An OBD II scanner is an invaluable tool for diagnosing car problems, offering insights into fault codes and live data. With CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can easily learn how to use an OBD2 scanner and understand what it reveals about your vehicle’s health. Equip yourself with this knowledge and gain a deeper understanding of your car’s diagnostics and auto repairs.
Contents
- 1. What Exactly Does an OBD2 Scanner Do?
- 1.1. Understanding the Core Functions of an OBD2 Scanner
- 1.2. The Significance of Fault Codes and Live Data
- 1.3. Advanced Diagnostic Capabilities
- 2. What Are the Different Types of OBD2 Scanners Available?
- 2.1. Basic Bluetooth OBD2 Code Readers
- 2.2. Mid-Range OBD2 Scanners
- 2.3. Professional-Grade OBD2 Diagnostic Tools
- 3. How Do I Read OBD2 Fault Codes?
- 3.1. Step 1: Locate and Connect the Scanner
- 3.2. Step 2: Turn On the Ignition
- 3.3. Step 3: Select Your Vehicle
- 3.4. Step 4: Scan for Fault Codes
- 3.5. Step 5: Interpret the Fault Codes
- 3.6. How to Use Live Data for Advanced Diagnostics
- 3.6.1. Access Live Data
- 3.6.2. Monitor Relevant Parameters
- 3.6.3. Analyze the Data
- 4. What Do the Fault Codes Really Mean?
- 4.1. Deciphering Common Fault Codes
- 4.2. Using Online Resources
- 4.3. The Importance of Cross-Referencing
- 5. How Can an OBD2 Scanner Help When Buying a Used Car?
- 5.1. Detecting Hidden Issues
- 5.2. Verifying Vehicle History
- 5.3. Negotiating a Fair Price
- 6. How to Clear OBD2 Fault Codes?
- 6.1. The Process of Clearing Codes
- 6.2. When to Clear Codes
- 6.3. Potential Consequences of Clearing Codes Prematurely
- 7. Can I Really Fix My Car Myself With an OBD2 Scanner?
- 7.1. DIY vs. Professional Repairs
- 7.2. Essential Tools and Equipment
- 7.3. Safety Precautions
- 8. Where to Buy OBD2 Scanners and Related Tools?
- 8.1. Reputable Online Retailers
- 8.2. Local Auto Parts Stores
- 8.3. Considering Warranties and Customer Support
- 9. How to Maintain Your OBD2 Scanner for Longevity?
- 9.1. Proper Storage
- 9.2. Regular Software Updates
- 9.3. Handling with Care
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions About OBD2 Scanners
- 10.1. Will an OBD2 scanner work on any car?
- 10.2. Can an OBD2 scanner diagnose ABS and airbag issues?
- 10.3. Is it safe to drive with an OBD2 scanner plugged in?
- 10.4. How often should I scan my car for fault codes?
- 10.5. Can an OBD2 scanner reset my car’s check engine light?
- 10.6. What does it mean when a fault code is intermittent?
- 10.7. Can an OBD2 scanner improve my car’s fuel efficiency?
- 10.8. How do I know if my OBD2 scanner is compatible with my smartphone?
- 10.9. Can I use an OBD2 scanner to program new keys for my car?
- 10.10. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner is not communicating with my car?
- Unlock Your Car’s Secrets with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
1. What Exactly Does an OBD2 Scanner Do?
An OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner is a device that connects to your car’s computer system, pulling data from its control units to help diagnose issues. This includes reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and accessing real-time data, such as temperature, pressure, and speed, making it an essential tool for automotive diagnostics.
The OBD2 scanner serves as a vital link between you and your vehicle’s internal systems. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), OBD2 systems provide standardized access to a wealth of information that can help pinpoint problems quickly and efficiently. The scanner essentially translates the complex language of your car’s computer into understandable terms, making it easier to identify and address potential issues.
1.1. Understanding the Core Functions of an OBD2 Scanner
The primary function of an OBD2 scanner is to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle’s computer. These codes are triggered when the car’s sensors detect a problem, such as an issue with the engine, transmission, or emissions system.
 OBD2 scanner
OBD2 scanner
This function is crucial for identifying potential problems early on, helping you avoid costly repairs down the road.
Additionally, an OBD2 scanner can display live data from various sensors throughout the vehicle. This real-time information can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent problems or monitoring the performance of specific components. For example, you can use the scanner to monitor the engine’s coolant temperature, fuel pressure, or oxygen sensor readings while the car is running. This data can help you identify patterns or anomalies that might indicate a problem.
