Diagnostics Mac refers to using diagnostic tools and software on macOS to identify and troubleshoot hardware or software issues on Apple Mac computers. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN can provide you with the information you need to keep your Mac running smoothly and efficiently. By choosing our products and services, you’re investing in the longevity and performance of your Mac, and you’ll also discover the importance of Mac repair tools, system diagnostics, and performance optimization.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Diagnostics Mac
- 1.1. Why is Diagnostics Mac Important?
- 1.2. What are the Common Issues Diagnosed by Diagnostics Mac?
- 1.3. What are the Benefits of Using Diagnostics Mac Regularly?
- 2. Key Diagnostic Tools for Mac
- 2.1. Apple Diagnostics
- 2.1.1. How to Use Apple Diagnostics?
- 2.1.2. Interpreting Apple Diagnostics Results
- 2.1.3. Limitations of Apple Diagnostics
- 2.2. Activity Monitor
- 2.2.1. How to Use Activity Monitor to Identify Performance Issues?
- 2.2.2. Understanding Activity Monitor Metrics
- 2.2.3. Troubleshooting with Activity Monitor
- 2.3. Disk Utility
- 2.3.1. How to Use Disk Utility to Repair Disk Errors?
- 2.3.2. Disk Utility Features and Functions
- 2.3.3. When to Use Disk Utility
- 2.4. Third-Party Diagnostic Tools
- 2.4.1. Overview of Popular Third-Party Tools
- 2.4.2. Features and Benefits of Third-Party Tools
- 2.4.3. Choosing the Right Third-Party Tool
- 3. How to Interpret Diagnostic Results
- 3.1. Understanding Common Error Codes
- 3.2. Identifying Hardware vs. Software Issues
- 3.3. When to Seek Professional Help
- 4. Preventive Maintenance for Mac
- 4.1. Regular Software Updates
- 4.1.1. Why are Software Updates Important?
- 4.1.2. How to Update macOS
- 4.1.3. Updating Apps
- 4.2. Disk Cleanup and Organization
- 4.2.1. Identifying Unnecessary Files
- 4.2.2. Deleting Temporary Files and Caches
- 4.2.3. Organizing Files and Folders
- 4.3. Managing Startup Items
- 4.3.1. Identifying Startup Items
- 4.3.2. Disabling Unnecessary Startup Items
- 4.3.3. Using Third-Party Tools to Manage Startup Items
- 4.4. Monitoring System Resources
- 4.4.1. Using Activity Monitor to Monitor Resources
- 4.4.2. Setting Up Alerts for Resource Usage
- 4.5. Physical Maintenance
- 4.5.1. Cleaning Your Mac
- 4.5.2. Proper Ventilation
- 4.5.3. Protecting Your Mac from Extreme Temperatures
- 5. Advanced Diagnostics Mac Techniques
- 5.1. Using the Terminal for Diagnostics
- 5.1.1. Essential Terminal Commands for Diagnostics
- 5.1.2. Interpreting Terminal Output
- 5.1.3. Automating Diagnostics with Scripts
- 5.2. Analyzing System Logs
- 5.2.1. Accessing System Logs
- 5.2.2. Filtering and Searching Logs
- 5.2.3. Identifying Errors and Warnings
- 5.3. Using Diagnostic Mode
- 5.3.1. Booting into Diagnostic Mode
- 5.3.2. Running Hardware Tests in Diagnostic Mode
- 5.3.3. Interpreting Diagnostic Mode Results
- 6. Troubleshooting Common Mac Issues
- 6.1. Slow Performance
- 6.1.1. Identifying the Cause of Slow Performance
- 6.1.2. Troubleshooting Steps for Slow Performance
- 6.1.3. When to Seek Professional Help
- 6.2. Freezing and Crashing
- 6.2.1. Identifying the Cause of Freezing and Crashing
- 6.2.2. Troubleshooting Steps for Freezing and Crashing
- 6.2.3. When to Seek Professional Help
- 6.3. Startup Problems
- 6.3.1. Identifying the Cause of Startup Problems
- 6.3.2. Troubleshooting Steps for Startup Problems
- 6.3.3. When to Seek Professional Help
- 6.4. Network Connectivity Issues
- 6.4.1. Identifying the Cause of Network Connectivity Issues
- 6.4.2. Troubleshooting Steps for Network Connectivity Issues
- 6.4.3. When to Seek Professional Help
- 7. Future Trends in Mac Diagnostics
- 7.1. AI and Machine Learning in Diagnostics
- 7.2. Remote Diagnostics and Support
- 7.3. Predictive Diagnostics
- 8. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Mac Diagnostics
- 8.1. How CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help
- 8.2. Contact Us for Assistance
- 9. FAQ About Diagnostics Mac
1. Understanding Diagnostics Mac
Diagnostics Mac involves utilizing various diagnostic tools and software on the macOS operating system to identify and resolve hardware and software issues affecting Apple Mac computers. This process is essential for maintaining the optimal performance and reliability of Mac devices, including desktops, laptops, and servers. By running diagnostics, users can pinpoint the root causes of problems, such as slow performance, system crashes, or hardware malfunctions, enabling them to take corrective actions promptly.
