Using a scanner on a car, also known as an OBD2 scanner, is a crucial skill for both car enthusiasts and professional mechanics. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides expert insights into automotive diagnostics, repair tools, and parts to empower you with the knowledge to maintain your vehicle effectively. Learn about diagnostic tools, fault codes, and live data analysis to keep your car running smoothly.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Role of an OBD2 Scanner
- 1.1. Key Functions of an OBD2 Scanner
- 1.2. The Evolution of On-Board Diagnostics
- 2. Different Types of OBD2 Scanners
- 2.1. Basic Bluetooth OBD2 Code Readers
- 2.2. Mid-Range OBD2 Scanners
- 2.3. Professional-Grade Diagnostic Tools
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use an OBD2 Scanner
- 3.1. Locating the OBD2 Port
- 3.2. Connecting the Scanner
- 3.3. Turning on the Ignition
- 3.4. Selecting Your Vehicle
- 3.5. Scanning for Fault Codes
- 3.6. Interpreting Fault Codes
- 4. Understanding OBD2 Fault Codes
- 4.1. Generic vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes
- 4.2. Common Fault Codes and Their Meanings
- 4.3. Using Online Resources to Decode Fault Codes
- 5. Reading Live Data with an OBD2 Scanner
- 5.1. What is Live Data?
- 5.2. Common Live Data Parameters to Monitor
- 5.3. Interpreting Live Data to Diagnose Problems
- 6. Advanced Functions of OBD2 Scanners
- 6.1. Bi-Directional Control
- 6.2. Module Programming
- 6.3. Accessing Manufacturer-Specific Diagnostic Procedures
- 7. Maintaining Your OBD2 Scanner
- 7.1. Keeping the Scanner Clean
- 7.2. Storing the Scanner Properly
- 7.3. Updating the Scanner’s Software
- 8. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 8.1. Misinterpreting Fault Codes
- 8.2. Neglecting Live Data
- 8.3. Failing to Research the Issue Properly
- 9. The Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for Automotive Diagnostics
- 9.1. Access to Expert Insights and Advice
- 9.2. Comprehensive Information on Repair Tools and Parts
- 9.3. Saving Time and Money on Automotive Repairs
- 10. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of OBD2 Scanner Use
- 10.1. Diagnosing a Misfire Issue
- 10.2. Identifying a Vacuum Leak
- 10.3. Resolving an Oxygen Sensor Problem
- FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 1. What Type of OBD2 Scanner is Best for Beginners?
- 2. Can an OBD2 Scanner Diagnose ABS and Airbag Issues?
- 3. How Often Should I Scan My Car for Fault Codes?
- 4. Can I Clear Fault Codes Without Fixing the Problem?
- 5. Are All OBD2 Scanners Compatible with All Cars?
- 6. What Does “Pending Code” Mean?
- 7. Can an OBD2 Scanner Improve Fuel Efficiency?
- 8. Do I Need to Turn off My Car Battery Before Scanning?
- 9. Can I Use an OBD2 Scanner on Multiple Cars?
- 10. What is the Difference Between OBD1 and OBD2?
1. Understanding the Role of an OBD2 Scanner
What does an OBD2 scanner do? An OBD2 scanner is a vital tool that connects to your car’s onboard computer system, retrieving diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and live data to help identify and resolve automotive issues. This device allows you to communicate with the car’s control units, accessing information about various parameters like engine temperature, speed, and sensor readings.
OBD2 scanners have revolutionized automotive diagnostics, providing a window into the complex electronic systems of modern vehicles. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Institute of Transportation Studies, OBD2 scanners can reduce diagnostic time by up to 50%, leading to faster and more accurate repairs.
1.1. Key Functions of an OBD2 Scanner
What are the key functions of an OBD2 scanner? The key functions include reading and clearing fault codes, accessing live data, performing diagnostic tests, and sometimes, advanced features like reprogramming certain vehicle functions.