1.2. The Significance of Fault Codes and Live Data
Fault codes, or Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), are like error messages from your car’s computer, signaling specific issues. Live data, on the other hand, gives you a real-time snapshot of your vehicle’s performance metrics.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 systems were mandated in all cars sold in the United States starting in 1996 to monitor emissions-related components. These systems use sensors to track various parameters, and when a sensor reading falls outside of the acceptable range, a fault code is stored.
- Fault Codes: These codes are standardized, meaning that a code like “P0300” will always indicate a random misfire in the engine, regardless of the vehicle’s make or model.
- Live Data: Live data provides a dynamic view of your car’s performance, allowing you to see how different components are functioning in real-time.
1.3. Advanced Diagnostic Capabilities
Beyond basic code reading, advanced OBD2 tools offer features like resetting service lights and performing specific service functions. These tools are incredibly valuable for more in-depth diagnostics and maintenance.
- Resetting Service Lights: Many modern cars have service lights that illuminate to remind you to perform routine maintenance, such as oil changes or tire rotations.
- Performing Service Functions: Some advanced OBD2 tools can also perform specific service functions, such as resetting the electronic parking brake or calibrating the throttle position sensor.
2. What Are the Different Types of OBD2 Scanners Available?
OBD2 scanners come in various forms, from basic Bluetooth code readers to advanced professional-grade tools. Understanding the different types can help you choose the right scanner for your needs.
2.1. Basic Bluetooth OBD2 Code Readers
These are the most affordable and user-friendly options, ideal for the average car owner. They pair with your smartphone to read fault codes and display basic live data.
Bluetooth OBD2 code readers are a convenient and cost-effective way to access basic diagnostic information about your car. These devices typically plug into the OBD2 port and communicate with your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth.
They are best suited for:
- Reading and clearing basic fault codes.
- Monitoring basic live data parameters such as engine temperature and RPM.
- Simple diagnostics for common issues.
2.2. Mid-Range OBD2 Scanners
Priced higher, these scanners offer more features, such as resetting service reminders and performing basic service functions. They are suited for DIY enthusiasts who need more than just basic diagnostics.
Mid-range OBD2 scanners offer a balance between affordability and functionality. These scanners typically have a built-in display screen and keypad, allowing you to navigate menus and access diagnostic information without the need for a smartphone or tablet.
They are best suited for:
- Reading and clearing a wider range of fault codes.
- Performing basic service functions such as resetting oil service lights and calibrating electronic parking brakes.
- Accessing more detailed live data parameters.
2.3. Professional-Grade OBD2 Diagnostic Tools
These high-end tools are designed for professional mechanics. They offer advanced coding and programming capabilities, along with comprehensive diagnostic functions.
Professional-grade OBD2 diagnostic tools are the top-of-the-line options, offering the most comprehensive diagnostic and programming capabilities. These tools are typically used by professional mechanics and automotive technicians in repair shops and dealerships.
They are best suited for:
- Reading and clearing all types of fault codes.
- Performing advanced service functions such as programming new control modules and coding keys.
- Accessing detailed live data parameters and performing advanced diagnostics.
- Bi-directional control, which allows you to activate and test specific components.
3. How Do I Read OBD2 Fault Codes?
Reading fault codes is a fundamental skill when using an OBD2 scanner. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
3.1. Step 1: Locate and Connect the Scanner
Find the OBD2 port in your car, usually under the steering wheel or in the center console. Plug in your OBD2 scanner.
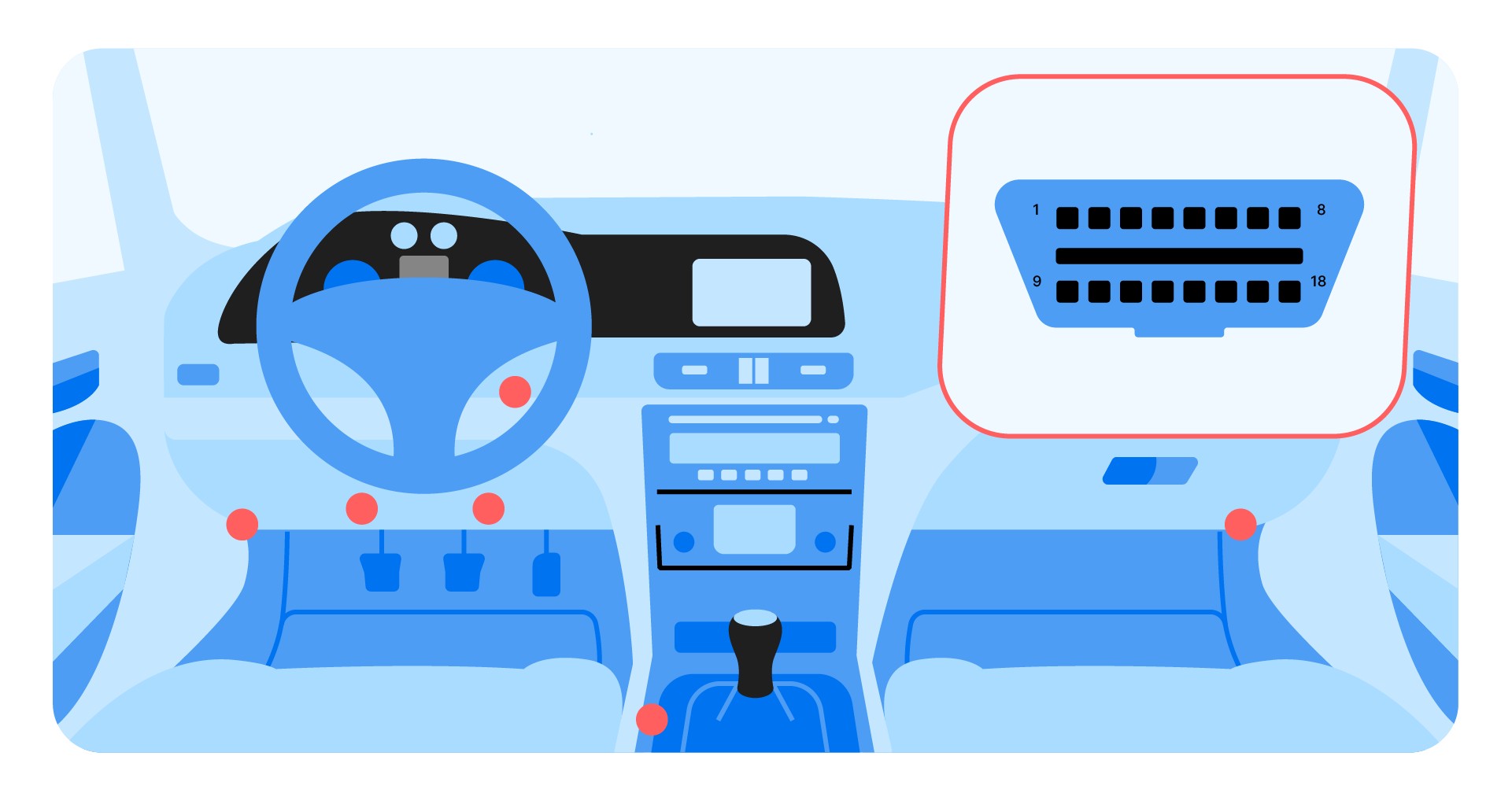 OBD2 scanner port location
OBD2 scanner port location
According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), the OBD2 port is standardized across all vehicles sold in the United States since 1996. This means that any OBD2 scanner should be compatible with any car that meets this standard.
3.2. Step 2: Turn On the Ignition
Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This powers up the car’s computer system and allows the scanner to communicate with it.
Turning on the ignition without starting the engine is important because it allows the scanner to access the car’s computer system without the engine running.
3.3. Step 3: Select Your Vehicle
Choose your car’s make, model, and specifications on the scanner. Some scanners have an auto-detect feature for VIN recognition.
Many modern diagnostic tools have an automatic recognition system that automatically reveals a car’s VIN number and sets up all the necessary information for you. Moreover, you can also enter a VIN manually if, for some reason, a scanner doesn’t find it automatically.
3.4. Step 4: Scan for Fault Codes
Navigate to the fault code reading option and initiate the scan. The scanner will check all available control units and display any stored fault codes.
Depending on a car’s model, a full scan should take between a few seconds and a few minutes.
3.5. Step 5: Interpret the Fault Codes
Examine the revealed fault codes. Some scanners provide descriptions, but you may need to look up the codes online for more information.
For example, the code “P0300” indicates a random misfire in the engine. This could be caused by a variety of factors, such as faulty spark plugs, a clogged fuel filter, or a vacuum leak.
3.6. How to Use Live Data for Advanced Diagnostics
Reading live data can significantly enhance your diagnostic capabilities. Here’s how to use it effectively:
3.6.1. Access Live Data
In the scanner’s menu, select the live data option. This allows you to view real-time readings from various sensors.
Most control units have an additional section for live data, allowing you to monitor it in real-time. How does that help?
3.6.2. Monitor Relevant Parameters
Choose the parameters relevant to your issue, such as fuel pressure, O2 sensor readings, or engine temperature.
Let’s say a car is low on power, and the only fault code that appears is a notification that the vehicle is in limp mode. In that case, you can check whether the fuel and boost pressures, intake airflow, and intake manifold pressures are normal.
3.6.3. Analyze the Data
Compare the live data readings with the expected values. Look for anomalies or readings outside the normal range.
By monitoring live data, you can often pinpoint the root cause of a problem more quickly and accurately.
4. What Do the Fault Codes Really Mean?
Understanding fault codes can be tricky, but it’s essential for accurate diagnostics. Here’s how to interpret them effectively:
4.1. Deciphering Common Fault Codes
Common fault codes, such as those related to the engine, transmission, and ABS, are usually straightforward. For example, a code indicating a faulty oxygen sensor or a misfire can point to specific issues.
Some codes are relatively straightforward, such as “00287 – ABS Wheel Speed Sensor; Rear Right”. It probably means that the rear right ABS sensor needs replacing.
4.2. Using Online Resources
There are many online databases and forums where you can look up fault codes and find detailed explanations. Websites like OBD-Codes.com and the forums on CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN are excellent resources.
However, the problems behind fault codes are often way more complicated than you may think. For example, “P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)” means that the fuel mixture is too lean, but it can be caused by a clogged fuel filter, a failing fuel pump, a vacuum leak, various sensor failures, and numerous other things.
4.3. The Importance of Cross-Referencing
Always cross-reference fault codes with other symptoms and data. A fault code is just one piece of the puzzle, and it’s important to consider all available information to make an accurate diagnosis.
After sourcing the problem, someone must fix it and check for faults again. If it doesn’t appear anymore, the problem is probably solved, and you can hit the road.
5. How Can an OBD2 Scanner Help When Buying a Used Car?
An OBD2 scanner is an invaluable tool when buying a used car, helping you uncover potential hidden problems.
5.1. Detecting Hidden Issues
Many used car sellers may try to hide existing problems. An OBD2 scanner can reveal stored fault codes that indicate underlying mechanical or electrical issues.
Modern used car markets are full of pitfalls for buyers. Used car sellers use the gullibility of buyers to sell cars with a bad history, electrical issues, or even legal problems.
5.2. Verifying Vehicle History
While vehicle history reports are useful, they don’t always tell the whole story. Using an OBD2 scanner can provide additional insights into the car’s condition.
While vehicle history reports can reveal lots of useful information about a car, a proper vehicle inspection is essential if you want to avoid huge repair costs.
5.3. Negotiating a Fair Price
Identifying potential issues with an OBD2 scanner can give you leverage to negotiate a lower price, accounting for future repair costs.
Always get a history report and check for fault codes before buying a used vehicle. If you don’t have an OBD2 scanner or still don’t know how to use one, take the car for a professional inspection.
6. How to Clear OBD2 Fault Codes?
Clearing fault codes is a straightforward process, but it’s important to understand when and why you should do it.
6.1. The Process of Clearing Codes
After addressing the underlying issue, you can clear the fault codes using the OBD2 scanner. Navigate to the clear codes option in the scanner’s menu and follow the prompts.
Scanning for fault codes is a part of diagnosing the car’s problem, therefore, fault codes often won’t reveal issues directly. Even if computer diagnostics show a faulty mass airflow sensor, automotive electricians test the sensor using a multimeter to ensure it’s faulty and avoid replacing the wrong part. You’d be surprised how often such fault codes appear due to damaged wiring, loose connections, and corrosion.
6.2. When to Clear Codes
Only clear codes after you have fixed the problem. Clearing codes without addressing the underlying issue will only result in the codes reappearing.
6.3. Potential Consequences of Clearing Codes Prematurely
Clearing codes before fixing the issue can mask the problem and potentially lead to more severe damage. Always ensure the issue is resolved before clearing the codes.
