Resetting car codes without a scanner is possible using various methods. How To Reset Codes On Car Without Scanner is a common question, and you can accomplish this by disconnecting the battery, using the fuse box, completing a drive cycle, or utilizing third-party apps with a Bluetooth OBD2 adapter, all detailed by CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN. These alternative methods can help you clear error messages, pass emissions tests, or temporarily turn off the check engine light while you plan a permanent repair.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Why Resetting Car Codes Is Necessary
- 1.1. Clearing Error Codes for Accurate Monitoring
- 1.2. Preparing for Emissions Tests
- 1.3. Temporary Solutions While Planning Permanent Repairs
- 2. Methods To Reset Car Codes Without a Scanner
- 2.1. Disconnecting the Car Battery
- 2.1.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Battery Disconnection
- 2.1.2. Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
- 2.2. Utilizing the Fuse Box
- 2.2.1. Detailed Steps for Fuse Box Reset
- 2.2.2. Important Precautions and Considerations
- 2.3. Performing a Drive Cycle
- 2.3.1. General Drive Cycle Procedure
- 2.3.2. Factors Influencing Drive Cycle Effectiveness
- 2.4. Utilizing Third-Party Apps with Bluetooth OBD2 Adapters
- 2.4.1. Steps for Using OBD2 Adapters and Apps
- 2.4.2. Popular Apps and Adapter Recommendations
- 3. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.1. Common DTC Categories
- 3.2. Interpreting DTCs
- 4. Tools and Equipment for Automotive Diagnostics
- 4.1. Essential Tools
- 4.2. Specialized Equipment
- 5. Maintaining Your Vehicle to Prevent Error Codes
- 5.1. Regular Maintenance Tasks
- 5.2. Importance of Timely Repairs
- 6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 6.1. Using a Scan Tool for Advanced Diagnostics
- 6.2. Electrical Testing
- 6.3. Mechanical Testing
- 7. Tips for Effective Troubleshooting
- 7.1. Gather Information
- 7.2. Consult Repair Manuals
- 7.3. Use Online Resources
- 7.4. Seek Professional Help
- 8. Automotive Safety Practices
- 8.1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- 8.2. Disconnecting the Battery
- 8.3. Jacking Up the Vehicle
- 8.4. Working with Flammable Materials
- 9. Environmental Considerations
- 9.1. Recycling Used Oil
- 9.2. Disposing of Used Fluids
- 10. Staying Updated with Automotive Technology
- 10.1. Attending Training Courses
- 10.2. Reading Industry Publications
- 10.3. Joining Online Communities
- 11. Common Myths About Resetting Car Codes
- 11.1. Resetting Codes Fixes the Problem
- 11.2. Resetting Codes Always Leads to Emission Test Failure
- 12. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
- 12.1. Comprehensive Information on Auto Parts
- 12.2. Comparison of Repair Tools
- 12.3. User Reviews and Testimonials
- 12.4. Trusted Suppliers
- 13. Getting Expert Advice from CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 14. Why Choose CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN?
- 14.1. Expertise and Reliability
- 14.2. Comprehensive Resources
- 14.3. User-Friendly Experience
- 15. Call to Action
- FAQs
- Can I reset my car’s check engine light without a scanner?
- Will resetting codes without a scanner affect my car’s performance?
- How long does it take to reset car codes without a scanner?
- Is it safe to reset car codes without a scanner?
- What if the check engine light comes back on after resetting?
- Will resetting codes help me pass an emissions test?
- Can I use a third-party app to reset car codes?
- What are the best OBD2 apps for resetting car codes?
- How do I find the ECU fuse in my car?
- What should I do if I’m not comfortable resetting codes myself?
1. Understanding Why Resetting Car Codes Is Necessary
Before diving into how to reset car codes, it’s crucial to understand why you might need to do so in the first place. Several scenarios may necessitate resetting your car’s diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
1.1. Clearing Error Codes for Accurate Monitoring
One of the primary reasons for resetting codes is to clear error messages from your dashboard. After addressing an issue, the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) might remain, causing confusion. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), technicians often reset codes after repairs to ensure accurate monitoring of the vehicle’s systems. Resetting the codes provides a clean slate, allowing you to promptly identify any new issues that may arise.
