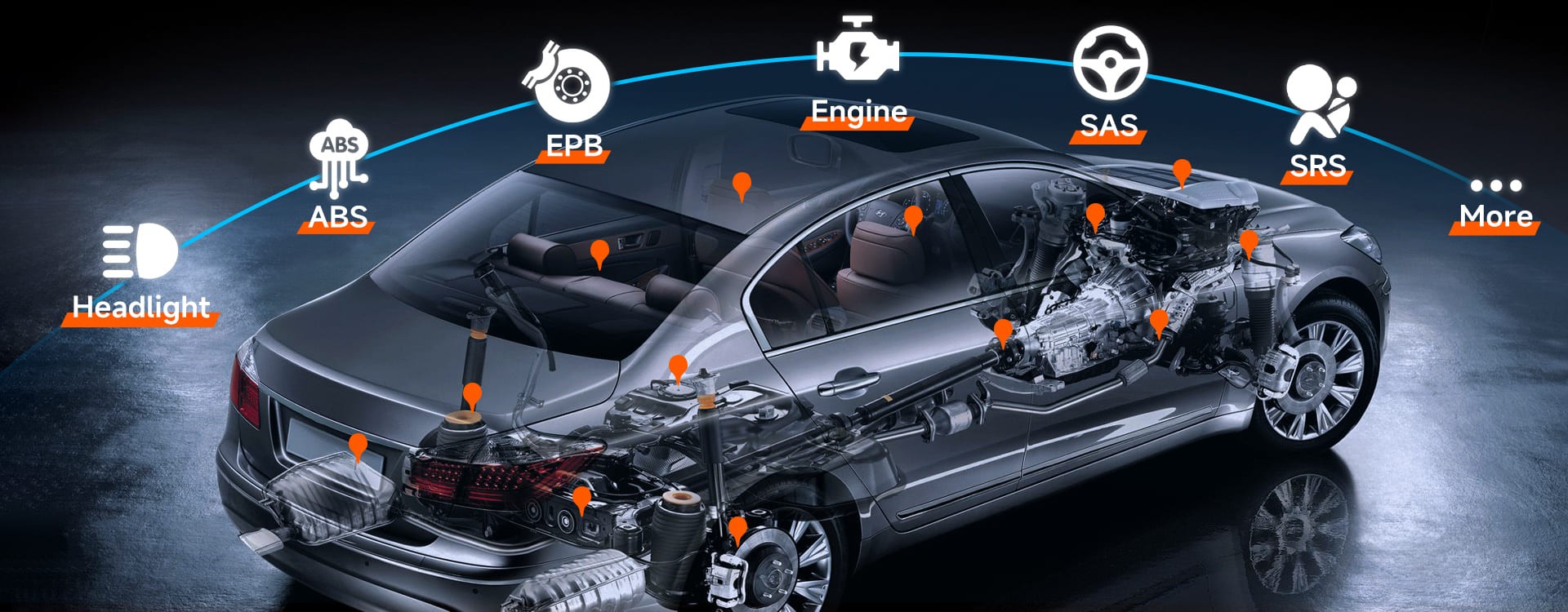
Yes, you can use a scan tool to check your car’s battery health, offering valuable insights into its condition and preventing potential breakdowns, allowing you to perform essential diagnostics. By identifying potential issues early and getting maintenance advice from CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for optimal electrical system maintenance, you can save on costly repairs by performing essential diagnostics. Key parameters to monitor include battery voltage, state of health (SOH), and cold cranking amps (CCA), all accessible through modern scan tools.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Role of Scan Tools in Battery Health Assessment
- 1.1 What is an OBD2 Scanner?
