Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in automobiles are codes that are crucial for diagnosing vehicle malfunctions, and CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN helps you decode and understand them effectively. Understanding DTCs empowers drivers and fleet managers to quickly identify vehicle issues and take appropriate action. With a clear understanding of DTCs, you can streamline your vehicle maintenance and repairs.
Contents
- 1. What Exactly Is a DTC Code in an Automobile?
- 1.1 The Role of the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) System
- 1.2 Distinguishing OBD-I from OBD-II and J1939
- 1.3 Manufacturer-Specific DTCs
- 2. Decoding OBD-II DTCs: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 2.1 The First Character: Identifying the Control System
- 2.2 The Second Character: Standardized vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes
- 2.3 The Third Character: Pinpointing the Subsystem
- 2.4 The Fourth and Fifth Characters: The Specific Fault Index
- 2.5 Example: Decoding P0128
- 3. Common DTCs and Their Meanings
- 4. Understanding J1939 DTCs
- 4.1 Key Fields in J1939 DTCs
- 5. DTC Scan Tools for Fleet Managers
- 5.1 Standalone OBD-II Scanners
- 5.2 Telematics Solutions with DTC Monitoring
- 5.3 Benefits of Telematics Solutions
- 6. Maximizing the Benefits of DTC Information with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 6.1 Comprehensive Parts Database
- 6.2 Expert Tool Recommendations
- 6.3 Step-by-Step Repair Guides
- 6.4 Community Forum
- 7. Understanding the Intent Behind DTC-Related Searches
- 8. Call to Action: Get Expert Assistance from CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 8.1 Contact Us for Expert Advice
- 8.2 Unlock the Potential of Your Vehicle
- 9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About DTCs in Automobiles
- 9.1 What does a DTC in an automobile mean?
- 9.2 How do I read a DTC from my car?
- 9.3 Can I fix a DTC myself, or do I need a mechanic?
- 9.4 Are all DTCs serious, or can some be ignored?
- 9.5 How do I clear a DTC after fixing the problem?
- 9.6 What is the difference between a generic DTC and a manufacturer-specific DTC?
- 9.7 Where can I find a list of DTCs and their meanings?
- 9.8 How often should I scan my car for DTCs?
- 9.9 Can a DTC indicate a problem with my car’s emissions system?
- 9.10 Are there any apps that can read DTCs from my smartphone?
- 10. Ensuring Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) and Adhering to Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) Standards
- 10.1 Demonstrating Expertise
- 10.2 Establishing Authoritativeness
- 10.3 Building Trustworthiness
- 10.4 Adhering to YMYL Standards
1. What Exactly Is a DTC Code in an Automobile?
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is a standardized code employed to pinpoint malfunctions within a vehicle’s systems, ranging from the engine to the transmission. These codes serve as crucial indicators of underlying issues, providing mechanics and vehicle owners with valuable insights into the nature and location of the problem. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), DTCs are designed to streamline the diagnostic process, ensuring efficient and accurate repairs. These alphanumeric codes are generated by the vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system whenever a fault is detected.
1.1 The Role of the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) System
The OBD system acts as the central monitoring hub for a vehicle’s various components and systems. It continuously monitors performance and emissions, and when it detects a problem, it generates a DTC. This DTC not only triggers a warning light on the dashboard, such as the check engine light, but also stores the code in the vehicle’s computer memory. This allows technicians to retrieve the code using a diagnostic scanner and begin the process of diagnosing the issue.
1.2 Distinguishing OBD-I from OBD-II and J1939
Over the years, different versions of OBD interfaces have been used, with the earlier versions classified as OBD-I. These interfaces varied significantly from manufacturer to manufacturer, making it challenging to interpret the codes. Today, there are two main standards that are widely used: OBD-II for light- and medium-duty vehicles and J1939 for heavy-duty vehicles and heavy equipment. The implementation of OBD-II brought about a standardized DTC list, containing codes common to all manufacturers, thanks to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE).
1.3 Manufacturer-Specific DTCs
While OBD-II introduced a standardized list of DTCs, manufacturers may still create their own codes to supplement the universal list if the vehicle requires it. These manufacturer-specific DTCs can be more difficult to interpret without specialized knowledge or access to manufacturer-specific diagnostic tools.
