for Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
- 19.2. Diagnosing Problems in Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
- 19.3. Safety Considerations
- 20. FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About OB2 Scanner Codes
- 20.1. What Does the Check Engine Light Mean?
- 20.2. Can I Drive My Car with the Check Engine Light On?
- 20.3. How Often Should I Scan My Car for OB2 Codes?
- 20.4. Can I Clear OB2 Codes Myself?
- 20.5. What Is the Difference Between Generic and Manufacturer-Specific OB2 Codes?
- 20.6. Where Can I Find the OB2 Port in My Car?
- 20.7. How Much Does an OB2 Scanner Cost?
- 20.8. Can I Use a Smartphone App to Read OB2 Codes?
- 20.9. What Is Freeze Frame Data?
- 20.10. How Can I Prevent OB2 Codes From Occurring?
1. What Exactly Are OB2 Scanner Codes?
OB2 scanner codes are alphanumeric codes used by a vehicle’s onboard computer to identify problems within its systems. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), these codes are standardized across most vehicles, providing a consistent way to diagnose issues. When a problem is detected, the computer stores a corresponding code, which can then be accessed using an OB2 scanner. These codes are a valuable tool for diagnosing and repairing vehicle issues, ranging from minor problems to significant malfunctions.
For example, the “Check Engine” light is a common indicator that an OB2 code has been triggered. Using an OB2 scanner, you can retrieve the specific code and begin troubleshooting the issue. This proactive approach helps in making informed decisions about necessary repairs and maintenance.
2. What Are the Primary Categories of OB2 Codes?
Understanding the different categories of OB2 codes is essential for accurate diagnosis and repair. These codes are generally divided into four main categories, each representing a different area of the vehicle:
2.1. Powertrain Codes
Powertrain codes (P-codes) relate to the engine, transmission, and related components. These are the most common types of OB2 codes. For example, P0300 indicates a random or multiple cylinder misfire. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), powertrain issues are a leading cause of vehicle breakdowns. Understanding these codes can help you address engine and transmission problems promptly.
2.2. Body Codes
Body codes (B-codes) pertain to the vehicle’s body systems, such as airbags, power windows, and electronic control units. For instance, B1000 indicates an issue with the airbag system. Addressing these codes is crucial for ensuring the safety and functionality of your vehicle’s body components.
2.3. Chassis Codes
Chassis codes (C-codes) involve the vehicle’s chassis, including the anti-lock braking system (ABS), suspension, and steering. For example, C0040 indicates a problem with the ABS. Proper diagnosis and repair of chassis-related issues are vital for maintaining vehicle stability and control.
2.4. Network Communication Codes
Network communication codes (U-codes) relate to the communication network within the vehicle, including the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus. A common U-code, U0100, indicates a loss of communication with the engine control module (ECM). Addressing these codes is essential for ensuring proper communication between the vehicle’s electronic systems.
