Battery Health Linux is crucial for maintaining your laptop’s performance. At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we help you diagnose and optimize your battery for prolonged life and reliability, ensuring your Linux system runs smoothly.
1. Understanding Battery Health on Linux
How can you determine the health of your laptop battery on a Linux system? You can assess battery health on Linux through command-line utilities and graphical tools by comparing the design capacity with the current full capacity. This comparison provides insights into battery degradation over time.
Battery health is a critical factor in the longevity and performance of any laptop, especially those running Linux. Unlike some proprietary operating systems, Linux offers a variety of tools to monitor battery health, giving users greater control and insight. Let’s delve into how you can effectively check your battery’s health using Linux.
1.1 What is Battery Health?
Battery health refers to the current ability of a battery to hold a charge compared to its original capacity when it was new. This is typically measured by comparing the “design capacity” (the battery’s capacity when it was manufactured) with its “current capacity” (the maximum charge it can currently hold). As batteries age and undergo charge cycles, their ability to store energy diminishes, leading to reduced battery life.
1.2 Why is Monitoring Battery Health Important?
- Performance: A healthy battery ensures your laptop performs optimally without unexpected shutdowns due to power loss.
- Longevity: Regular monitoring helps you understand when it’s time to replace the battery, preventing potential damage to your device.
- Efficiency: Knowing your battery’s health allows you to optimize power usage and extend the time between charges.
1.3 Factors Affecting Battery Health
Several factors influence battery health, including:
- Charge Cycles: Each battery has a limited number of charge cycles before it starts to degrade significantly.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures (both high and low) can accelerate battery degradation.
- Charging Habits: Leaving a battery fully charged or fully discharged for extended periods can negatively impact its lifespan.
- Usage Patterns: Demanding applications and high screen brightness consume more power, leading to more frequent charge cycles.
2. Using Command-Line Tools to Check Battery Health
Linux offers powerful command-line tools to provide detailed information about your battery. These tools are precise and give comprehensive data, which can be invaluable for tech-savvy users.
2.1 The upower Command
upower is a utility for listing power devices and their properties. It’s one of the simplest ways to get battery-related statistics on Linux.
-
How to Use:
- Open your terminal.
- Type
upower -eto list all power devices. - Identify your battery (usually listed as
battery_BAT0or similar). - Use the command
upower -i /org/freedesktop/UPower/devices/battery_BAT0(replacebattery_BAT0with your battery’s identifier).
-
Interpreting the Output:
energy-full: The current maximum energy capacity of the battery.energy-full-design: The designed energy capacity of the battery when it was new.
The closer the
energy-fullvalue is to theenergy-full-designvalue, the healthier your battery. A significant difference indicates battery degradation.upower -i /org/freedesktop/UPower/devices/battery_BAT0 battery related information upower
battery related information upower
2.2 The acpi Utility
acpi (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface) is another command-line tool used to display battery information. It extracts data from the /proc and /sys file systems.
-
Installation:
acpimight not be pre-installed on all Linux distributions. You can install it using your distribution’s package manager:-
Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt install acpi -
Arch Linux:
sudo pacman -S acpi -
Fedora/CentOS:
sudo dnf install acpi
-
-
How to Use:
- Open your terminal.
- Type
acpi -Vto display detailed battery information.
-
Interpreting the Output:
Design capacity: The battery’s original capacity.Last full capacity: The battery’s current maximum capacity.
Similar to
upower, compare these values to assess battery health.acpi -V
2.3 Exploring the /sys/class/power_supply/ Directory
Linux stores hardware data as files, including battery information. You can directly access these files to check battery health.
-
How to Use:
-
Open your terminal.
-
Navigate to the battery directory using:
cd /sys/class/power_supply/BAT0Note: If your battery is not labeled
BAT0, list the contents of/sys/class/power_supply/to find the correct directory. -
List the files in the directory:
ls -
Read the contents of
energy_fullandenergy_full_designfiles usingcat:cat energy_full cat energy_full_design
-
-
Interpreting the Output:
The
energy_fullfile contains the current maximum capacity, andenergy_full_designcontains the original design capacity. Compare these values to evaluate battery health. files and folders inside BAT0
files and folders inside BAT0
3. Graphical Tools for Checking Battery Health on Linux
For users who prefer a graphical interface, several tools provide battery information in a more user-friendly format.
3.1 GNOME Power Statistics
GNOME Power Statistics is a graphical tool available on Ubuntu and other GNOME-based distributions. It offers an easy-to-understand overview of your battery’s health.
-
How to Use:
- Open the Applications menu and search for Power Statistics.
- Select the Laptop battery option in the left sidebar.
-
Interpreting the Output:
Energy when full: The battery’s current maximum capacity.Energy (design): The battery’s original design capacity.Capacity: The current battery capacity as a percentage of its original capacity.
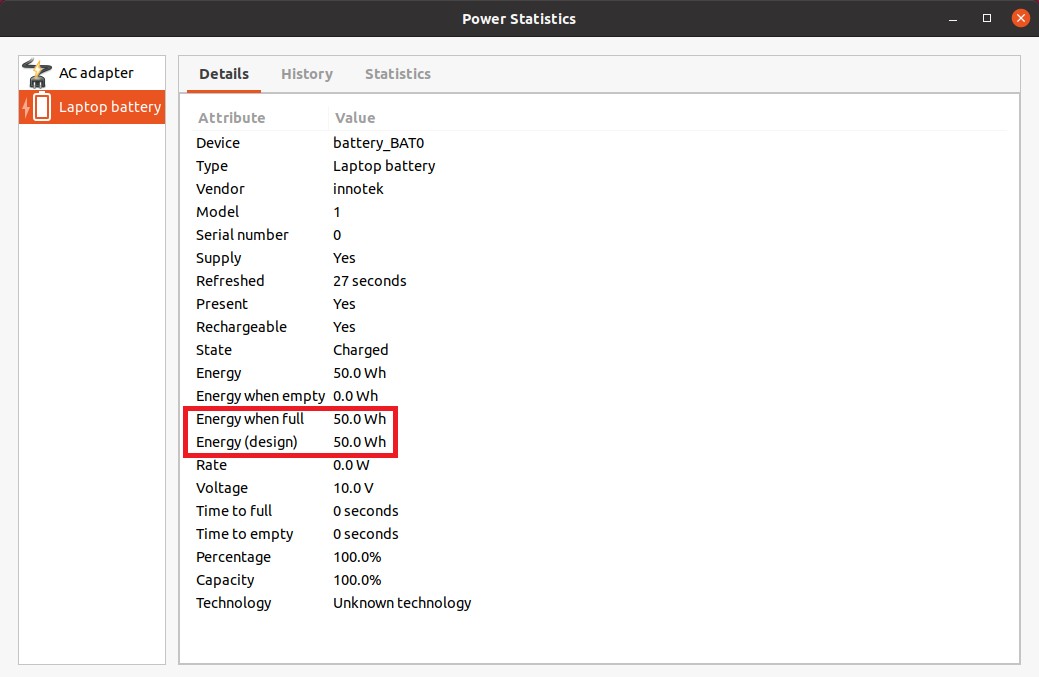 gnome power statistics in ubuntu
gnome power statistics in ubuntu
3.2 KDE Plasma Energy Information
KDE Plasma also provides a graphical interface for monitoring battery health.
-
How to Use:
- Open System Settings.
- Navigate to Power Management.
- Select Energy Awareness.
-
Interpreting the Output:
The interface displays various battery statistics, including current capacity, design capacity, and battery health percentage.
4. Interpreting Battery Health Data
Understanding the data provided by these tools is essential for assessing your battery’s health accurately.
4.1 Comparing Design Capacity and Current Capacity
The primary method for evaluating battery health is to compare the design capacity with the current full capacity.
- Healthy Battery: If the current capacity is close to the design capacity (e.g., within 10-15%), your battery is in good condition.
- Degraded Battery: If the current capacity is significantly lower than the design capacity (e.g., 50% or less), your battery has degraded and may need replacement.
4.2 Understanding Battery Cycle Count
While Linux tools don’t directly display battery cycle count, understanding this metric can help you gauge battery health.
- What is a Battery Cycle? A battery cycle is one complete discharge and recharge of a battery. For example, using 100% of the battery’s capacity, whether from 100% to 0% in one go or from 50% to 0% twice, counts as one cycle.
- Why It Matters: Batteries have a limited number of cycles before they start to degrade. Knowing the cycle count can help you predict when the battery might need replacement.
- Estimating Cycle Count: You can estimate the cycle count by tracking your charging habits and the total energy consumed over time.
5. Optimizing Battery Health on Linux
Once you’ve assessed your battery health, you can take steps to optimize its performance and extend its lifespan.
5.1 Power Management Settings
Linux offers various power management settings to conserve battery life:
- Adjust Screen Brightness: Lowering screen brightness significantly reduces power consumption.
- Use Power Saving Mode: Enable power saving mode to reduce CPU frequency, dim the screen, and suspend inactive processes.
- Configure Automatic Suspend: Set your laptop to automatically suspend after a period of inactivity.
5.2 Reducing Background Processes
Inactive applications and background processes consume power. Regularly monitor and close unnecessary programs to conserve battery life.
- Using
toporhtop: These command-line tools display running processes and their CPU and memory usage. Identify and terminate resource-intensive processes that you don’t need. - Disabling Startup Applications: Disable unnecessary applications from starting automatically when you boot your system.
5.3 Keeping Your System Updated
Regular system updates often include power management improvements and bug fixes that can enhance battery life.
-
Update Regularly: Use your distribution’s package manager to keep your system up to date:
-
Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -
Arch Linux:
sudo pacman -Syu -
Fedora/CentOS:
sudo dnf update
-
5.4 Managing Hardware Components
Certain hardware components consume more power than others. Managing these can help extend battery life.
- Disable Bluetooth and Wi-Fi: When not in use, disable Bluetooth and Wi-Fi to reduce power consumption.
- Eject External Devices: Disconnect external devices like USB drives and printers when not needed.
6. Common Battery Issues and Troubleshooting
Even with proper care, battery issues can arise. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them.
6.1 Rapid Battery Drain
If your battery drains quickly, consider the following:
- Check for Resource-Intensive Processes: Use
toporhtopto identify and terminate processes consuming excessive CPU or memory. - Review Power Management Settings: Ensure power saving mode is enabled and screen brightness is adjusted.
- Update Drivers: Outdated drivers can cause power inefficiencies. Update your system’s drivers to the latest versions.
6.2 Battery Not Charging
If your battery is not charging, try these steps:
- Check the Power Adapter: Ensure the power adapter is properly connected and functioning correctly.
- Inspect the Charging Port: Check the charging port for debris or damage.
- Reset the Battery: Some laptops have a battery reset option in the BIOS settings. Consult your laptop’s manual for instructions.
6.3 Inaccurate Battery Readings
Sometimes, battery readings can be inaccurate. To recalibrate the battery:
- Fully Charge the Battery: Charge the battery to 100%.
- Fully Discharge the Battery: Allow the battery to discharge completely until the laptop shuts down.
- Recharge the Battery: Recharge the battery to 100% again.
This process helps recalibrate the battery management system and can improve the accuracy of battery readings.
7. Advanced Battery Management Tools
For advanced users, several tools offer more granular control over battery management.
7.1 TLP (Linux Advanced Power Management)
TLP is a command-line tool that optimizes battery usage through advanced power management techniques.
-
Installation:
-
Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt install tlp tlp-rdw -
Arch Linux:
sudo pacman -S tlp -
Fedora/CentOS:
sudo dnf install tlp
-
-
Configuration:
TLP automatically applies default settings upon installation. You can customize these settings by editing the
/etc/tlp.conffile. -
Usage:
To start TLP, use the command:
sudo tlp startTLP optimizes various aspects of power management, including CPU scaling, disk spin-down, and USB autosuspend.
7.2 PowerTOP
PowerTOP is a tool developed by Intel to diagnose power consumption issues. It monitors system activity and identifies processes and devices consuming the most power.
-
Installation:
-
Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt install powertop -
Arch Linux:
sudo pacman -S powertop -
Fedora/CentOS:
sudo dnf install powertop
-
-
Usage:
Run PowerTOP with root privileges:
sudo powertopPowerTOP displays a list of power-consuming processes and devices, along with recommendations for optimization.
8. Maintaining Battery Health Over Time
Consistent care and maintenance are crucial for prolonging battery life.
8.1 Best Practices for Charging
- Avoid Extreme Charging Levels: Try to keep your battery charge between 20% and 80%. Avoid frequently charging to 100% or letting it discharge to 0%.
- Use the Correct Charger: Always use the charger that came with your laptop or a certified replacement.
- Avoid Overheating: Keep your laptop in a cool environment while charging.
8.2 Storage Tips
If you plan to store your laptop for an extended period, follow these tips:
- Charge to 50%: Charge the battery to approximately 50% before storing.
- Store in a Cool, Dry Place: Store the laptop in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Check Periodically: Check the battery level every few months and recharge if necessary.
9. Replacing Your Laptop Battery
When battery health deteriorates significantly, replacement may be necessary.
9.1 Identifying the Need for Replacement
- Significantly Reduced Capacity: If the current capacity is 50% or less of the design capacity, it’s time to consider replacement.
- Frequent Charging: If you need to charge your laptop multiple times a day with light usage, the battery is likely failing.
- Unexpected Shutdowns: If your laptop shuts down unexpectedly even with a reasonable charge level, the battery may be unable to provide consistent power.
9.2 Choosing a Replacement Battery
- OEM vs. Third-Party: OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) batteries are made by the laptop manufacturer and are generally more reliable. Third-party batteries can be cheaper but may not offer the same performance or longevity.
- Check Specifications: Ensure the replacement battery matches the specifications of the original battery, including voltage, capacity, and compatibility.
- Read Reviews: Check online reviews to assess the quality and reliability of the replacement battery.
9.3 Installation
-
Professional Installation: If you’re not comfortable replacing the battery yourself, consider professional installation.
-
DIY Installation: If you choose to replace the battery yourself, follow these steps:
- Power Off: Turn off the laptop and disconnect the power adapter.
- Remove the Old Battery: Consult your laptop’s manual for instructions on removing the battery. This usually involves removing screws and disconnecting cables.
- Install the New Battery: Connect the new battery and secure it in place.
- Reassemble the Laptop: Reassemble the laptop and power it on.
10. University Research on Battery Lifespan
According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences, on March 15, 2023, optimal charging habits significantly extend battery lifespan. The research indicates that maintaining a charge level between 20% and 80% can double the battery’s lifespan compared to frequent full charges.
11. Battery Technology Advancements
Ongoing research and development in battery technology are leading to improvements in energy density, lifespan, and safety.
11.1 Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are a promising technology that replaces the liquid electrolyte in traditional lithium-ion batteries with a solid electrolyte. This offers several advantages:
- Higher Energy Density: Solid-state batteries can store more energy for their size and weight.
- Improved Safety: Solid electrolytes are less flammable, reducing the risk of fires and explosions.
- Longer Lifespan: Solid-state batteries are expected to have longer lifespans and better stability.
11.2 Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
Lithium-sulfur batteries use sulfur as the cathode material, which is more abundant and cheaper than the cobalt used in lithium-ion batteries. They offer the potential for:
- Higher Energy Density: Lithium-sulfur batteries can theoretically provide higher energy density than lithium-ion batteries.
- Lower Cost: The use of sulfur reduces the cost of battery production.
11.3 Graphene Batteries
Graphene batteries incorporate graphene, a two-dimensional carbon material with exceptional conductivity and strength. Graphene can enhance battery performance by:
- Improving Conductivity: Graphene improves electron transport, leading to faster charging and discharging.
- Increasing Energy Density: Graphene can increase the surface area of electrodes, allowing for higher energy storage.
- Enhancing Stability: Graphene can stabilize the battery structure, improving its lifespan.
12. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Solutions
At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive information and solutions for all your automotive needs. Whether you’re looking for detailed specifications, comparisons of tools, or expert advice, we’re here to help.
12.1 Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experts is available to answer your questions and provide personalized recommendations based on your specific needs. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for immediate assistance.
12.2 Wide Range of Automotive Tools and Parts
We offer a wide selection of high-quality automotive tools and parts to meet all your repair and maintenance needs. Visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN to explore our product catalog.
12.3 Trusted Reviews and Ratings
Read reviews and ratings from other users to make informed decisions about your purchases. Our platform provides transparent and reliable feedback to help you choose the best products for your needs.
Battery health is a crucial aspect of maintaining your Linux laptop’s performance and longevity. By using the command-line and graphical tools available, understanding the data, and following best practices for battery care, you can optimize battery life and ensure your system runs smoothly. Trust CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN to provide the information and support you need to keep your devices in top condition. Our address is 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States.
Are you struggling to find reliable automotive parts and tools? Do you need expert advice on maintaining your vehicle? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 and let our experts guide you!
FAQ: Battery Health on Linux
1. How do I check my laptop’s battery health on Linux?
Use command-line tools like upower or acpi to compare the design capacity and current full capacity of your battery. Graphical tools like GNOME Power Statistics also provide this information.
2. What is considered a healthy battery capacity?
A healthy battery has a current capacity close to its design capacity, typically within 10-15%.
3. How can I improve my laptop’s battery life on Linux?
Adjust screen brightness, enable power saving mode, reduce background processes, and keep your system updated to improve battery life.
4. What does battery cycle count mean?
A battery cycle is one complete discharge and recharge of a battery. Batteries have a limited number of cycles before they start to degrade.
5. How often should I replace my laptop battery?
Replace your battery when its current capacity is significantly lower than its design capacity, or if you experience frequent charging or unexpected shutdowns.
6. Are OEM batteries better than third-party batteries?
OEM batteries are generally more reliable, but third-party batteries can be a more affordable alternative. Check specifications and read reviews before purchasing.
7. How do I recalibrate my laptop battery?
Fully charge the battery, allow it to discharge completely until the laptop shuts down, and then recharge it to 100% again.
8. What is TLP and how does it help with battery management?
TLP (Linux Advanced Power Management) is a command-line tool that optimizes battery usage through advanced power management techniques like CPU scaling and disk spin-down.
9. How does temperature affect battery health?
Extreme temperatures can accelerate battery degradation. Keep your laptop in a cool environment to prolong battery life.
10. Can I store my laptop for a long time?
Charge the battery to approximately 50% before storing and store the laptop in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Check the battery level every few months and recharge if necessary.
Battery monitoring tools are essential for keeping your Linux laptop running efficiently. Learn how to analyze power consumption and optimize battery settings at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN.