Have You Checked The Wheel Bearings For Play Or Noise? Recognizing these symptoms early can prevent catastrophic failures. At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive information and tools to help you diagnose and address wheel bearing issues, ensuring your vehicle’s safety and performance. Explore our resources to find detailed specifications, brand comparisons, and user reviews for quality auto parts and repair tools, ensuring a smooth and safe ride with proper wheel maintenance.
Contents
- 1. What Are Wheel Bearings And Why Should You Check Them?
- 1.1. What Is The Primary Function Of Wheel Bearings?
- 1.2. Why Is It Important To Regularly Inspect Wheel Bearings?
- 1.3. How Often Should Wheel Bearings Be Inspected?
- 2. What Are The Common Symptoms Of Worn Wheel Bearings?
- 2.1. How To Recognize A Noisy Wheel Bearing?
- 2.2. What Does Wheel Bearing Play Indicate?
- 2.3. What Kind Of Noise Should I Listen For?
- 2.4. How To Identify Vibration?
- 2.5. What Are The Handling Issues?
- 2.6. How Does Wheel Bearing Noise Change During Turns?
- 3. How To Perform A Wheel Bearing Check For Play And Noise?
- 3.1. What Tools Will I Need?
- 3.2. How To Lift The Vehicle Safely?
- 3.3. How To Check For Wheel Bearing Play?
- 3.4. How To Check For Wheel Bearing Noise?
- 3.5. What Should I Do If I Find Play Or Noise?
- 4. What Are The Different Types Of Wheel Bearings?
- 4.1. What Are Ball Bearings?
- 4.2. What Are Roller Bearings?
- 4.3. What Are Tapered Roller Bearings?
- 4.4. What Are Hub Unit Bearings?
- 4.5. What Are The Pros And Cons Of Each Type?
- 5. What Are The Factors That Affect Wheel Bearing Life?
- 5.1. How Does Driving Condition Affect Wheel Bearings?
- 5.2. How Does Maintenance Affect Wheel Bearings?
- 5.3. How Does Bearing Quality Affect Wheel Bearings?
- 5.4. What Is The Impact Of Improper Installation?
- 5.5. What Are The Effects Of Contamination?
- 6. What Is The Process For Replacing Wheel Bearings?
- 6.1. What Tools Are Required For Replacement?
- 6.2. How To Remove The Old Wheel Bearing?
- 6.3. How To Install The New Wheel Bearing?
- 6.4. What Are The Common Mistakes To Avoid?
- 6.5. What Is The Recommended Torque?
- 7. What Are The Best Practices For Wheel Bearing Maintenance?
- 7.1. How Often Should Wheel Bearings Be Lubricated?
- 7.2. What Type Of Grease Is Recommended?
- 7.3. How To Properly Grease Wheel Bearings?
- 7.4. What Is The Importance Of Wheel Alignment?
- 7.5. What Driving Habits Can Prolong Bearing Life?
- 8. How Do I Select Quality Replacement Wheel Bearings?
- 8.1. What Are The Top Brands Of Wheel Bearings?
- 8.2. What Are The Factors To Consider When Selecting?
- 8.3. What Is The Difference Between OEM And Aftermarket Bearings?
- 8.4. How To Read Wheel Bearing Specifications?
- 8.5. How Does Bearing Material Impact Durability?
- 9. How Can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Help You With Wheel Bearing Issues?
- 9.1. What Information And Resources Does CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Offer?
- 9.2. How Can I Find The Right Wheel Bearing For My Vehicle?
- 9.3. What Tools And Equipment Are Recommended?
- 9.4. Can I Get Expert Advice From CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN?
- 9.5. What Are The Benefits Of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN?
- 10. FAQ About Wheel Bearings
- 10.1. What Causes Wheel Bearings To Fail Prematurely?
- 10.2. Can I Drive With A Noisy Wheel Bearing?
- 10.3. How Much Does It Cost To Replace A Wheel Bearing?
- 10.4. Are Front And Rear Wheel Bearings The Same?
- 10.5. How Do I Know If My ABS Sensor Is Affected?
- 10.6. What Is The Lifespan Of A Wheel Bearing?
- 10.7. Can I Replace Just One Wheel Bearing?
- 10.8. What Happens If A Wheel Bearing Fails Completely?
- 10.9. How Can I Prevent Wheel Bearing Noise?
- 10.10. What Are The Signs Of A Bad Hub Assembly?
1. What Are Wheel Bearings And Why Should You Check Them?
Wheel bearings are critical components that allow your wheels to rotate smoothly. They connect the wheel to the axle and support the vehicle’s weight. Regular inspections are essential to detect early signs of wear or damage, preventing potential wheel failure. According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), bearing failures are a significant contributor to vehicle accidents.
1.1. What Is The Primary Function Of Wheel Bearings?
The primary function of wheel bearings is to reduce friction and enable smooth wheel rotation. They support the vehicle’s weight, absorb road shocks, and maintain proper wheel alignment. This ensures optimal handling, stability, and safety.
1.2. Why Is It Important To Regularly Inspect Wheel Bearings?
Regular inspection of wheel bearings is crucial for several reasons:
- Safety: Worn or damaged bearings can lead to wheel instability and potential loss of control.
- Performance: Properly functioning bearings ensure smooth and efficient vehicle operation.
- Cost Savings: Early detection of issues can prevent more extensive and costly repairs.
- Longevity: Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of the bearings and related components.
1.3. How Often Should Wheel Bearings Be Inspected?
Wheel bearings should be inspected at least every 25,000 miles or during routine maintenance checks. Vehicles subjected to heavy use, off-road driving, or extreme conditions may require more frequent inspections.
2. What Are The Common Symptoms Of Worn Wheel Bearings?
Identifying the symptoms of worn wheel bearings early can prevent severe mechanical issues. Keep an ear out for unusual noises, vibrations, and changes in handling.
2.1. How To Recognize A Noisy Wheel Bearing?
A noisy wheel bearing typically emits a rumbling, grinding, or humming sound that varies with vehicle speed. The noise may increase when turning or changing lanes. Listening carefully for these sounds can help diagnose a worn bearing.
2.2. What Does Wheel Bearing Play Indicate?
Wheel bearing play refers to excessive movement or looseness in the wheel bearing. It indicates wear or damage, which can compromise the bearing’s ability to support the wheel properly.
2.3. What Kind Of Noise Should I Listen For?
Listen for noises such as:
- Rumbling: A low-frequency, deep sound that increases with speed.
- Grinding: A harsh, abrasive sound indicating internal damage.
- Humming: A constant, monotone sound that changes with speed.
- Clicking: A rhythmic sound that may indicate loose components.
2.4. How To Identify Vibration?
Vibration from a bad wheel bearing can be felt through the steering wheel, floorboard, or seat. The vibration may increase with speed and worsen during turns.
2.5. What Are The Handling Issues?
Handling issues related to worn wheel bearings include:
- Wandering: The vehicle drifts or pulls to one side.
- Looseness: A vague or imprecise steering feel.
- Instability: Difficulty maintaining a straight line, especially at higher speeds.
2.6. How Does Wheel Bearing Noise Change During Turns?
Wheel bearing noise often changes during turns. The noise may increase or decrease depending on whether the load is shifted to the affected bearing. For example, if the right wheel bearing is failing, the noise may worsen when turning left.
3. How To Perform A Wheel Bearing Check For Play And Noise?
Checking for wheel bearing play and noise involves a few simple steps that can be performed in your garage. This helps determine the condition of your wheel bearings and identify potential issues.
3.1. What Tools Will I Need?
Essential tools for checking wheel bearings include:
- Jack
- Jack stands
- Wheel chocks
- Gloves
- Safety glasses
3.2. How To Lift The Vehicle Safely?
- Park on a Level Surface: Ensure the vehicle is on a flat, stable surface.
- Engage the Parking Brake: Apply the parking brake firmly.
- Chock the Wheels: Place wheel chocks behind the rear wheels.
- Position the Jack: Consult the vehicle’s manual for proper jacking points.
- Raise the Vehicle: Lift the vehicle high enough to place jack stands underneath.
- Secure with Jack Stands: Position jack stands under the frame and lower the vehicle onto them.
- Verify Stability: Ensure the vehicle is stable before proceeding.
3.3. How To Check For Wheel Bearing Play?
- Grip the Tire: Hold the tire at the 12 o’clock and 6 o’clock positions.
- Rock the Wheel: Push and pull the tire back and forth, feeling for any play or looseness.
- Assess the Movement: Excessive play indicates a worn or damaged wheel bearing.
3.4. How To Check For Wheel Bearing Noise?
- Spin the Wheel: Manually spin the wheel and listen for any unusual noises, such as rumbling, grinding, or humming.
- Use a Stethoscope: A mechanic’s stethoscope can help isolate the noise. Place the probe on the suspension components while spinning the wheel.
- Evaluate the Sound: A healthy wheel bearing should spin quietly and smoothly. Any abnormal noise indicates a potential issue.
3.5. What Should I Do If I Find Play Or Noise?
If you detect play or noise during the wheel bearing check, it’s essential to take action:
- Consult a Mechanic: Seek professional diagnosis and repair.
- Replace the Bearing: Replace the worn or damaged wheel bearing promptly.
- Inspect Related Components: Check the hub, axle, and suspension for any additional damage.
4. What Are The Different Types Of Wheel Bearings?
Understanding the different types of wheel bearings can help you choose the right replacement for your vehicle. Each type has its own design and application.
4.1. What Are Ball Bearings?
Ball bearings use spherical balls to maintain separation between the bearing races. They are suitable for lighter loads and higher speeds, commonly found in front wheels of passenger cars.
4.2. What Are Roller Bearings?
Roller bearings use cylindrical rollers to distribute loads over a larger area. They can handle heavier loads and are often used in rear wheels and trucks.
4.3. What Are Tapered Roller Bearings?
Tapered roller bearings use conical rollers and races, designed to handle both radial and axial loads. They are frequently used in heavy-duty applications and older vehicles.
4.4. What Are Hub Unit Bearings?
Hub unit bearings are pre-assembled units that include the bearing, hub, and sometimes the ABS sensor. They simplify installation and are common in modern vehicles.
4.5. What Are The Pros And Cons Of Each Type?
| Bearing Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Ball Bearings | High-speed capability, Low friction | Lower load capacity |
| Roller Bearings | Higher load capacity, Durable | Lower speed capability |
| Tapered Roller Bearings | Handles radial and axial loads, Adjustable | More complex installation |
| Hub Unit Bearings | Easy installation, Integrated design | Higher replacement cost, Less adjustable |
5. What Are The Factors That Affect Wheel Bearing Life?
Several factors can impact the lifespan of wheel bearings, including driving conditions, maintenance practices, and the quality of the bearings themselves.
5.1. How Does Driving Condition Affect Wheel Bearings?
- Rough Roads: Bumpy and uneven surfaces can accelerate wear and tear.
- Off-Road Driving: Exposes bearings to dirt, debris, and impacts.
- Frequent Braking: Generates heat, which can degrade bearing lubrication.
- Heavy Loads: Overloading the vehicle puts extra stress on the bearings.
5.2. How Does Maintenance Affect Wheel Bearings?
- Proper Lubrication: Adequate grease reduces friction and prevents overheating.
- Correct Installation: Improper installation can cause premature failure.
- Regular Inspections: Early detection of issues allows for timely repairs.
- Wheel Alignment: Misalignment can cause uneven wear on the bearings.
5.3. How Does Bearing Quality Affect Wheel Bearings?
- Material Composition: High-quality steel and precise manufacturing tolerances ensure durability.
- Sealing: Effective seals prevent contaminants from entering the bearing.
- Brand Reputation: Reputable brands often offer better quality and reliability.
5.4. What Is The Impact Of Improper Installation?
Improper installation can significantly reduce wheel bearing life. Common mistakes include:
- Over-tightening: Can cause excessive preload and overheating.
- Under-tightening: Leads to play and premature wear.
- Using Incorrect Tools: Can damage the bearing or hub.
- Neglecting Lubrication: Insufficient grease increases friction and heat.
5.5. What Are The Effects Of Contamination?
Contamination from dirt, water, or debris can damage wheel bearings. Contaminants can:
- Abrasive Wear: Cause grinding and wear on the bearing surfaces.
- Corrosion: Rust and corrode the bearing components.
- Reduced Lubrication: Dilute or displace the grease, leading to increased friction.
6. What Is The Process For Replacing Wheel Bearings?
Replacing wheel bearings involves a detailed process that requires specific tools and knowledge. It’s crucial to follow the correct steps to ensure proper function and longevity.
6.1. What Tools Are Required For Replacement?
- Jack and jack stands
- Wheel chocks
- Socket set
- Wrench set
- Torque wrench
- Bearing press or puller
- Hammer
- Punch
- Grease
6.2. How To Remove The Old Wheel Bearing?
- Loosen Lug Nuts: Loosen the lug nuts on the wheel.
- Lift the Vehicle: Jack up the vehicle and secure it with jack stands.
- Remove the Wheel: Take off the wheel and tire assembly.
- Detach Brake Components: Remove the brake caliper and rotor.
- Disconnect ABS Sensor: If equipped, disconnect the ABS sensor.
- Remove Hub Assembly: Remove the hub assembly from the spindle.
- Press Out Old Bearing: Use a bearing press or puller to remove the old bearing from the hub.
6.3. How To Install The New Wheel Bearing?
- Clean the Hub: Clean the hub assembly thoroughly.
- Lubricate the Bearing: Apply grease to the new wheel bearing.
- Press In New Bearing: Use a bearing press to install the new bearing into the hub.
- Reassemble Hub Assembly: Reassemble the hub assembly onto the spindle.
- Reconnect ABS Sensor: Reconnect the ABS sensor, if applicable.
- Reattach Brake Components: Reinstall the brake caliper and rotor.
- Mount the Wheel: Put the wheel and tire assembly back on.
- Torque Lug Nuts: Torque the lug nuts to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
- Lower the Vehicle: Lower the vehicle to the ground.
6.4. What Are The Common Mistakes To Avoid?
- Improper Tool Usage: Using the wrong tools can damage components.
- Neglecting Cleanliness: Dirt and debris can contaminate the new bearing.
- Incorrect Bearing Orientation: Installing the bearing backward can cause immediate failure.
- Over- or Under-Tightening: Improper torque can damage the bearing or hub.
- Forgetting Lubrication: Insufficient grease increases friction and heat.
6.5. What Is The Recommended Torque?
The recommended torque for wheel bearing components varies by vehicle make and model. Consult the vehicle’s service manual for the specific torque specifications.
7. What Are The Best Practices For Wheel Bearing Maintenance?
Maintaining your wheel bearings through proper lubrication, regular inspections, and careful driving habits can significantly extend their lifespan.
7.1. How Often Should Wheel Bearings Be Lubricated?
Wheel bearings should be lubricated according to the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations, typically every 25,000 to 30,000 miles. Some sealed bearings may not require lubrication.
7.2. What Type Of Grease Is Recommended?
Use a high-quality, lithium-based grease designed for wheel bearings. Synthetic grease can offer better performance and longevity.
7.3. How To Properly Grease Wheel Bearings?
- Clean the Bearing: Remove any old grease and dirt from the bearing.
- Pack the Bearing: Pack the bearing with fresh grease, ensuring it fills all voids.
- Apply Grease to Hub: Apply a thin layer of grease to the hub surfaces.
- Reassemble: Reassemble the bearing and hub components.
7.4. What Is The Importance Of Wheel Alignment?
Proper wheel alignment ensures even load distribution on the wheel bearings, preventing premature wear. Misalignment can cause excessive stress on one side of the bearing, leading to early failure.
7.5. What Driving Habits Can Prolong Bearing Life?
- Avoid Potholes: Reduce impacts that can damage bearings.
- Moderate Speed: High speeds generate more heat and stress.
- Smooth Braking: Avoid hard braking, which generates heat.
- Proper Loading: Avoid overloading the vehicle.
8. How Do I Select Quality Replacement Wheel Bearings?
Choosing the right replacement wheel bearings is essential for ensuring your vehicle’s safety and performance. Consider brand reputation, material quality, and compatibility.
8.1. What Are The Top Brands Of Wheel Bearings?
Top brands of wheel bearings include:
- SKF
- FAG
- Timken
- National
- Moog
8.2. What Are The Factors To Consider When Selecting?
- Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure the bearing fits your vehicle’s make and model.
- Load Capacity: Choose a bearing with the appropriate load capacity for your vehicle’s weight.
- Sealing: Look for bearings with effective seals to prevent contamination.
- Material Quality: Opt for bearings made from high-quality steel.
8.3. What Is The Difference Between OEM And Aftermarket Bearings?
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): Bearings made by the original manufacturer or a supplier to the manufacturer. They guarantee fit and performance.
- Aftermarket: Bearings made by third-party manufacturers. Quality can vary, so choose reputable brands.
8.4. How To Read Wheel Bearing Specifications?
Wheel bearing specifications typically include:
- Inner Diameter (ID): The diameter of the bearing’s inner race.
- Outer Diameter (OD): The diameter of the bearing’s outer race.
- Width: The thickness of the bearing.
- Load Capacity: The maximum load the bearing can handle.
- Dynamic Load Rating: The load the bearing can handle while rotating.
- Static Load Rating: The load the bearing can handle while stationary.
8.5. How Does Bearing Material Impact Durability?
High-quality bearing materials, such as chrome steel, offer superior durability and resistance to wear. Better materials ensure longer bearing life and improved performance.
9. How Can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Help You With Wheel Bearing Issues?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive information and resources to help you diagnose, maintain, and replace wheel bearings effectively.
9.1. What Information And Resources Does CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Offer?
- Detailed Guides: Step-by-step instructions for checking and replacing wheel bearings.
- Product Reviews: Expert reviews and user feedback on various wheel bearing brands and tools.
- Technical Specifications: Comprehensive specs for different types of wheel bearings.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Solutions for common wheel bearing problems.
- Maintenance Advice: Best practices for prolonging wheel bearing life.
9.2. How Can I Find The Right Wheel Bearing For My Vehicle?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a vehicle-specific search tool that allows you to find the right wheel bearing for your car, truck, or SUV. Simply enter your vehicle’s make, model, and year to find compatible bearings.
9.3. What Tools And Equipment Are Recommended?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN recommends high-quality tools and equipment for wheel bearing maintenance and replacement, including:
- Bearing presses and pullers
- Torque wrenches
- Socket sets
- Grease guns
- Mechanic’s stethoscopes
9.4. Can I Get Expert Advice From CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN?
Yes, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides access to expert advice through:
- Online Forums: Connect with other car enthusiasts and professionals.
- Live Chat: Get immediate assistance from our technical support team.
- Contact Form: Submit your questions and receive a detailed response.
 pelican wheel bearing bolts
pelican wheel bearing bolts
9.5. What Are The Benefits Of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN?
- Comprehensive Information: Access a wealth of knowledge about wheel bearings and related topics.
- Expert Guidance: Get advice from experienced mechanics and automotive professionals.
- Reliable Products: Find high-quality tools and parts from trusted brands.
- Cost Savings: Learn how to perform maintenance and repairs yourself.
- Safety: Ensure your vehicle is safe and reliable.
10. FAQ About Wheel Bearings
Here are some frequently asked questions about wheel bearings, providing quick answers to common concerns.
10.1. What Causes Wheel Bearings To Fail Prematurely?
Premature wheel bearing failure can be caused by factors such as poor road conditions, improper installation, lack of lubrication, and contamination.
10.2. Can I Drive With A Noisy Wheel Bearing?
It is not recommended to drive with a noisy wheel bearing. A worn bearing can lead to wheel instability and potential loss of control.
10.3. How Much Does It Cost To Replace A Wheel Bearing?
The cost to replace a wheel bearing varies depending on the vehicle make and model, the type of bearing, and labor costs. Typically, it ranges from $200 to $500 per wheel.
10.4. Are Front And Rear Wheel Bearings The Same?
Front and rear wheel bearings may differ in design and specifications. It’s essential to use the correct bearing for each location.
10.5. How Do I Know If My ABS Sensor Is Affected?
If your ABS light is on, and you notice issues with your wheel bearings, the ABS sensor may be affected. Inspect the sensor for damage and replace if necessary.
10.6. What Is The Lifespan Of A Wheel Bearing?
The lifespan of a wheel bearing typically ranges from 85,000 to 100,000 miles. However, factors such as driving conditions and maintenance practices can affect longevity.
10.7. Can I Replace Just One Wheel Bearing?
While it’s possible to replace just one wheel bearing, it’s often recommended to replace them in pairs to ensure even wear and performance.
10.8. What Happens If A Wheel Bearing Fails Completely?
If a wheel bearing fails completely, it can cause the wheel to seize, leading to loss of control and potentially an accident.
10.9. How Can I Prevent Wheel Bearing Noise?
To prevent wheel bearing noise, ensure proper lubrication, regular inspections, and avoid driving on rough roads or overloading the vehicle.
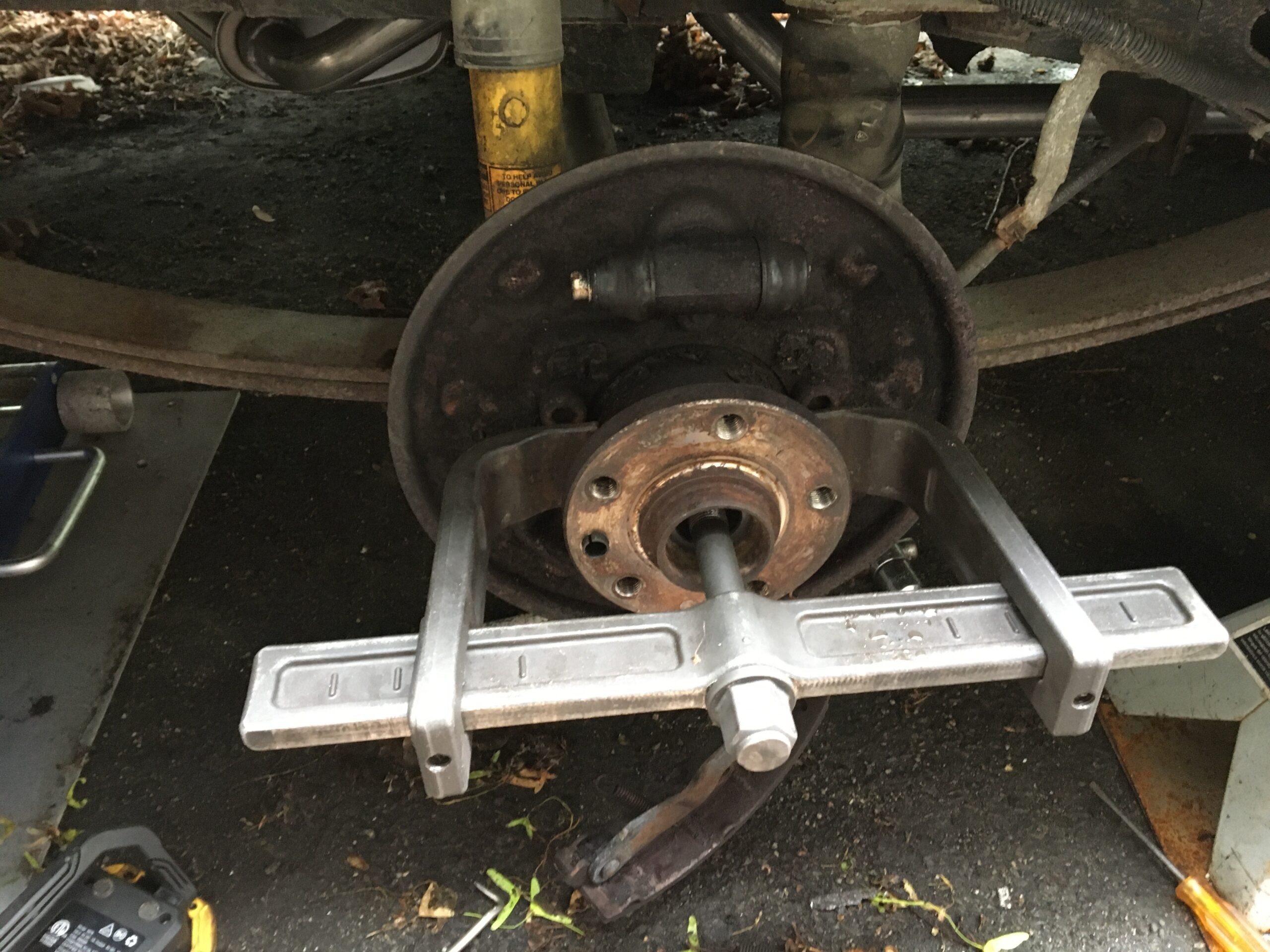 bearing puller tool
bearing puller tool
10.10. What Are The Signs Of A Bad Hub Assembly?
Signs of a bad hub assembly include noise, vibration, play in the wheel, and ABS issues. Inspect the hub for damage and replace if necessary.
Don’t wait until a minor issue becomes a major problem. Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or call us on Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and top-quality wheel bearings and tools. Ensure your vehicle’s safety and performance with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN. Visit our website CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information.