3. How to Interpret OB2 Code Structure?
OB2 codes are structured in a specific format, consisting of five characters: a letter followed by four digits. Each character provides specific information about the problem. Understanding this structure can significantly aid in diagnosing vehicle issues.
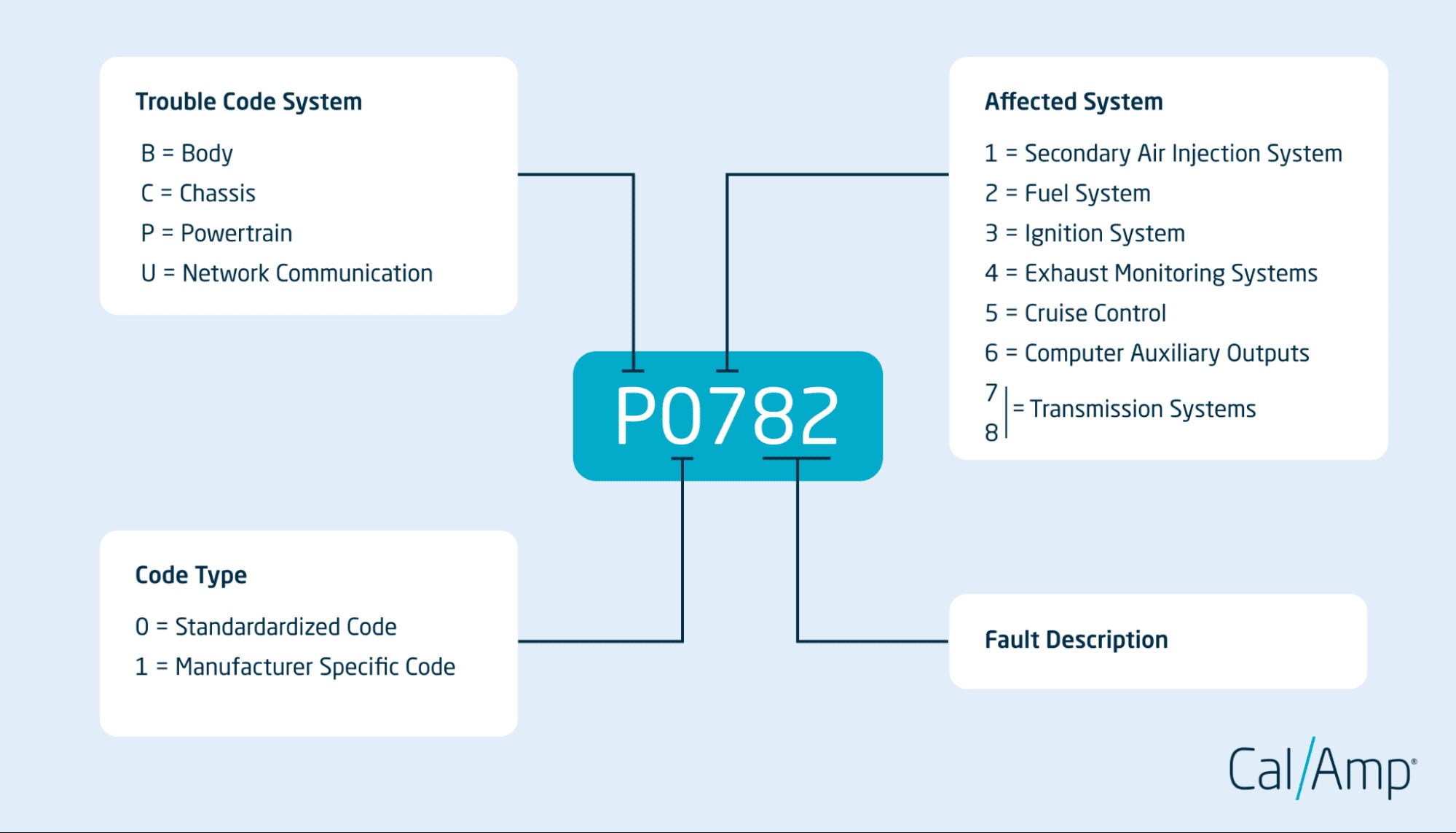 OBD2 Code Structure
OBD2 Code Structure
Alt: OBD2 code breakdown showing each section of the code and what it represents.
The first character indicates the system affected:
- P: Powertrain
- B: Body
- C: Chassis
- U: Network Communication
The second character indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1). The third digit identifies the specific subsystem, such as fuel system or ignition system. The last two digits provide a specific fault code, detailing the exact nature of the problem.
For example, in the code P0301:
- P indicates a powertrain issue.
- 0 indicates a generic code.
- 3 indicates the ignition system.
- 01 indicates a misfire in cylinder 1.
This structured approach allows mechanics and vehicle owners to pinpoint the exact problem, facilitating quicker and more accurate repairs.
4. What Tools Are Needed to Read OB2 Codes?
Reading OB2 codes requires a diagnostic tool, commonly known as an OB2 scanner. These scanners connect to the vehicle’s diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard. Several types of scanners are available, ranging from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools.
4.1. Basic OB2 Code Readers
Basic code readers are inexpensive and easy to use. They display the OB2 code and provide a brief description of the problem. While they are useful for identifying the issue, they may not offer detailed diagnostic information.
4.2. Advanced Diagnostic Scanners
Advanced diagnostic scanners provide more comprehensive information, including live data streams, freeze frame data, and the ability to perform advanced tests. These scanners are commonly used by professional mechanics and offer a more thorough diagnostic capability.
4.3. Smartphone-Based Scanners
Smartphone-based scanners use a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi adapter that connects to the vehicle’s OB2 port. These scanners work with smartphone apps to display codes and provide diagnostic information. They are convenient and often offer additional features such as data logging and performance monitoring.
Choosing the right scanner depends on your needs and budget. Basic code readers are suitable for simple diagnostics, while advanced scanners are necessary for more complex issues.
5. How to Use an OB2 Scanner to Retrieve Codes?
Using an OB2 scanner is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to retrieve OB2 codes from your vehicle:
- Locate the OB2 port: The OB2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Connect the scanner: Plug the OB2 scanner into the port.
- Turn on the ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Read the codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored codes. The scanner will display the codes and a brief description of each.
- Record the codes: Write down the codes and their descriptions for further diagnosis.