7. Can I Really Fix My Car Myself With an OBD2 Scanner?
Using an OBD2 scanner can empower you to perform basic car repairs, but it’s important to know your limits.
7.1. DIY vs. Professional Repairs
Simple repairs, such as replacing a faulty sensor or fixing a loose connection, can often be done yourself with the help of an OBD2 scanner. However, more complex repairs may require professional expertise.
7.2. Essential Tools and Equipment
In addition to an OBD2 scanner, you may need other tools, such as a multimeter, wrenches, and sockets, to perform certain repairs.
7.3. Safety Precautions
Always follow safety precautions when working on your car. Wear safety glasses, disconnect the battery, and consult a repair manual before attempting any repairs.
8. Where to Buy OBD2 Scanners and Related Tools?
Choosing the right place to purchase your OBD2 scanner and tools is essential for quality and reliability.
8.1. Reputable Online Retailers
Websites like Amazon, Summit Racing, and CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offer a wide selection of OBD2 scanners and automotive tools from reputable brands.
8.2. Local Auto Parts Stores
Local auto parts stores, such as AutoZone and O’Reilly Auto Parts, are also good options for buying OBD2 scanners and tools.
8.3. Considering Warranties and Customer Support
When buying an OBD2 scanner, consider the warranty and customer support offered by the manufacturer. A good warranty can protect you from defects, and reliable customer support can help you troubleshoot any issues.
9. How to Maintain Your OBD2 Scanner for Longevity?
Proper maintenance can extend the life of your OBD2 scanner, ensuring it remains a reliable tool for years to come.
9.1. Proper Storage
Store your OBD2 scanner in a clean, dry place away from extreme temperatures.
9.2. Regular Software Updates
Keep your OBD2 scanner’s software up to date. Manufacturers often release updates to improve performance and add new features.
9.3. Handling with Care
Handle your OBD2 scanner with care to avoid damage. Avoid dropping it or exposing it to excessive moisture.
10. Frequently Asked Questions About OBD2 Scanners
10.1. Will an OBD2 scanner work on any car?
OBD2 scanners are compatible with all cars sold in the United States since 1996. However, some older vehicles may require an adapter.
10.2. Can an OBD2 scanner diagnose ABS and airbag issues?
Yes, many OBD2 scanners can diagnose ABS and airbag issues, as well as other system-specific problems.
10.3. Is it safe to drive with an OBD2 scanner plugged in?
It is generally safe to drive with an OBD2 scanner plugged in, but it’s important to ensure that the scanner doesn’t interfere with your driving.
10.4. How often should I scan my car for fault codes?
You should scan your car for fault codes whenever you notice a warning light or suspect a problem.
10.5. Can an OBD2 scanner reset my car’s check engine light?
Yes, an OBD2 scanner can reset your car’s check engine light after you have fixed the underlying issue.
10.6. What does it mean when a fault code is intermittent?
An intermittent fault code means that the problem is not always present. This can make the issue more difficult to diagnose.
10.7. Can an OBD2 scanner improve my car’s fuel efficiency?
While an OBD2 scanner cannot directly improve your car’s fuel efficiency, it can help you identify issues that may be affecting it, such as a faulty oxygen sensor.
10.8. How do I know if my OBD2 scanner is compatible with my smartphone?
Check the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure that your OBD2 scanner is compatible with your smartphone’s operating system.
10.9. Can I use an OBD2 scanner to program new keys for my car?
Some professional-grade OBD2 scanners can program new keys for your car, but this feature is not available on all models.
10.10. What should I do if my OBD2 scanner is not communicating with my car?
Check the connection between the scanner and the OBD2 port, and ensure that the ignition is turned on. If the problem persists, consult the scanner’s user manual or contact customer support.
Unlock Your Car’s Secrets with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
Ready to take control of your car’s diagnostics? At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide detailed information on a wide range of auto parts and tools to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly. Whether you’re looking for technical specifications, brand comparisons, or user reviews, our website has you covered.
Understanding the nuances of auto repair can be challenging, but with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, you gain access to a wealth of knowledge that simplifies the process. We focus on delivering accurate, reliable information so you can make informed decisions about your vehicle’s care.
Do you want personalized advice on the best tools and parts for your car? Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Our team of experts is ready to help you find the perfect solutions. Visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN or stop by our location at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States. Let CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in automotive maintenance and repair. Contact us today to discover how we can assist you! By integrating these elements, you can attract visitors, increase engagement, and establish CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN as a leading resource in the automotive information sector.