1.1. Why is Diagnostics Mac Important?
Diagnostics Mac is important because it helps users identify and resolve issues that can affect the performance and reliability of their Mac computers. According to a study by Statista, approximately 30% of computer users experience hardware or software issues each year. By using diagnostic tools, users can prevent these issues from escalating and causing more significant problems.
Regular diagnostics can also help users optimize the performance of their Macs. According to a report by Macworld, running routine maintenance tasks, such as disk cleanup and software updates, can improve a Mac’s performance by up to 20%. Diagnostics Mac provides the insights needed to perform these tasks effectively.
1.2. What are the Common Issues Diagnosed by Diagnostics Mac?
Diagnostics Mac can help identify a wide range of issues, including:
- Hardware failures: Identifying failing components such as hard drives, memory modules, or graphics cards.
- Software conflicts: Detecting conflicts between applications or system software that can cause instability.
- Performance bottlenecks: Pinpointing processes or applications that are consuming excessive resources, leading to slowdowns.
- Network connectivity problems: Diagnosing issues with Wi-Fi or Ethernet connections that prevent access to the internet or local network resources.
- Startup issues: Resolving problems that prevent the Mac from booting properly.
1.3. What are the Benefits of Using Diagnostics Mac Regularly?
Using Diagnostics Mac regularly offers several benefits:
- Early detection of problems: Identifying potential issues before they cause significant disruptions.
- Improved performance: Optimizing system settings and removing unnecessary files or applications.
- Extended lifespan of hardware: Preventing hardware failures through timely maintenance and repairs.
- Reduced downtime: Minimizing disruptions caused by system crashes or other issues.
- Cost savings: Avoiding expensive repairs or replacements by addressing problems early on.
 macOS Diagnostics running progress bar
macOS Diagnostics running progress bar
macOS Diagnostics running progress bar
2. Key Diagnostic Tools for Mac
There are several diagnostic tools available for Mac, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. These tools can be broadly categorized into built-in utilities and third-party applications. Let’s explore some of the most popular and effective options:
2.1. Apple Diagnostics
Apple Diagnostics, formerly known as Apple Hardware Test, is a built-in utility that can check your Mac for hardware issues. It is designed to help determine which hardware component might be at fault and suggests solutions and ways to contact Apple Support for assistance.
2.1.1. How to Use Apple Diagnostics?
The process for starting Apple Diagnostics varies depending on whether your Mac has Apple silicon or an Intel processor:
For Macs with Apple silicon:
- Press and hold the power button on your Mac.
- As you continue to hold the power button, your Mac turns on and loads startup options. Release the power button when you see Options.
- Press and hold Command (⌘)-D on your keyboard.
For Macs with Intel processors:
- Turn on your Mac, then immediately press and hold the D key on your keyboard as your Mac starts up.
- Release when you see a progress bar or you’re asked to choose a language.
If using the D key doesn’t work, press and hold Option (⌥)-D at startup instead.
2.1.2. Interpreting Apple Diagnostics Results
Apple Diagnostics shows a progress bar while it’s checking your Mac. When testing is complete, it displays the results, including reference codes. These codes can help you identify the specific hardware component that is experiencing issues.
To repeat the test, click “Run the test again” or press Command-R. To restart your Mac, click Restart or press R. To shut down, click Shut Down or press S. To get information about your service and support options, ensure your Mac is connected to the internet, then click ”Get started” or press Command-G.
2.1.3. Limitations of Apple Diagnostics
While Apple Diagnostics is a useful tool, it has some limitations:
- It primarily focuses on hardware issues and may not detect software-related problems.
- The reference codes provided can be cryptic and may require further research to understand.
- It may not be able to diagnose intermittent issues that are difficult to reproduce.