- 1.2 How Scan Tools Communicate with Your Car’s Battery Management System
- 2. Key Battery Parameters You Can Monitor with a Scan Tool
- 2.1 Battery Voltage: A Basic Indicator of Battery Condition
- 2.2 State of Health (SOH): Assessing the Battery’s Overall Lifespan
- 2.3 State of Charge (SOC): Determining the Current Charge Level
- 2.4 Cold Cranking Amps (CCA): Measuring the Battery’s Starting Power
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide: Checking Battery Health with a Scan Tool
- 3.1 Connecting the Scan Tool to Your Vehicle
- 3.2 Navigating to the Battery Health Menu
- 3.3 Reading and Interpreting the Battery Parameters
- 3.4 Performing Additional Tests: Load Test and Charging System Test
- 4. Choosing the Right Scan Tool for Battery Diagnostics
- 4.1 Compatibility with Your Vehicle Make and Model
- 4.2 Essential Features for Battery Health Monitoring
- 4.3 User-Friendliness and Ease of Navigation
- 4.4 Top Scan Tool Brands and Models for Battery Diagnostics
- 5. Understanding OBD2 Error Codes Related to Battery Issues
- 5.1 Common Error Codes and Their Meanings
- 5.2 How to Interpret Error Codes and Troubleshoot Battery Problems
- 5.3 When to Consult a Professional Mechanic
- 6. Maintaining Your Car Battery and Electrical System for Longevity
- 6.1 Regular Inspections and Cleaning of Battery Terminals
- 6.2 Proper Charging Habits and Avoiding Deep Discharges
- 6.3 Monitoring the Charging System and Alternator Performance
- 7. What To Do After Detecting a Battery Issue
- 7.1 Testing the Battery with a Load Tester
- 7.2 Considering Battery Replacement Based on Age and Condition
- 7.3 Checking the Alternator and Charging System
- 8. Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for Automotive Information
- 8.1 Access to Detailed Parts Information
- 8.2 Side-by-Side Product Comparisons
- 8.3 User Reviews and Ratings
- 9. Call to Action: Get Expert Advice from CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 9.1 Contact Information
- 9.2 Why Contact Us?
- 9.3 Immediate Assistance and Expert Consultation
- 10. Conclusion
- FAQs
- 10.1 How to Check Battery Voltage With OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.2 Will an OBD2 Scanner Read Battery Light?
- 10.3 Can an OBD2 Scanner Test an Alternator?
- 10.4 What Does State of Health (SOH) Mean for a Car Battery?
- 10.5 How Often Should I Check My Car Battery’s Health?
- 10.6 Can a Scan Tool Detect a Parasitic Battery Drain?
- 10.7 What is Cold Cranking Amps (CCA), and Why Is It Important?
- 10.8 Are Wireless OBD2 Scanners as Reliable as Wired Ones?
- 10.9 What Should I Do if My OBD2 Scanner Shows a “No Communication” Error?
- 10.10 Where Can I Find Reliable Information About OBD2 Error Codes?
1. Understanding the Role of Scan Tools in Battery Health Assessment
Scan tools, also known as OBD2 scanners, have revolutionized automotive diagnostics, evolving from simple code readers to comprehensive diagnostic devices. According to a 2022 report by Grand View Research, the global automotive diagnostic scan tools market is expected to reach $8.23 billion by 2030, reflecting their increasing importance in vehicle maintenance. Scan tools can access a wealth of data from your vehicle’s onboard computer, including information about the battery’s health. Modern scan tools do more than just read basic voltage; they offer a detailed analysis of the battery’s overall condition.
1.1 What is an OBD2 Scanner?
OBD2 stands for On-Board Diagnostics II, a standardized system used in most vehicles since 1996 to monitor engine performance and other critical systems. An OBD2 scanner is a device that connects to your car’s OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard, and retrieves data stored by the vehicle’s computer. This data includes diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), live sensor readings, and other valuable information that can help you diagnose a variety of automotive problems, including battery issues.
1.2 How Scan Tools Communicate with Your Car’s Battery Management System
Your car’s Battery Management System (BMS) is responsible for monitoring and controlling the battery’s charging and discharging processes. The BMS collects data on various battery parameters, such as voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge (SOC). This data is then transmitted to the vehicle’s computer, which can be accessed by a scan tool. By reading this data, a scan tool can provide you with a comprehensive overview of your battery’s health and performance.
