Near Patient Testing Versus Point-of-care Diagnostics both describe medical testing performed outside of a traditional laboratory setting, bringing healthcare closer to the patient. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN helps you understand these terms and their significance in modern healthcare with in-depth analysis and expert insights. Discover the nuances of these diagnostic approaches and empower your understanding of innovative healthcare solutions.
Contents
- 1. What Is Near Patient Testing Versus Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
- 2. Why Are Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Important?
- 3. Who Benefits From Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
- 4. What Are the Key Differences in Regulations for Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Globally?
- 5. How Does Technical Complexity Influence the Use of Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
- 6. What Role Does External Quality Assessment (EQA) Play in Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
- 7. How Can EQA Reproducibility Indicate the Reliability of Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Devices?
- 8. What SARS-CoV-2 NAAT Systems Have Been Evaluated for EQA Reproducibility?
- 9. What Are the Limitations of Using EQA Reproducibility for Initial Certification of NPT/POCT Devices?
- 10. How Can Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Improve Healthcare Accessibility in Underserved Areas?
- 11. What Specific Skills Are Required to Perform Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Accurately?
- 12. How Does the European IVDR Regulation Impact the Requirements for Near Patient Testing Devices?
- 13. What Types of Errors Can Occur in Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics, and How Can They Be Prevented?
- 14. How Are Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Used in Managing Chronic Diseases?
- 15. What Are the Ethical Considerations in Implementing Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
- 16. How Is Data Management Handled in Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Settings?
- 17. What Future Innovations Are Expected in Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
- 18. How Can Telehealth Integrate With Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics to Improve Patient Care?
- 19. What Are the Cost-Effectiveness Considerations for Implementing Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
- 20. How Can Patients and Healthcare Providers Stay Informed About the Latest Advances in Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Near Patient Testing Versus Point-of-Care Diagnostics
- 1. What types of tests can be performed using near patient testing devices?
- 2. Where can near patient testing be performed?
- 3. Is near patient testing as accurate as lab testing?
- 4. What training is required to perform near patient testing?
- 5. What are the advantages of near patient testing over traditional lab testing?
- 6. What are the disadvantages of near patient testing?
- 7. How is the quality of near patient testing ensured?
- 8. What regulations govern near patient testing?
- 9. How can I find a reliable near patient testing device?
- 10. How can I learn more about near patient testing?
1. What Is Near Patient Testing Versus Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
Near patient testing (NPT) and point-of-care diagnostics (POCT) are essentially synonymous terms referring to medical diagnostic testing performed close to or at the site of patient care, rather than in a central laboratory. According to a study by the National Institutes of Health, POCT enhances clinical decision-making and patient outcomes by providing rapid results. This approach decentralizes testing, making it more accessible and efficient, especially in critical situations.
2. Why Are Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Important?
NPT/POCT offers numerous advantages in healthcare, including faster turnaround times for results, improved patient outcomes, and increased accessibility to testing in remote or underserved areas. A report by the World Health Organization (WHO) highlights that POCT can significantly reduce the time to diagnosis and treatment, leading to better management of diseases. This is particularly crucial in emergency situations where rapid diagnosis is essential for effective intervention.
3. Who Benefits From Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
Patients, healthcare providers, and healthcare systems all benefit from NPT/POCT. Patients experience reduced wait times and quicker treatment decisions, healthcare providers can make informed decisions more rapidly, and healthcare systems see improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness. According to a study in the “Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA),” POCT can lead to decreased hospital stays and lower overall healthcare costs.
4. What Are the Key Differences in Regulations for Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Globally?
Regulatory frameworks for NPT/POCT vary across different regions, impacting the implementation and standards for these diagnostic methods. The European Union’s In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) 2017/746 defines NPT as testing performed outside a laboratory environment by healthcare professionals, emphasizing user training and safety. In contrast, the United States and Australia have broader definitions for POCT, focusing on the location of testing rather than the qualifications of the operator. The U.S. FDA categorizes tests based on complexity, with “waived complexity” tests having minimal requirements for operator training. Australia’s Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) uses a risk-based approach to accredit IVD devices, ensuring safety and performance.
These regulatory differences influence the accessibility and implementation of NPT/POCT across different healthcare systems, highlighting the need for manufacturers to comply with specific regional requirements.
5. How Does Technical Complexity Influence the Use of Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
The technical complexity of NPT/POCT devices significantly affects their suitability for use outside traditional laboratory settings, influencing who can operate them and where they can be deployed. According to IVDR, test systems should be easy to use and interpret, reducing the risk of errors by non-laboratory professionals. The American system categorizes tests by complexity, which affects the training and experience needed to operate them.
| Technical Complexity | Description | Operator Competence Required | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Simple visual examination or results unequivocally visible on the test system. | Low | Rapid antigen tests, rapid antibody tests |
| Medium | Test system automatically carries out reactions, reads signals, and provides results. | Medium | Automated antigen, antibody, and NAAT tests |
| High | Multiple-step non-automated analytic procedures requiring significant operator intervention. | High | Non-automated nucleic amplification and sequencing assays, virus neutralization tests |
6. What Role Does External Quality Assessment (EQA) Play in Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
External Quality Assessment (EQA) is crucial for ensuring the reliability and accuracy of NPT/POCT devices. EQA schemes involve multiple devices of the same type analyzing identical samples simultaneously. The reproducibility of measurement results across different operators and locations, as determined by EQA, serves as an indicator of a device’s independence from operator activities. A study published in the “Journal of Clinical Chemistry” highlights the importance of EQA in harmonizing quantitative results and determining reproducibility.
7. How Can EQA Reproducibility Indicate the Reliability of Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Devices?
EQA reproducibility measures the variability of measurement results obtained from identical samples using the same type of device but operated by different users in various locations. High EQA reproducibility indicates that the device is less influenced by operator-dependent factors, making it suitable for NPT/POCT use. In a retrospective evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 NAAT systems, devices designated for POCT use showed better reproducibility than laboratory-based devices.
8. What SARS-CoV-2 NAAT Systems Have Been Evaluated for EQA Reproducibility?
Several SARS-CoV-2 NAAT systems have been evaluated for EQA reproducibility to determine their suitability for NPT/POCT use. The evaluation included both point-of-care devices and automated laboratory devices.
| Method | Number of Samples | Ct Value Range | Target Gene(s) | Mean Reproducibility at Ct (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | 21 | ||
| Near-Patient Use Devices | ||||
| Cepheid GeneXpert/Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2/Flu/RSV plus | 18 | 23.8 | 33.5 | RdRP, N2, E |
| Cepheid GeneXpert/Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2/Flu/RSV | 60 | 20.1 | 35.5 | N2, E |
| Roche Cobas Liat/LIAT SARS-CoV-2 | 12 | 21.1 | 28.8 | orf1a/b, N |
| Roche Cobas Liat/LIAT SARS-CoV-2 & Influenza A/B | 20 | 20.5 | 35.6 | orf1a/b, N |
| DiaSorin Liaison MDX/Simplexa COVID-19 Direct Reaction Mix | 47 | 18.0 | 34.6 | orf1a/b, S |
| Cepheid GeneXpert/Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 | 87 | 20.5 | 34.3 | N2, E |
| Automated Laboratory Device (Non-POCT) | ||||
| Roche Cobas 6800/COBAS SARS-CoV-2 Test | 89 | 21.7 | 35.9 | orf1, E |
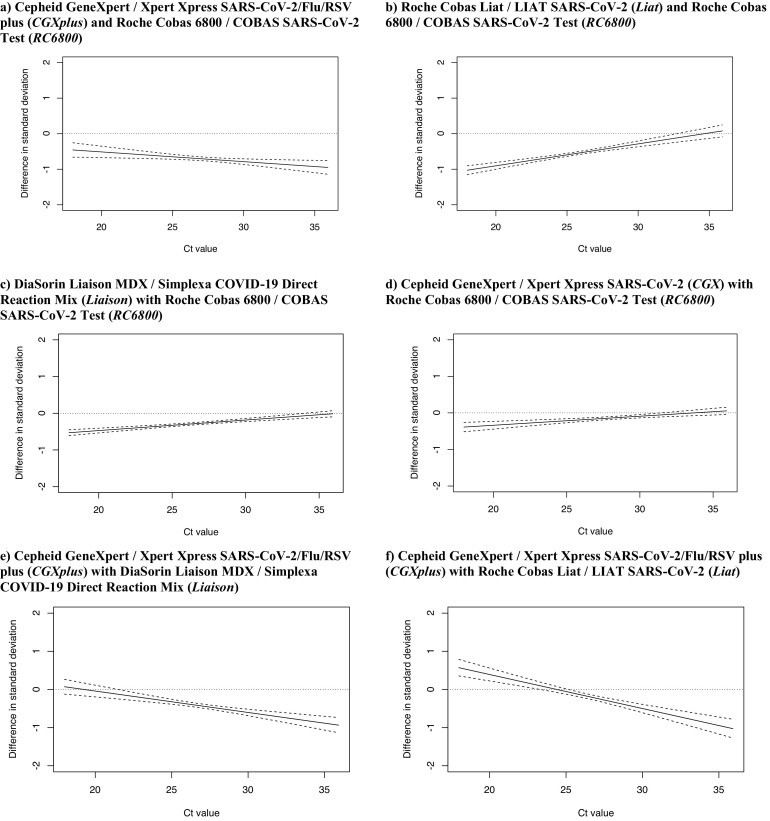 Comparison of the difference in EQA reproducibility between each two assays
Comparison of the difference in EQA reproducibility between each two assays
9. What Are the Limitations of Using EQA Reproducibility for Initial Certification of NPT/POCT Devices?
One limitation of using EQA reproducibility is that assays are only included in EQA schemes once they are already on the market. This means that EQA data is not available for the initial certification process. However, EQA reproducibility plays a crucial role in post-market surveillance, helping to monitor the ongoing performance and reliability of NPT/POCT devices in routine use. According to a study in “Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine,” EQA provides valuable insights into the long-term stability and performance of diagnostic assays.
10. How Can Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Improve Healthcare Accessibility in Underserved Areas?
NPT/POCT can significantly improve healthcare accessibility in underserved areas by bringing diagnostic testing closer to the patient. This is particularly important in remote or rural locations where access to central laboratories is limited. The ability to perform tests at the point of care reduces turnaround times, enabling faster diagnosis and treatment initiation. A report by the National Rural Health Association highlights the critical role of POCT in addressing healthcare disparities in rural communities.
11. What Specific Skills Are Required to Perform Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Accurately?
Performing NPT/POCT accurately requires a range of skills depending on the complexity of the test system. For low-complexity tests, minimal training may be sufficient, focusing on following the manufacturer’s instructions and interpreting visual results. Higher complexity tests require more in-depth training, including sample preparation, quality control procedures, and troubleshooting. According to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), operators of non-waived POCT devices should be well-trained and pass an appropriate examination.
12. How Does the European IVDR Regulation Impact the Requirements for Near Patient Testing Devices?
The European IVDR (2017/746) sets stringent requirements for NPT devices, emphasizing the need for clear instructions, user training, and minimization of user errors. The regulation requires manufacturers to specify the level of training, qualifications, and experience needed by users. It also mandates that NPT devices can be used safely and accurately by the intended user after appropriate training. This regulatory framework aims to ensure the reliability and safety of NPT devices used outside traditional laboratory settings.
13. What Types of Errors Can Occur in Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics, and How Can They Be Prevented?
Several types of errors can occur in NPT/POCT, including pre-analytical errors (e.g., incorrect sample collection), analytical errors (e.g., instrument malfunction), and post-analytical errors (e.g., misinterpretation of results). Prevention strategies include thorough training of operators, adherence to manufacturer’s instructions, regular quality control checks, and participation in EQA schemes. A study in “Point of Care: The Journal of Near-Patient Testing & Technology” emphasizes the importance of implementing robust quality management systems to minimize errors in POCT settings.
14. How Are Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Used in Managing Chronic Diseases?
NPT/POCT plays a significant role in managing chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and HIV. For example, point-of-care blood glucose monitoring allows diabetic patients to manage their condition effectively. In cardiovascular disease, rapid testing for cardiac markers can aid in the diagnosis and treatment of acute coronary syndromes. In HIV management, point-of-care CD4 counts can help monitor immune status and guide treatment decisions. A review in “Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics” highlights the benefits of POCT in improving chronic disease management and patient outcomes.
15. What Are the Ethical Considerations in Implementing Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
Implementing NPT/POCT raises several ethical considerations, including patient privacy, data security, and equitable access to testing. Ensuring patient confidentiality and protecting sensitive health information are critical. It is also essential to address disparities in access to NPT/POCT, particularly in underserved populations. Additionally, healthcare providers must be adequately trained to interpret and communicate test results to patients effectively. A policy brief by the Hastings Center explores the ethical implications of POCT and offers recommendations for responsible implementation.
16. How Is Data Management Handled in Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics Settings?
Data management in NPT/POCT settings involves collecting, storing, and transmitting test results securely and efficiently. Many POCT devices are equipped with connectivity features that allow data to be automatically transferred to electronic health records (EHRs). It is crucial to implement robust data security measures to protect patient information and comply with privacy regulations. A guideline from the College of American Pathologists (CAP) provides recommendations for data management in point-of-care testing.
17. What Future Innovations Are Expected in Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
Future innovations in NPT/POCT are expected to focus on developing more portable, user-friendly, and connected devices. Advances in microfluidics, nanotechnology, and biosensors are driving the development of new POCT platforms that can perform a wider range of tests with greater accuracy and speed. Telehealth and remote monitoring technologies are also being integrated with NPT/POCT to enable remote patient management. A forecast by “MarketsandMarkets” projects significant growth in the POCT market, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for decentralized testing.
18. How Can Telehealth Integrate With Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics to Improve Patient Care?
Telehealth and NPT/POCT can be integrated to provide remote patient monitoring and management, particularly for chronic conditions. Patients can perform tests at home using POCT devices, and the results can be transmitted to healthcare providers via telehealth platforms. This enables timely intervention and adjustments to treatment plans, improving patient outcomes and reducing the need for in-person visits. A study in the “Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare” demonstrates the effectiveness of integrating POCT with telehealth in managing chronic diseases.
19. What Are the Cost-Effectiveness Considerations for Implementing Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
Implementing NPT/POCT can be cost-effective by reducing turnaround times, decreasing hospital stays, and improving patient outcomes. While the initial investment in POCT devices may be higher, the long-term benefits can outweigh the costs. A cost-effectiveness analysis published in “Health Affairs” shows that POCT can be a cost-effective strategy for managing certain medical conditions.
20. How Can Patients and Healthcare Providers Stay Informed About the Latest Advances in Near Patient Testing and Point-of-Care Diagnostics?
Staying informed about the latest advances in NPT/POCT requires continuous learning and engagement with professional resources. Healthcare providers can attend conferences, participate in continuing education programs, and subscribe to relevant journals. Patients can consult with their healthcare providers, review reputable online resources, and participate in patient advocacy groups. Websites like CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provide valuable information and updates on NPT/POCT technologies and applications.
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Automotive Repairs with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
Are you looking for reliable automotive parts and tools? Do you need expert advice to ensure you’re making the right choices? At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges you face in finding quality products and trustworthy information. That’s why we’re dedicated to providing you with detailed specifications, product comparisons, and user reviews to make your decision-making process easier and more efficient.
Don’t waste time and money on subpar parts and tools. Contact us today for personalized assistance. Our team of experts is ready to help you find the perfect solutions for your automotive needs.
Contact Information:
- Address: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Near Patient Testing Versus Point-of-Care Diagnostics
1. What types of tests can be performed using near patient testing devices?
Near patient testing devices can perform a wide range of tests, including glucose monitoring, cardiac marker testing, infectious disease screening, and coagulation testing.
2. Where can near patient testing be performed?
Near patient testing can be performed in various settings, including hospitals, clinics, physician offices, ambulances, and even at home.
3. Is near patient testing as accurate as lab testing?
When performed correctly, near patient testing can be as accurate as lab testing. However, it is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and implement quality control measures.
4. What training is required to perform near patient testing?
The training required to perform near patient testing depends on the complexity of the test. Simple tests may require minimal training, while more complex tests may require extensive training.
5. What are the advantages of near patient testing over traditional lab testing?
The advantages of near patient testing include faster turnaround times, improved patient outcomes, increased accessibility, and reduced costs.
6. What are the disadvantages of near patient testing?
The disadvantages of near patient testing include the potential for errors, the need for quality control measures, and the limited range of tests that can be performed.
7. How is the quality of near patient testing ensured?
The quality of near patient testing is ensured through training, quality control measures, participation in external quality assessment schemes, and adherence to regulatory requirements.
8. What regulations govern near patient testing?
Near patient testing is governed by various regulations, including the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) in the United States and the In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) in Europe.
9. How can I find a reliable near patient testing device?
You can find a reliable near patient testing device by researching different manufacturers, reading user reviews, and consulting with healthcare professionals.
10. How can I learn more about near patient testing?
You can learn more about near patient testing by attending conferences, reading journals, consulting with healthcare professionals, and visiting websites like CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN.