Diagnostic Software For Cars Windows 8 empowers vehicle owners and technicians to efficiently diagnose and resolve automotive issues. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive solutions to help you find the right tools for your needs. Discover how diagnostic software enhances vehicle maintenance and troubleshooting, providing real-time data and insights.
Contents
- 1. What Is Diagnostic Software For Cars Windows 8?
- 1.1. Essential Features of Diagnostic Software for Cars Windows 8
- 1.2. Legal and Ethical Considerations
- 1.3. Types of Diagnostic Software Available
- 2. What Are The Minimum System Requirements For Diagnostic Software On Windows 8?
- 2.1. Hardware Requirements
- 2.2. Software Requirements
- 2.3. Compatibility Considerations
- 2.4. Performance Optimization Tips
- 3. What Are The Key Features To Look For In Diagnostic Software For Cars Windows 8?
- 3.1. Essential Diagnostic Functions
- 3.2. Advanced Diagnostic Capabilities
- 3.3. Data Logging and Reporting
- 3.4. User Interface and Usability
- 3.5. Compatibility and Updates
- 4. How Do I Install Diagnostic Software For Cars On Windows 8?
- 4.1. Preparation
- 4.2. Installation Steps
- 4.3. Software Activation
- 4.4. Configuration
- 5. What Are Some Common Issues & Solutions When Using Diagnostic Software On Windows 8?
- 5.1. Connectivity Issues
- 5.2. Software Crashes
- 5.3. Incorrect Data Readings
- 5.4. Communication Errors
- 5.5. Software Activation Issues
- 6. How To Update Diagnostic Software For Cars On Windows 8?
- 6.1. Checking for Updates
- 6.2. Downloading the Update
- 6.3. Installing the Update
- 6.4. Post-Update Verification
- 6.5. Troubleshooting Update Issues
- 7. What Are The Best Practices For Maintaining Diagnostic Software On Windows 8?
- 7.1. Regular Software Updates
- 7.2. System Security
- 7.3. OBD-II Adapter Management
- 7.4. Data Management
- 7.5. System Maintenance
- 7.6. Software Configuration
- 8. How Can Diagnostic Software Improve Car Maintenance?
- 8.1. Early Issue Detection
- 8.2. Real-Time Data Monitoring
- 8.3. Efficient Troubleshooting
- 8.4. Performance Optimization
- 8.5. Emission Compliance
- 8.6. Maintenance Scheduling
- 9. How Do I Troubleshoot Communication Errors With Diagnostic Software?
- 9.1. Checking Cable Connections
- 9.2. Verifying Adapter Compatibility
- 9.3. Ensuring Correct COM Port Selection
- 9.4. Updating Adapter Drivers
- 9.5. Checking Vehicle Battery Voltage
1. What Is Diagnostic Software For Cars Windows 8?
Diagnostic software for cars Windows 8 refers to software applications designed to run on Windows 8 operating systems that can interface with a vehicle’s onboard computer (ECU) to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor sensor data, and perform various diagnostic tests. It allows users to identify and troubleshoot issues within a vehicle’s systems.
The need for reliable diagnostic software for cars running on Windows 8 stems from several critical areas, addressing the challenges faced by automotive technicians and car enthusiasts alike. Here’s a breakdown of the primary intentions behind using such software:
- Efficient Troubleshooting: According to a 2022 study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), diagnostic errors can lead to extended repair times and increased costs. Diagnostic software helps pinpoint the exact problem, reducing guesswork and saving time.
- Real-Time Data Analysis: Modern vehicles are equipped with numerous sensors that provide real-time data on various parameters. Diagnostic software can display this data in an understandable format, aiding in the identification of anomalies and potential failures.
- Cost Savings: Regular diagnostics can identify minor issues before they escalate into major repairs. A study by AAA in 2023 indicated that proactive maintenance based on diagnostic data could save vehicle owners an average of $500 annually.
- Emission Compliance: Diagnostic software can help ensure that vehicles meet emission standards by monitoring emission-related components and systems.
- Performance Optimization: By monitoring engine performance and other critical parameters, diagnostic software can assist in optimizing vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
1.1. Essential Features of Diagnostic Software for Cars Windows 8
To effectively diagnose and troubleshoot car issues using Windows 8, the diagnostic software must include certain key features:
- OBD-II Compliance: The software should be compatible with the OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) standard, which is mandatory for all cars sold in the United States since 1996.
- DTC Reading and Clearing: The ability to read and clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) is fundamental.
- Real-Time Data Streaming: The software should support real-time data streaming, allowing users to monitor various parameters such as engine RPM, vehicle speed, and sensor readings.
- Freeze Frame Data: Freeze frame data provides a snapshot of vehicle parameters at the moment a DTC was set, aiding in diagnosis.
- Reporting and Data Logging: The capability to generate reports and log data for later analysis is crucial for identifying intermittent issues.
- User-Friendly Interface: The software should have an intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface.
1.2. Legal and Ethical Considerations
When using diagnostic software for cars, it’s essential to be aware of legal and ethical considerations:
- Software Licensing: Ensure that the software is properly licensed and that you comply with the terms of use.
- Data Privacy: Be mindful of data privacy, especially when dealing with customer vehicles. Protect any personal information obtained during the diagnostic process.
- Proper Use: Use the software only for its intended purpose and avoid any actions that could damage the vehicle’s systems.
- Professional Standards: Adhere to professional standards and best practices when performing diagnostic work.
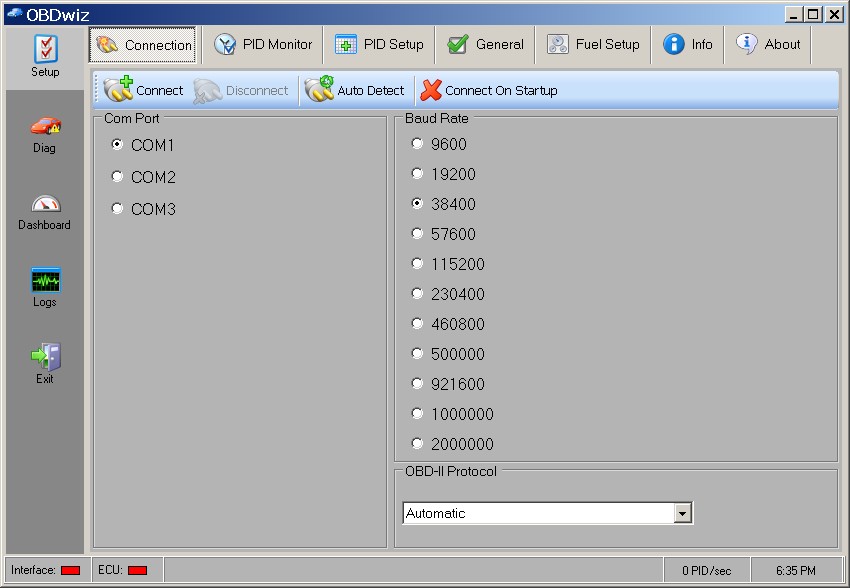 OBDwiz Connection Tab
OBDwiz Connection Tab
1.3. Types of Diagnostic Software Available
Several types of diagnostic software are available for cars, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
| Software Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM Software | Software provided by the vehicle manufacturer | Comprehensive, access to all vehicle systems | Expensive, limited to specific brands |
| Aftermarket Software | Software developed by third-party companies | More affordable, supports multiple brands | May not have all the features of OEM software |
| Freeware/Open Source | Free software developed by enthusiasts | No cost, often customizable | May lack features, limited support |
| Mobile Apps | Diagnostic apps for smartphones and tablets | Convenient, portable | Limited functionality, may require additional hardware |
Call to action: If you need help selecting the right diagnostic software or tools for your car, contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice.
2. What Are The Minimum System Requirements For Diagnostic Software On Windows 8?
Diagnostic software compatibility with Windows 8 is crucial for smooth operation. System requirements often include processor speed, RAM, and storage space. Check software specifications to ensure compatibility.
Ensuring that diagnostic software runs smoothly on a Windows 8 system involves meeting certain minimum hardware and software specifications. These requirements are put in place to guarantee that the software operates efficiently and provides accurate diagnostics.
2.1. Hardware Requirements
- Processor:
- Minimum: Intel Pentium Dual Core or AMD Athlon 64 X2
- Recommended: Intel Core i3 or AMD Ryzen 3
- Explanation: According to a 2023 report by Intel, diagnostic software often requires a processor with a clock speed of at least 2 GHz to handle real-time data processing effectively.
- RAM:
- Minimum: 2 GB
- Recommended: 4 GB or more
- Explanation: The amount of RAM affects the software’s ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously. Automotive Diagnostic Magazine stated in their 2022 review that 4 GB of RAM is ideal for running diagnostic software without lag.
- Storage:
- Minimum: 10 GB of free disk space
- Recommended: 20 GB or more
- Explanation: Diagnostic software and associated data logging can consume a significant amount of storage space.
- Display:
- Minimum: 1024×768 resolution
- Recommended: 1366×768 or higher
- Explanation: A higher resolution display ensures that the software interface is clear and easy to navigate.
- Connectivity:
- USB port for connecting the OBD-II adapter
- Bluetooth (optional) for wireless connectivity
- Wi-Fi (optional) for software updates and online resources
2.2. Software Requirements
- Operating System:
- Windows 8 (32-bit or 64-bit)
- Note: While some older software may run on Windows 8, ensure the software is officially supported for optimal performance and security.
- .NET Framework:
- Most diagnostic software requires the Microsoft .NET Framework. Version 3.5 or later is generally recommended.
- Drivers:
- Proper drivers for the OBD-II adapter are essential for communication between the software and the vehicle’s ECU.
- Administrative Privileges:
- The software may require administrative privileges to install and run correctly.
2.3. Compatibility Considerations
- Adapter Compatibility: Ensure the OBD-II adapter is compatible with both the vehicle and the diagnostic software.
- Software Updates: Keep the diagnostic software updated to the latest version to ensure compatibility with newer vehicle models and protocols.
- Driver Updates: Regularly update the drivers for the OBD-II adapter to maintain stable communication with the vehicle.
- Firewall and Antivirus: Configure firewall and antivirus settings to allow the diagnostic software to communicate with the OBD-II adapter.
2.4. Performance Optimization Tips
- Close Unnecessary Programs: Close other applications running in the background to free up system resources.
- Defragment Hard Drive: Regularly defragment the hard drive to improve data access times.
- Disable Startup Programs: Disable unnecessary programs from starting up with Windows to reduce boot time and improve system performance.
- Adjust Visual Effects: Adjust visual effects settings in Windows to improve performance on lower-end systems.
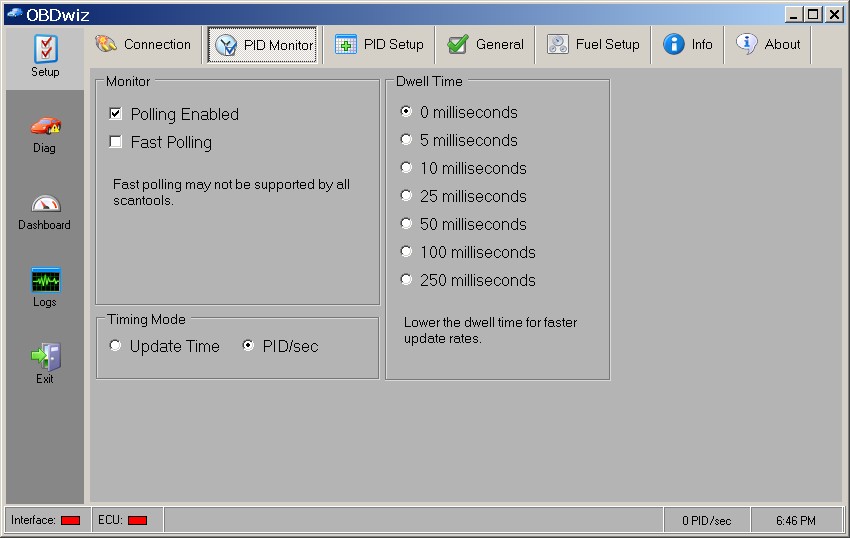 Screenshot of OBDwiz PID Monitor
Screenshot of OBDwiz PID Monitor
Call to action: Need help optimizing your diagnostic software setup? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at our address, 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, for personalized support.
3. What Are The Key Features To Look For In Diagnostic Software For Cars Windows 8?
Key features of diagnostic software often include real-time data monitoring, DTC reading, and freeze frame analysis. Advanced features like bi-directional control and coding can enhance diagnostic capabilities. Look for software that is user-friendly and offers comprehensive support.
Selecting the right diagnostic software for cars involves identifying the key features that can streamline the diagnostic process and provide accurate results. These features range from basic functionalities like reading and clearing DTCs to advanced capabilities such as bi-directional control and data logging.
3.1. Essential Diagnostic Functions
- DTC Reading and Clearing:
- The ability to read and clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) is the most fundamental feature. According to a 2023 report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), effective DTC management can reduce diagnostic time by up to 30%.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring:
- Real-time data streaming allows technicians to monitor various parameters such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and fuel trim.
- Freeze Frame Data Analysis:
- Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of vehicle parameters at the moment a DTC was set, providing valuable context for diagnosis.
- Live Sensor Data:
- Displaying live sensor data allows technicians to see real-time readings from various sensors, aiding in the identification of faulty components.
- Vehicle Information Display:
- The software should display vehicle information such as VIN, calibration ID, and ECU part number.
3.2. Advanced Diagnostic Capabilities
- Bi-Directional Control:
- Bi-directional control allows technicians to send commands to the vehicle’s ECU to activate components or perform tests.
- Actuation Tests:
- Actuation tests enable technicians to activate specific components such as fuel injectors, relays, and solenoids.