Once you have the codes, you can research their meaning and begin troubleshooting the issue.
6. Where Can I Find a Comprehensive OB2 Code List?
Having access to a comprehensive OB2 code list is essential for accurate diagnosis and repair. Several resources are available, both online and in print, that provide detailed information about OB2 codes.
6.1. Online Databases
Numerous websites offer searchable OB2 code databases. These databases typically include code descriptions, possible causes, and potential solutions. Some popular online resources include:
- CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- OBD-Codes.com
- AutoCodes.com
6.2. Repair Manuals
Repair manuals, such as those from Haynes and Chilton, often include comprehensive OB2 code lists. These manuals provide detailed information about vehicle systems and components, making them a valuable resource for DIY mechanics.
6.3. Smartphone Apps
Several smartphone apps provide access to OB2 code databases. These apps often include additional features such as diagnostic tips and repair guides. Popular apps include:
- OBD Auto Doctor
- Torque Pro
- Car Scanner ELM OBD2
By utilizing these resources, you can quickly find the meaning of OB2 codes and begin the diagnostic process.
7. How to Diagnose Common OB2 Codes?
Diagnosing OB2 codes involves a systematic approach to identify the root cause of the problem. Here are some common OB2 codes and steps for diagnosing them:
7.1. P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
A P0300 code indicates that the engine is misfiring, but the specific cylinder is not identified. Possible causes include:
- Faulty spark plugs
- Defective ignition coils
- Vacuum leaks
- Fuel injector problems
To diagnose a P0300 code:
- Check spark plugs and ignition coils for damage or wear.
- Inspect vacuum lines for leaks.
- Test fuel injectors for proper function.
7.2. P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
A P0171 code indicates that the engine is running lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel. Possible causes include:
- Vacuum leaks
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Dirty mass airflow (MAF) sensor
- Fuel pump problems
To diagnose a P0171 code:
- Check vacuum lines for leaks.
- Test the oxygen sensor for proper function.
- Clean or replace the MAF sensor.
- Check fuel pressure.
7.3. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
A P0420 code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently. Possible causes include:
- Faulty catalytic converter
- Exhaust leaks
- Faulty oxygen sensors
To diagnose a P0420 code:
- Inspect the catalytic converter for damage.
- Check for exhaust leaks.
- Test the oxygen sensors before and after the catalytic converter.
By following these diagnostic steps, you can identify the root cause of common OB2 codes and perform the necessary repairs.
8. What Are Some Common Mistakes When Diagnosing OB2 Codes?
Diagnosing OB2 codes can be challenging, and it is easy to make mistakes. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
8.1. Replacing Parts Without Proper Diagnosis
A common mistake is to replace parts based solely on the OB2 code without performing thorough diagnostics. This can lead to unnecessary expenses and may not fix the problem. Always perform diagnostic tests to confirm the root cause before replacing any parts.
8.2. Ignoring Related Symptoms
OB2 codes are just one piece of the puzzle. Ignoring related symptoms can lead to misdiagnosis. Pay attention to how the vehicle is performing and look for any unusual noises, smells, or behaviors.
8.3. Using Inexpensive Code Readers for Complex Problems
Basic code readers are useful for simple diagnostics, but they may not provide enough information for complex problems. Using an advanced diagnostic scanner can provide more detailed data and help you pinpoint the exact issue.
8.4. Neglecting Basic Maintenance
Neglecting basic maintenance, such as oil changes and spark plug replacements, can lead to OB2 codes. Regularly maintaining your vehicle can prevent many common problems.
9. How Can I Clear OB2 Codes?
Clearing OB2 codes is a simple process, but it is important to address the underlying issue first. Once you have repaired the problem, you can clear the code using an OB2 scanner.
9.1. Using an OB2 Scanner to Clear Codes
Most OB2 scanners have a “clear codes” or “erase codes” function. Follow these steps to clear the codes:
- Connect the scanner to the OB2 port.
- Turn on the ignition.
- Select the “clear codes” function.
- Follow the scanner’s instructions to erase the codes.
9.2. Disconnecting the Battery
Disconnecting the battery can also clear OB2 codes, but this method is not recommended as it can erase other important data, such as radio presets and vehicle settings. If you choose to disconnect the battery, follow these steps:
- Turn off the ignition.
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Wait for 15-20 minutes.
- Reconnect the battery cable.
After clearing the codes, drive the vehicle to see if the code returns. If it does, the underlying issue has not been resolved.
10. What Role Do Oxygen Sensors Play in OB2 Codes?
Oxygen sensors play a critical role in monitoring the exhaust gases and providing feedback to the engine control module (ECM). Faulty oxygen sensors can trigger various OB2 codes related to fuel mixture and emissions.