2.2. Activity Monitor
Activity Monitor is a built-in macOS utility that provides real-time information about system resource usage. It allows you to monitor CPU usage, memory usage, energy consumption, disk activity, and network activity.
2.2.1. How to Use Activity Monitor to Identify Performance Issues?
To use Activity Monitor effectively, follow these steps:
- Open Activity Monitor from the /Applications/Utilities/ folder.
- Select the category you want to monitor (CPU, Memory, Energy, Disk, or Network).
- Sort the processes by the relevant column (e.g., % CPU for CPU usage, Memory for memory usage).
- Identify any processes that are consuming an unusually high amount of resources.
2.2.2. Understanding Activity Monitor Metrics
Activity Monitor provides several key metrics that can help you diagnose performance issues:
- % CPU: The percentage of CPU time being used by a process. High CPU usage can indicate a process is running inefficiently or is stuck in a loop.
- Memory (Real Memory): The amount of physical memory being used by a process. High memory usage can lead to slowdowns and system instability.
- Energy Impact: A measure of the energy being used by a process. High energy impact can drain the battery on a laptop.
- Disk I/O: The amount of data being read from and written to the disk by a process. High disk I/O can slow down overall system performance.
- Network I/O: The amount of data being sent and received over the network by a process. High network I/O can indicate a process is consuming excessive bandwidth.
2.2.3. Troubleshooting with Activity Monitor
When you identify a process that is consuming an unusually high amount of resources, you can take several actions:
- Quit the process: If the process is not essential, you can quit it to free up resources.
- Investigate the process: Research the process to determine its purpose and whether it is legitimate.
- Update the process: If the process is outdated, updating it to the latest version may resolve performance issues.
- Uninstall the process: If the process is unnecessary or potentially malicious, you can uninstall it.
2.3. Disk Utility
Disk Utility is a built-in macOS utility that allows you to manage disks and volumes. It can be used to repair disk errors, format disks, create disk images, and more.
2.3.1. How to Use Disk Utility to Repair Disk Errors?
To repair disk errors using Disk Utility, follow these steps:
- Open Disk Utility from the /Applications/Utilities/ folder.
- Select the disk or volume you want to repair.
- Click the “First Aid” button.
- Click “Run” to start the repair process.
Disk Utility will check the disk for errors and attempt to repair them. If it finds errors that it cannot repair, you may need to consider replacing the disk.
2.3.2. Disk Utility Features and Functions
In addition to repairing disk errors, Disk Utility offers several other useful features:
- Erase: Erases a disk or volume, securely deleting all data.
- Partition: Divides a disk into multiple volumes.
- Restore: Restores a disk or volume from a disk image.
- Mount/Unmount: Mounts or unmounts a disk or volume.
- Disk Image: Creates a disk image from a disk or volume.
2.3.3. When to Use Disk Utility
Disk Utility should be used when you experience disk-related issues, such as:
- Slow performance
- Files that cannot be opened or saved
- Error messages related to disk errors
- Startup problems
2.4. Third-Party Diagnostic Tools
In addition to the built-in utilities, several third-party diagnostic tools are available for Mac. These tools often offer more advanced features and capabilities.
2.4.1. Overview of Popular Third-Party Tools
Some of the most popular third-party diagnostic tools for Mac include:
- TechTool Pro: A comprehensive diagnostic utility that can test hardware components, repair disk errors, and optimize system performance.
- DriveDx: A disk monitoring tool that provides detailed information about the health and performance of your hard drive or SSD.
- iStat Menus: A system monitoring tool that displays real-time information about CPU usage, memory usage, network activity, and more in the menu bar.
- CleanMyMac X: A system cleanup and optimization tool that can remove unnecessary files, uninstall applications, and improve overall system performance.
2.4.2. Features and Benefits of Third-Party Tools
Third-party diagnostic tools often offer features and benefits that are not available in the built-in utilities:
- Advanced hardware diagnostics: More detailed testing of hardware components, such as memory, CPU, and graphics card.
- Disk health monitoring: Real-time monitoring of disk health and performance, with alerts for potential issues.
- System optimization: Tools for removing unnecessary files, disabling startup items, and optimizing system settings.
- User-friendly interface: A more intuitive and user-friendly interface than the built-in utilities.
2.4.3. Choosing the Right Third-Party Tool
When choosing a third-party diagnostic tool, consider the following factors:
- Features: What features do you need? Do you need advanced hardware diagnostics, disk health monitoring, or system optimization?
- Price: How much are you willing to spend? Third-party diagnostic tools range in price from free to several hundred dollars.
- User reviews: What do other users say about the tool? Read user reviews to get an idea of the tool’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Compatibility: Is the tool compatible with your version of macOS?
- Support: Does the tool offer good customer support?
3. How to Interpret Diagnostic Results
Interpreting diagnostic results can be challenging, especially for users who are not familiar with technical terms. However, understanding the results is essential for taking corrective actions and resolving issues.
3.1. Understanding Common Error Codes
Error codes are often displayed when a diagnostic test detects a problem. These codes can provide valuable information about the nature of the issue. Here are some common error codes and their meanings:
| Error Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| 4xxx/1/4000000: | Indicates a problem with the memory module. | Faulty memory module, incompatible memory module, or improperly installed memory module. |
| HDD/SSD | Indicates a problem with the hard drive or solid-state drive. | Failing hard drive or SSD, corrupted file system, or loose cable connection. |
| PPN001, PPN002, PPN003 | Indicates a problem with the power adapter. | Faulty power adapter, damaged power cable, or power outlet issue. |
| VFD001, VFD002, VFD003 | Indicates a problem with the display. | Faulty display panel, damaged display cable, or graphics card issue. |
| NDX006 | Indicates a problem with the Wi-Fi adapter. | Faulty Wi-Fi adapter, outdated drivers, or network configuration issue. |
| MOT004, MOT005, MOT006 | Indicates a problem with the fan. | Faulty fan, obstructed fan, or overheating issue. |
| CPU | Indicates a problem with the processor. | Overheating, failing processor, or BIOS issues. |
When you encounter an error code, research it online to learn more about the possible causes and solutions. Apple’s support website and other online resources can provide valuable information.
3.2. Identifying Hardware vs. Software Issues
One of the key challenges in interpreting diagnostic results is determining whether the issue is hardware-related or software-related. Here are some tips for distinguishing between the two:
- Hardware issues: Often manifest as intermittent problems, such as system crashes, freezes, or unexpected shutdowns. They may also be accompanied by physical symptoms, such as unusual noises or smells.
- Software issues: Typically manifest as consistent problems, such as application crashes, error messages, or slow performance. They may also be related to specific software or operating system features.
If you suspect a hardware issue, run Apple Diagnostics or a third-party hardware diagnostic tool to confirm your suspicions. If you suspect a software issue, try troubleshooting the software or reinstalling the operating system.
3.3. When to Seek Professional Help
Sometimes, diagnostic results can be inconclusive, or the issue may be too complex to resolve on your own. In these cases, it is best to seek professional help.
Consider seeking professional help if:
- You are unable to interpret the diagnostic results.
- You have tried troubleshooting the issue without success.
- The issue is causing significant disruptions to your work or personal life.
- You are not comfortable disassembling or repairing your Mac.
Apple offers several support options, including online support, phone support, and in-person service at Apple Stores and authorized service providers. You can also seek help from independent Mac repair shops.
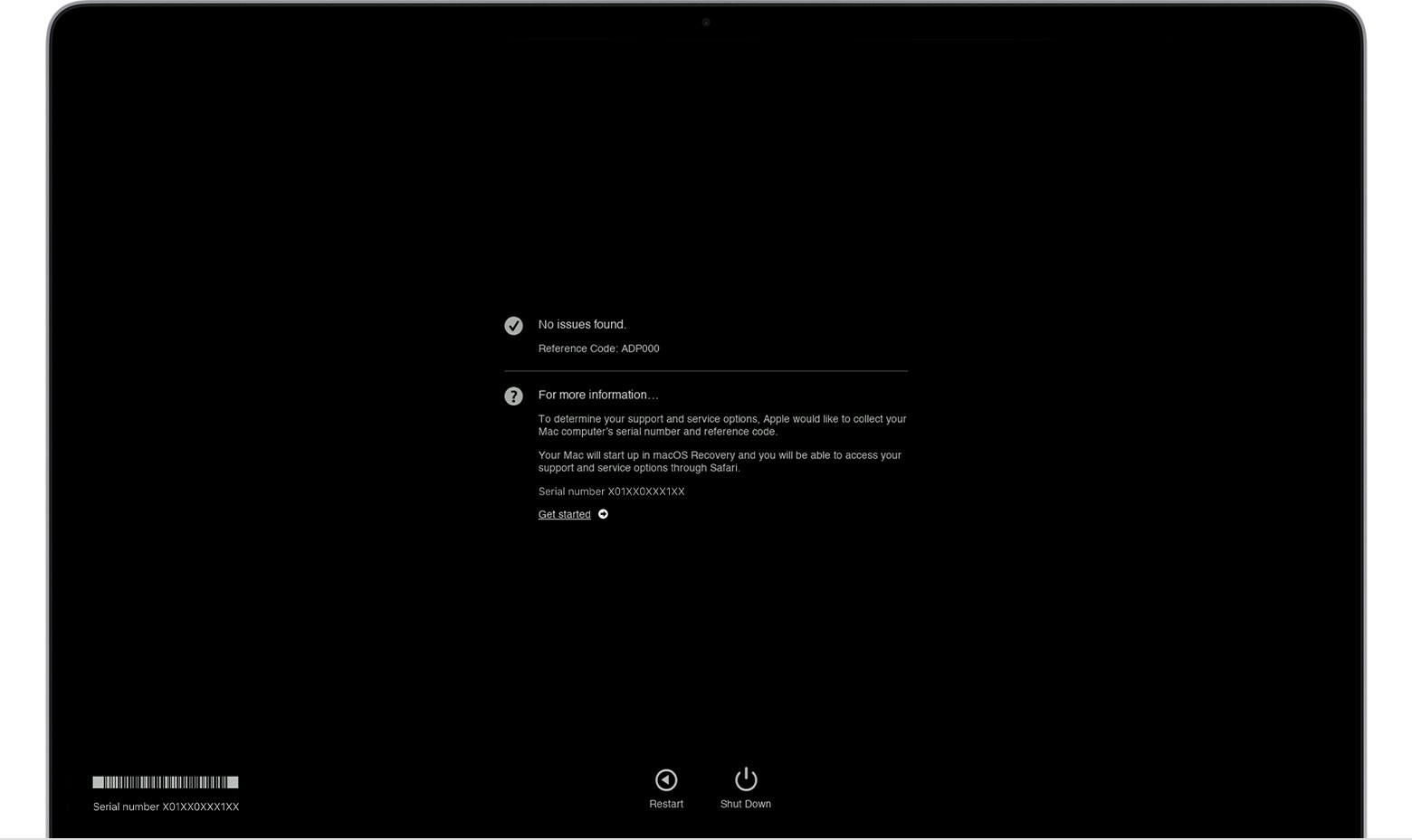 macOS Diagnostics results. No issues found.
macOS Diagnostics results. No issues found.
macOS Diagnostics results. No issues found.
4. Preventive Maintenance for Mac
Preventive maintenance is essential for keeping your Mac running smoothly and reliably. By performing regular maintenance tasks, you can prevent problems from developing and extend the lifespan of your Mac.
4.1. Regular Software Updates
Keeping your software up to date is one of the most important things you can do to maintain your Mac. Software updates often include bug fixes, security patches, and performance improvements.
4.1.1. Why are Software Updates Important?
Software updates are important for several reasons:
- Bug fixes: Updates often include fixes for known bugs that can cause problems.
- Security patches: Updates can patch security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers.
- Performance improvements: Updates can improve the performance of your Mac by optimizing system settings and removing unnecessary code.
- New features: Updates may include new features that enhance the functionality of your Mac.
4.1.2. How to Update macOS
To update macOS, follow these steps:
- Click the Apple menu in the upper-left corner of your screen.
- Select “System Preferences.”
- Click “Software Update.”
- If updates are available, click “Update Now” to install them.
You can also enable automatic updates by checking the “Automatically keep my Mac up to date” box.
4.1.3. Updating Apps
In addition to updating macOS, it is also important to update your apps. App updates often include bug fixes, security patches, and new features.
To update your apps, open the Mac App Store and click the “Updates” tab. If updates are available, click “Update” next to each app you want to update.
4.2. Disk Cleanup and Organization
Over time, your hard drive can become cluttered with unnecessary files, such as temporary files, cache files, and duplicate files. This can slow down your Mac and reduce its overall performance.
4.2.1. Identifying Unnecessary Files
To identify unnecessary files, you can use a disk cleanup utility, such as CleanMyMac X or Disk Drill. These utilities can scan your hard drive and identify files that can be safely deleted.
You can also manually identify unnecessary files by browsing your hard drive and deleting files that you no longer need. Be careful not to delete any important files.
4.2.2. Deleting Temporary Files and Caches
Temporary files and caches are created by apps and the operating system to store data temporarily. These files can accumulate over time and take up a significant amount of disk space.
To delete temporary files and caches, you can use a disk cleanup utility or manually delete them from the following locations:
- ~/Library/Caches
- /Library/Caches
- /tmp
4.2.3. Organizing Files and Folders
Organizing your files and folders can also improve your Mac’s performance. When your files are organized, it is easier for the operating system to find them, which can speed up file access.
To organize your files and folders, create a logical folder structure and move your files into the appropriate folders. You can also use tags to categorize your files.
4.3. Managing Startup Items
Startup items are apps and processes that automatically start when you turn on your Mac. These items can slow down your Mac’s startup time and consume system resources.
4.3.1. Identifying Startup Items
To identify startup items, follow these steps:
- Click the Apple menu in the upper-left corner of your screen.
- Select “System Preferences.”
- Click “Users & Groups.”
- Select your user account.
- Click the “Login Items” tab.
The “Login Items” tab displays a list of apps and processes that automatically start when you log in.
4.3.2. Disabling Unnecessary Startup Items
To disable unnecessary startup items, select the item in the list and click the “-” button. Be careful not to disable any essential startup items, such as those related to the operating system or security software.
4.3.3. Using Third-Party Tools to Manage Startup Items
You can also use third-party tools, such as CleanMyMac X, to manage startup items. These tools often provide more advanced features, such as the ability to delay startup items or disable them temporarily.
4.4. Monitoring System Resources
Monitoring your system resources can help you identify potential problems before they cause significant disruptions.
4.4.1. Using Activity Monitor to Monitor Resources
Activity Monitor is a built-in macOS utility that provides real-time information about system resource usage. It allows you to monitor CPU usage, memory usage, energy consumption, disk activity, and network activity.
Use Activity Monitor to identify processes that are consuming an unusually high amount of resources. This can help you identify potential problems and take corrective actions.
4.4.2. Setting Up Alerts for Resource Usage
You can also set up alerts to notify you when system resources are being used excessively. This can help you identify problems early on and prevent them from escalating.
To set up alerts, you can use a third-party system monitoring tool, such as iStat Menus. These tools allow you to set up alerts for CPU usage, memory usage, disk space, and other system resources.
4.5. Physical Maintenance
In addition to software maintenance, physical maintenance is also important for keeping your Mac running smoothly and reliably.
4.5.1. Cleaning Your Mac
Dust and debris can accumulate inside your Mac and cause it to overheat. This can lead to performance problems and even hardware failures.
Clean your Mac regularly using a soft, lint-free cloth. You can also use compressed air to remove dust from hard-to-reach areas.
4.5.2. Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation is essential for keeping your Mac cool. Make sure that your Mac is placed in a well-ventilated area and that the vents are not blocked.
Avoid placing your Mac on soft surfaces, such as carpets or blankets, as this can restrict airflow.
4.5.3. Protecting Your Mac from Extreme Temperatures
Extreme temperatures can damage your Mac. Avoid exposing your Mac to direct sunlight or extreme heat or cold.
If you must transport your Mac in extreme temperatures, keep it in a protective case and allow it to warm up or cool down gradually before using it.
5. Advanced Diagnostics Mac Techniques
For advanced users, there are several advanced diagnostics techniques that can be used to troubleshoot complex issues.
5.1. Using the Terminal for Diagnostics
The Terminal is a powerful command-line interface that can be used to perform a wide range of diagnostics tasks.
5.1.1. Essential Terminal Commands for Diagnostics
Here are some essential Terminal commands for diagnostics:
- system_profiler: Displays detailed information about your Mac’s hardware and software.
- top: Displays a list of the most resource-intensive processes.
- ps: Displays a list of all running processes.
- netstat: Displays network statistics.
- ping: Tests network connectivity.
- traceroute: Traces the route that network packets take to reach a destination.
5.1.2. Interpreting Terminal Output
Interpreting Terminal output can be challenging, but it can provide valuable information about your Mac’s performance and health.
Research the commands and their output online to learn more about what they mean. Apple’s developer website and other online resources can provide valuable information.
5.1.3. Automating Diagnostics with Scripts
You can automate diagnostics tasks by writing scripts that run Terminal commands and analyze their output.
This can save you time and effort and can help you identify potential problems more quickly.
5.2. Analyzing System Logs
System logs contain detailed information about system events, errors, and warnings. Analyzing system logs can help you troubleshoot complex issues.
5.2.1. Accessing System Logs
To access system logs, open the Console app from the /Applications/Utilities/ folder.
The Console app displays a list of system logs. You can filter the logs by date, time, process, and other criteria.
5.2.2. Filtering and Searching Logs
To find specific information in the logs, you can use the Console app’s filtering and searching capabilities.
Filter the logs by date, time, process, and other criteria to narrow down the results. Search the logs for specific keywords or error messages.
5.2.3. Identifying Errors and Warnings
Errors and warnings in the system logs can indicate potential problems.
Research the errors and warnings online to learn more about their possible causes and solutions. Apple’s developer website and other online resources can provide valuable information.
5.3. Using Diagnostic Mode
Diagnostic Mode is a special mode that allows you to run diagnostics tests without loading the operating system.
5.3.1. Booting into Diagnostic Mode
To boot into Diagnostic Mode, follow these steps:
- Shut down your Mac.
- Press and hold the D key while turning on your Mac.
- Release the D key when you see the Apple logo.
Your Mac will boot into Diagnostic Mode.
5.3.2. Running Hardware Tests in Diagnostic Mode
In Diagnostic Mode, you can run hardware tests to check for hardware problems.
The available tests vary depending on your Mac model.
5.3.3. Interpreting Diagnostic Mode Results
The results of the hardware tests will be displayed on the screen.
Research the results online to learn more about their possible causes and solutions. Apple’s support website and other online resources can provide valuable information.
6. Troubleshooting Common Mac Issues
Even with regular maintenance and diagnostics, you may still encounter issues with your Mac. Here are some common Mac issues and how to troubleshoot them:
6.1. Slow Performance
Slow performance is a common Mac issue that can be caused by a variety of factors.
6.1.1. Identifying the Cause of Slow Performance
To identify the cause of slow performance, use Activity Monitor to monitor system resources.
Look for processes that are consuming an unusually high amount of resources.
6.1.2. Troubleshooting Steps for Slow Performance
Here are some troubleshooting steps for slow performance:
- Close unnecessary apps and processes.
- Free up disk space by deleting unnecessary files.
- Disable unnecessary startup items.
- Run Disk Utility to repair disk errors.
- Update macOS and your apps.
- Add more RAM.
- Replace your hard drive with an SSD.
- Reinstall macOS.
6.1.3. When to Seek Professional Help
If you have tried all of the troubleshooting steps and your Mac is still slow, you may need to seek professional help.
6.2. Freezing and Crashing
Freezing and crashing are serious Mac issues that can cause data loss and frustration.
6.2.1. Identifying the Cause of Freezing and Crashing
To identify the cause of freezing and crashing, check the system logs for errors and warnings.
Look for patterns in the freezing and crashing, such as whether they occur when using a specific app or performing a specific task.
6.2.2. Troubleshooting Steps for Freezing and Crashing
Here are some troubleshooting steps for freezing and crashing:
- Force quit the app that is causing the problem.
- Restart your Mac.
- Update macOS and your apps.
- Run Disk Utility to repair disk errors.
- Check for hardware problems using Apple Diagnostics or a third-party hardware diagnostic tool.
- Reinstall macOS.
6.2.3. When to Seek Professional Help
If you have tried all of the troubleshooting steps and your Mac is still freezing and crashing, you may need to seek professional help.
6.3. Startup Problems
Startup problems can prevent you from using your Mac.
6.3.1. Identifying the Cause of Startup Problems
To identify the cause of startup problems, try booting into Safe Mode.
If your Mac starts up in Safe Mode, the problem is likely related to a software issue.
6.3.2. Troubleshooting Steps for Startup Problems
Here are some troubleshooting steps for startup problems:
- Try booting into Safe Mode.
- Run Disk Utility to repair disk errors.
- Reset the PRAM or NVRAM.
- Reinstall macOS.
6.3.3. When to Seek Professional Help
If you have tried all of the troubleshooting steps and your Mac is still not starting up, you may need to seek professional help.
6.4. Network Connectivity Issues
Network connectivity issues can prevent you from accessing the internet or local network resources.
6.4.1. Identifying the Cause of Network Connectivity Issues
To identify the cause of network connectivity issues, check your network settings and make sure that your Mac is properly connected to the network.
Use the ping command to test network connectivity.
6.4.2. Troubleshooting Steps for Network Connectivity Issues
Here are some troubleshooting steps for network connectivity issues:
- Check your network settings.