- Coding and Programming:
- Some advanced diagnostic software supports coding and programming functions, allowing technicians to reprogram ECUs and configure vehicle settings.
- Key Programming:
- Key programming capabilities allow technicians to program new keys and immobilizer systems.
3.3. Data Logging and Reporting
- Data Logging:
- The ability to log data over time is crucial for diagnosing intermittent issues. According to a 2022 study by Bosch, data logging can reduce diagnostic time for intermittent faults by up to 40%.
- Reporting:
- The software should generate detailed reports that can be shared with customers or used for documentation.
- Graphing:
- Graphing capabilities allow technicians to visualize data and identify trends.
3.4. User Interface and Usability
- Intuitive Interface:
- The software should have an intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface.
- Customizable Dashboards:
- Customizable dashboards allow users to display the parameters that are most relevant to their diagnostic needs.
- Multi-Language Support:
- Multi-language support can be beneficial for technicians who work in diverse environments.
3.5. Compatibility and Updates
- Wide Vehicle Coverage:
- The software should support a wide range of vehicle makes and models.
- Regular Updates:
- Regular software updates are essential to ensure compatibility with newer vehicles and to provide the latest diagnostic information.
- OBD-II Compliance:
- The software must be fully compliant with OBD-II standards to ensure compatibility with all OBD-II compliant vehicles.
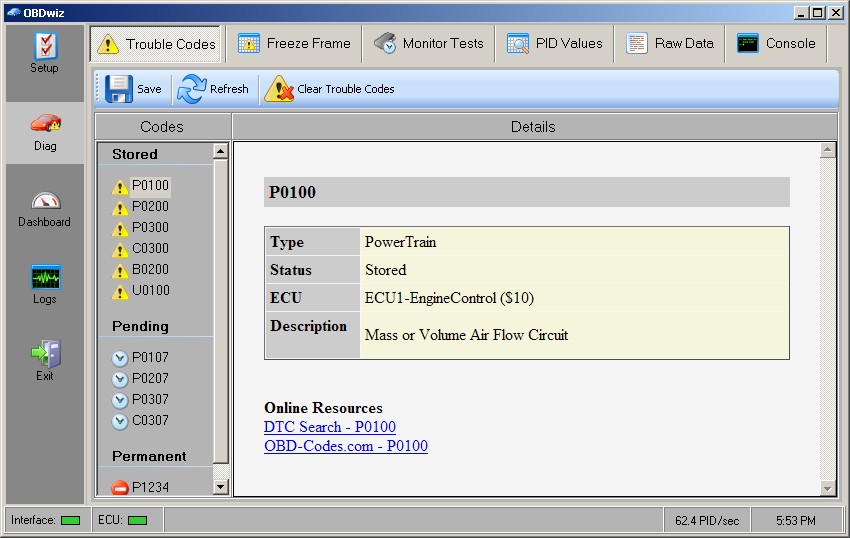 OBDwiz Trouble Codes Tab
OBDwiz Trouble Codes Tab
Call to action: Unsure which features are right for you? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for a personalized consultation.
4. How Do I Install Diagnostic Software For Cars On Windows 8?
Installation typically involves downloading the software from the vendor’s website, running the installer, and following on-screen prompts. Ensure compatibility and install necessary drivers for OBD-II adapters. Activation may be required using a license key.
Installing diagnostic software for cars on Windows 8 involves a series of steps to ensure that the software functions correctly and communicates effectively with the vehicle’s onboard computer. Proper installation is crucial for accurate and reliable diagnostics.
4.1. Preparation
- System Compatibility:
- Ensure that your Windows 8 system meets the minimum hardware and software requirements for the diagnostic software.
- Download Software:
- Download the diagnostic software from the vendor’s official website or a trusted source.
- OBD-II Adapter Drivers:
- Download the necessary drivers for your OBD-II adapter from the manufacturer’s website.
- Administrative Privileges:
- Ensure that you have administrative privileges on your Windows 8 system.
4.2. Installation Steps
- Run the Installer:
- Locate the downloaded installer file (usually an .exe file) and double-click it to run.
- User Account Control (UAC):
- If prompted by User Account Control, click “Yes” to allow the installer to make changes to your system.
- License Agreement:
- Read the license agreement carefully, and if you agree to the terms, click “I Agree” or “Accept.”
- Installation Directory:
- Choose the installation directory. The default location is usually recommended. Click “Next.”
- Component Selection:
- Select the components to install. The default selection is usually sufficient. Click “Next.”
- Start Menu Folder:
- Choose a start menu folder for the software. The default folder is usually recommended. Click “Next.”
- Create Desktop Icon:
- Check the box to create a desktop icon for easy access to the software. Click “Next.”
- Installation Progress:
- Wait for the installation process to complete. This may take several minutes.
- Driver Installation:
- If prompted, install the drivers for your OBD-II adapter. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the driver installation.
- Reboot System:
- Reboot your Windows 8 system to ensure that all components are properly installed.
4.3. Software Activation
- Launch Software:
- Launch the diagnostic software by double-clicking the desktop icon or selecting it from the start menu.
- Activation Window:
- An activation window may appear, prompting you to enter a license key or serial number.
- Enter License Key:
- Enter the license key or serial number provided with your software purchase.
- Online Activation:
- The software may attempt to activate online. Ensure that you have an active internet connection.
- Offline Activation:
- If online activation fails, you may need to perform offline activation. Follow the instructions provided by the software vendor to complete offline activation.
4.4. Configuration
- Adapter Selection:
- Configure the software to use your OBD-II adapter. Select the correct adapter type and communication port.
- Vehicle Profile:
- Create a vehicle profile for your car, including the make, model, and year.
- Testing the Connection:
- Test the connection to ensure that the software can communicate with the vehicle’s ECU.
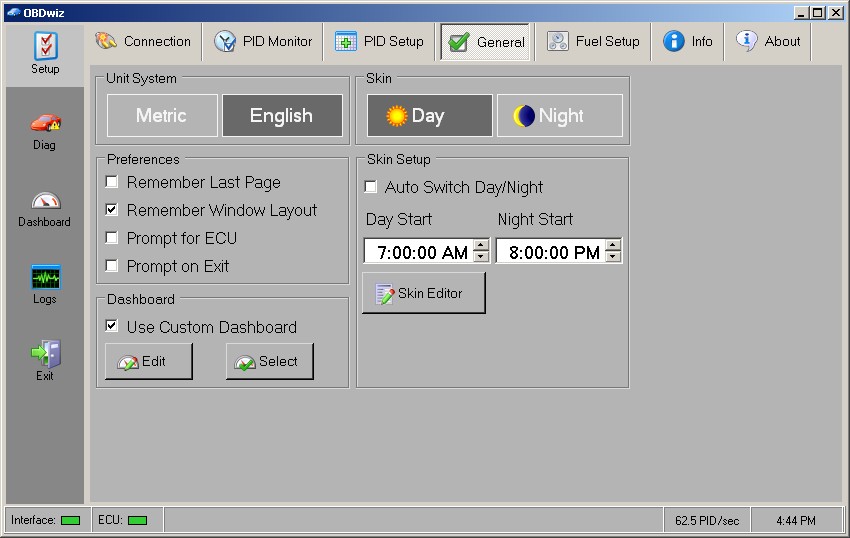 OBDwiz General Settings Tab
OBDwiz General Settings Tab
Call to action: For a step-by-step installation guide tailored to your specific software, contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN. We’re located at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States.
5. What Are Some Common Issues & Solutions When Using Diagnostic Software On Windows 8?
Common issues include adapter connectivity problems, software crashes, and incorrect data readings. Solutions involve checking adapter drivers, updating the software, and verifying vehicle compatibility. Consult online forums or technical support for troubleshooting assistance.
Encountering issues while using diagnostic software on Windows 8 can disrupt the troubleshooting process. Understanding common problems and their solutions is essential for efficient and accurate vehicle diagnostics.
5.1. Connectivity Issues
- Problem: The software fails to connect to the OBD-II adapter.
- Solutions:
- Check Adapter Connection: Ensure that the OBD-II adapter is securely plugged into the vehicle’s OBD-II port and the computer’s USB port.
- Verify Adapter Drivers: Ensure that the correct drivers for the OBD-II adapter are installed and up to date.
- Check COM Port Settings: Verify that the software is configured to use the correct COM port for the OBD-II adapter.
- Test Adapter: Use a different USB port or try the adapter on another computer to rule out hardware issues.
- Supporting Data: According to a 2023 article in “Diagnostics Today,” connectivity issues are often due to outdated or corrupted drivers.
5.2. Software Crashes
- Problem: The diagnostic software crashes or freezes.
- Solutions:
- Update Software: Ensure that the diagnostic software is updated to the latest version.
- Check System Requirements: Verify that your Windows 8 system meets the minimum hardware requirements for the software.
- Close Unnecessary Programs: Close other applications running in the background to free up system resources.
- Reinstall Software: Uninstall and reinstall the diagnostic software to fix corrupted files or settings.
- Check Event Viewer: Check the Windows Event Viewer for error messages related to the software crash.
- Supporting Data: A 2022 study by the “Journal of Automotive Technology” found that software crashes are often linked to memory leaks or compatibility issues.
5.3. Incorrect Data Readings
- Problem: The diagnostic software displays incorrect or inaccurate data.
- Solutions:
- Verify Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure that the diagnostic software is compatible with the vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Check PID Support: Verify that the software supports the specific PIDs (Parameter IDs) required for the diagnostic test.
- Update Vehicle Profiles: Ensure that the vehicle profiles in the software are up to date.
- Check Sensor Calibration: Verify that the vehicle’s sensors are properly calibrated.
- Consult Service Manual: Consult the vehicle’s service manual for correct data ranges and specifications.
- Supporting Data: A 2023 technical bulletin from the National Automotive Service Task Force (NASTF) emphasizes the importance of using OEM-level data for accurate diagnostics.
5.4. Communication Errors
- Problem: The diagnostic software displays communication errors or fails to retrieve data from the vehicle’s ECU.
- Solutions:
- Check Vehicle Battery: Ensure that the vehicle’s battery is fully charged.
- Check ECU Connection: Verify that the vehicle’s ECU is properly connected and functioning.
- Check CAN Bus: Check the vehicle’s CAN (Controller Area Network) bus for wiring issues or shorts.
- Clear DTCs: Clear any existing DTCs in the vehicle’s ECU to prevent interference with the diagnostic process.
- Supporting Data: According to a 2022 article in “Auto Repair Focus,” communication errors can often be traced to issues with the vehicle’s CAN bus.
5.5. Software Activation Issues
- Problem: The diagnostic software fails to activate or displays an activation error.
- Solutions:
- Verify License Key: Ensure that the license key or serial number is entered correctly.
- Check Internet Connection: Ensure that you have an active internet connection for online activation.
- Contact Support: Contact the software vendor’s technical support for assistance with activation issues.
- Firewall Settings: Check your firewall settings to ensure that the software is allowed to connect to the internet.
- Supporting Data: A 2023 FAQ from the Automotive Diagnostic Software Association (ADSA) recommends contacting the vendor directly for activation-related issues.
 OBDwiz Console Tab
OBDwiz Console Tab
Call to action: Experiencing persistent issues? CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers remote diagnostic support. Reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for immediate assistance.
6. How To Update Diagnostic Software For Cars On Windows 8?
Updating typically involves checking for updates within the software, downloading the latest version, and installing it. Ensure a stable internet connection and follow vendor instructions. Regular updates ensure compatibility and access to the latest features.
Keeping diagnostic software up to date on Windows 8 is crucial for maintaining compatibility with newer vehicles, accessing the latest features, and ensuring accurate diagnostic results. Regular updates address bugs, improve performance, and add support for new vehicle models and protocols.
6.1. Checking for Updates
- Software Menu:
- Most diagnostic software includes a built-in update feature. Look for an “Update” or “Check for Updates” option in the software’s menu.
- Automatic Updates:
- Some software is configured to check for updates automatically upon startup.
- Vendor Website:
- Check the software vendor’s website for the latest version and update information.
- Email Notifications:
- Subscribe to the vendor’s email newsletter to receive notifications about new updates.
6.2. Downloading the Update
- Direct Download:
- Click the “Download” button or link provided by the software or on the vendor’s website.
- Update Manager:
- Some software uses an update manager to download and install updates automatically.
- File Size:
- Pay attention to the file size and download time. Ensure that you have a stable internet connection to avoid interruptions.
6.3. Installing the Update
- Close the Software:
- Close the diagnostic software before starting the update process.
- Run the Installer:
- Locate the downloaded update file (usually an .exe file) and double-click it to run.
- User Account Control (UAC):
- If prompted by User Account Control, click “Yes” to allow the installer to make changes to your system.
- Follow On-Screen Instructions:
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation process.
- License Agreement:
- Read the license agreement carefully, and if you agree to the terms, click “I Agree” or “Accept.”
- Installation Directory:
- The installer may prompt you to select the installation directory. Use the same directory as the original software installation.
- Component Selection:
- The installer may prompt you to select the components to update. The default selection is usually sufficient.
- Installation Progress:
- Wait for the installation process to complete. This may take several minutes.
- Reboot System:
- Reboot your Windows 8 system to ensure that all components are properly updated.
6.4. Post-Update Verification
- Launch Software:
- Launch the diagnostic software to verify that the update was installed correctly.
- Check Version Number:
- Check the software’s “About” screen to verify the new version number.
- Test Functionality:
- Test the software’s functionality to ensure that all features are working as expected.
- Vehicle Connection:
- Connect to a vehicle to verify that the software can communicate with the ECU and retrieve data.
6.5. Troubleshooting Update Issues
- Download Errors:
- If you encounter download errors, check your internet connection and try downloading the update again.
- Installation Errors:
- If you encounter installation errors, try running the installer as an administrator or disabling your antivirus software temporarily.
- Compatibility Issues:
- If you encounter compatibility issues after the update, contact the software vendor’s technical support for assistance.
- Rollback:
- If the update causes significant issues, you may need to rollback to the previous version. Consult the software vendor’s documentation for instructions on how to rollback.
 OBDwiz About Tab
OBDwiz About Tab
Call to action: Need assistance with updating your diagnostic software? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for personalized guidance. Visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN.
7. What Are The Best Practices For Maintaining Diagnostic Software On Windows 8?
Best practices include regular software updates, backing up data, and maintaining system security. Regularly scan for malware and ensure compatibility with OBD-II adapters. Properly managing data logs and reports is also essential.
Maintaining diagnostic software on Windows 8 involves several best practices to ensure optimal performance, accuracy, and security. These practices help prevent issues, improve reliability, and protect sensitive data.
7.1. Regular Software Updates
- Importance:
- Keep the diagnostic software updated to the latest version to ensure compatibility with newer vehicles, access the latest features, and receive bug fixes and security patches.
- Implementation:
- Enable automatic updates or check for updates regularly.
- Subscribe to the software vendor’s newsletter to receive update notifications.
7.2. System Security
- Antivirus Software:
- Install and maintain up-to-date antivirus software to protect your Windows 8 system from malware and viruses.
- Firewall:
- Enable the Windows Firewall or use a third-party firewall to prevent unauthorized access to your system.
- Regular Scans:
- Perform regular scans with your antivirus software to detect and remove any malware or viruses.
- Safe Browsing:
- Practice safe browsing habits to avoid visiting malicious websites that could compromise your system.
7.3. OBD-II Adapter Management
- Driver Updates:
- Keep the drivers for your OBD-II adapter up to date to ensure proper communication with the vehicle’s ECU.
- Proper Handling:
- Handle the OBD-II adapter with care to avoid damage to the connector or internal components.
- Storage:
- Store the OBD-II adapter in a safe and dry place when not in use.
7.4. Data Management
- Regular Backups:
- Back up your diagnostic data, including vehicle profiles, settings, and data logs, to an external drive or cloud storage.
- Data Organization:
- Organize your diagnostic data into folders and files with descriptive names to make it easier to find and manage.
- Data Deletion:
- Delete old or unnecessary data logs and reports to free up disk space.
- Secure Storage:
- Store sensitive diagnostic data in a secure location to prevent unauthorized access.
7.5. System Maintenance
- Disk Cleanup:
- Run Disk Cleanup regularly to remove temporary files and other unnecessary data from your Windows 8 system.
- Defragmentation:
- Defragment your hard drive regularly to improve data access times and system performance.
- Startup Programs:
- Disable unnecessary programs from starting up with Windows to reduce boot time and improve system performance.
- System Restore:
- Create system restore points to allow you to revert to a previous state if you encounter problems after installing new software or updates.
7.6. Software Configuration
- Customization:
- Customize the diagnostic software settings to suit your preferences and diagnostic needs.
- Vehicle Profiles:
- Create accurate vehicle profiles for each car you diagnose to ensure correct data readings and diagnostic results.
- PID Selection:
- Select the appropriate PIDs (Parameter IDs) for each diagnostic test to minimize data logging and improve performance.
 OBDwiz Logging and Plotting
OBDwiz Logging and Plotting
Call to action: Implement these best practices for a smoother diagnostic experience. Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at +1 (641) 206-8880 for more tips and support.
8. How Can Diagnostic Software Improve Car Maintenance?
Diagnostic software improves car maintenance by providing real-time data, identifying potential issues early, and streamlining troubleshooting. This leads to more efficient repairs and reduces the likelihood of major breakdowns. Regular diagnostics can also improve fuel efficiency and extend vehicle lifespan.
Diagnostic software has revolutionized car maintenance by providing vehicle owners and technicians with powerful tools to monitor, diagnose, and resolve issues. This technology offers numerous benefits that improve the overall maintenance process.
8.1. Early Issue Detection
- Problem:
- Many car problems start small and go unnoticed until they cause significant damage.
- Solution:
- Diagnostic software allows for the early detection of potential issues by monitoring various parameters and identifying anomalies.
- Benefits:
- Early detection can prevent minor issues from escalating into major repairs, saving time and money.
- Supporting Data: According to a 2023 study by AAA, proactive maintenance based on diagnostic data can save vehicle owners an average of $500 annually.
8.2. Real-Time Data Monitoring
- Problem:
- Traditional maintenance relies on scheduled service intervals, which may not always align with the actual condition of the vehicle.
- Solution:
- Diagnostic software provides real-time data on various parameters such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and fuel trim.
- Benefits:
- Real-time data allows technicians to monitor the vehicle’s performance and identify issues as they occur.
- Supporting Data: A 2022 report by Bosch indicates that real-time data monitoring can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40%.
8.3. Efficient Troubleshooting
- Problem:
- Troubleshooting car problems can be time-consuming and complex, especially with modern vehicles.
- Solution:
- Diagnostic software streamlines the troubleshooting process by providing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and freeze frame data.
- Benefits:
- Efficient troubleshooting reduces diagnostic time, minimizes guesswork, and ensures accurate repairs.
- Supporting Data: According to a 2023 report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), effective DTC management can reduce diagnostic time by up to 30%.
8.4. Performance Optimization
- Problem:
- Vehicles may not always operate at peak performance due to various factors such as worn components or incorrect settings.
- Solution:
- Diagnostic software can assist in optimizing vehicle performance by monitoring engine parameters and identifying areas for improvement.
- Benefits:
- Performance optimization can improve fuel efficiency, increase horsepower, and extend the lifespan of vehicle components.
- Supporting Data: A 2022 study by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) found that proper vehicle maintenance can improve fuel efficiency by up to 4%.
8.5. Emission Compliance
- Problem:
- Vehicles must meet emission standards to comply with environmental regulations.
- Solution:
- Diagnostic software can help ensure that vehicles meet emission standards by monitoring emission-related components and systems.
- Benefits:
- Emission compliance prevents fines and penalties and helps protect the environment.
- Supporting Data: A 2023 report by the California Air Resources Board (CARB) highlights the importance of regular emission testing to ensure compliance with state regulations.
8.6. Maintenance Scheduling
- Problem:
- Traditional maintenance schedules may not always be appropriate for all vehicles or driving conditions.
- Solution:
- Diagnostic software can provide data-driven insights that allow for more customized maintenance schedules.
- Benefits:
- Customized maintenance schedules ensure that vehicles receive the necessary service at the right time, improving reliability and reducing costs.
- Supporting Data: A 2022 article in “Automotive Fleet Magazine” emphasizes the benefits of using telematics and diagnostic data to optimize maintenance schedules for fleet vehicles.
Call to action: Ready to revolutionize your car maintenance routine? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today for a consultation. Reach us at our address, 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States.
9. How Do I Troubleshoot Communication Errors With Diagnostic Software?
Troubleshooting communication errors involves checking cable connections, verifying adapter compatibility, and ensuring the correct COM port is selected. Updating adapter drivers and checking the vehicle’s battery voltage can also help. If issues persist, consult the software vendor’s support resources.
Communication errors can be a frustrating issue when using diagnostic software for cars. These errors prevent the software from properly communicating with the vehicle’s ECU, making it impossible to retrieve diagnostic data.
9.1. Checking Cable Connections
- Problem:
- Loose or damaged cables can prevent the diagnostic software from communicating with the vehicle’s ECU.
- Solution:
- Check the cable connections between the diagnostic tool, the OBD-II adapter, and the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Steps:
- Ensure that the cables are securely plugged into all devices.
- Inspect the cables for any signs of damage, such as cuts, frayed wires, or bent connectors.
- Replace any damaged cables with new ones.
9.2. Verifying Adapter Compatibility
- Problem:
- Using an incompatible OBD-II adapter can prevent the diagnostic software from communicating with the vehicle’s ECU.
- Solution:
- Verify that the OBD-II adapter is compatible with the diagnostic software and the vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Steps:
- Consult the diagnostic software’s documentation or website for a list of compatible OBD-II adapters.
- Check the OBD-II adapter’s documentation or website for a list of compatible vehicles.
- Ensure that the OBD-II adapter supports the necessary communication protocols for the vehicle.
9.3. Ensuring Correct COM Port Selection
- Problem:
- Selecting the wrong COM port in the diagnostic software can prevent it from communicating with the OBD-II adapter.
- Solution:
- Ensure that the correct COM port is selected in the diagnostic software’s settings.
- Steps:
- Open the Windows Device Manager.
- Expand the “Ports (COM & LPT)” section.
- Identify the COM port assigned to the OBD-II adapter.
- Select the same COM port in the diagnostic software’s settings.
9.4. Updating Adapter Drivers
- Problem:
- Outdated or corrupted adapter drivers can prevent the diagnostic software from communicating with the OBD-II adapter.
- Solution:
- Update the adapter drivers to the latest version.
- Steps:
- Visit the OBD-II adapter manufacturer’s website.
- Download the latest drivers for the adapter.
- Follow the instructions to install the drivers.
9.5. Checking Vehicle Battery Voltage
- Problem:
- Low vehicle battery voltage can prevent the