10.1. How Oxygen Sensors Work
Oxygen sensors measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. This information is used by the ECM to adjust the fuel mixture, ensuring optimal combustion. There are typically two oxygen sensors: one before the catalytic converter (upstream) and one after (downstream).
10.2. Common OB2 Codes Related to Oxygen Sensors
Some common OB2 codes related to oxygen sensors include:
- P0130: O2 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0135: O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
10.3. Diagnosing Oxygen Sensor Problems
To diagnose oxygen sensor problems, use a multimeter to test the sensor’s voltage and resistance. An advanced diagnostic scanner can also provide live data streams, allowing you to monitor the sensor’s performance in real time.
11. What Is Freeze Frame Data and How to Use It?
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment an OB2 code was triggered. This data can provide valuable insights into the cause of the problem.
11.1. What Information Does Freeze Frame Data Include?
Freeze frame data typically includes:
- Engine speed (RPM)
- Vehicle speed
- Engine load
- Fuel trim
- Coolant temperature
- Intake air temperature
11.2. How to Access Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data can be accessed using an advanced diagnostic scanner. The scanner will display the data associated with each OB2 code.
11.3. Interpreting Freeze Frame Data
Interpreting freeze frame data requires an understanding of how vehicle systems operate. For example, if the engine load is high and the fuel trim is lean, it may indicate a vacuum leak or fuel delivery problem.
12. How Can I Prevent OB2 Codes From Occurring?
Preventing OB2 codes is essential for maintaining the reliability and longevity of your vehicle. Regular maintenance and proactive care can significantly reduce the likelihood of OB2 codes.
12.1. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance tasks include:
- Oil changes
- Spark plug replacements
- Air filter replacements
- Fuel filter replacements
- Fluid checks and top-ups
12.2. Using High-Quality Parts and Fluids
Using high-quality parts and fluids can help prevent premature wear and failure. Choose parts and fluids that meet or exceed the manufacturer’s recommendations.
12.3. Addressing Minor Issues Promptly
Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent them from escalating into major problems that trigger OB2 codes. Pay attention to any unusual noises, smells, or behaviors and have them checked by a mechanic.
Alt: A mechanic performs routine maintenance, ensuring optimal engine performance and preventing potential OBD-II code triggers.
12.4. Driving Habits
Aggressive driving habits, such as hard acceleration and braking, can put extra stress on vehicle components and lead to premature wear. Smooth and controlled driving can help extend the life of your vehicle.
13. Where Can I Get Professional Help with OB2 Codes?
If you are unable to diagnose or repair OB2 codes on your own, it is best to seek professional help. Several options are available for getting expert assistance.
13.1. Local Mechanics
Local mechanics are a great resource for diagnosing and repairing OB2 codes. Choose a reputable mechanic with experience in diagnosing and repairing your vehicle make and model.
13.2. Dealership Service Centers
Dealership service centers have specialized knowledge and equipment for working on your vehicle. They can provide accurate diagnostics and perform repairs using genuine parts.
13.3. Online Diagnostic Services
Several online services offer remote diagnostic assistance. These services typically involve connecting a diagnostic tool to your vehicle and working with a remote technician to diagnose the problem.
14. How Can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Help with OB2 Codes?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wide range of resources to help you understand and address OB2 codes. Whether you are a DIY mechanic or a professional technician, our website provides the tools and information you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
14.1. Comprehensive Product Listings
We offer detailed listings of auto parts and repair tools, including specifications, features, and prices. You can easily compare products and find the best options for your needs.
14.2. User Reviews and Ratings
Our website includes user reviews and ratings for auto parts and repair tools. This feedback can help you make informed decisions and choose reliable products.
14.3. Expert Advice and Guides
We provide expert advice and guides on diagnosing and repairing OB2 codes. Our articles and videos cover a wide range of topics, from basic diagnostics to advanced repair techniques.
14.4. Contact Us for Personalized Assistance
If you need personalized assistance, our team of experts is here to help. Contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States for support and guidance.
15. What Are Some Advanced OB2 Diagnostic Techniques?
For complex OB2 code issues, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary. These techniques often require specialized tools and knowledge.
15.1. Performing a Compression Test
A compression test measures the compression in each cylinder. Low compression can indicate problems such as worn piston rings or valve issues.
15.2. Performing a Leak-Down Test
A leak-down test measures the rate at which air escapes from each cylinder. This test can help identify leaks caused by worn piston rings, valves, or head gaskets.
15.3. Using an Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope can be used to analyze electrical signals, such as those from oxygen sensors and ignition coils. This tool can help identify intermittent or subtle problems.
16. How Do Aftermarket Performance Parts Affect OB2 Codes?
Aftermarket performance parts can sometimes trigger OB2 codes, especially if they alter the engine’s operating parameters.
16.1. Common Issues with Aftermarket Parts
Common issues include:
- Increased emissions
- Altered fuel mixture
- Problems with the oxygen sensors
16.2. Tuning the Engine Control Module (ECM)
Tuning the ECM can help prevent OB2 codes when using aftermarket performance parts. Tuning involves adjusting the ECM’s parameters to match the new parts and ensure optimal performance.
16.3. Using High-Quality Aftermarket Parts
Using high-quality aftermarket parts can also help prevent OB2 codes. Choose parts that are designed to work with your vehicle and meet or exceed the manufacturer’s recommendations.
17. How to Stay Updated on the Latest OB2 Code Information?
The world of OB2 codes is constantly evolving, with new codes and diagnostic techniques being developed all the time. Staying updated on the latest information is essential for accurate diagnosis and repair.
17.1. Subscribing to Industry Publications
Subscribing to industry publications, such as Automotive Engineering International, can provide valuable insights into the latest developments in automotive technology.
17.2. Attending Training Seminars
Attending training seminars and workshops can help you stay updated on the latest diagnostic techniques and repair procedures.
17.3. Following Online Forums and Communities
Following online forums and communities can provide a wealth of information and insights from experienced mechanics and technicians.
18. What Are the Legal Implications of Ignoring OB2 Codes?
Ignoring OB2 codes can have legal implications, especially if they relate to emissions control systems.
18.1. Emissions Testing
Many states require vehicles to pass emissions testing. If your vehicle has an active OB2 code related to emissions, it may fail the test.
18.2. Fines and Penalties
Ignoring emissions-related OB2 codes can result in fines and penalties.
18.3. Environmental Impact
Ignoring emissions-related OB2 codes can have a negative impact on the environment.
19. How Do Electric and Hybrid Vehicles Use OB2 Codes?
Electric and hybrid vehicles also use OB2 codes to diagnose problems, although the codes may be different from those used in gasoline-powered vehicles.
19.1. Unique Codes for Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
Electric and hybrid vehicles have unique OB2 codes related to the battery, electric motor, and regenerative braking system.
19.2. Diagnosing Problems in Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
Diagnosing problems in electric and hybrid vehicles requires specialized knowledge and equipment.
19.3. Safety Considerations
Working on electric and hybrid vehicles can be dangerous due to the high-voltage systems. Always follow safety precautions and consult with a qualified technician.
20. FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About OB2 Scanner Codes
20.1. What Does the Check Engine Light Mean?
The check engine light indicates that there is a problem with one or more of your vehicle’s systems. An OB2 scanner can be used to retrieve the specific code and begin troubleshooting the issue.
20.2. Can I Drive My Car with the Check Engine Light On?
It depends on the severity of the problem. If the check engine light is flashing, it indicates a serious issue that could cause damage to your vehicle. In this case, it is best to stop driving and have the vehicle checked by a mechanic.
20.3. How Often Should I Scan My Car for OB2 Codes?
You should scan your car for OB2 codes whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms.
20.4. Can I Clear OB2 Codes Myself?
Yes, you can clear OB2 codes yourself using an OB2 scanner. However, it is important to address the underlying issue first.
20.5. What Is the Difference Between Generic and Manufacturer-Specific OB2 Codes?
Generic OB2 codes are standardized across all vehicles, while manufacturer-specific codes are unique to each carmaker.
20.6. Where Can I Find the OB2 Port in My Car?
The OB2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
20.7. How Much Does an OB2 Scanner Cost?
OB2 scanners range in price from around $20 for a basic code reader to several hundred dollars for an advanced diagnostic scanner.
20.8. Can I Use a Smartphone App to Read OB2 Codes?
Yes, several smartphone apps are available that can be used to read OB2 codes. These apps require a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi adapter that connects to the vehicle’s OB2 port.
20.9. What Is Freeze Frame Data?
Freeze frame data is a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment an OB2 code was triggered.
20.10. How Can I Prevent OB2 Codes From Occurring?
Regular maintenance, using high-quality parts and fluids, and addressing minor issues promptly can help prevent OB2 codes from occurring.
Understanding OB2 scanner codes is crucial for maintaining the health and performance of your vehicle. With the right tools and knowledge, you can diagnose and repair many common issues, saving time and money. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to provide the resources you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Contact us today for personalized assistance.
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s diagnostics? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States. Let us help you find the right auto parts and repair tools to keep your vehicle running at its best!