- Restart your modem and router.
- Update your network drivers.
- Reset your network settings.
- Contact your internet service provider.
6.4.3. When to Seek Professional Help
If you have tried all of the troubleshooting steps and you are still experiencing network connectivity issues, you may need to seek professional help.
7. Future Trends in Mac Diagnostics
The field of Mac diagnostics is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques emerging all the time.
7.1. AI and Machine Learning in Diagnostics
AI and machine learning are being used to develop more advanced diagnostics tools that can automatically identify and resolve complex issues.
7.2. Remote Diagnostics and Support
Remote diagnostics and support are becoming increasingly popular, allowing technicians to troubleshoot and repair Macs remotely.
7.3. Predictive Diagnostics
Predictive diagnostics uses machine learning to predict when a Mac is likely to experience a problem, allowing users to take preventive actions before the problem occurs.
8. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Mac Diagnostics
At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of keeping your Mac running smoothly and reliably. That’s why we offer a wide range of diagnostic tools, repair services, and maintenance tips to help you keep your Mac in top condition.
8.1. How CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN can help you with all of your Mac diagnostics needs:
- We offer a wide range of diagnostic tools, both built-in and third-party.
- We provide expert repair services for all types of Mac issues.
- We offer maintenance tips and advice to help you keep your Mac running smoothly.
- We have experienced technicians who can diagnose and resolve complex issues.
- We offer affordable prices and excellent customer service.
8.2. Contact Us for Assistance
If you are experiencing issues with your Mac, don’t hesitate to contact us for assistance.
Our experienced technicians are available to help you diagnose and resolve any problems you may be experiencing.
You can contact us at:
- Address: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
- Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
We look forward to helping you keep your Mac running smoothly and reliably.
Maintaining your Mac’s health is essential for its longevity and performance. Regular diagnostics, preventive maintenance, and prompt troubleshooting can help you keep your Mac running smoothly and reliably. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to support you with all your Mac diagnostics needs.
Ready to ensure your Mac runs at its best? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert diagnostics and repair services. Reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for immediate assistance!
9. FAQ About Diagnostics Mac
9.1. What is Diagnostics Mac?
Diagnostics Mac refers to the process of using diagnostic tools and software on the macOS operating system to identify and troubleshoot hardware or software issues affecting Apple Mac computers.
9.2. Why is Diagnostics Mac Important?
Diagnostics Mac is crucial for identifying and resolving issues that can impact the performance and reliability of Mac computers. Regular diagnostics can help prevent problems from escalating, optimize system performance, and extend the lifespan of hardware.
9.3. What are Common Issues Diagnosed by Diagnostics Mac?
Diagnostics Mac can identify a wide range of issues, including hardware failures, software conflicts, performance bottlenecks, network connectivity problems, and startup issues.
9.4. What are the Benefits of Using Diagnostics Mac Regularly?
Using Diagnostics Mac regularly provides benefits such as early detection of problems, improved performance, extended hardware lifespan, reduced downtime, and cost savings by addressing issues early on.
9.5. How Do I Use Apple Diagnostics?
To use Apple Diagnostics, start your Mac and press and hold the D key during startup (for Intel Macs) or hold the power button and then Command-D (for Apple silicon Macs). Follow the on-screen instructions to run the tests.
9.6. What is Activity Monitor?
Activity Monitor is a built-in macOS utility that provides real-time information about system resource usage, including CPU, memory, energy, disk, and network activity.
9.7. How Can Disk Utility Help with Diagnostics?
Disk Utility can help diagnose and repair disk-related issues, such as file system errors, by using the “First Aid” feature. It can also be used to erase, partition, and restore disks.
9.8. What are Some Popular Third-Party Diagnostic Tools for Mac?
Popular third-party diagnostic tools for Mac include TechTool Pro, DriveDx, iStat Menus, and CleanMyMac X, which offer advanced features for hardware diagnostics, disk health monitoring, and system optimization.
9.9. How Do I Interpret Error Codes from Diagnostic Tests?
Error codes provide valuable information about the nature of the issue. Research the error code online to understand its possible causes and solutions. Apple’s support website and other online resources can provide helpful information.
9.10. When Should I Seek Professional Help for Mac Diagnostics?
You should seek professional help when you are unable to interpret diagnostic results, have tried troubleshooting without success, the issue is causing significant disruptions, or you are not comfortable disassembling or repairing your Mac.