 Operating Car Scanner | Foxwell
Operating Car Scanner | Foxwell
An automotive technician operating a car scanner, highlighting the importance of clearing error codes after repairs for accurate system monitoring.
1.2. Preparing for Emissions Tests
Another critical reason to reset codes is to prepare your vehicle for emissions testing. Many states and regions require vehicles to pass emissions tests to ensure they meet environmental standards. A check engine light, triggered by stored DTCs, can cause your vehicle to fail the test, even if the underlying problem has been resolved. Resetting the codes allows the car’s system to undergo a readiness cycle, ensuring all parameters are within acceptable limits. As reported by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), vehicles with cleared codes often need to complete a drive cycle for all systems to be marked as “ready” for testing.
1.3. Temporary Solutions While Planning Permanent Repairs
In some situations, resetting codes can serve as a temporary solution while you plan a more comprehensive repair. If you’re experiencing a minor issue that doesn’t immediately affect your vehicle’s drivability, resetting the codes can turn off the check engine light and provide temporary relief. However, it’s important to note that this is not a long-term fix, and the underlying problem should be addressed as soon as possible. Delaying repairs can lead to more severe issues and potential safety hazards, according to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA).
2. Methods To Reset Car Codes Without a Scanner
Now, let’s explore the various methods to reset car codes without relying on a dedicated OBD2 scanner. These techniques range from simple battery disconnection to utilizing smartphone apps with Bluetooth adapters.
2.1. Disconnecting the Car Battery
One of the most straightforward methods to reset car codes is by disconnecting the vehicle’s battery. This process effectively clears the car’s computer memory, including stored DTCs.
2.1.1. Step-by-Step Guide to Battery Disconnection
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the car is completely turned off to prevent electrical surges during the disconnection process.
- Locate the Battery: Open the hood and identify the car battery, typically located near the front of the engine bay.
- Disconnect the Negative Terminal: Using a wrench, carefully disconnect the negative terminal (usually marked with a “-” sign and a black cable). This step prevents accidental short circuits.
- Wait for 15-30 Minutes: Allow sufficient time for the car’s computer to reset. Some experts recommend pressing the brake pedal to drain any residual power.
- Reconnect the Battery: After waiting, reconnect the negative terminal and securely tighten it with the wrench.
- Turn On the Ignition: Start the car and observe if the check engine light is off. If so, the reset was successful.
2.1.2. Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
While disconnecting the battery is a simple method, it’s essential to consider potential drawbacks. This process will also reset other settings, such as your radio presets, clock, and potentially even your car’s security system. Be prepared to reset these settings after reconnecting the battery. Additionally, disconnecting the battery may not be suitable for all vehicles, especially those with advanced electronic systems. Consult your car’s manual for specific instructions and warnings.
2.2. Utilizing the Fuse Box
Another method to reset car codes involves removing the fuse that powers the car’s Engine Control Unit (ECU). This process effectively cuts off power to the ECU, causing it to reset and clear stored DTCs.
2.2.1. Detailed Steps for Fuse Box Reset
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the car is turned off to prevent electrical surges while removing the fuse.
- Locate the Fuse Box: Consult your car’s manual to find the fuse box, typically located under the dashboard or in the engine compartment.
- Identify the ECU Fuse: Use the manual to identify the fuse specifically designated for the ECU. The fuse layout diagram will guide you.
- Remove the Fuse: Carefully pull out the fuse using a fuse puller or pliers. Handle the fuse gently to avoid damage.
- Wait for 15-30 Minutes: Allow sufficient time for the system to reset.
- Reinsert the Fuse: Place the fuse back into its designated slot, ensuring it is securely in place.
- Turn On the Ignition: Start the car and check if the codes have been reset. If the check engine light is off, the method was successful.
2.2.2. Important Precautions and Considerations
When using the fuse box method, it’s crucial to exercise caution. Always consult your car’s manual to identify the correct fuse for the ECU. Removing the wrong fuse can potentially damage other electronic components. Additionally, ensure the fuse is properly seated when reinserting it to avoid any electrical issues.