- Reading and Clearing Fault Codes: This is the most basic function, allowing you to identify why your check engine light is on and clear the code after addressing the issue.
- Accessing Live Data: This feature provides real-time information from various sensors and systems in your car, such as engine speed (RPM), coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- Performing Diagnostic Tests: Some scanners can perform specific tests, like an oxygen sensor test or an EVAP system test, to help pinpoint problems.
- Advanced Features: High-end scanners may offer advanced functions like module reprogramming, key programming, and bi-directional control, allowing you to command the car’s systems.
1.2. The Evolution of On-Board Diagnostics
How has on-board diagnostics evolved? On-board diagnostics have evolved from basic emissions monitoring to comprehensive system-wide diagnostics, mandated in the United States since 1996 and in Europe since 2004. This evolution has made it easier for mechanics and car owners to diagnose and repair vehicles, reducing emissions and improving fuel efficiency.
The standardization of the OBD2 port and protocols has been a game-changer for the automotive industry. A report by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) indicates that OBD2 systems have contributed to a 20% reduction in vehicle emissions since their introduction.
2. Different Types of OBD2 Scanners
What are the different types of OBD2 scanners available? The types range from basic Bluetooth code readers to advanced professional-grade diagnostic tools, each catering to different needs and budgets. Choosing the right scanner depends on your level of expertise and the complexity of the repairs you intend to undertake.
 OBD2 scanner
OBD2 scanner
2.1. Basic Bluetooth OBD2 Code Readers
What are basic Bluetooth OBD2 code readers? These are inexpensive devices that pair with your smartphone to read fault codes and display basic live data. They are ideal for the average driver who wants to quickly check and understand the cause of a check engine light.
These readers typically cost around $20-$50 and are user-friendly, making them a great entry point into automotive diagnostics. However, their capabilities are limited compared to more advanced scanners.
2.2. Mid-Range OBD2 Scanners
What are mid-range OBD2 scanners? Mid-range scanners offer more functionality than basic code readers, including the ability to reset service reminders, activate servicing functions, and read more detailed live data. These are suitable for DIY enthusiasts and those who perform their own maintenance.
Priced between $100 and $500, these scanners provide a good balance of features and affordability. They often come with a built-in screen and intuitive interface, making them easy to use.
2.3. Professional-Grade Diagnostic Tools
What are professional-grade diagnostic tools? These are advanced, expensive tools used by professional mechanics for comprehensive diagnostics, coding, and programming. They offer extensive capabilities, including access to manufacturer-specific codes, bi-directional control, and module reprogramming.
These tools can cost thousands of dollars and require specialized training to use effectively. They are designed to handle the most complex automotive issues and are essential for any professional repair shop.
3. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use an OBD2 Scanner
How do you use an OBD2 scanner step-by-step? The process involves connecting the scanner to the OBD2 port, turning on the ignition, selecting your vehicle’s information, scanning for fault codes, and interpreting the results.
3.1. Locating the OBD2 Port
Where is the OBD2 port located? The OBD2 port is typically located under the steering wheel or in the center console, often hidden beneath a plastic cover. Consult your vehicle’s manual if you have trouble finding it.