2. Key Battery Parameters You Can Monitor with a Scan Tool
A scan tool provides access to several critical battery parameters, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of its health. These parameters include voltage, state of health (SOH), state of charge (SOC), and cold cranking amps (CCA). Understanding these parameters is essential for interpreting the scan tool’s readings and making informed decisions about battery maintenance or replacement.
2.1 Battery Voltage: A Basic Indicator of Battery Condition
Battery voltage is a fundamental indicator of a battery’s condition. A healthy battery should have a voltage of around 12.6 volts when the engine is off. According to Battery Council International, a voltage below 12.4 volts indicates that the battery is partially discharged and may require charging. A voltage below 12.0 volts suggests that the battery is significantly discharged and may be damaged.
2.2 State of Health (SOH): Assessing the Battery’s Overall Lifespan
State of Health (SOH) is a percentage that indicates the battery’s overall condition compared to its original condition. A new battery has an SOH of 100%, while a degraded battery will have a lower SOH. A battery with an SOH below 80% may need replacement soon, as it indicates a significant decline in its ability to hold a charge and deliver power.
2.3 State of Charge (SOC): Determining the Current Charge Level
State of Charge (SOC) is a percentage that indicates the amount of energy stored in the battery relative to its maximum capacity. A fully charged battery has an SOC of 100%, while a discharged battery has a lower SOC. Monitoring the SOC can help you identify potential charging issues or excessive battery drain.
2.4 Cold Cranking Amps (CCA): Measuring the Battery’s Starting Power
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) is a measure of the battery’s ability to start the engine in cold weather. It indicates the amount of current the battery can deliver at 0°F (-18°C) for 30 seconds while maintaining a voltage of 7.2 volts or higher. A healthy battery should have a CCA rating that meets or exceeds the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications. A low CCA reading indicates that the battery may struggle to start the engine in cold conditions.
 Car Scanner Functions | Foxwell
Car Scanner Functions | Foxwell
3. Step-by-Step Guide: Checking Battery Health with a Scan Tool
Checking your car’s battery health with a scan tool is a straightforward process that can be completed in a few simple steps. This guide provides a step-by-step walkthrough, ensuring you can accurately assess your battery’s condition.
3.1 Connecting the Scan Tool to Your Vehicle
The first step is to connect the scan tool to your vehicle’s OBD2 port. The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard, on the driver’s side. Once you’ve located the port, plug the scan tool into it. The scan tool should power on automatically. If it doesn’t, check the connection and ensure the vehicle’s ignition is turned on.
3.2 Navigating to the Battery Health Menu
Once the scan tool is connected and powered on, navigate to the battery health menu. The exact location of this menu may vary depending on the scan tool model, so consult the user manual for specific instructions. In general, you’ll want to look for options like “Battery Test,” “Electrical System Test,” or “Voltage Test.”
3.3 Reading and Interpreting the Battery Parameters
Once you’ve accessed the battery health menu, the scan tool will display various battery parameters, such as voltage, SOH, SOC, and CCA. Record these readings and compare them to the manufacturer’s specifications or industry standards. As mentioned earlier, a healthy battery should have a voltage of around 12.6 volts when the engine is off. An SOH above 80% indicates a healthy battery, while an SOC close to 100% suggests a fully charged battery. The CCA rating should meet or exceed the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications.
3.4 Performing Additional Tests: Load Test and Charging System Test
In addition to reading the basic battery parameters, some scan tools also allow you to perform additional tests, such as a load test and a charging system test. A load test measures the battery’s ability to deliver power under load, simulating the conditions when starting the engine. A charging system test checks the alternator’s output voltage to ensure it’s properly charging the battery. These tests can provide valuable insights into the battery’s overall health and the performance of the charging system.
4. Choosing the Right Scan Tool for Battery Diagnostics
Selecting the right scan tool is crucial for accurate and effective battery diagnostics. With a wide range of options available, it’s essential to consider factors like compatibility, features, and user-friendliness. This section offers guidance on choosing the best scan tool for your needs.
4.1 Compatibility with Your Vehicle Make and Model
The first thing to consider is whether the scan tool is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Not all scan tools are created equal, and some may only work with specific vehicle brands or models. Check the scan tool’s product specifications or consult the manufacturer’s website to ensure it’s compatible with your car.
4.2 Essential Features for Battery Health Monitoring
When choosing a scan tool for battery health monitoring, look for features like voltage measurement, SOH and SOC readings, CCA testing, load testing, and charging system testing. These features will provide you with a comprehensive overview of your battery’s health and performance.
4.3 User-Friendliness and Ease of Navigation
A scan tool should be easy to use and navigate, even for beginners. Look for a scan tool with a clear display, intuitive menus, and a user-friendly interface. Some scan tools also offer helpful features like built-in tutorials or troubleshooting guides.
4.4 Top Scan Tool Brands and Models for Battery Diagnostics
Several reputable brands offer high-quality scan tools for battery diagnostics. Some of the top brands include:
- Foxwell: Known for their comprehensive diagnostic capabilities and user-friendly interfaces. The Foxwell BT705 is a popular choice for battery testing.
- Autel: Offers a wide range of scan tools, from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tablets. Their products are known for their accuracy and reliability.
- Bosch: A trusted brand in the automotive industry, Bosch offers scan tools with advanced features and robust performance.
- BlueDriver: A smartphone-based scan tool that provides detailed diagnostic information and is known for its ease of use.
According to a 2023 survey by Auto Trends Magazine, Foxwell and Autel are the most popular scan tool brands among professional mechanics, with Bosch and BlueDriver also receiving high ratings.
5. Understanding OBD2 Error Codes Related to Battery Issues
OBD2 error codes can provide valuable clues when diagnosing battery issues. These codes can point to specific problems, such as low voltage, charging system malfunctions, or battery drain. Understanding these codes can help you narrow down the potential causes of battery problems and take appropriate action.
5.1 Common Error Codes and Their Meanings
Here are some common OBD2 error codes related to battery issues:
- P0562: System Voltage Low. This code indicates that the vehicle’s electrical system voltage is lower than expected, which could be due to a weak battery, a faulty alternator, or a wiring problem.
- P0563: System Voltage High. This code indicates that the vehicle’s electrical system voltage is higher than expected, which could be due to a faulty alternator regulator.
- P0620: Generator Control Circuit Malfunction. This code indicates a problem with the alternator control circuit, which could affect the battery’s charging process.
- P0625: Generator Field Terminal Circuit Low. This code indicates a problem with the alternator field terminal circuit, which could also affect the battery’s charging process.
- B1000: Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Malfunction. While not always directly related to the battery, this code can sometimes indicate a problem with the ECU that is affecting the battery’s performance.
5.2 How to Interpret Error Codes and Troubleshoot Battery Problems
When you encounter an OBD2 error code related to the battery, the first step is to research the code and understand its potential causes. Use a reliable online resource like CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN to look up the code and learn about its possible symptoms and solutions. Once you have a good understanding of the code, you can begin troubleshooting the problem. Start by checking the battery voltage and the alternator output. If the voltage is low, try charging the battery or replacing it if it’s old or damaged. If the alternator output is not within the specified range, the alternator may need to be repaired or replaced. Also, inspect the wiring and connections for any signs of damage or corrosion.
5.3 When to Consult a Professional Mechanic
While a scan tool can be a valuable tool for diagnosing battery problems, it’s not a substitute for professional expertise. If you’re not comfortable working on your car’s electrical system or if you’re unable to resolve the problem yourself, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic. Electrical problems can be complex and dangerous, so it’s important to seek professional help when needed. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN recommends seeking the advice of a trusted mechanic for any unresolved issues.
6. Maintaining Your Car Battery and Electrical System for Longevity
Preventive maintenance is key to extending the life of your car battery and electrical system. Regular inspections, proper charging habits, and timely repairs can help you avoid unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.
6.1 Regular Inspections and Cleaning of Battery Terminals
Regularly inspect your battery terminals for corrosion, which can interfere with the battery’s ability to charge and discharge properly. If you notice any corrosion, clean the terminals with a mixture of baking soda and water. Apply the mixture to the terminals, let it sit for a few minutes, and then scrub them with a wire brush. Rinse the terminals with water and dry them thoroughly before reconnecting the cables. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), corroded battery terminals are a common cause of battery problems and can reduce battery life by up to 20%.