2.3. Performing a Drive Cycle
In some cases, simply driving your car in a specific manner, known as a drive cycle, can reset the codes. A drive cycle involves a series of driving conditions that allow the car’s computer to run various diagnostic tests.
2.3.1. General Drive Cycle Procedure
- Cold Start: Start the car after it has been sitting for at least 8 hours to ensure all components are at ambient temperature.
- Idle for 2 Minutes: Allow the car to idle in park or neutral for a couple of minutes to stabilize the engine.
- Drive at a Steady Speed: Drive at a steady speed (around 55 mph) for approximately 15 minutes. This allows the system to check under normal driving conditions.
- Stop and Go: Drive in stop-and-go traffic for another 15 minutes to simulate urban driving conditions.
- Idle for 2 Minutes: Let the car idle again for a couple of minutes before turning it off. This completes the checks.
2.3.2. Factors Influencing Drive Cycle Effectiveness
The effectiveness of a drive cycle can vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle. Some cars may require multiple drive cycles to reset all the codes. Consult your car’s manual for specific drive cycle procedures recommended by the manufacturer. Additionally, environmental factors such as temperature and altitude can also influence the outcome of a drive cycle.
2.4. Utilizing Third-Party Apps with Bluetooth OBD2 Adapters
While not entirely “without a scanner,” using third-party apps with a Bluetooth OBD2 adapter offers a low-cost alternative to traditional scanners. These adapters plug into your car’s OBD2 port and communicate with your smartphone via Bluetooth, allowing you to read and reset codes.
2.4.1. Steps for Using OBD2 Adapters and Apps
- Plug in the OBD2 Adapter: Insert the Bluetooth OBD2 adapter into the OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard near the steering column.
- Download a Smartphone App: Download a compatible app, such as Torque (for Android) or OBD Fusion (for iOS).
- Pair the Adapter with Your Phone: Use Bluetooth to connect the adapter to your phone, following the app’s instructions.
- Reset Codes Using the App: Follow the app’s instructions to read and reset the codes. These apps typically have user-friendly interfaces.
2.4.2. Popular Apps and Adapter Recommendations
Several reputable apps and adapters are available on the market. Some popular apps include Torque Pro, OBD Fusion, and Carista. When selecting an adapter, consider factors such as compatibility with your phone and vehicle, features offered, and user reviews. Brands like Veepeak and BAFX Products are known for producing reliable OBD2 adapters. According to a survey conducted by Consumer Reports, users generally prefer apps with clear interfaces and comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
 Car Scanner Functions | Foxwell
Car Scanner Functions | Foxwell
The various functions of a car scanner, highlighting the capabilities of third-party apps when paired with a Bluetooth OBD2 adapter.
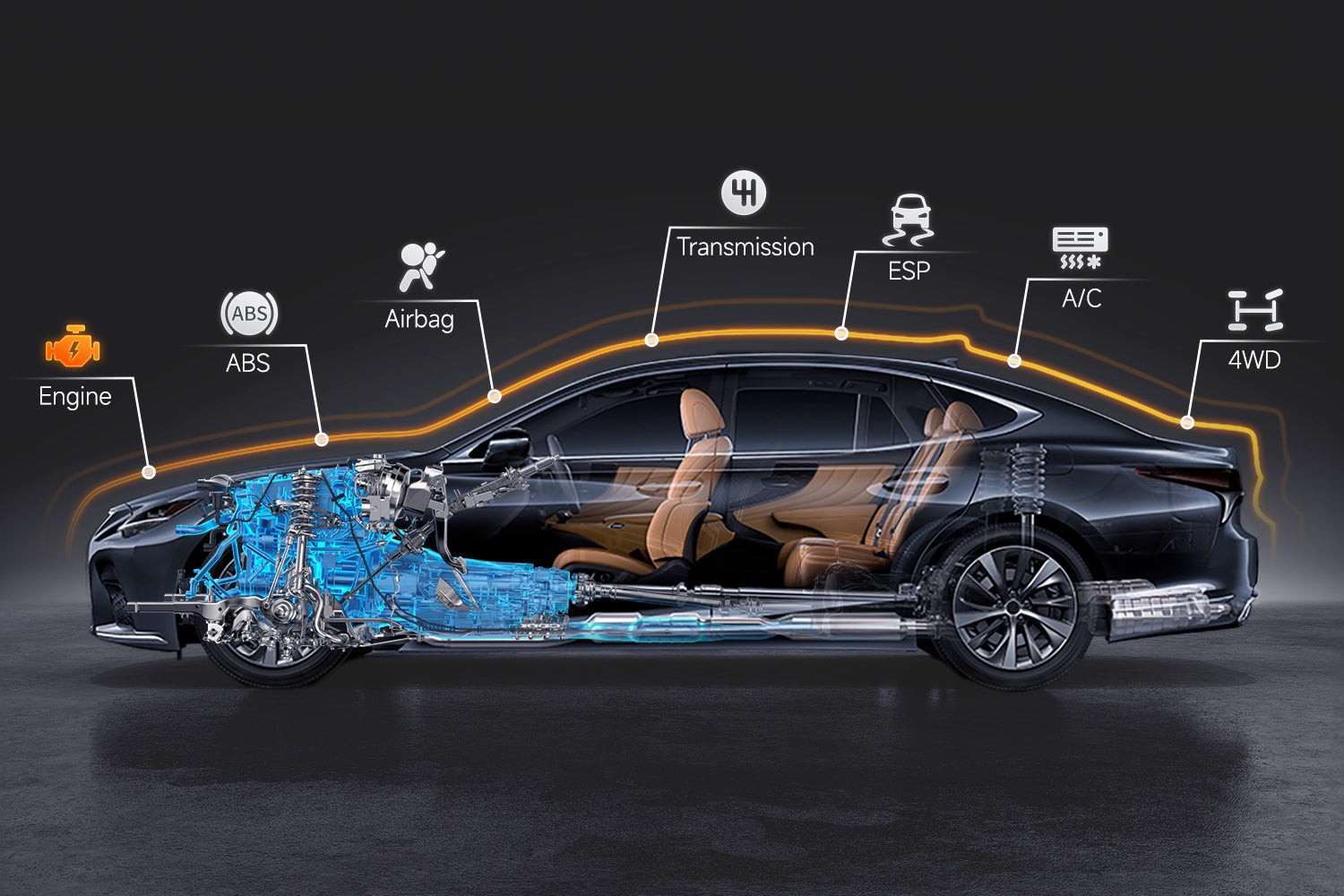
3. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes that are stored in your car’s computer when a problem is detected. These codes can help you identify the source of the problem. It is important to understand what these codes mean so you can take the appropriate action.
3.1. Common DTC Categories
There are many different DTCs, but they can be broadly categorized into four main groups:
- P (Powertrain): These codes relate to the engine, transmission, and related components.
- B (Body): These codes relate to body systems, such as airbags, power windows, and locks.
- C (Chassis): These codes relate to chassis systems, such as ABS, traction control, and suspension.
- U (Network): These codes relate to the vehicle’s communication network.
3.2. Interpreting DTCs
Each DTC is a five-character code. The first character indicates the system the code relates to (P, B, C, or U). The second character indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1). The third character indicates the subsystem the code relates to (e.g., fuel system, ignition system). The fourth and fifth characters indicate the specific fault.
For example, the code P0300 indicates a generic powertrain code for a random or multiple cylinder misfire. You can use online resources or a repair manual to look up the meaning of specific DTCs. Websites like OBD-Codes.com and the CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offer detailed information on a wide range of DTCs.
4. Tools and Equipment for Automotive Diagnostics
While this guide focuses on resetting codes without a scanner, understanding the tools and equipment used in automotive diagnostics can enhance your knowledge.
4.1. Essential Tools
- OBD2 Scanner: An OBD2 scanner is a tool that can read and clear DTCs. It plugs into your car’s OBD2 port and allows you to communicate with the car’s computer.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is an essential tool for electrical testing. It can measure voltage, current, and resistance.
- Socket Set: A socket set is needed for various tasks, such as removing and installing bolts and nuts.
- Wrench Set: A wrench set is another essential tool for mechanical repairs.
- Screwdriver Set: A screwdriver set is needed for removing and installing screws.
- Pliers: Pliers are useful for gripping, cutting, and bending wires and components.