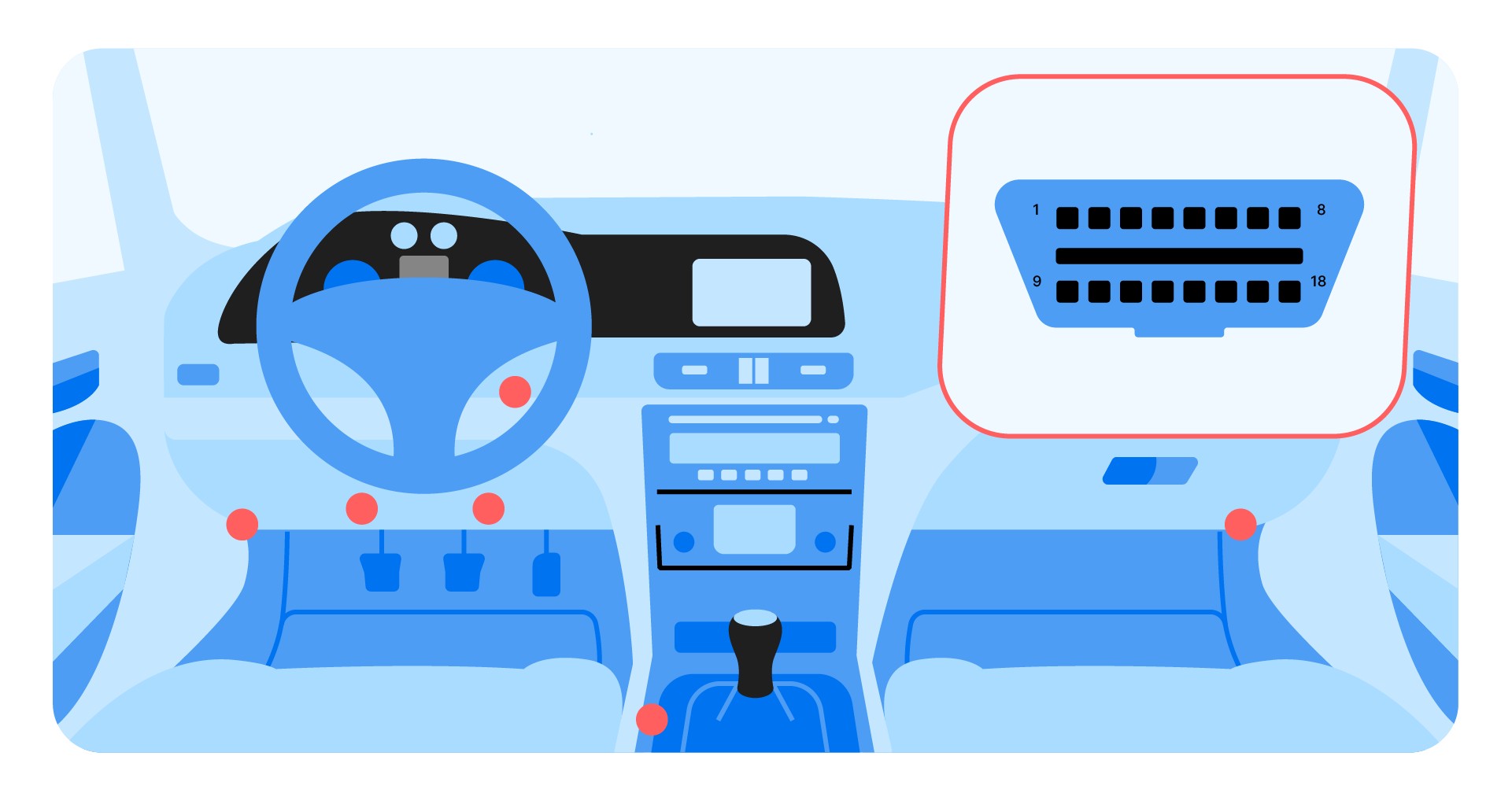 OBD2 scanner port location
OBD2 scanner port location
The OBD2 port is standardized, so it will look the same in all vehicles manufactured after 1996 in the US and 2004 in Europe.
3.2. Connecting the Scanner
How do you connect the scanner? Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. If using a Bluetooth scanner, pair it with your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth. Ensure the connection is secure and stable.
3.3. Turning on the Ignition
Why do you need to turn on the ignition? Turning on the ignition powers up the car’s computer system, allowing the scanner to communicate with the vehicle’s control units. Turn off accessories like headlights and the radio to minimize electrical load.
3.4. Selecting Your Vehicle
How do you select your vehicle on the scanner? Choose your car’s make, model, and year from the scanner’s menu. Some scanners automatically detect the vehicle’s VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) to streamline this process.
Entering the correct vehicle information is crucial for accurate diagnostics. The scanner uses this information to access the correct diagnostic protocols and data parameters.
3.5. Scanning for Fault Codes
How do you scan for fault codes? Select the option to scan for fault codes, often labeled as “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Scan.” The scanner will communicate with the car’s computer and display any stored trouble codes.
A full scan can take a few seconds to several minutes, depending on the vehicle and the scanner’s capabilities. Be patient and allow the scan to complete without interruption.
3.6. Interpreting Fault Codes
What do the fault codes mean? Fault codes are alphanumeric codes that indicate a specific problem within the vehicle’s systems. Use a reliable online database or the scanner’s built-in help function to look up the meaning of each code.
For example, a code like “P0300” indicates a random or multiple cylinder misfire. Understanding the code is the first step in diagnosing and repairing the issue.
4. Understanding OBD2 Fault Codes
What should you know about OBD2 fault codes? These codes provide valuable information about potential issues but often require further investigation to pinpoint the exact cause. Fault codes can be generic (common to all vehicles) or manufacturer-specific.
4.1. Generic vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes
What is the difference between generic and manufacturer-specific codes? Generic codes are standardized across all makes and models, while manufacturer-specific codes are unique to a particular car manufacturer and provide more detailed information.
Generic codes are often prefixed with “P0,” “C0,” “B0,” or “U0,” while manufacturer-specific codes are prefixed with “P1,” “C1,” “B1,” or “U1.”
4.2. Common Fault Codes and Their Meanings
What are some common fault codes and their meanings? Examples include P0171 (System Too Lean), P0300 (Random Misfire), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold). Each code indicates a specific area of concern, but further diagnosis is often needed.
- P0171 (System Too Lean): Indicates that the air-fuel mixture is too lean, which can be caused by a vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, or fuel system issue.
- P0300 (Random Misfire): Indicates that one or more cylinders are misfiring, which can be caused by faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors.
- P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold): Indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently, which can lead to increased emissions.
4.3. Using Online Resources to Decode Fault Codes
Where can you find resources to decode fault codes? Websites like OBD-Codes.com and the CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN blog offer extensive databases of fault codes and their possible causes. Always consult multiple sources to get a comprehensive understanding.
5. Reading Live Data with an OBD2 Scanner
How do you read live data with an OBD2 scanner? Accessing live data allows you to monitor real-time parameters and diagnose intermittent issues that may not trigger a fault code. This feature is essential for advanced diagnostics and troubleshooting.
5.1. What is Live Data?
What is live data in the context of OBD2 scanners? Live data refers to real-time information from various sensors and systems in your car, such as engine speed (RPM), coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and fuel trim values.
Monitoring live data can help you identify problems like a faulty sensor, a vacuum leak, or a failing fuel pump.
5.2. Common Live Data Parameters to Monitor
What are some common live data parameters to monitor? Key parameters include engine RPM, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor voltage, fuel trim, mass airflow (MAF), and manifold absolute pressure (MAP).
- Engine RPM: Indicates the speed at which the engine is running, which can help diagnose issues like stalling or rough idling.
- Coolant Temperature: Indicates the temperature of the engine coolant, which can help diagnose overheating issues.
- Oxygen Sensor Voltage: Indicates the voltage output of the oxygen sensors, which can help diagnose fuel mixture issues.
- Fuel Trim: Indicates the adjustments the engine control unit (ECU) is making to the fuel mixture, which can help diagnose lean or rich conditions.
- Mass Airflow (MAF): Indicates the amount of air entering the engine, which can help diagnose air intake issues.
- Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP): Indicates the pressure in the intake manifold, which can help diagnose vacuum leaks.
5.3. Interpreting Live Data to Diagnose Problems
How do you interpret live data to diagnose problems? By comparing live data values to expected ranges, you can identify anomalies that indicate a problem. For example, a high fuel trim value may indicate a vacuum leak or a faulty oxygen sensor.
According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), using live data can improve diagnostic accuracy by up to 30%.
6. Advanced Functions of OBD2 Scanners
What advanced functions do OBD2 scanners offer? High-end scanners provide advanced functions like bi-directional control, module programming, and access to manufacturer-specific diagnostic procedures.
6.1. Bi-Directional Control
What is bi-directional control? Bi-directional control allows you to command the car’s systems to perform specific actions, such as activating a fuel pump or cycling an ABS module. This feature is invaluable for testing components and diagnosing complex issues.
6.2. Module Programming
What is module programming? Module programming involves reprogramming or updating the software in the car’s control modules. This is often necessary when replacing a module or to address software-related issues.
6.3. Accessing Manufacturer-Specific Diagnostic Procedures
How do you access manufacturer-specific diagnostic procedures? Some scanners provide access to manufacturer-specific diagnostic procedures, which offer detailed instructions and troubleshooting steps for specific issues. This can be a significant advantage when dealing with complex problems that require specialized knowledge.
7. Maintaining Your OBD2 Scanner
How do you maintain your OBD2 scanner? Proper maintenance ensures your scanner remains accurate and reliable. Keep the scanner clean, store it in a safe place, and update its software regularly.
7.1. Keeping the Scanner Clean
Why is it important to keep the scanner clean? Clean the scanner regularly with a soft cloth to remove dirt and grime. Avoid using harsh chemicals or solvents that could damage the device.
7.2. Storing the Scanner Properly
How should you store the scanner? Store the scanner in a case or protective bag to prevent damage from dust, moisture, and impact. Keep it in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
7.3. Updating the Scanner’s Software
Why is it important to update the software? Regularly update the scanner’s software to ensure it has the latest diagnostic information and features. Software updates often include bug fixes and improvements to performance and compatibility.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner
What are some common mistakes to avoid when using an OBD2 scanner? Common mistakes include misinterpreting fault codes, neglecting live data, and failing to properly research the issue before attempting repairs.
8.1. Misinterpreting Fault Codes
Why is it important to accurately interpret fault codes? Always research the meaning of fault codes thoroughly before assuming the cause of the problem. A fault code may indicate a symptom rather than the root cause.
8.2. Neglecting Live Data
Why should you pay attention to live data? Live data provides valuable insights into the operation of the car’s systems and can help you diagnose issues that may not trigger a fault code.
8.3. Failing to Research the Issue Properly
Why is research important? Before attempting any repairs, research the issue thoroughly using online resources, repair manuals, and technical forums. This will help you understand the problem and avoid making costly mistakes.
9. The Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for Automotive Diagnostics
What are the benefits of using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for automotive diagnostics? CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wealth of information on automotive diagnostics, repair tools, and parts, helping you make informed decisions and save time and money.
9.1. Access to Expert Insights and Advice
How does CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provide expert insights and advice? Our website features articles, guides, and videos from experienced mechanics and automotive experts, providing valuable insights and advice on diagnosing and repairing vehicles.
9.2. Comprehensive Information on Repair Tools and Parts
What kind of information on repair tools and parts can you find on CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN? We offer comprehensive information on a wide range of repair tools and parts, including specifications, reviews, and comparisons. This helps you choose the right tools and parts for your specific needs.
9.3. Saving Time and Money on Automotive Repairs
How can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN help you save time and money? By providing the knowledge and resources you need to diagnose and repair your vehicle effectively, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN can help you avoid costly trips to the mechanic and save time on automotive repairs.
10. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of OBD2 Scanner Use
How can OBD2 scanners be used in real-world scenarios? Real-world examples demonstrate the practical applications of OBD2 scanners in diagnosing and resolving automotive issues.