6.2 Proper Charging Habits and Avoiding Deep Discharges
Avoid deep discharges of your car battery, as this can shorten its lifespan. If you frequently drain your battery by leaving the lights on or running accessories for extended periods, consider investing in a battery maintainer or charger. A battery maintainer will keep your battery fully charged without overcharging it, which can help extend its lifespan. Also, avoid letting your car sit idle for long periods, as this can also drain the battery. If you’re not going to be driving your car for several weeks or months, disconnect the battery or use a battery tender to keep it charged.
6.3 Monitoring the Charging System and Alternator Performance
Regularly monitor your car’s charging system and alternator performance to ensure they’re functioning properly. Use a scan tool or a multimeter to check the alternator’s output voltage while the engine is running. The voltage should be within the specified range, typically between 13.5 and 14.5 volts. If the voltage is outside this range, the alternator may need to be repaired or replaced.
 Diagnosis Oil Car Scanner | Foxwell
Diagnosis Oil Car Scanner | Foxwell
7. What To Do After Detecting a Battery Issue
After using a scan tool and identifying a battery issue, it’s important to take the right steps to address the problem. Whether it’s a simple fix or a more complex issue, this section provides guidance on what to do next.
7.1 Testing the Battery with a Load Tester
If your scan tool indicates a potential battery issue, it’s a good idea to perform a load test to verify the results. A load tester applies a heavy load to the battery and measures its voltage under load. This test can help you determine whether the battery is capable of delivering the power needed to start the engine and run the vehicle’s electrical systems. If the battery voltage drops below a certain threshold during the load test, it indicates that the battery is weak and needs to be replaced.
7.2 Considering Battery Replacement Based on Age and Condition
Car batteries typically last between three and five years, depending on usage, climate, and maintenance. If your battery is more than three years old and showing signs of weakness, it may be time to replace it, even if it still passes a load test. As batteries age, they gradually lose their ability to hold a charge and deliver power, which can lead to starting problems and other electrical issues. When replacing your battery, be sure to choose a high-quality battery that meets or exceeds the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications.
7.3 Checking the Alternator and Charging System
A faulty alternator can quickly ruin a new battery, so it’s essential to check the alternator and charging system whenever you replace a battery. Use a scan tool or a multimeter to check the alternator’s output voltage while the engine is running. The voltage should be within the specified range, typically between 13.5 and 14.5 volts. If the voltage is outside this range, the alternator may need to be repaired or replaced. Also, check the charging system wiring and connections for any signs of damage or corrosion.
8. Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for Automotive Information
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is your go-to resource for detailed information on automotive parts and tools. Our platform provides specifications, comparisons, and user reviews to help you make informed decisions.
8.1 Access to Detailed Parts Information
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive details on a wide range of auto parts, including batteries, alternators, scan tools, and more. You can find specifications, compatibility information, and expert advice to help you choose the right parts for your vehicle.
8.2 Side-by-Side Product Comparisons
Our platform allows you to compare different products side-by-side, making it easy to evaluate their features, benefits, and drawbacks. You can compare batteries from different brands, scan tools with different capabilities, and more.
8.3 User Reviews and Ratings
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN features user reviews and ratings to provide you with real-world feedback on various auto parts and tools. You can read what other car owners and mechanics have to say about their experiences with different products.
9. Call to Action: Get Expert Advice from CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
Need help choosing the right scan tool or diagnosing a battery problem? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert advice and personalized recommendations.
9.1 Contact Information
Address: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
9.2 Why Contact Us?
Our team of experienced automotive professionals can help you find the right parts and tools for your needs. We can also provide you with expert advice on diagnosing and repairing battery problems.
9.3 Immediate Assistance and Expert Consultation
Contact us today for immediate assistance and expert consultation. We’re here to help you keep your car running smoothly and reliably.
10. Conclusion
Using a scan tool to check your car’s battery health is a simple yet effective way to prevent unexpected breakdowns and extend the life of your battery. By monitoring key battery parameters, understanding OBD2 error codes, and performing regular maintenance, you can keep your car’s electrical system in top condition. Remember to visit CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for detailed information on auto parts and tools, and don’t hesitate to contact us for expert advice.
FAQs
10.1 How to Check Battery Voltage With OBD2 Scanner?
To check battery voltage with an OBD2 scanner, connect the scanner to your car’s diagnostic port, usually under the dashboard. Navigate to the “Battery Test” or “Voltage Test” option in the scanner’s menu. The scanner will display the battery’s current voltage. A healthy battery should read around 12.6V when the car is off.
10.2 Will an OBD2 Scanner Read Battery Light?
Yes, an OBD2 scanner can read issues related to the battery light. When the battery light illuminates on your dashboard, it indicates a potential problem with the charging system or the battery itself. The scanner can retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that explain why the battery light is on, helping you identify problems such as a weak battery, alternator failure, or other electrical issues.
10.3 Can an OBD2 Scanner Test an Alternator?
Yes, an OBD2 scanner can test an alternator by reading the voltage levels while the engine is running. Connect the scanner, start the engine, and navigate to the “Charging System Test” option. The scanner will display the alternator’s output voltage. A properly functioning alternator should produce a voltage between 13.5V and 14.5V. If the voltage is outside this range, it indicates a problem with the alternator.
10.4 What Does State of Health (SOH) Mean for a Car Battery?
State of Health (SOH) is a percentage that indicates the overall condition of a car battery compared to when it was new. A new battery has an SOH of 100%, while a degraded battery will have a lower SOH. An SOH below 80% suggests the battery’s capacity and performance have significantly declined, and it may need to be replaced soon.
10.5 How Often Should I Check My Car Battery’s Health?
It is advisable to check your car battery’s health at least twice a year, typically before the start of winter and summer. Extreme temperatures can strain the battery, so checking before these seasons can help prevent unexpected failures. Regular checks are also recommended if you notice any signs of battery weakness, such as slow engine cranking or dimming headlights.
10.6 Can a Scan Tool Detect a Parasitic Battery Drain?
Yes, some advanced scan tools can detect a parasitic battery drain by monitoring the current draw when the vehicle is turned off. A parasitic drain occurs when electrical components continue to draw power from the battery even when the car is off, leading to a discharged battery. The scan tool can help identify the source of the drain, such as a faulty sensor or module.
10.7 What is Cold Cranking Amps (CCA), and Why Is It Important?
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) is a measure of a car battery’s ability to start an engine in cold temperatures. It indicates the amount of current the battery can deliver at 0°F (-18°C) for 30 seconds while maintaining a voltage of 7.2 volts or higher. A higher CCA rating is better, especially in colder climates, as it ensures the battery can provide enough power to start the engine even in freezing conditions.
10.8 Are Wireless OBD2 Scanners as Reliable as Wired Ones?
Wireless OBD2 scanners, which connect to your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, can be just as reliable as wired scanners, provided they are from reputable brands and have good reviews. Wireless scanners offer the convenience of portability and ease of use, but it’s essential to ensure they have a stable connection and accurate data readings.
10.9 What Should I Do if My OBD2 Scanner Shows a “No Communication” Error?
If your OBD2 scanner shows a “No Communication” error, it means the scanner cannot establish a connection with the vehicle’s computer. First, ensure the scanner is properly plugged into the OBD2 port and that the vehicle’s ignition is turned on. Check the scanner’s cable and connections for any damage. If the problem persists, the issue may be with the vehicle’s computer or the OBD2 port itself, requiring professional diagnosis.
10.10 Where Can I Find Reliable Information About OBD2 Error Codes?
You can find reliable information about OBD2 error codes on websites like CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, which offer comprehensive databases of error codes with detailed descriptions, potential causes, and troubleshooting tips. Additionally, automotive forums and professional mechanic websites can provide valuable insights and solutions for specific error codes. Always cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy.