Windows 7 Car Diagnostic Software empowers mechanics, car enthusiasts, and vehicle owners to troubleshoot issues, monitor performance, and maintain their vehicles effectively. Choosing the best software depends on factors like compatibility, features, and ease of use, all of which we’ll explore.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Windows 7 Car Diagnostic Software
- 1.1 What is Car Diagnostic Software?
- 1.2 Why Use Windows 7 for Car Diagnostics?
- 1.3 Key Benefits of Using Car Diagnostic Software
- 2. Essential Features to Look for in Windows 7 Car Diagnostic Software
- 2.1 OBD-II Protocol Support
- 2.2 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Reading and Clearing
- 2.3 Real-Time Data Monitoring
- 2.4 Freeze Frame Data
- 2.5 Data Logging and Graphing
- 2.6 Vehicle Information (VIN, Calibration ID)
- 2.7 Enhanced Diagnostics and OEM-Specific Data
- 2.8 User Interface and Ease of Use
- 3. Top Windows 7 Car Diagnostic Software Options
- 3.1 OBDwiz
- 3.2 ScanXL Pro
- 3.3 Forscan
- 3.4 FiatECUScan/MultiECUScan
- 3.5 EasyOBDII
- 4. Choosing the Right OBD-II Adapter
- 4.1 Types of OBD-II Adapters
- 4.2 Key Considerations When Choosing an Adapter
- 4.3 Recommended OBD-II Adapters
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide to Using Windows 7 Car Diagnostic Software
- 5.1 Installation and Setup
- 5.2 Connecting to Your Vehicle
- 5.3 Performing Diagnostics
- 5.4 Interpreting the Results
- 6. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- 6.1 Connection Problems
- 6.2 Software Errors
- 6.3 Inaccurate Data
- 6.4 Compatibility Issues
- 7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 7.1 Bi-Directional Control
- 7.2 Module Programming and Configuration
- 7.3 Oscilloscope Diagnostics
- 8. Staying Updated with the Latest Technology
- 8.1 Software Updates
- 8.2 Training and Education
- 8.3 Online Resources and Communities
- 9. The Future of Car Diagnostics
- 9.1 Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 9.2 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 9.3 Telematics Integration
- 10. Finding Reliable Automotive Information and Parts with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 10.1 Detailed Product Information
- 10.2 Tool Comparisons and Recommendations
- 10.3 User Reviews and Testimonials
- 10.4 Expert Advice and Guidance
- FAQ: Windows 7 Car Diagnostic Software
- What is the best free car diagnostic software for Windows 7?
- Can I use car diagnostic software on other Windows versions?
- Do I need an internet connection to use car diagnostic software?
- What is the difference between OBD-II and OEM-specific diagnostic software?
- Is it safe to clear trouble codes?
- Can I damage my car by using diagnostic software?
- What is PID in car diagnostics?
- How do I update my car diagnostic software?
- Where can I find support for my car diagnostic software?
- What are the legal considerations when using car diagnostic software?
- Final Thoughts
1. Understanding Windows 7 Car Diagnostic Software
Windows 7 car diagnostic software allows you to interface with your vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system using a computer running Windows 7. This software, combined with an OBD adapter, reads data from your car’s sensors, decodes trouble codes, and provides insights into its overall health.
1.1 What is Car Diagnostic Software?
Car diagnostic software is a computer program that allows you to communicate with your vehicle’s computer system. This software interprets data from the Engine Control Unit (ECU) and other modules to help identify problems. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global automotive diagnostics market is expected to reach $47.94 billion by 2030, highlighting the increasing reliance on diagnostic tools.
1.2 Why Use Windows 7 for Car Diagnostics?
While Windows 7 is an older operating system, it’s often preferred in professional automotive settings due to its stability, compatibility with legacy hardware, and lower resource requirements. Many older diagnostic tools and interfaces were specifically designed for Windows 7, making it a practical choice for certain applications.
1.3 Key Benefits of Using Car Diagnostic Software
- Troubleshooting: Identifies the cause of the “Check Engine” light and other issues.
- Performance Monitoring: Tracks real-time data like engine temperature, RPM, and fuel efficiency.
- Maintenance: Helps anticipate maintenance needs and prevent costly repairs.
- Cost Savings: Reduces reliance on expensive professional diagnostic services.