10.1. Diagnosing a Misfire Issue
How can an OBD2 scanner help diagnose a misfire issue? An OBD2 scanner can identify a misfire by displaying a fault code such as P0300 (Random Misfire) or P0301 (Cylinder 1 Misfire). By monitoring live data, you can pinpoint the cause of the misfire, such as a faulty spark plug, ignition coil, or fuel injector.
10.2. Identifying a Vacuum Leak
How can an OBD2 scanner help identify a vacuum leak? An OBD2 scanner can identify a vacuum leak by displaying a fault code such as P0171 (System Too Lean). By monitoring live data, you can observe high fuel trim values, indicating that the engine is running lean due to the vacuum leak.
10.3. Resolving an Oxygen Sensor Problem
How can an OBD2 scanner help resolve an oxygen sensor problem? An OBD2 scanner can identify an oxygen sensor problem by displaying a fault code such as P0131 (O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage Bank 1 Sensor 1). By monitoring live data, you can observe the oxygen sensor voltage fluctuating abnormally, indicating a faulty sensor.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Using an OBD2 Scanner
What are some frequently asked questions about using an OBD2 scanner? Here are answers to some common questions to help you better understand and utilize this tool.
1. What Type of OBD2 Scanner is Best for Beginners?
Which OBD2 scanner is easiest to use for someone just starting out? A basic Bluetooth OBD2 code reader paired with a smartphone app is often the best choice for beginners due to its ease of use and affordability.
2. Can an OBD2 Scanner Diagnose ABS and Airbag Issues?
Can OBD2 scanners diagnose problems beyond the engine? Yes, many OBD2 scanners can diagnose ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and airbag issues, although this functionality is typically found in mid-range and professional-grade scanners.
3. How Often Should I Scan My Car for Fault Codes?
How often should you use an OBD2 scanner on your car? You should scan your car for fault codes whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms, such as rough idling or reduced performance.
4. Can I Clear Fault Codes Without Fixing the Problem?
Is it okay to clear fault codes without fixing the underlying issue? While you can clear fault codes without fixing the problem, the check engine light will likely return if the underlying issue persists. It is always best to diagnose and repair the problem before clearing the code.
5. Are All OBD2 Scanners Compatible with All Cars?
Are there compatibility issues with OBD2 scanners and different car models? Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with all cars manufactured after 1996 in the United States and 2004 in Europe. However, some scanners may have limited functionality or compatibility with certain makes and models.
6. What Does “Pending Code” Mean?
What does it mean when an OBD2 scanner shows a “pending code?” A “pending code” indicates that the car’s computer has detected a potential problem, but it has not yet met the criteria to trigger the check engine light.
7. Can an OBD2 Scanner Improve Fuel Efficiency?
Can an OBD2 scanner help improve my car’s fuel economy? By diagnosing and resolving issues that affect engine performance, an OBD2 scanner can help improve fuel efficiency.
8. Do I Need to Turn off My Car Battery Before Scanning?
Is it necessary to disconnect the car battery before using an OBD2 scanner? No, it is not necessary to disconnect the car battery before scanning, but make sure the ignition is turned on.
9. Can I Use an OBD2 Scanner on Multiple Cars?
Can I use the same OBD2 scanner on different vehicles? Yes, you can use an OBD2 scanner on multiple cars, as long as they are OBD2 compliant.
10. What is the Difference Between OBD1 and OBD2?
What are the key differences between OBD1 and OBD2 systems? OBD1 is an older, non-standardized system used in cars manufactured before 1996, while OBD2 is a standardized system used in cars manufactured after 1996. OBD2 offers more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities and a standardized connector.
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is your go-to resource for all things automotive. We understand the challenges you face when searching for reliable auto parts and tools, comparing prices and features, and ensuring the durability and effectiveness of new equipment. That’s why we offer detailed information on auto parts, comparisons of repair tools, user reviews, and a directory of reputable suppliers.
Ready to take control of your car’s health? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert advice and support. Reach us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or give us a call on Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. For more information, visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN. Let us help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
