Where is a car’s diagnostic port? The car’s diagnostic port, typically an OBD2 port, is your gateway to understanding your vehicle’s health, and CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides the resources you need to locate and utilize it effectively. This port allows mechanics and car owners to access the vehicle’s computer, read error codes, and assess overall performance, leading to better maintenance and informed decisions. You’ll also find valuable insights into automotive diagnostics, scan tools, and vehicle data.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Car’s Diagnostic Port: The OBD2 Explained
- 1.1. History of On-Board Diagnostics
- 1.2. Key Features of OBD2
- 1.3. OBD2 vs. OBD1: What’s the Difference?
- 2. Finding the OBD2 Port: Location, Location, Location
- 2.1. Common OBD2 Port Locations by Vehicle Type
- 2.2. How to Use an OBD2 Port Finder Online
- 2.3. What to Do If You Can’t Find the Port
- 3. The OBD2 Connector and Pinout: A Technical Overview
- 3.1. Detailed Explanation of Each Pin
- 3.2. Communication Protocols Used by OBD2
- 3.3. Common Issues with the OBD2 Connector
- 4. Why Is the OBD2 Port Important? The Benefits of Vehicle Diagnostics
- 4.1. Monitoring Vehicle Health
- 4.2. Improving Fuel Efficiency
- 4.3. Reducing Emissions
- 5. How to Use the OBD2 Port: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 5.1. Choosing the Right Diagnostic Tool
- 5.2. Reading and Interpreting Fault Codes
- 5.3. Clearing Fault Codes
- 6. Take Vehicle Diagnostics to the Next Level with Advanced Tools
- 6.1. Introduction to AutoPi CAN-FD Pro
- 6.2. Benefits of Using Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- 6.3. Connecting AutoPi CAN-FD Pro to Your OBD2 Port
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Ports
- 8. Conclusion: The Power of the OBD2 Port at Your Fingertips
1. Understanding the Car’s Diagnostic Port: The OBD2 Explained
What is the OBD2 port and what does it do? The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port is a standardized interface in vehicles that allows access to the vehicle’s computer system. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all cars and light trucks manufactured after 1996 in the United States are required to have an OBD2 port. This standardization ensures compatibility with a wide range of diagnostic tools. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) defines the standards for OBD2, ensuring consistency across different vehicle manufacturers.
1.1. History of On-Board Diagnostics
What is the history of on-board diagnostics? The evolution of on-board diagnostics began with the need for better emission control. In the early days, vehicles had limited diagnostic capabilities. As environmental regulations became stricter, manufacturers started implementing more sophisticated systems. OBD-I was the first generation, but it lacked standardization. OBD-II, introduced in the mid-1990s, brought about a universal standard, making it easier to diagnose and repair vehicles. According to a study by the California Air Resources Board (CARB), OBD-II significantly improved the effectiveness of emission control systems.
1.2. Key Features of OBD2
What are the key features of OBD2? OBD2 offers several key features that make it an essential tool for vehicle diagnostics:
- Standardization: OBD2 uses a standardized connector (SAE J1962) and communication protocols, ensuring compatibility across different vehicle makes and models.
- Emission Monitoring: It monitors emission-related components and systems to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): OBD2 generates DTCs that provide specific information about detected faults or malfunctions.
- Data Parameters: It provides access to a wide range of real-time data parameters, such as engine speed, temperature, and sensor readings.
- Readiness Tests: OBD2 performs readiness tests to verify that emission-related systems are functioning correctly.
1.3. OBD2 vs. OBD1: What’s the Difference?
What is the difference between OBD2 and OBD1? OBD1 was the predecessor to OBD2 and was used in vehicles before the mid-1990s. Here’s a comparison:
| Feature | OBD1 | OBD2 |
|---|---|---|
| Standardization | Lacked standardization | Standardized connector and communication protocols |
| Connector | Varies by manufacturer | Standardized 16-pin connector (SAE J1962) |
| DTCs | Limited and manufacturer-specific | Standardized DTCs with specific definitions |
| Data Parameters | Limited real-time data | Access to a wide range of real-time data parameters |
| Emission Focus | Primarily focused on emissions | Comprehensive monitoring of emissions and other systems |
| Compatibility | Limited to specific manufacturers | Universal compatibility across different makes and models |
 Comparison of OBD1 and OBD2 ports, highlighting the standardized 16-pin connector of OBD2.
Comparison of OBD1 and OBD2 ports, highlighting the standardized 16-pin connector of OBD2.
2. Finding the OBD2 Port: Location, Location, Location
Where can you find the OBD2 port in your car? The OBD2 port is typically located inside the passenger compartment of the vehicle. According to the SAE J1962 standard, the port must be located within two feet of the steering wheel. Common locations include:
- Under the dashboard on the driver’s side
- Near the center console
- Inside the glove compartment
- Behind an access panel
2.1. Common OBD2 Port Locations by Vehicle Type
Where are some common OBD2 port locations by vehicle type?
- Cars: Typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Trucks: Often located near the center console or under the dashboard.
- SUVs: Similar to cars and trucks, the port is usually under the dashboard or near the center console.
- Vans: Can be found in various locations, including under the dashboard or near the glove compartment.
2.2. How to Use an OBD2 Port Finder Online
How can an OBD2 port finder help you locate the port? Online OBD2 port finders can be helpful if you’re having trouble locating the port in your vehicle. These tools typically allow you to enter the year, make, and model of your vehicle to find the most likely location of the OBD2 port. Websites like “OBD2 Port Finder” and apps like “EOBD Facile” provide detailed information and diagrams to help you locate the port quickly and easily.
2.3. What to Do If You Can’t Find the Port
What should you do if you can’t find the OBD2 port? If you’ve checked the common locations and still can’t find the OBD2 port, here are some steps you can take:
- Consult the Owner’s Manual: The owner’s manual should provide the exact location of the OBD2 port.
- Search Online Forums: Online forums and communities dedicated to your vehicle’s make and model may have specific information or tips.
- Contact a Mechanic: If all else fails, contact a professional mechanic who can help you locate the port.
 Diagram showing possible OBD2 port locations in a typical vehicle, including under the dashboard and near the steering wheel.
Diagram showing possible OBD2 port locations in a typical vehicle, including under the dashboard and near the steering wheel.
3. The OBD2 Connector and Pinout: A Technical Overview
What is the OBD2 connector and what are the pinouts? The OBD2 connector is a 16-pin (2×8) J1962 female connector. Each pin has a specific function, allowing for communication between the diagnostic tool and the vehicle’s computer. Understanding the pinout is essential for advanced diagnostics and troubleshooting. According to the SAE J1979 standard, the OBD2 connector must provide access to specific data parameters, such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
3.1. Detailed Explanation of Each Pin
What is a detailed explanation of each pin in the OBD2 connector? Here’s a detailed explanation of each pin in the OBD2 connector:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manufacturer Discretion | May be used for manufacturer-specific purposes |
| 2 | SAE J1850 Bus+ | Positive wire for SAE J1850 communication protocol |
| 3 | Manufacturer Discretion | May be used for manufacturer-specific purposes |
| 4 | Chassis Ground | Ground connection for the vehicle chassis |
| 5 | Signal Ground | Ground connection for the diagnostic tool |
| 6 | CAN High (J-2284) | High wire for CAN (Controller Area Network) communication protocol |
| 7 | ISO 9141-2 K Line | K-line for ISO 9141-2 communication protocol |
| 8 | Manufacturer Discretion | May be used for manufacturer-specific purposes |
| 9 | Manufacturer Discretion | May be used for manufacturer-specific purposes |
| 10 | SAE J1850 Bus- | Negative wire for SAE J1850 communication protocol |
| 11 | Manufacturer Discretion | May be used for manufacturer-specific purposes |
| 12 | Manufacturer Discretion | May be used for manufacturer-specific purposes |
| 13 | Manufacturer Discretion | May be used for manufacturer-specific purposes |
| 14 | CAN Low (J-2284) | Low wire for CAN (Controller Area Network) communication protocol |
| 15 | ISO 9141-2 L Line | L-line for ISO 9141-2 communication protocol |
| 16 | Battery Power | Provides power to the diagnostic tool |
3.2. Communication Protocols Used by OBD2
What are the communication protocols used by OBD2? OBD2 uses several communication protocols to transmit data between the diagnostic tool and the vehicle’s computer. These protocols include:
- SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width Modulation): Used by General Motors.
- SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used by Ford.
- ISO 9141-2: Used by European and Asian manufacturers.
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000): Used by European and Asian manufacturers.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): Used by most modern vehicles.
3.3. Common Issues with the OBD2 Connector
What are some common issues with the OBD2 connector?
- Bent or Broken Pins: Can prevent proper communication.
- Corrosion: Can cause poor electrical contact.
- Loose Connector: Can result in intermittent connection.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or frayed wires can disrupt communication.
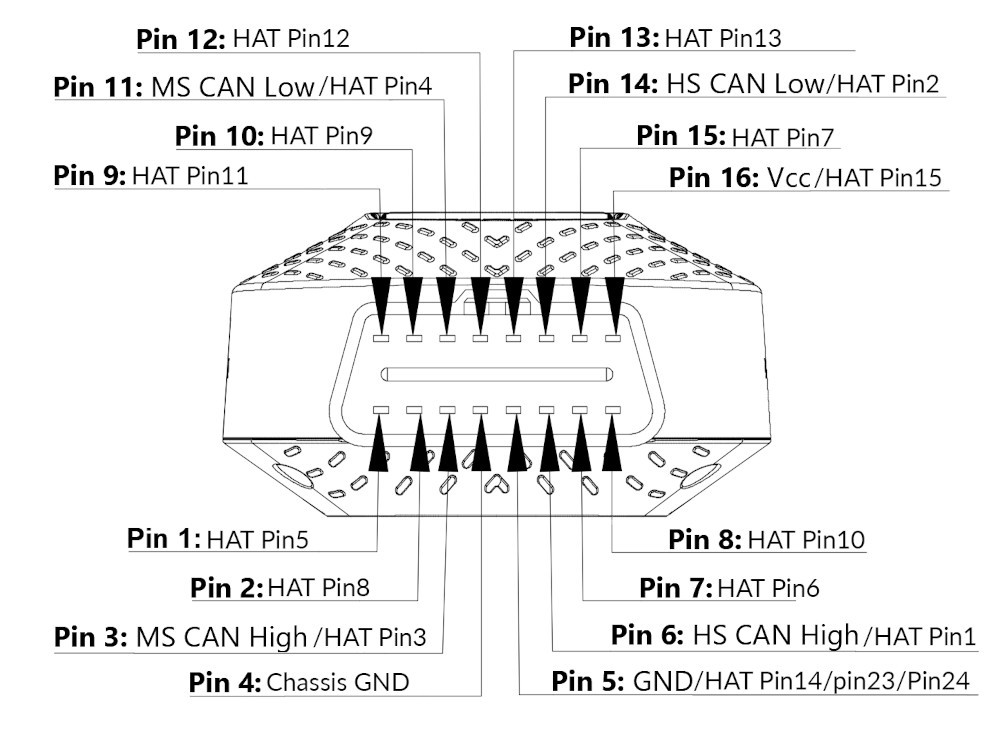 Diagram illustrating the OBD2 connector pinouts, highlighting the functions of each pin for data transmission and power.
Diagram illustrating the OBD2 connector pinouts, highlighting the functions of each pin for data transmission and power.
4. Why Is the OBD2 Port Important? The Benefits of Vehicle Diagnostics
Why is the OBD2 port so important? The OBD2 port is important because it allows you to access valuable information about your vehicle’s health and performance. According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), regular vehicle maintenance and diagnostics can significantly reduce the risk of accidents caused by mechanical failures. By using the OBD2 port, you can identify potential issues early on, preventing costly repairs and ensuring your vehicle is running efficiently.
4.1. Monitoring Vehicle Health
How does the OBD2 port help monitor vehicle health? The OBD2 port allows you to monitor various aspects of your vehicle’s health, including:
- Engine Performance: Monitor engine speed, load, and fuel consumption.