- DIY Repairs: Enables informed decision-making for do-it-yourself repairs.
2. Essential Features to Look for in Windows 7 Car Diagnostic Software
The best Windows 7 car diagnostic software should offer a blend of user-friendliness, comprehensive features, and reliable performance. Consider the following features:
2.1 OBD-II Protocol Support
The software should support all OBD-II protocols (ISO 9141-2, KWP2000, SAE J1850 PWM, SAE J1850 VPW, and CAN) to ensure compatibility with a wide range of vehicles. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all cars and light trucks sold in the United States since 1996 are OBD-II compliant.
2.2 Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Reading and Clearing
The ability to read and clear DTCs is fundamental. The software should provide clear descriptions of the codes and allow you to reset the “Check Engine” light after addressing the underlying issue.
2.3 Real-Time Data Monitoring
Real-time data, also known as live data, allows you to monitor various engine parameters as you drive. This includes:
- Engine RPM: Revolutions per minute, indicating engine speed.
- Coolant Temperature: Helps identify overheating issues.
- Fuel Trim: Indicates how the ECU is adjusting fuel delivery.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Monitors the performance of the oxygen sensors.
- Vehicle Speed: Displays the current speed of the vehicle.
- Intake Manifold Pressure (MAP): Measures pressure in the intake manifold.
2.4 Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the vehicle’s parameters at the moment a DTC was triggered. This information provides valuable context for diagnosing intermittent issues.
2.5 Data Logging and Graphing
Data logging allows you to record real-time data for later analysis. Graphing tools help visualize trends and identify anomalies in the data. A study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) highlights the importance of accurate data logging in automotive diagnostics.
2.6 Vehicle Information (VIN, Calibration ID)
The software should be able to retrieve vehicle information such as the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) and Calibration ID. This helps ensure you’re using the correct diagnostic information for your specific vehicle.
2.7 Enhanced Diagnostics and OEM-Specific Data
Some advanced software packages offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities, including access to OEM-specific data and bi-directional control. These features are typically found in professional-grade tools.
2.8 User Interface and Ease of Use
A well-designed user interface is crucial for efficient diagnostics. The software should be intuitive, easy to navigate, and provide clear visualizations of data.
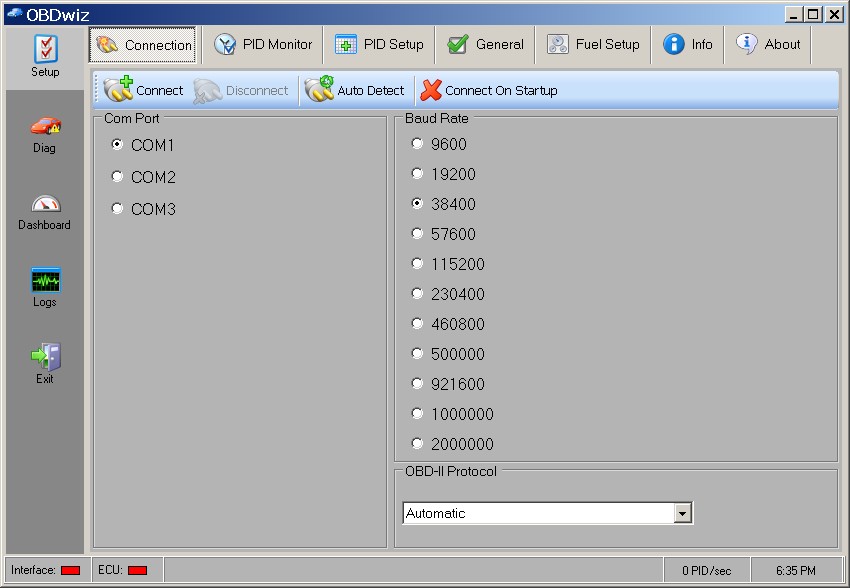 OBDwiz – Connection
OBDwiz – Connection
3. Top Windows 7 Car Diagnostic Software Options
While several software options are available, some stand out for their features, reliability, and compatibility with Windows 7. Here are some top contenders:
3.1 OBDwiz
OBDwiz is a popular choice for its ease of use and comprehensive features. It’s compatible with all PC-based scan tools sold on ScanTool.net and supports all OBD-II compliant vehicles.
