Understanding the Bosch Number Ecu is crucial for anyone involved in engine diagnostics, repair, or performance tuning. This comprehensive guide, brought to you by CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, will help you easily identify and interpret Bosch ECU numbers, ensuring you find the correct replacement parts and perform accurate modifications. Dive in to learn more about engine control unit identification, ECU programming tools, and automotive diagnostic equipment.
Contents
- 1. What is a Bosch Number ECU?
- 1.1 Why is the Bosch Number ECU Important?
- 1.2 What Information Does a Bosch Number ECU Provide?
- 2. Understanding Bosch ECU Numbering Logic
- 2.1 Decoding Common Bosch ECU References
- 2.1.1 MED17.1.1
- 2.1.2 MG1CS201
- 2.1.3 MD1CP002
- 2.2 Key Components of a Bosch ECU Number
- 3. Methods to Easily Identify a Bosch Number ECU
- 3.1 Online Bosch ECU Identification Tools
- 3.2 Physical Inspection of the ECU
- 3.3 Using Diagnostic Tools
- 4. Common Applications of Bosch ECUs
- 4.1 ECUs for Gasoline Engines
- 4.2 ECUs for Diesel Engines
- 4.3 ECUs for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
- 5. Troubleshooting Common Issues with Bosch ECUs
- 5.1 Symptoms of a Faulty Bosch ECU
- 5.2 Common Error Codes Related to Bosch ECUs
- 5.3 Basic Troubleshooting Steps for Bosch ECUs
- 6. Benefits of Using the Correct Bosch Number ECU
- 6.1 Enhanced Engine Performance
- 6.2 Improved Fuel Efficiency
- 6.3 Reduced Emissions
- 7. Where to Find Bosch ECUs and Parts
- 7.1 Authorized Bosch Dealers
- 7.2 Online Retailers
- 7.3 Local Auto Parts Stores
- 8. ECU Programming and Reprogramming Tools
- 8.1 Overview of ECU Programming Tools
- 8.2 Key Features to Look for in an ECU Programmer
- 8.3 Safety Precautions When Reprogramming ECUs
- 9. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Bosch ECUs
- 9.1 Using Oscilloscopes for ECU Diagnostics
- 9.2 Advanced Error Code Analysis
- 9.3 CAN Bus Diagnostics
- 10. Future Trends in Bosch ECU Technology
- 10.1 Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 10.2 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
- 10.3 Cybersecurity Measures
- FAQ: Bosch Number ECU
- 1. How do I find the Bosch number on my ECU?
- 2. Can I use a different Bosch ECU number than the original in my car?
- 3. What does the “M” in MED17.1.1 Bosch ECU reference mean?
- 4. Where can I buy a replacement Bosch ECU?
- 5. What are the symptoms of a failing Bosch ECU?
- 6. How can I test a Bosch ECU to see if it’s working correctly?
- 7. Is it possible to reprogram a Bosch ECU?
- 8. What is the CAN bus, and why is it important for Bosch ECUs?
- 9. What safety precautions should I take when reprogramming a Bosch ECU?
- 10. How does AI integration improve Bosch ECU technology?
1. What is a Bosch Number ECU?
A Bosch number ECU is a unique identifier assigned by Bosch to their engine control units (ECUs). This number provides essential information about the ECU’s specific design, application, and compatibility. Understanding this number is vital for automotive technicians and enthusiasts to ensure they are working with the correct ECU for a particular vehicle. The Bosch ECU number helps in identifying the right ECU for replacement, reprogramming, or tuning, thereby preventing potential compatibility issues and ensuring optimal engine performance.
1.1 Why is the Bosch Number ECU Important?
The Bosch number ECU is crucial for several reasons:
- Identification: It uniquely identifies a specific ECU model.
- Compatibility: Ensures the ECU is compatible with the vehicle’s engine and other systems.
- Replacement: Facilitates the correct replacement of a faulty ECU.
- Reprogramming: Essential for accurate ECU reprogramming and tuning.