- Fuse Puller: A fuse puller makes it easier to remove fuses from the fuse box without damaging them.
4.2. Specialized Equipment
- Compression Tester: A compression tester is used to measure the compression in each cylinder of the engine.
- Leak-Down Tester: A leak-down tester is used to identify leaks in the cylinders, such as leaking valves or piston rings.
- Fuel Pressure Tester: A fuel pressure tester is used to measure the fuel pressure in the fuel system.
5. Maintaining Your Vehicle to Prevent Error Codes
Preventing error codes in the first place is often the best strategy. Regular maintenance and timely repairs can help keep your vehicle running smoothly and reduce the likelihood of diagnostic trouble codes.
5.1. Regular Maintenance Tasks
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes are essential for keeping the engine lubricated and preventing wear.
- Fluid Checks: Regularly check and top off fluids such as coolant, brake fluid, and power steering fluid.
- Air Filter Replacement: Replace the air filter regularly to ensure proper airflow to the engine.
- Spark Plug Replacement: Replace spark plugs as recommended to maintain optimal engine performance.
- Tire Maintenance: Keep tires properly inflated and rotated to ensure even wear and safe handling.
- Battery Maintenance: Clean battery terminals and check the battery’s charge regularly to prevent starting issues.
5.2. Importance of Timely Repairs
Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent them from escalating into more significant problems that trigger DTCs. For example, replacing a faulty oxygen sensor can prevent damage to the catalytic converter and improve fuel efficiency.
6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
For more complex issues, advanced diagnostic techniques may be required. These techniques often involve using specialized equipment and a deeper understanding of automotive systems.
6.1. Using a Scan Tool for Advanced Diagnostics
A professional-grade scan tool can provide more detailed information than a basic OBD2 scanner. These tools can access manufacturer-specific codes, perform advanced tests, and provide live data streams.
6.2. Electrical Testing
Electrical testing involves using a multimeter to check the voltage, current, and resistance in various circuits. This can help identify faulty wiring, sensors, and actuators.
6.3. Mechanical Testing
Mechanical testing involves using specialized tools to assess the condition of mechanical components. This can include compression testing, leak-down testing, and fuel pressure testing.
7. Tips for Effective Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting automotive problems can be challenging, but following a systematic approach can increase your chances of success.
7.1. Gather Information
Start by gathering as much information as possible about the problem. This can include the symptoms, the conditions under which the problem occurs, and any recent repairs or maintenance.
7.2. Consult Repair Manuals
Repair manuals provide valuable information on the vehicle’s systems and components. They can also provide troubleshooting procedures and wiring diagrams.
7.3. Use Online Resources
Numerous online resources are available to help with troubleshooting. Websites like the CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, online forums, and video tutorials can provide valuable insights and assistance.
7.4. Seek Professional Help
If you are unable to resolve the problem yourself, it is best to seek professional help from a qualified technician.
8. Automotive Safety Practices
When working on your vehicle, it is essential to follow safety practices to prevent injury.
8.1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Wear appropriate PPE, such as safety glasses, gloves, and a respirator, when working on your vehicle.
8.2. Disconnecting the Battery
Disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components to prevent electrical shock.
8.3. Jacking Up the Vehicle
Use jack stands when working under the vehicle to prevent it from falling.
8.4. Working with Flammable Materials
Take precautions when working with flammable materials, such as gasoline and brake cleaner. Work in a well-ventilated area and avoid sparks and open flames.
9. Environmental Considerations
Properly dispose of used fluids, such as oil, coolant, and brake fluid, to protect the environment.
9.1. Recycling Used Oil
Recycle used oil at a designated collection center.
9.2. Disposing of Used Fluids
Dispose of used fluids properly to prevent contamination of soil and water.
10. Staying Updated with Automotive Technology
Automotive technology is constantly evolving, so it is essential to stay updated with the latest advancements.
10.1. Attending Training Courses
Attend training courses to learn about new technologies and diagnostic techniques.
10.2. Reading Industry Publications
Read industry publications to stay informed about the latest trends and developments.
10.3. Joining Online Communities
Join online communities to connect with other technicians and share knowledge.
11. Common Myths About Resetting Car Codes
There are several misconceptions about resetting car codes that need clarification.
11.1. Resetting Codes Fixes the Problem
Resetting codes only clears the error message; it doesn’t fix the underlying issue.
11.2. Resetting Codes Always Leads to Emission Test Failure
Resetting codes doesn’t automatically lead to emission test failure if the issue is resolved and the car completes a drive cycle.
12. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges you face in finding reliable information about auto parts and repair tools. Our mission is to provide you with detailed specifications, comparisons, user reviews, and trustworthy suppliers. We aim to simplify your search and empower you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
12.1. Comprehensive Information on Auto Parts
We offer extensive details on various auto parts, including technical specifications, brands, and durability information. Our platform ensures you have access to the data needed to select the right components for your vehicle.
12.2. Comparison of Repair Tools
Our site features in-depth comparisons of auto repair tools, highlighting their features, pros, cons, and prices. This allows you to evaluate different tools and choose the ones that best fit your needs and budget.
12.3. User Reviews and Testimonials
Benefit from the experiences of other users through our review and testimonial sections. Gain insights into the real-world performance and reliability of different parts and tools.
12.4. Trusted Suppliers
We connect you with reputable suppliers known for their quality products and excellent service. This ensures you receive genuine parts and tools, minimizing the risk of purchasing substandard items.
13. Getting Expert Advice from CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
Need personalized assistance or have specific questions? Contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States. Our team is ready to provide expert advice and immediate support to address your automotive needs. At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are committed to helping you keep your vehicle running smoothly with the right parts and tools.
14. Why Choose CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN?
Choosing CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN means opting for reliability, expertise, and convenience in your automotive diagnostic and repair needs. We are dedicated to providing you with the best resources and support, ensuring you make informed decisions and keep your vehicle in optimal condition.
14.1. Expertise and Reliability
Our platform is built on a foundation of expertise and reliability. We ensure that all information, from product specifications to repair guides, is thoroughly researched and accurate. You can trust CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN to provide you with dependable knowledge and solutions for your automotive challenges.
14.2. Comprehensive Resources
We offer a wide array of resources designed to meet all your automotive needs. Whether you’re looking for detailed product information, comparative analyses, user reviews, or expert advice, our site has you covered. Our comprehensive approach saves you time and effort by centralizing all the information you need in one place.
14.3. User-Friendly Experience
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is designed to provide a user-friendly experience. Our intuitive interface and clear navigation make it easy for you to find the information you need quickly. We prioritize simplicity and efficiency, ensuring that your search for automotive solutions is as seamless as possible.
15. Call to Action
Ready to tackle your car’s diagnostic codes? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert guidance on selecting the right parts and tools. Reach us at +1 (641) 206-8880 on WhatsApp or visit our store at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States. Let us help you keep your vehicle running smoothly!
FAQs
Can I reset my car’s check engine light without a scanner?
Yes, you can reset it by disconnecting the car battery for a few minutes or by removing the ECU fuse.
Will resetting codes without a scanner affect my car’s performance?
No, resetting codes typically does not affect performance, but consult your manual for specifics.
How long does it take to reset car codes without a scanner?
It usually takes around 15-30 minutes to reset the codes without a scanner, especially when disconnecting the battery or removing a fuse.
Is it safe to reset car codes without a scanner?
Yes, it is generally safe, but always follow the correct procedures and consult your car’s manual.
What if the check engine light comes back on after resetting?
If the check engine light returns, it indicates that the underlying issue still exists and needs to be addressed.
Will resetting codes help me pass an emissions test?
Resetting codes can help, but your car needs to complete a drive cycle to ensure all systems are ready for the test.
Can I use a third-party app to reset car codes?
Yes, you can use a third-party app with a Bluetooth OBD2 adapter to read and reset codes.
What are the best OBD2 apps for resetting car codes?
Popular OBD2 apps include Torque Pro (Android) and OBD Fusion (iOS).
How do I find the ECU fuse in my car?
Consult your car’s manual to locate the fuse box and identify the fuse specifically designated for the ECU.
What should I do if I’m not comfortable resetting codes myself?
If you’re not comfortable, seek professional help from a qualified technician.