- Key Features: Customizable dashboards, fuel economy calculations, real-time plotting, data logging, DTC reading and clearing, battery voltage display, freeze frame data, and support for over 90 PIDs.
- Pros: User-friendly interface, free updates, and extensive PID support.
- Cons: Limited advanced diagnostic features compared to professional-grade software.
3.2 ScanXL Pro
ScanXL Pro is another robust option for Windows 7, offering advanced diagnostic capabilities and support for a wide range of vehicles.
- Key Features: Enhanced diagnostics, OEM-specific data, bi-directional control, data logging, graphing, and customizable dashboards.
- Pros: Advanced features, wide vehicle support, and extensive customization options.
- Cons: Higher price point compared to basic OBD-II software.
3.3 Forscan
Forscan is specifically designed for Ford, Lincoln, and Mercury vehicles. It offers advanced diagnostic capabilities comparable to OEM tools.
- Key Features: Module configuration, bi-directional control, DTC reading and clearing, real-time data monitoring, and access to OEM-specific functions.
- Pros: Powerful features for Ford vehicles, free version available, and active community support.
- Cons: Limited to Ford, Lincoln, and Mercury vehicles.
3.4 FiatECUScan/MultiECUScan
FiatECUScan, now known as MultiECUScan, is tailored for Fiat, Alfa Romeo, Lancia, and other European vehicles. It provides in-depth diagnostic capabilities for these makes.
- Key Features: Module diagnostics, parameter resetting, actuator testing, and access to manufacturer-specific diagnostic functions.
- Pros: Excellent support for European vehicles, comprehensive diagnostic features, and user-friendly interface.
- Cons: Primarily focused on European vehicles.
3.5 EasyOBDII
EasyOBDII is a simple and affordable option for basic OBD-II diagnostics on Windows 7. It offers essential features for reading and clearing DTCs and monitoring real-time data.
- Key Features: DTC reading and clearing, real-time data monitoring, freeze frame data, and vehicle information display.
- Pros: Affordable, easy to use, and suitable for basic diagnostics.
- Cons: Limited advanced features compared to more comprehensive software packages.
4. Choosing the Right OBD-II Adapter
The OBD-II adapter is a crucial component of your car diagnostic setup. It connects your computer to your vehicle’s OBD-II port and transmits data to the diagnostic software.
4.1 Types of OBD-II Adapters
- Bluetooth Adapters: Connect wirelessly to your computer via Bluetooth. Offer convenience and portability.
- Wi-Fi Adapters: Similar to Bluetooth adapters but use Wi-Fi for connectivity. Can be useful if your computer doesn’t have Bluetooth.
- USB Adapters: Connect directly to your computer via USB cable. Offer a stable and reliable connection.
4.2 Key Considerations When Choosing an Adapter
- Compatibility: Ensure the adapter is compatible with your chosen diagnostic software and vehicle.
- Protocol Support: The adapter should support all OBD-II protocols.
- Speed: Faster adapters provide quicker data transfer rates.
- Reliability: Choose a reputable brand with positive reviews.
- Security: Opt for adapters with built-in security features to protect against unauthorized access.
4.3 Recommended OBD-II Adapters
- OBDLink MX+: A high-performance Bluetooth adapter with excellent compatibility and security features.
- OBDLink EX: A USB adapter designed for use with Forscan.
- Veepeak Mini Bluetooth OBD2 Scanner: A compact and affordable option for basic OBD-II diagnostics.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Using Windows 7 Car Diagnostic Software
Using car diagnostic software involves a few simple steps. Here’s a general guide:
5.1 Installation and Setup
- Install the Software: Download and install the diagnostic software on your Windows 7 computer.
- Install Adapter Drivers: Install the necessary drivers for your OBD-II adapter.
- Connect the Adapter: Plug the OBD-II adapter into your vehicle’s OBD-II port (typically located under the dashboard).
- Pair the Adapter (Bluetooth/Wi-Fi): If using a wireless adapter, pair it with your computer via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
5.2 Connecting to Your Vehicle
- Launch the Software: Open the diagnostic software on your computer.
- Select the Adapter: Choose your OBD-II adapter from the software’s connection settings.
- Establish Connection: Click the “Connect” button to establish a connection with your vehicle’s ECU.
- Allow the software to automatically find it:
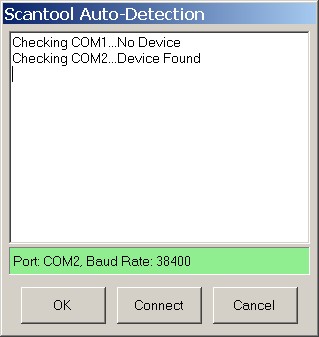 OBDwiz – Connection
OBDwiz – Connection
5.3 Performing Diagnostics
- Read Trouble Codes: Select the “Read Trouble Codes” option to retrieve any stored DTCs.
- View Live Data: Choose the “Live Data” or “Real-Time Data” option to monitor engine parameters.
- Record Data: Use the data logging feature to record data for later analysis.
- Clear Trouble Codes: After addressing the underlying issue, select the “Clear Trouble Codes” option to reset the “Check Engine” light.
5.4 Interpreting the Results
- Research Trouble Codes: Use online resources or the software’s built-in database to research the meaning of any DTCs.
- Analyze Live Data: Monitor real-time data for any anomalies or out-of-range values.
- Consult Repair Manuals: Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for specific diagnostic procedures and repair instructions.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you’re unsure about the diagnosis or repair process, consult a qualified mechanic.
6. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Even with the best software, you may encounter some issues. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
6.1 Connection Problems
- Problem: The software can’t connect to the OBD-II adapter or vehicle.
- Possible Solutions:
- Ensure the adapter is properly plugged into the OBD-II port.
- Verify the adapter is paired correctly with your computer (Bluetooth/Wi-Fi).
- Check the adapter drivers are installed correctly.
- Try a different USB port or Bluetooth adapter.
- Make sure the vehicle’s ignition is turned on.
6.2 Software Errors
- Problem: The software crashes, freezes, or displays error messages.
- Possible Solutions:
- Restart the software and your computer.
- Reinstall the software.
- Check for software updates.
- Ensure your Windows 7 system meets the minimum requirements for the software.
- Contact the software vendor for support.
6.3 Inaccurate Data
- Problem: The software displays inaccurate or inconsistent data.
- Possible Solutions:
- Verify the OBD-II adapter is compatible with your vehicle.
- Check for loose or corroded connections in the OBD-II port.
- Try a different OBD-II adapter.
- Consult a qualified mechanic to verify the data.
6.4 Compatibility Issues
- Problem: The software is not compatible with your vehicle or OBD-II adapter.
- Possible Solutions:
- Check the software’s compatibility list.
- Try a different diagnostic software package.
- Ensure the OBD-II adapter supports all necessary protocols.
7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
For experienced users, advanced diagnostic techniques can provide deeper insights into vehicle performance.
7.1 Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s ECU to test various components. This can include:
- Activating Fuel Injectors: Testing the functionality of individual fuel injectors.
- Cycling the A/C Compressor: Verifying the operation of the air conditioning compressor.
- Controlling the Cooling Fan: Testing the cooling fan’s response to temperature changes.
7.2 Module Programming and Configuration
Some advanced software packages allow you to reprogram or reconfigure vehicle modules. This can be useful for:
- Updating Software: Installing the latest software updates for various modules.
- Replacing Modules: Configuring a new module to work with your vehicle.
- Customizing Settings: Adjusting various vehicle settings to your preferences.
7.3 Oscilloscope Diagnostics
Using an oscilloscope in conjunction with diagnostic software can provide detailed analysis of electrical signals within the vehicle. This is particularly useful for diagnosing complex electrical problems.
8. Staying Updated with the Latest Technology
The automotive industry is constantly evolving, so it’s important to stay updated with the latest diagnostic technology.
8.1 Software Updates
Regularly update your diagnostic software to ensure you have the latest features, bug fixes, and vehicle coverage.
8.2 Training and Education
Consider taking courses or workshops on advanced automotive diagnostics to improve your skills and knowledge.
8.3 Online Resources and Communities
Utilize online resources, forums, and communities to stay informed about the latest diagnostic techniques and tools.
9. The Future of Car Diagnostics
The future of car diagnostics is likely to involve more advanced technologies and greater integration with cloud-based services.
9.1 Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Cloud-based diagnostic platforms offer several advantages, including:
- Remote Diagnostics: Allowing technicians to diagnose vehicles remotely.
- Data Sharing: Enabling collaboration and data sharing among technicians.
- Predictive Maintenance: Using data analytics to predict maintenance needs.
9.2 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is increasingly being used in car diagnostics to:
- Automate Diagnostic Procedures: Streamlining the diagnostic process.
- Identify Patterns: Detecting subtle patterns in data that may indicate potential problems.
- Provide Expert Guidance: Offering guidance and recommendations to technicians.
9.3 Telematics Integration
Telematics systems, which are integrated into many modern vehicles, provide real-time data on vehicle performance. This data can be used for:
- Remote Monitoring: Tracking vehicle health and performance.
- Proactive Maintenance: Identifying potential issues before they become major problems.
- Improved Diagnostics: Providing more comprehensive data for diagnostics.
10. Finding Reliable Automotive Information and Parts with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
Navigating the world of automotive diagnostics and repairs can be overwhelming. That’s where CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN comes in. We provide detailed information on various auto parts, diagnostic tools, and repair procedures to help you make informed decisions.
10.1 Detailed Product Information
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive information on a wide range of auto parts, including specifications, compatibility details, and user reviews.
10.2 Tool Comparisons and Recommendations
We provide in-depth comparisons of different diagnostic tools and repair equipment, helping you choose the best tools for your needs and budget.
10.3 User Reviews and Testimonials
Read reviews and testimonials from other users to gain valuable insights into the performance and reliability of various products.
10.4 Expert Advice and Guidance
Our team of automotive experts provides valuable advice and guidance on diagnostic procedures, repair techniques, and maintenance best practices.
Finding reliable auto parts and diagnostic tools doesn’t have to be a challenge. Let CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN be your trusted resource for all your automotive needs.
Address: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
FAQ: Windows 7 Car Diagnostic Software
What is the best free car diagnostic software for Windows 7?
While professional-grade software often comes with a cost, some free options offer basic functionality. EasyOBDII is a simple, free option for reading and clearing DTCs. However, be aware that free software may have limited features and vehicle coverage.
Can I use car diagnostic software on other Windows versions?
Yes, most modern car diagnostic software is compatible with newer versions of Windows, such as Windows 10 and Windows 11. However, if you’re using older hardware or software, Windows 7 may be a better choice due to compatibility reasons.
Do I need an internet connection to use car diagnostic software?
An internet connection is not always required, but it can be helpful for:
- Software Updates: Downloading the latest software updates.
- Trouble Code Lookups: Accessing online databases for DTC definitions.
- Remote Diagnostics: Using cloud-based diagnostic platforms.
What is the difference between OBD-II and OEM-specific diagnostic software?
OBD-II software provides standardized diagnostic information that is common to all vehicles. OEM-specific software, on the other hand, offers access to manufacturer-specific data and functions, providing deeper diagnostic capabilities for specific makes and models.
Is it safe to clear trouble codes?
Clearing trouble codes is generally safe, but it’s important to address the underlying issue first. Clearing codes without fixing the problem will only temporarily turn off the “Check Engine” light, and the code will likely return.
Can I damage my car by using diagnostic software?
Using diagnostic software correctly is generally safe. However, improper use of advanced functions, such as bi-directional control or module programming, can potentially damage your vehicle. Always follow the software’s instructions and consult a qualified mechanic if you’re unsure.
What is PID in car diagnostics?
PID stands for Parameter Identification. PIDs are codes used to request data from a vehicle’s ECU, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and fuel trim.
How do I update my car diagnostic software?
Most car diagnostic software packages have a built-in update feature. Check the software’s menu or settings for an “Update” or “Check for Updates” option.
Where can I find support for my car diagnostic software?
Most software vendors offer online support resources, such as FAQs, user manuals, and forums. You can also contact the vendor directly for technical support.
What are the legal considerations when using car diagnostic software?
Using car diagnostic software for personal use is generally legal. However, using it for commercial purposes may require a license or certification. Additionally, tampering with vehicle emissions systems is illegal in many jurisdictions.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right Windows 7 car diagnostic software can empower you to troubleshoot issues, monitor performance, and maintain your vehicle effectively. By considering the essential features, exploring the top software options, and following the step-by-step guide, you can unlock the power of car diagnostics and keep your vehicle running smoothly. Remember to leverage the resources available at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for reliable automotive information and expert guidance.
Don’t let vehicle problems slow you down. Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert advice and solutions!