2. Decoding OBD-II DTCs: A Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding the structure of OBD-II DTCs can empower you to decipher the codes and gain valuable insights into the nature of the vehicle’s issues. Each DTC consists of five characters, each providing a specific piece of information about the problem.
2.1 The First Character: Identifying the Control System
The first character of the DTC is always a letter, indicating which control system has an issue:
- P (Powertrain): Refers to the engine, transmission, fuel system, and associated accessories.
- C (Chassis): Relates to mechanical systems generally outside the passenger compartment, such as steering, suspension, and braking.
- B (Body): Pertains to parts mainly found in the passenger compartment area, such as airbags, power windows, and seats.
- U (Network): Indicates issues with the vehicle’s onboard computers and related systems, such as the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus.
2.2 The Second Character: Standardized vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes
The second character is a digit, typically 0 or 1, indicating whether the code is standardized or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: Indicates that the code is a generic, standardized SAE code. Generic codes are adopted by all cars that follow the OBD-II standard.
- 1: Indicates that the code is vehicle manufacturer-specific. These codes are unique to a specific car make or model and are typically less common.
- 2 or 3: Are more rare and their meanings are dependent on the preceding letter of the code. Most of the time, 2 or 3 indicates that a code is manufacturer-specific, with only a few exceptions.
2.3 The Third Character: Pinpointing the Subsystem
The third character is also a digit, ranging from 1 to 8, revealing the subsystem at fault:
- 1: Refers to the fuel or air metering system.
- 2: Refers to the fuel or air metering injection system.
- 3: Refers to the ignition system.
- 4: Refers to the emissions system.
- 5: Refers to the vehicle speed controls and idle control system.
- 6: Refers to the computer output circuit.
- 7 and 8: Indicate that the issue is transmission-related.
2.4 The Fourth and Fifth Characters: The Specific Fault Index
The fourth and fifth characters are read together as a two-digit number between 0 and 99, known as the specific fault index. These characters identify the exact issue of the vehicle, providing a more granular level of detail.
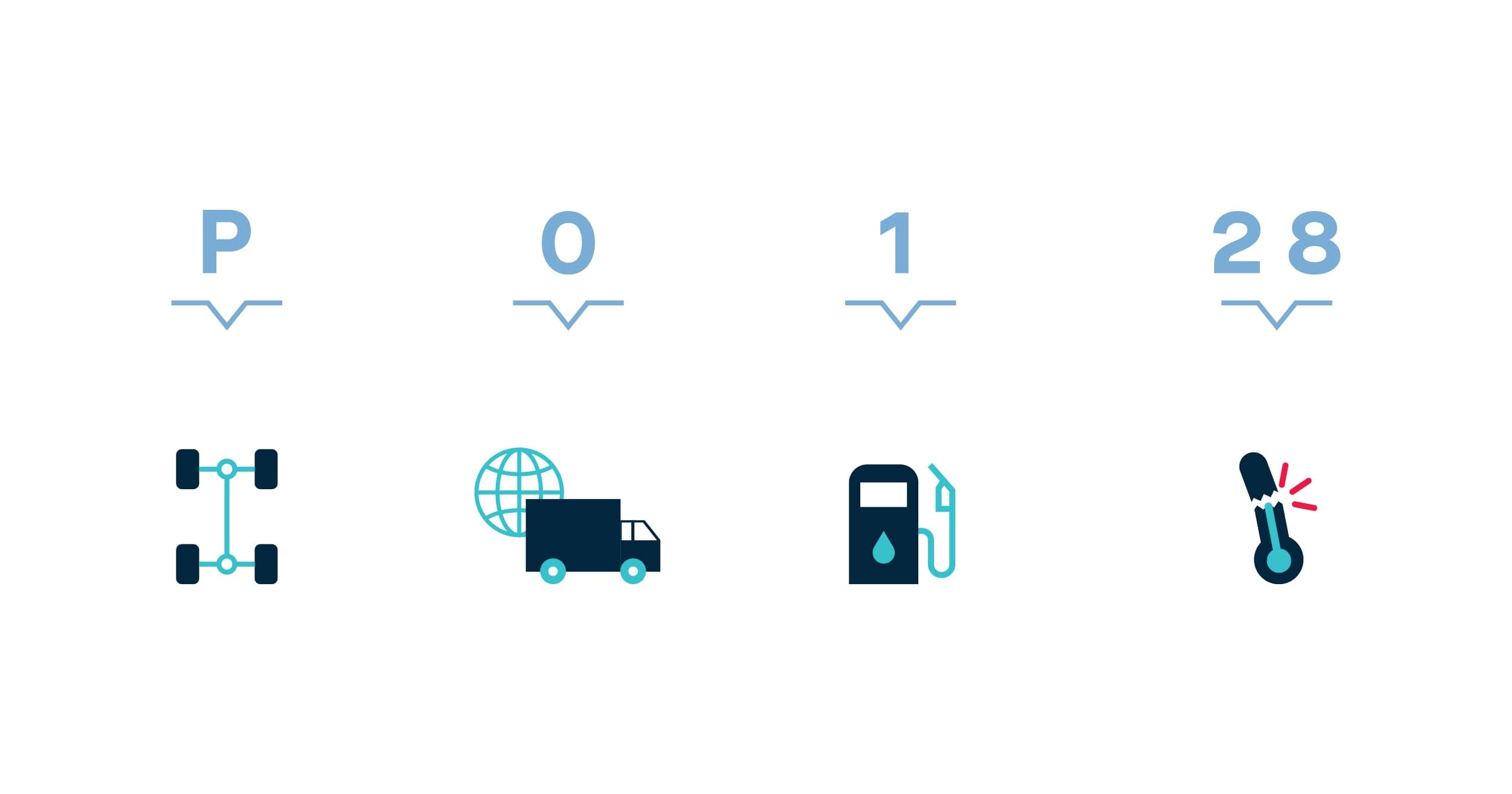
2.5 Example: Decoding P0128
Let’s take the common DTC P0128 as an example:
- P: Indicates that the issue lies in the powertrain.
- 0: Indicates that the code is not manufacturer-specific and is standardized.
- 1: Reveals that the issue is within the fuel and air metering subsystem.
- 28: Is the specific fault index.
Based on this reading, code P0128 refers to an issue with the engine coolant temperature being below the thermostat regulating temperature.
3. Common DTCs and Their Meanings
While there are thousands of possible DTCs, certain codes are more likely to appear than others. Here’s a list of common DTCs you may encounter and their corresponding malfunctions:
| DTC | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak) | Loose or damaged gas cap, cracked or damaged EVAP system hoses, faulty purge valve, faulty vent valve |
| P0606 | PCM (Powertrain Control Module) Malfunction | Faulty PCM, wiring issues, sensor malfunctions |
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, intake air leaks, wiring issues |
| P0110 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues |
| P0500 | Vehicle Speed Sensor Malfunction | Faulty VSS sensor, wiring issues, ABS issues |
| P0706 | Transmission Range Sensor Circuit Range/Performance | Faulty transmission range sensor, wiring issues, low transmission fluid level |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty oxygen sensors |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, dirty MAF sensor, faulty oxygen sensor, low fuel pressure |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, low compression, vacuum leak |
| P0011 | A Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Faulty camshaft position actuator, low oil level, dirty oil, timing chain issues |
| P0131 | O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1) | Faulty oxygen sensor, exhaust leaks, wiring issues |
| P0135 | O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1) | Faulty oxygen sensor, wiring issues |
| P0340 | Camshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit (Bank 1 or Single Sensor) | Faulty camshaft position sensor, wiring issues, timing chain issues |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected | Blocked EGR passages, faulty EGR valve, vacuum leaks |
| P0455 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Gross Leak/No Flow) | Missing or loose gas cap, damaged EVAP system components, faulty purge valve, faulty vent valve |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Faulty IAC valve, throttle body issues, vacuum leaks |
| P0740 | Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Malfunction | Faulty torque converter clutch solenoid, wiring issues, low transmission fluid level |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues |
| P0118 | Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High Input | Faulty ECT sensor, wiring issues |
Note: While DTCs are helpful in identifying a vehicle’s malfunction, they are not a substitute for proper diagnosis. A qualified mechanic should further diagnose the vehicle to identify and address the root cause of the issue.
 Automobile parts
Automobile parts
4. Understanding J1939 DTCs
J1939 DTCs are commonly used in heavy-duty vehicles and equipment. These DTCs contain four fields that relay information about the fault being reported.
4.1 Key Fields in J1939 DTCs
- Suspect Parameter Number (SPN): Represents the SPN with the error. Every defined SPN can be used in a DTC.
- Failure Mode Identifier (FMI): Represents the nature and type of error that occurred, e.g., value range violation (high or low), sensor short-circuits, incorrect update rate, or calibration error.
- Occurrence Counter (OC): A counter that counts the occurrence of the error condition for each SPN and stores this even when the error is no longer active.
- SPN Conversion Method (CM): Defines the byte alignment within the DTC.
5. DTC Scan Tools for Fleet Managers
For fleet managers responsible for numerous vehicles, manually checking each vehicle every time the check engine light turns on can be inefficient. Fortunately, there are various DTC scan tools available to streamline the diagnostic process.
5.1 Standalone OBD-II Scanners
Standalone OBD-II scanners are widely available for purchase and provide a cost-effective solution for reading and clearing DTCs. These scanners typically plug directly into the vehicle’s OBD-II port and display the DTCs on a screen.
5.2 Telematics Solutions with DTC Monitoring
Telematics solutions, such as those offered by Samsara and CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, offer advanced maintenance tools that make identifying DTCs fast and easy. These solutions involve vehicle gateways that plug directly into the vehicle’s OBD-II or J1939 port and send vehicle-related data, including DTCs, to the cloud. This allows fleet managers to monitor DTCs remotely and receive alerts when issues arise.
5.3 Benefits of Telematics Solutions
- Remote Monitoring: Fleet managers can monitor DTCs remotely, without having to physically inspect each vehicle.
- Real-Time Alerts: Receive alerts when DTCs occur, allowing for proactive maintenance and preventing potential breakdowns.
- Data Analysis: Track DTC trends over time, identifying recurring issues and potential maintenance needs.
- Improved Efficiency: Streamline the diagnostic process, reducing downtime and improving overall fleet efficiency.
6. Maximizing the Benefits of DTC Information with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
Understanding DTCs is just the first step. To truly maximize the benefits of this information, you need a reliable resource that can provide detailed information about specific parts, tools, and repair procedures. This is where CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN comes in.
6.1 Comprehensive Parts Database
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive database of automotive parts, complete with detailed specifications, compatibility information, and customer reviews. This allows you to quickly identify the correct parts for your vehicle and make informed purchasing decisions.
6.2 Expert Tool Recommendations
Choosing the right tools for the job is crucial for efficient and effective repairs. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides expert recommendations on a wide range of automotive tools, from basic hand tools to advanced diagnostic equipment.
6.3 Step-by-Step Repair Guides
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers step-by-step repair guides that walk you through common automotive repairs. These guides provide clear instructions, diagrams, and videos to help you complete the repairs safely and effectively.
6.4 Community Forum
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN also hosts a community forum where you can connect with other automotive enthusiasts, ask questions, and share your knowledge. This is a great resource for getting advice and support from experienced mechanics and DIYers.
7. Understanding the Intent Behind DTC-Related Searches
When users search for information related to DTCs, their intent can vary significantly. Understanding these different intents is crucial for providing relevant and helpful content. Here are five common intents behind DTC-related searches:
- Informational: Users seeking to understand what a DTC is, how it works, and how to interpret the codes. They want to learn the basics of DTCs and their significance in vehicle diagnostics.
- Diagnostic: Users looking to diagnose a specific issue based on a DTC they have retrieved from their vehicle. They want to find out the possible causes of the DTC and potential solutions.
- Troubleshooting: Users trying to troubleshoot a problem they are experiencing with their vehicle, using DTCs as a starting point. They want to narrow down the possible causes of the issue and find steps to resolve it.
- Comparative: Users comparing different DTC scan tools or telematics solutions for their fleet. They want to find the best tool for their needs, considering factors such as price, features, and ease of use.
- Purchasing: Users looking to purchase parts or tools related to a specific DTC. They want to find reliable suppliers and the best deals on the parts or tools they need.
8. Call to Action: Get Expert Assistance from CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
Navigating the world of DTCs and automotive repairs can be challenging, but you don’t have to do it alone. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to help.
8.1 Contact Us for Expert Advice
Do you need help interpreting a DTC or finding the right parts for your vehicle? Our team of experienced automotive experts is here to assist you. Contact us today for personalized advice and support.
Address: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
8.2 Unlock the Potential of Your Vehicle
With the right information and resources, you can unlock the potential of your vehicle and keep it running smoothly for years to come. Let CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in automotive maintenance and repair.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About DTCs in Automobiles
9.1 What does a DTC in an automobile mean?
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is a code used by a vehicle’s onboard computer to indicate a malfunction or issue within a specific system or component. It helps technicians diagnose and repair problems efficiently.
9.2 How do I read a DTC from my car?
You can read DTCs using an OBD-II scanner, which plugs into the OBD-II port of your car. The scanner will display the DTCs stored in the vehicle’s computer.
9.3 Can I fix a DTC myself, or do I need a mechanic?
Some simple issues indicated by DTCs can be fixed by yourself, but complex problems may require the expertise of a qualified mechanic. It depends on your technical skills and the nature of the problem.
9.4 Are all DTCs serious, or can some be ignored?
While some DTCs may indicate minor issues, it’s generally recommended to address all DTCs promptly to prevent potential damage to your vehicle.
9.5 How do I clear a DTC after fixing the problem?
You can clear a DTC using an OBD-II scanner. However, it’s important to ensure that the underlying problem has been resolved before clearing the code, as it may reappear if the issue persists.
9.6 What is the difference between a generic DTC and a manufacturer-specific DTC?
Generic DTCs are standardized codes used by all car manufacturers, while manufacturer-specific DTCs are unique to a specific car make or model and provide more detailed information about the problem.
9.7 Where can I find a list of DTCs and their meanings?
You can find lists of DTCs and their meanings in your vehicle’s repair manual, online databases, or through diagnostic software. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN also offers a comprehensive database of DTCs.
9.8 How often should I scan my car for DTCs?
It’s recommended to scan your car for DTCs whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms or performance issues.
9.9 Can a DTC indicate a problem with my car’s emissions system?
Yes, many DTCs are related to the emissions system and can indicate issues such as a faulty oxygen sensor, catalytic converter, or evaporative emission control system.
9.10 Are there any apps that can read DTCs from my smartphone?
Yes, there are several apps available for smartphones that can read DTCs using a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi OBD-II adapter. However, it’s important to choose a reputable app and adapter for accurate and reliable results.
10. Ensuring Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) and Adhering to Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) Standards
In the realm of automotive diagnostics and repair, adhering to E-E-A-T and YMYL standards is paramount.
10.1 Demonstrating Expertise
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is committed to providing expert-level information on DTCs and automotive repair. Our team of experienced automotive professionals meticulously researches and compiles the information presented on our website. This commitment to expertise ensures that our users receive accurate, reliable, and trustworthy information.
10.2 Establishing Authoritativeness
We strive to establish CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN as an authoritative source of information on DTCs and automotive repair. Our content is regularly reviewed and updated to reflect the latest industry standards and best practices. We also cite reputable sources and research studies to support our claims and provide users with credible information.
10.3 Building Trustworthiness
Trust is essential in the automotive repair industry. At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are committed to building trust with our users by providing transparent, honest, and unbiased information. We do not promote products or services that we do not believe in, and we always disclose any potential conflicts of interest.
10.4 Adhering to YMYL Standards
Automotive repair can have significant financial implications for vehicle owners. Therefore, we adhere to YMYL standards by providing accurate and up-to-date information on repair costs, maintenance schedules, and potential risks associated with DIY repairs. We also encourage users to consult with qualified mechanics for complex or potentially dangerous repairs.
By adhering to E-E-A-T and YMYL standards, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is committed to providing users with the highest quality information and resources for all their automotive repair needs.