- Diagnostics: Aids in diagnosing ECU-related issues.
The Bosch number ECU helps prevent errors in automotive repairs and modifications, ensuring that the correct ECU is used for the specific application.
1.2 What Information Does a Bosch Number ECU Provide?
A Bosch number ECU provides a wealth of information, including:
- ECU Type: Whether it is a Motronic, Diesel, or Gasoline ECU.
- Injection System: Type of fuel injection system (e.g., direct injection, common rail).
- Injector Type: Whether it uses solenoid or piezo injectors.
- Bosch Version: The specific Bosch version of the ECU.
- Application: The vehicle makes and models the ECU is designed for.
This information is essential for technicians and enthusiasts to properly diagnose, repair, or modify engine control units.
2. Understanding Bosch ECU Numbering Logic
Bosch uses a specific coding system to designate their ECUs. This system provides valuable information about the ECU’s function, application, and technical specifications. Deciphering this code can greatly assist in identifying and understanding different Bosch ECU models.
2.1 Decoding Common Bosch ECU References
Let’s break down some common Bosch ECU references to understand their numbering logic:
2.1.1 MED17.1.1
- M: Motronic – This indicates the electronic control unit is a Motronic system.
- E: Electronic throttle control system (not cable-operated).
- D: Direct injection system.
- 17: Bosch version of the ECU.
- 1.1: ECU type (often reserved for VAG – Volkswagen Audi Group).
2.1.2 MG1CS201
- M: Motronic – Signifies a Motronic electronic control unit.
- G: Gasoline – Indicates the ECU is designed for gasoline engines.
- 1: Bosch version of the ECU.
- C: Common rail – Denotes a common rail injection system.
- S: Solenoid – Specifies the use of solenoid injectors.
- 201: ECU type (often reserved for BMW).
2.1.3 MD1CP002
- M: Motronic – Identifies a Motronic electronic control unit.
- D: Diesel – Indicates the ECU is designed for diesel engines.
- 1: Bosch version of the ECU.
- C: Common rail – Denotes a common rail injection system.
- P: Piezo – Specifies the use of piezo-electric injectors.
- 002: ECU type (often reserved for Mercedes).
2.2 Key Components of a Bosch ECU Number
Understanding the key components helps in quick identification:
- Prefix (M): Indicates the type of ECU (Motronic).
- Engine Type (E, G, D): Specifies the engine type (Electronic throttle, Gasoline, Diesel).
- Version Number (17, 1, 1): Denotes the Bosch version of the ECU.
- Injection System (C): Indicates the type of injection system (Common Rail).
- Injector Type (S, P): Specifies the type of injectors (Solenoid, Piezo).
- ECU Type (1.1, 201, 002): Reserved for specific manufacturers.
By understanding these components, you can quickly decode the Bosch ECU number and determine its application and specifications.
3. Methods to Easily Identify a Bosch Number ECU
Identifying a Bosch number ECU can be done through various methods, both online and offline. These methods ensure accurate identification, whether you are in a workshop or researching from home.
3.1 Online Bosch ECU Identification Tools
Several online tools can help you identify a Bosch number ECU:
-
Online Database: One useful resource is a specialized online database. By entering the part number (without spaces), you can quickly identify the ECU type.
- Link: While the original link (http://121.201.38.244:19320/bosch.htm) might be in Chinese, the ECU type is usually displayed in a recognizable format.
-
KMTech BED Database: This website allows you to identify the brand of ECUs by part number.
- Link: https://bed.kmtech.fr/index_en.php
- This database provides detailed information about various ECU models, making it a reliable resource.
-
Bosch ECU Database Software: There are also software programs available, such as the Bosch ECU Database, which can provide comprehensive information. Note that some of these programs may require a subscription or purchase.
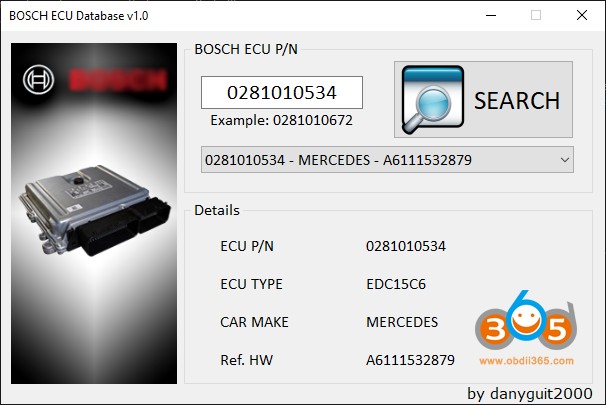 BOSCH ECU Database 1
BOSCH ECU Database 1
3.2 Physical Inspection of the ECU
The Bosch number ECU can also be identified by physically inspecting the ECU unit:
- Location: Locate the ECU in the vehicle. It is typically found in the engine bay, under the dashboard, or in the passenger compartment.
- Visual Check: Examine the ECU casing for a label or engraving that contains the Bosch part number. This number is usually printed clearly on the ECU.
- Documentation: Check the vehicle’s documentation, such as the owner’s manual or service records, as they may contain the ECU part number.
By combining online resources with physical inspection, you can confidently identify the Bosch number ECU.
3.3 Using Diagnostic Tools
Automotive diagnostic tools can also help identify the Bosch number ECU:
- Connect the Tool: Connect an OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Read ECU Information: Use the scanner to read the ECU information, which typically includes the Bosch part number and other relevant details.
- Verify: Verify the information obtained from the diagnostic tool with other sources, such as online databases or the ECU itself.
Diagnostic tools provide a quick and accurate way to identify the Bosch number ECU, especially in modern vehicles.
4. Common Applications of Bosch ECUs
Bosch ECUs are used in a wide range of vehicles and engine types. Understanding these applications can help you narrow down the correct ECU for your specific needs.
4.1 ECUs for Gasoline Engines
Bosch ECUs for gasoline engines are designed to optimize performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. Common models include:
- Motronic ECUs: These are used in a variety of gasoline-powered vehicles.
- Direct Injection ECUs: Designed for engines with direct fuel injection.
- Electronic Throttle Control ECUs: Manage the electronic throttle for improved response.
These ECUs are crucial for maintaining the performance and efficiency of gasoline engines.
4.2 ECUs for Diesel Engines
Bosch ECUs for diesel engines are tailored to meet the unique demands of diesel combustion, including high-pressure fuel injection and turbocharging. Common models include:
- Common Rail ECUs: Used in modern diesel engines with common rail injection systems.
- Piezo Injector ECUs: Designed for engines using piezo-electric injectors.
- Diesel Motronic ECUs: Control various aspects of diesel engine management.
These ECUs ensure optimal performance and reduced emissions in diesel vehicles.
4.3 ECUs for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
Bosch also produces ECUs for hybrid and electric vehicles, managing the complex interplay between electric motors and internal combustion engines. These ECUs control:
- Energy Management: Optimizing energy flow between the battery, motor, and engine.
- Regenerative Braking: Capturing and storing energy during braking.
- Electric Motor Control: Managing the performance of the electric motor.
These ECUs are essential for the efficient and reliable operation of hybrid and electric vehicles.
5. Troubleshooting Common Issues with Bosch ECUs
Identifying and addressing common issues with Bosch ECUs can save time and money on repairs. This section outlines typical problems and troubleshooting steps.
5.1 Symptoms of a Faulty Bosch ECU
Recognizing the symptoms of a faulty Bosch ECU is the first step in troubleshooting:
- Engine Misfires: Random or consistent misfires can indicate ECU issues.
- Poor Fuel Economy: A sudden drop in fuel economy may be due to ECU malfunction.
- Difficulty Starting: An ECU problem can prevent the engine from starting.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light may illuminate with various error codes.
- Performance Issues: Reduced power, hesitation, or stalling can be signs of ECU problems.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to investigate further.
5.2 Common Error Codes Related to Bosch ECUs
Certain error codes are commonly associated with Bosch ECU failures:
- P0600-P0699: These codes typically indicate issues with the ECU’s internal control functions.
- P0200-P0299: These codes relate to fuel injector circuit malfunctions, which can be caused by ECU problems.
- P0300-P0399: These codes indicate misfires, which can be triggered by ECU faults.
- U0001-U0999: These codes denote communication issues on the vehicle’s network, often linked to ECU failures.
Identifying these error codes can help pinpoint ECU-related problems.
5.3 Basic Troubleshooting Steps for Bosch ECUs
Follow these basic troubleshooting steps to diagnose ECU issues:
- Check Connections: Inspect all wiring and connectors leading to the ECU for corrosion or damage.
- Test Power Supply: Ensure the ECU is receiving the correct voltage and ground.
- Scan for Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to read and record any error codes.
- Inspect Sensors: Check the input signals from various sensors, such as the mass airflow sensor and oxygen sensors.
- ECU Reset: Try resetting the ECU by disconnecting the battery for a period of time.
If these steps do not resolve the issue, professional diagnostic services may be required.
6. Benefits of Using the Correct Bosch Number ECU
Using the correct Bosch number ECU offers numerous benefits, ensuring optimal vehicle performance and reliability.
6.1 Enhanced Engine Performance
The correct ECU ensures that the engine operates at its designed performance levels:
- Optimal Fuel Delivery: Accurate fuel injection for efficient combustion.
- Precise Ignition Timing: Correct timing for maximum power and efficiency.
- Efficient Emissions Control: Proper management of exhaust emissions.
These factors contribute to enhanced engine performance and overall vehicle efficiency.
6.2 Improved Fuel Efficiency
Using the correct Bosch number ECU can significantly improve fuel efficiency:
- Optimized Air-Fuel Ratio: Ensures the engine runs at the ideal air-fuel mixture.
- Reduced Fuel Waste: Prevents over-fueling and inefficient combustion.
- Efficient Engine Management: Manages engine parameters for optimal fuel consumption.
Improved fuel efficiency can save you money on fuel costs and reduce your carbon footprint.
6.3 Reduced Emissions
The correct Bosch number ECU helps reduce harmful emissions:
- Effective Catalytic Converter Control: Ensures the catalytic converter operates efficiently.
- Precise Oxygen Sensor Monitoring: Monitors and adjusts the air-fuel mixture for optimal emissions.
- Reduced Pollutants: Minimizes the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere.
Reducing emissions helps protect the environment and ensures compliance with emission regulations.
7. Where to Find Bosch ECUs and Parts
Finding reliable sources for Bosch ECUs and parts is essential for ensuring quality and compatibility.
7.1 Authorized Bosch Dealers
Purchasing from authorized Bosch dealers offers several advantages:
- Genuine Parts: Ensures you receive genuine Bosch products.
- Warranty: Provides warranty coverage for added peace of mind.
- Expert Advice: Offers access to knowledgeable staff who can assist with selection and troubleshooting.
Authorized dealers are the best source for guaranteed quality and support.
7.2 Online Retailers
Many online retailers offer Bosch ECUs and parts:
- CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN: A trusted online retailer specializing in automotive tools and equipment, including Bosch ECUs.
- Amazon and eBay: Offer a wide selection of ECUs and parts, but verify the seller’s reputation and product authenticity.
- Specialized Auto Parts Websites: Websites dedicated to auto parts often carry Bosch ECUs.
When purchasing online, ensure the retailer is reputable and the product is genuine.
7.3 Local Auto Parts Stores
Local auto parts stores can also be a good source for Bosch ECUs and parts:
- Immediate Availability: Allows you to obtain parts quickly.
- In-Person Assistance: Provides the opportunity to discuss your needs with knowledgeable staff.
- Return Options: Offers easier return options compared to online retailers.
Local stores can be convenient for urgent repairs and personalized service.
8. ECU Programming and Reprogramming Tools
ECU programming and reprogramming tools are essential for modifying and updating ECU software.
8.1 Overview of ECU Programming Tools
ECU programming tools allow technicians to modify the software within the ECU to improve performance, fuel efficiency, or address specific issues. Common tools include:
- Flash Programmers: Used to flash new software onto the ECU.
- Chip Tuners: Allow for modifying the ECU’s parameters for performance tuning.
- Diagnostic Scanners with Programming Capabilities: Combine diagnostic functions with ECU programming.
These tools require specialized knowledge and should be used with caution.
8.2 Key Features to Look for in an ECU Programmer
When selecting an ECU programmer, consider the following features:
- Compatibility: Ensure the programmer is compatible with the Bosch ECU model you are working with.
- User-Friendliness: Choose a programmer with an intuitive interface and clear instructions.
- Reliability: Select a programmer from a reputable brand with a proven track record.
- Support and Updates: Ensure the programmer comes with adequate technical support and regular software updates.
Choosing the right ECU programmer is crucial for successful and safe ECU modifications.
8.3 Safety Precautions When Reprogramming ECUs
Reprogramming ECUs can be risky if not done correctly. Follow these safety precautions:
- Backup Original Data: Always create a backup of the original ECU software before making any changes.
- Use a Stable Power Source: Ensure the vehicle has a stable power source during programming to prevent interruptions.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Follow the programmer’s instructions and manufacturer’s guidelines precisely.
- Verify Compatibility: Double-check the compatibility of the new software with the ECU and vehicle.
By following these precautions, you can minimize the risk of damaging the ECU during reprogramming.
9. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Bosch ECUs
Advanced diagnostic techniques are necessary for troubleshooting complex ECU-related issues.
9.1 Using Oscilloscopes for ECU Diagnostics
Oscilloscopes can be used to analyze the electrical signals within the ECU:
- Signal Analysis: Analyze the waveforms of signals from sensors and actuators to identify abnormalities.
- Circuit Testing: Test the integrity of circuits within the ECU.
- Component Testing: Verify the performance of individual components within the ECU.
Oscilloscopes provide a detailed view of the ECU’s electrical behavior.
9.2 Advanced Error Code Analysis
Go beyond basic error code reading with advanced analysis:
- Freeze Frame Data: Analyze the data captured when the error code was triggered to understand the conditions that led to the fault.
- Live Data Monitoring: Monitor real-time data from sensors and actuators to identify inconsistencies.
- Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs): Consult TSBs for known issues and solutions related to specific error codes.
Advanced error code analysis can provide valuable insights into the root cause of ECU problems.
9.3 CAN Bus Diagnostics
The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus is the communication network within the vehicle. CAN bus diagnostics involve:
- Network Testing: Verify the integrity of the CAN bus network.
- Data Monitoring: Monitor the data transmitted on the CAN bus to identify communication issues.
- Node Identification: Identify and troubleshoot individual nodes on the CAN bus.
CAN bus diagnostics are essential for addressing communication-related ECU problems.
10. Future Trends in Bosch ECU Technology
Bosch is continuously innovating in ECU technology. Understanding future trends can help you stay ahead of the curve.
10.1 Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is increasingly being integrated into Bosch ECUs:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms can analyze data to predict potential issues and schedule maintenance proactively.
- Adaptive Learning: ECUs can learn from driving patterns and adjust engine parameters for optimal performance.
- Enhanced Diagnostics: AI can assist in diagnosing complex issues by analyzing vast amounts of data.
AI integration will make ECUs more intelligent and efficient.
10.2 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
OTA updates allow for remote software updates:
- Remote Updates: ECUs can be updated remotely without requiring a visit to a service center.
- Bug Fixes: Software bugs can be quickly addressed and resolved.
- New Features: New features and improvements can be added to the ECU over time.
OTA updates will keep ECUs up-to-date and improve vehicle performance.
10.3 Cybersecurity Measures
Cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important for ECUs:
- Encryption: Encrypting data transmitted to and from the ECU to prevent unauthorized access.
- Intrusion Detection: Implementing systems to detect and prevent cyber attacks.
- Secure Boot: Ensuring that only authorized software can be loaded onto the ECU.
Cybersecurity measures will protect ECUs from hacking and ensure vehicle safety.
Understanding the Bosch number ECU is essential for anyone working with modern automotive systems. By decoding the numbering logic, utilizing online tools, and following proper diagnostic procedures, you can ensure accurate identification, troubleshooting, and repair of Bosch ECUs.
Are you having trouble finding the right Bosch ECU or the tools you need for your automotive projects? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information and expert advice. Let us help you find the perfect solutions for your automotive needs.
FAQ: Bosch Number ECU
1. How do I find the Bosch number on my ECU?
The Bosch number ECU is typically located on a label affixed to the ECU unit itself. The ECU is often found in the engine bay, under the dashboard, or inside the passenger compartment. Look for a series of numbers and letters, usually starting with “0 261” or similar, clearly printed on the label.
2. Can I use a different Bosch ECU number than the original in my car?
Using a different Bosch ECU number than the original is generally not recommended unless it is a specifically approved replacement. ECUs are programmed to work with specific engine and vehicle configurations. Using an incorrect ECU can lead to performance issues, compatibility problems, or even damage to the engine and other systems.
3. What does the “M” in MED17.1.1 Bosch ECU reference mean?
In the Bosch ECU reference MED17.1.1, the “M” stands for “Motronic.” This indicates that the electronic control unit is part of Bosch’s Motronic engine management system, which is designed to control various aspects of the engine, such as fuel injection and ignition timing.
4. Where can I buy a replacement Bosch ECU?
You can buy a replacement Bosch ECU from several sources, including authorized Bosch dealers, online retailers like CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, and local auto parts stores. Ensure you verify the seller’s reputation and the product’s authenticity to guarantee you are getting a genuine Bosch ECU that is compatible with your vehicle.
5. What are the symptoms of a failing Bosch ECU?
Symptoms of a failing Bosch ECU can include engine misfires, poor fuel economy, difficulty starting the engine, the check engine light illuminating, and various performance issues such as reduced power, hesitation, or stalling. If you notice these symptoms, it’s important to have your ECU diagnosed by a professional.
6. How can I test a Bosch ECU to see if it’s working correctly?
Testing a Bosch ECU typically involves using an OBD-II scanner to read error codes and monitor live data from sensors and actuators. You can also use an oscilloscope to analyze electrical signals within the ECU. If you lack the necessary tools or expertise, it’s best to consult a qualified technician for ECU testing.
7. Is it possible to reprogram a Bosch ECU?
Yes, it is possible to reprogram a Bosch ECU using specialized ECU programming tools. Reprogramming can improve performance, fuel efficiency, or address specific issues. However, it requires specialized knowledge and should be done with caution to avoid damaging the ECU.
8. What is the CAN bus, and why is it important for Bosch ECUs?
The CAN (Controller Area Network) bus is a communication network within the vehicle that allows various electronic control units, including the Bosch ECU, to communicate with each other. It is important for Bosch ECUs because it enables the ECU to receive data from sensors and send commands to actuators, coordinating engine management functions.
9. What safety precautions should I take when reprogramming a Bosch ECU?
When reprogramming a Bosch ECU, always back up the original data before making any changes, use a stable power source to prevent interruptions, follow the programmer’s instructions carefully, and verify the compatibility of the new software with the ECU and vehicle. Taking these precautions can minimize the risk of damaging the ECU during reprogramming.
10. How does AI integration improve Bosch ECU technology?
AI integration improves Bosch ECU technology by enabling predictive maintenance, adaptive learning, and enhanced diagnostics. AI algorithms can analyze data to predict potential issues, adjust engine parameters for optimal performance, and assist in diagnosing complex issues by analyzing vast amounts of data, making ECUs more intelligent and efficient.