- Emission System: Check the status of emission-related components and systems.
- Sensor Readings: Monitor sensor readings, such as oxygen sensors and temperature sensors.
- Fault Codes: Identify and diagnose fault codes that indicate potential issues.
4.2. Improving Fuel Efficiency
How can the OBD2 port help improve fuel efficiency? By monitoring engine performance and sensor readings, you can identify issues that may be affecting fuel efficiency. For example, a faulty oxygen sensor can cause the engine to run rich, resulting in poor fuel economy. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, maintaining proper tire inflation, using the recommended grade of motor oil, and addressing engine issues can improve fuel efficiency by up to 15%.
4.3. Reducing Emissions
How can the OBD2 port help reduce emissions? The OBD2 port plays a crucial role in reducing emissions by monitoring emission-related components and systems. If a fault is detected in the emission system, the OBD2 system will generate a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and alert the driver. Addressing these issues promptly can help ensure that your vehicle is meeting emission standards and reducing its environmental impact.
 Keywords related to the OBD2 connector, emphasizing its importance as a gateway for vehicle health monitoring and diagnostics.
Keywords related to the OBD2 connector, emphasizing its importance as a gateway for vehicle health monitoring and diagnostics.
5. How to Use the OBD2 Port: A Step-by-Step Guide
How do you use the OBD2 port for diagnostics? Using the OBD2 port is straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port in your vehicle (refer to Section 2 for common locations).
- Plug in the Diagnostic Tool: Connect the diagnostic tool to the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Follow the Tool’s Instructions: Follow the instructions provided by the diagnostic tool to read fault codes, monitor data parameters, or perform other diagnostic tests.
- Interpret the Results: Interpret the results provided by the diagnostic tool and take appropriate action.
5.1. Choosing the Right Diagnostic Tool
How do you choose the right diagnostic tool for your needs? There are various types of diagnostic tools available, ranging from basic code readers to advanced scan tools. Consider the following factors when choosing a diagnostic tool:
- Compatibility: Ensure the tool is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Features: Determine the features you need, such as code reading, data monitoring, and advanced diagnostics.
- Ease of Use: Choose a tool that is easy to use and has a user-friendly interface.
- Price: Set a budget and choose a tool that offers the best value for your money.
5.2. Reading and Interpreting Fault Codes
How do you read and interpret fault codes using an OBD2 scanner? When a fault is detected, the OBD2 system generates a diagnostic trouble code (DTC). These codes are standardized and provide specific information about the fault. Here’s how to read and interpret fault codes:
- Connect the Diagnostic Tool: Connect the diagnostic tool to the OBD2 port and turn on the ignition.
- Read the Codes: Use the diagnostic tool to read the fault codes.
- Interpret the Codes: Refer to a code database or online resource to interpret the meaning of the codes.
- Troubleshoot the Issue: Use the information provided by the codes to troubleshoot the issue and take appropriate action.
5.3. Clearing Fault Codes
How do you clear fault codes using an OBD2 scanner? Clearing fault codes should only be done after the underlying issue has been resolved. Here’s how to clear fault codes:
- Connect the Diagnostic Tool: Connect the diagnostic tool to the OBD2 port and turn on the ignition.
- Clear the Codes: Use the diagnostic tool to clear the fault codes.
- Verify the Repair: After clearing the codes, verify that the issue has been resolved and that the codes do not reappear.
6. Take Vehicle Diagnostics to the Next Level with Advanced Tools
How can you enhance your vehicle diagnostics with advanced tools? While basic OBD2 scanners provide valuable information, advanced tools can take your vehicle diagnostics to the next level. Tools like the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro offer faster, more detailed insights into your vehicle’s performance. According to a study by Grand View Research, the automotive diagnostics market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by the increasing complexity of vehicle systems and the need for advanced diagnostic capabilities.
6.1. Introduction to AutoPi CAN-FD Pro
What is the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro and what are its features? The AutoPi CAN-FD Pro is an advanced diagnostic tool that connects to your vehicle’s OBD2 port and provides faster, more detailed insights into your vehicle’s performance. Key features include:
- Real-time Data Logging: Captures real-time data from your vehicle’s systems.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Performs advanced diagnostic tests and troubleshooting.
- Remote Access: Allows remote access to your vehicle’s data and diagnostics.
- Customizable Dashboards: Creates customizable dashboards to monitor specific parameters.
- CAN Bus Support: Supports CAN bus communication for advanced diagnostics.
6.2. Benefits of Using Advanced Diagnostic Tools
What are the benefits of using advanced diagnostic tools like AutoPi CAN-FD Pro?
- Faster Diagnostics: Provides faster and more accurate diagnostics.
- Detailed Insights: Offers detailed insights into your vehicle’s performance.
- Remote Monitoring: Allows remote monitoring of your vehicle’s health.
- Preventive Maintenance: Helps identify potential issues early on, preventing costly repairs.
- Improved Performance: Optimizes vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
6.3. Connecting AutoPi CAN-FD Pro to Your OBD2 Port
How do you connect AutoPi CAN-FD Pro to your vehicle’s OBD2 port? Connecting the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro is simple:
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port in your vehicle.
- Plug in the Device: Connect the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro to the OBD2 port.
- Configure the Device: Follow the instructions provided by AutoPi to configure the device and connect it to your network.
- Start Diagnostics: Start using the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro to monitor your vehicle’s health and performance.
 Image of the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro device, highlighting its features and connectivity options for advanced vehicle diagnostics.
Image of the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro device, highlighting its features and connectivity options for advanced vehicle diagnostics.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Ports
What are some frequently asked questions about OBD2 ports?
7.1. What If I Can’t Find the OBD2 Location?
Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the exact location, or search online for your specific vehicle’s diagnostic connector location.
7.2. Are All OBD2 Ports the Same?
Yes, all OBD2 ports and connectors follow the same standardization (SAE J1962).
7.3. How Many OBD2 Ports Does a Car Have?
Typically, a standard passenger car has one OBD2 port.
7.4. Can I Use Any OBD2 Scanner on My Car?
Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with all vehicles manufactured after 1996, but it’s always a good idea to check the scanner’s compatibility list.
7.5. Is It Safe to Leave an OBD2 Scanner Plugged In?
Leaving a scanner plugged in can drain the battery, so it’s best to unplug it when not in use.
7.6. Can I Diagnose ABS and Airbag Problems with an OBD2 Scanner?
Some advanced OBD2 scanners can diagnose ABS and airbag problems, but basic scanners may not have this capability.
7.7. What Does “OBD” Stand For?
OBD stands for On-Board Diagnostics.
7.8. Where Can I Buy an OBD2 Scanner?
OBD2 scanners are available at most auto parts stores, online retailers, and from CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN.
7.9. How Much Does an OBD2 Scanner Cost?
The cost of an OBD2 scanner can range from $20 for a basic code reader to several hundred dollars for an advanced scan tool.
7.10. Do I Need to Be a Mechanic to Use an OBD2 Scanner?
No, anyone can use an OBD2 scanner, but understanding the results may require some technical knowledge.
8. Conclusion: The Power of the OBD2 Port at Your Fingertips
How can understanding the OBD2 port empower you to maintain your vehicle? The OBD2 port is more than just a plug in your car; it’s a portal to understanding your vehicle’s health and status. By using the OBD2 port and diagnostic tools, you can monitor your vehicle’s performance, improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and prevent costly repairs. Explore the range of OBD2 tools and automotive data loggers available at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN to keep your vehicle in top condition and leverage the power of advanced diagnostics today. With the right tools and knowledge, you can take control of your vehicle’s maintenance and ensure it runs smoothly and efficiently for years to come.
At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of having access to reliable information and quality tools. That’s why we offer a comprehensive range of OBD2 scanners, diagnostic tools, and resources to help you maintain your vehicle’s health. Whether you’re a professional mechanic or a car enthusiast, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN has everything you need to take control of your vehicle’s maintenance.
Contact us today for personalized advice on selecting the right diagnostic tools for your needs and explore the latest advancements in automotive technology. Reach us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information.