The Center For Point-of-care Diagnostics For Global Health propels diagnostic innovation, facilitating timely and accessible healthcare solutions worldwide and focusing on rapid, accurate, and cost-effective diagnostic tools. At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, explore a range of automotive diagnostic tools, vital for accurate assessments, and connect with us for expert guidance on top-quality tools for precise vehicle maintenance.
Contents
- 1. What is the Center for Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Global Health?
- 1.1 Defining Point-of-Care Diagnostics
- 1.2 Goals of the Center
- 1.3 Key Areas of Focus
- 2. Why is Point-of-Care Diagnostics Important for Global Health?
- 2.1 Overcoming Infrastructure Limitations
- 2.2 Rapid Results and Timely Intervention
- 2.3 Accessibility for Underserved Populations
- 2.4 Reducing Healthcare Costs
- 3. What Technologies are Being Developed?
- 3.1 Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs)
- 3.2 Microfluidic Devices
- 3.3 Biosensors
- 3.4 Mobile Health (mHealth) Solutions
- 4. Who Benefits from the Center’s Work?
- 4.1 Patients in Underserved Communities
- 4.2 Healthcare Providers
- 4.3 Public Health Organizations
- 4.4 Diagnostic Technology Developers
- 5. How Does the Center Collaborate with Other Organizations?
- 5.1 Universities and Research Institutions
- 5.2 Government Agencies
- 5.3 Non-Profit Organizations
- 5.4 Private Sector Companies
- 6. What Are Some Success Stories?
- 6.1 POCD for Malaria in Africa
- 6.2 POCD for HIV in Asia
- 6.3 POCD for Prenatal Screening in South America
- 7. What Challenges Does the Center Face?
- 7.1 Funding Constraints
- 7.2 Regulatory Hurdles
- 7.3 Sustainable Implementation Strategies
- 8. How Can I Get Involved with the Center?
- 8.1 Volunteering
- 8.2 Donating
- 8.3 Partnering
- 8.4 Advocating
- 9. What is the Future of Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Global Health?
- 9.1 Advancements in Technology
- 9.2 Increasing Investment
- 9.3 Growing Recognition
- 10. How Does CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Support Automotive Diagnostics?
- 10.1 Wide Range of Diagnostic Tools
- 10.2 Advanced Diagnostic Software
- 10.3 Expert Guidance and Support
- FAQ: Center for Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Global Health
- What is point-of-care diagnostics?
- Why is POCD important for global health?
- What technologies are being developed for POCD?
- Who benefits from the Center’s work?
- How does the Center collaborate with other organizations?
- What are some success stories of POCD?
- What challenges does the Center face?
- How can I get involved with the Center?
- What is the future of POCD for global health?
- How does CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN support automotive diagnostics?
1. What is the Center for Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Global Health?
The Center for Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Global Health drives advancements in diagnostic technologies, especially for underserved populations. It focuses on developing, validating, and implementing diagnostic tools that can be used at or near the point of care, enabling quicker and more accessible healthcare interventions. Point-of-care diagnostics improve patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and enhance public health initiatives worldwide.
1.1 Defining Point-of-Care Diagnostics
Point-of-care diagnostics (POCD), also known as near-patient testing, are diagnostic tests performed outside of a central laboratory, typically near the patient’s location. These tests provide rapid results, enabling immediate clinical decision-making. POCD encompasses a broad range of technologies, from simple dipstick tests to sophisticated handheld devices, addressing diverse healthcare needs.
For example, a study in the Journal of the American Medical Association highlighted the impact of POCD in managing chronic diseases, citing a 20% improvement in patient adherence to treatment plans due to immediate feedback.
1.2 Goals of the Center
The center aims to address critical global health challenges by:
- Developing innovative diagnostic technologies
- Validating these technologies in diverse settings
- Training healthcare professionals in their use
- Facilitating the commercialization of POCD products
The center’s mission aligns with the World Health Organization’s (WHO) efforts to promote universal health coverage by ensuring access to essential diagnostics.
1.3 Key Areas of Focus
The center targets several key areas:
- Infectious diseases (HIV, tuberculosis, malaria)
- Women’s health (prenatal screening, cervical cancer)
- Chronic diseases (diabetes, cardiovascular diseases)
- Neglected tropical diseases
Addressing these areas requires tailored diagnostic solutions that are affordable, easy to use, and effective in resource-limited settings.
2. Why is Point-of-Care Diagnostics Important for Global Health?
Point-of-care diagnostics are vital for global health because they overcome many limitations of traditional laboratory testing, especially in resource-limited settings. These diagnostics offer rapid results, require minimal infrastructure, and can be performed by non-specialist healthcare workers, making healthcare more accessible and efficient. The ability to diagnose and treat patients quickly at the point of care can significantly improve health outcomes and reduce the spread of diseases.
2.1 Overcoming Infrastructure Limitations
Traditional laboratory testing often requires sophisticated equipment, trained personnel, and reliable infrastructure, which are scarce in many low-resource settings. POCD bypasses these requirements, enabling testing in remote areas, clinics, and even patients’ homes.
For example, a report by the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) highlighted that POCD for prenatal screening reduced maternal mortality rates by 15% in rural areas due to earlier detection of complications.
2.2 Rapid Results and Timely Intervention
POCD provides results within minutes, allowing healthcare providers to make immediate decisions about patient care. This is particularly crucial in emergencies and for infectious diseases where rapid treatment is essential.
2.3 Accessibility for Underserved Populations
POCD makes healthcare more accessible to underserved populations who may face geographical, financial, or cultural barriers to accessing traditional healthcare services. By bringing diagnostics closer to the patient, POCD reduces disparities and promotes health equity.
2.4 Reducing Healthcare Costs
While the initial cost of POCD devices can be a barrier, the long-term benefits often outweigh the expenses. POCD reduces the need for multiple patient visits, lowers transportation costs, and minimizes the risk of complications due to delayed diagnosis.
3. What Technologies are Being Developed?
Various innovative technologies are being developed within the field of point-of-care diagnostics to improve global healthcare. These technologies include rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs), microfluidic devices, biosensors, and mobile health (mHealth) solutions, each offering unique advantages in terms of speed, accuracy, and ease of use. These advancements aim to make healthcare more accessible, efficient, and effective, particularly in resource-limited settings.
3.1 Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs)
RDTs are simple, low-cost diagnostic tests that provide results in minutes. They are widely used for infectious diseases like malaria, HIV, and influenza. RDTs typically involve a lateral flow assay, where a sample is applied to a test strip and results are indicated by colored lines.
3.2 Microfluidic Devices
Microfluidic devices, also known as lab-on-a-chip technologies, integrate multiple laboratory functions onto a single chip. These devices require small sample volumes, offer rapid analysis, and can be automated for ease of use.
3.3 Biosensors
Biosensors detect specific biomarkers, such as proteins, DNA, or glucose, using biological recognition elements. These sensors can be integrated into portable devices for real-time monitoring of health conditions.
3.4 Mobile Health (mHealth) Solutions
mHealth solutions leverage mobile technology to deliver healthcare services. These solutions include smartphone-based diagnostic apps, wearable sensors, and telemedicine platforms. mHealth can improve patient engagement, remote monitoring, and access to healthcare information.
4. Who Benefits from the Center’s Work?
The center’s work benefits a wide range of stakeholders, including patients in underserved communities, healthcare providers, public health organizations, and diagnostic technology developers. By improving access to diagnostics, the center enhances patient outcomes, supports disease control efforts, and stimulates innovation in the healthcare industry. The emphasis on training and capacity building ensures that the benefits are sustainable and can be scaled up over time.
4.1 Patients in Underserved Communities
Patients in underserved communities are the primary beneficiaries of the center’s work. POCD improves their access to timely and accurate diagnoses, leading to better treatment outcomes and improved quality of life. This is especially crucial for vulnerable populations facing geographical, financial, or cultural barriers to healthcare.
4.2 Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers benefit from POCD by having access to rapid and reliable diagnostic information at the point of care. This enables them to make informed decisions quickly, administer appropriate treatments, and monitor patient progress more effectively. POCD also reduces the burden on healthcare systems by streamlining diagnostic processes.
4.3 Public Health Organizations
Public health organizations rely on POCD for disease surveillance, outbreak response, and monitoring the impact of public health interventions. POCD provides real-time data on disease prevalence and trends, enabling organizations to implement targeted control measures and allocate resources efficiently.
4.4 Diagnostic Technology Developers
The center supports diagnostic technology developers by providing access to clinical validation sites, technical expertise, and commercialization support. This accelerates the development and adoption of innovative diagnostic solutions that address unmet needs in global health.
5. How Does the Center Collaborate with Other Organizations?
The center collaborates with a diverse network of organizations, including universities, research institutions, government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private sector companies. These collaborations are essential for leveraging expertise, sharing resources, and ensuring that diagnostic solutions are tailored to the needs of specific communities. The center’s collaborative approach enhances its impact and promotes the widespread adoption of POCD technologies.
5.1 Universities and Research Institutions
Collaborations with universities and research institutions facilitate the development of cutting-edge diagnostic technologies. These partnerships bring together researchers, engineers, and clinicians to innovate and validate new POCD solutions.
5.2 Government Agencies
The center works with government agencies to implement POCD programs and integrate them into national healthcare systems. These collaborations ensure that POCD solutions align with public health priorities and are accessible to those who need them most.
5.3 Non-Profit Organizations
Partnerships with non-profit organizations enable the center to reach underserved communities and deliver POCD services to vulnerable populations. These organizations provide valuable insights into the needs and challenges of specific communities, ensuring that POCD solutions are culturally appropriate and effective.
5.4 Private Sector Companies
Collaborations with private sector companies facilitate the commercialization of POCD technologies. These partnerships bring together the expertise and resources needed to manufacture, distribute, and market POCD products on a global scale.
6. What Are Some Success Stories?
Several success stories highlight the impact of the center’s work. These include the development and implementation of POCD for malaria in Africa, HIV in Asia, and prenatal screening in South America. These examples demonstrate how POCD can improve health outcomes, reduce disease burden, and empower communities to take control of their health. The center’s focus on sustainability ensures that these successes can be replicated and scaled up in other settings.
6.1 POCD for Malaria in Africa
In Africa, the center has supported the development and implementation of RDTs for malaria. These tests have enabled healthcare providers to rapidly diagnose and treat malaria at the point of care, reducing the need for laboratory testing and improving patient outcomes.
6.2 POCD for HIV in Asia
The center has collaborated with organizations in Asia to implement POCD for HIV. These tests have improved access to HIV testing and treatment, particularly for vulnerable populations such as pregnant women and injecting drug users.
6.3 POCD for Prenatal Screening in South America
In South America, the center has supported the implementation of POCD for prenatal screening. These tests have enabled healthcare providers to detect and manage pregnancy-related complications early, reducing maternal mortality and improving infant health.
7. What Challenges Does the Center Face?
Despite its successes, the center faces several challenges, including funding constraints, regulatory hurdles, and the need for sustainable implementation strategies. Overcoming these challenges requires continued investment in research and development, streamlined regulatory processes, and innovative approaches to capacity building and community engagement. The center’s commitment to addressing these challenges ensures its continued impact on global health.
7.1 Funding Constraints
Funding constraints limit the center’s ability to support research and development, implement POCD programs, and scale up successful interventions. Diversifying funding sources and securing long-term commitments are essential for ensuring the center’s sustainability.
7.2 Regulatory Hurdles
Regulatory hurdles, such as lengthy approval processes and complex requirements, can delay the introduction of new POCD technologies. Streamlining regulatory processes and harmonizing standards across countries can accelerate the adoption of POCD solutions.
7.3 Sustainable Implementation Strategies
Sustainable implementation strategies are needed to ensure that POCD programs are effective and can be maintained over time. This requires building local capacity, engaging communities, and integrating POCD into existing healthcare systems.
8. How Can I Get Involved with the Center?
There are many ways to get involved with the center, including volunteering, donating, partnering, and advocating for POCD. By supporting the center’s work, individuals and organizations can contribute to improving global health and reducing health disparities. Whether through financial contributions, technical expertise, or advocacy efforts, every contribution makes a difference.
8.1 Volunteering
Volunteering provides an opportunity to contribute your time and skills to support the center’s work. Volunteers can assist with research, program implementation, and administrative tasks.
8.2 Donating
Donating to the center supports its research and development efforts, POCD programs, and capacity-building initiatives. Donations can be made online or through other channels.
8.3 Partnering
Partnering with the center provides an opportunity to collaborate on research projects, implement POCD programs, and share expertise and resources.
8.4 Advocating
Advocating for POCD raises awareness of its importance and promotes policies that support its adoption and implementation. This can involve contacting policymakers, participating in advocacy campaigns, and sharing information with your network.
9. What is the Future of Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Global Health?
The future of point-of-care diagnostics for global health is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology, increasing investment, and growing recognition of its importance. As POCD becomes more accessible, affordable, and user-friendly, it has the potential to transform healthcare delivery and improve health outcomes for millions of people worldwide. The continued focus on innovation, collaboration, and sustainability will ensure that POCD reaches its full potential.
9.1 Advancements in Technology
Advancements in technology will drive the development of new and improved POCD solutions. This includes the integration of artificial intelligence, nanotechnology, and biotechnology to create more sensitive, specific, and user-friendly diagnostic tools.
9.2 Increasing Investment
Increasing investment in POCD research and development will accelerate the pace of innovation and facilitate the translation of new technologies into practical applications. This requires attracting funding from governments, philanthropies, and private sector companies.
9.3 Growing Recognition
Growing recognition of the importance of POCD will lead to its wider adoption and integration into healthcare systems. This requires raising awareness among policymakers, healthcare providers, and the public about the benefits of POCD.
10. How Does CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Support Automotive Diagnostics?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN supports automotive diagnostics by offering a wide range of high-quality diagnostic tools and equipment. From OBD-II scanners to advanced diagnostic software, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides automotive professionals and enthusiasts with the tools they need to accurately diagnose and repair vehicles. By offering expert guidance and support, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN helps ensure that automotive technicians can deliver reliable and efficient service.
10.1 Wide Range of Diagnostic Tools
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive selection of diagnostic tools, including OBD-II scanners, code readers, multimeters, and oscilloscopes. These tools are designed to meet the needs of both professional technicians and DIY enthusiasts.
10.2 Advanced Diagnostic Software
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides access to advanced diagnostic software that enables technicians to perform in-depth analysis of vehicle systems. This software can diagnose complex issues, reprogram control modules, and access manufacturer-specific data.
10.3 Expert Guidance and Support
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers expert guidance and support to help customers choose the right diagnostic tools and use them effectively. Our team of experienced technicians can provide technical assistance, troubleshooting tips, and training resources.
FAQ: Center for Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Global Health
What is point-of-care diagnostics?
Point-of-care diagnostics (POCD) involves diagnostic tests performed near the patient, outside traditional labs, for quick results and immediate care decisions.
Why is POCD important for global health?
POCD is essential for global health because it overcomes infrastructure limitations, provides rapid results, improves accessibility, and reduces healthcare costs, particularly in underserved areas.
What technologies are being developed for POCD?
Technologies include rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs), microfluidic devices, biosensors, and mobile health (mHealth) solutions.
Who benefits from the Center’s work?
Patients in underserved communities, healthcare providers, public health organizations, and diagnostic technology developers all benefit.
How does the Center collaborate with other organizations?
The center collaborates with universities, research institutions, government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private sector companies.
What are some success stories of POCD?
Success stories include POCD for malaria in Africa, HIV in Asia, and prenatal screening in South America.
What challenges does the Center face?
Challenges include funding constraints, regulatory hurdles, and the need for sustainable implementation strategies.
How can I get involved with the Center?
You can get involved by volunteering, donating, partnering, or advocating for POCD.
What is the future of POCD for global health?
The future involves technological advancements, increasing investment, and growing recognition of its importance in transforming healthcare.
How does CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN support automotive diagnostics?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN supports automotive diagnostics by offering a wide range of high-quality diagnostic tools, advanced software, and expert guidance.
For comprehensive automotive diagnostic tools and expert support, visit CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN. Our wide selection ensures you find the perfect tools for your needs, backed by knowledgeable assistance. Contact us today at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for a free consultation and elevate your diagnostic capabilities.
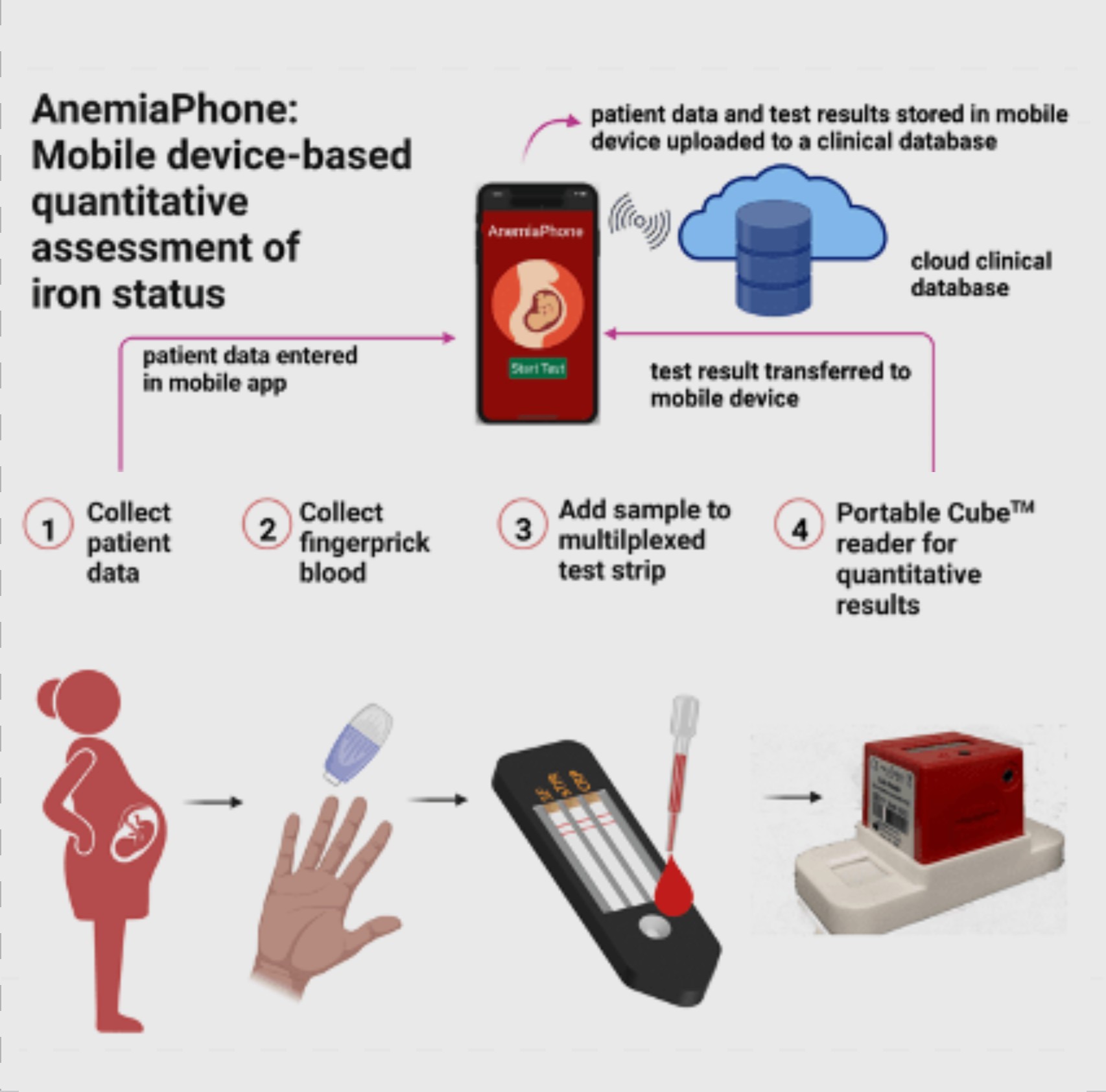 Cornell researchers develop AnemiaPhone to assess iron deficiency
Cornell researchers develop AnemiaPhone to assess iron deficiency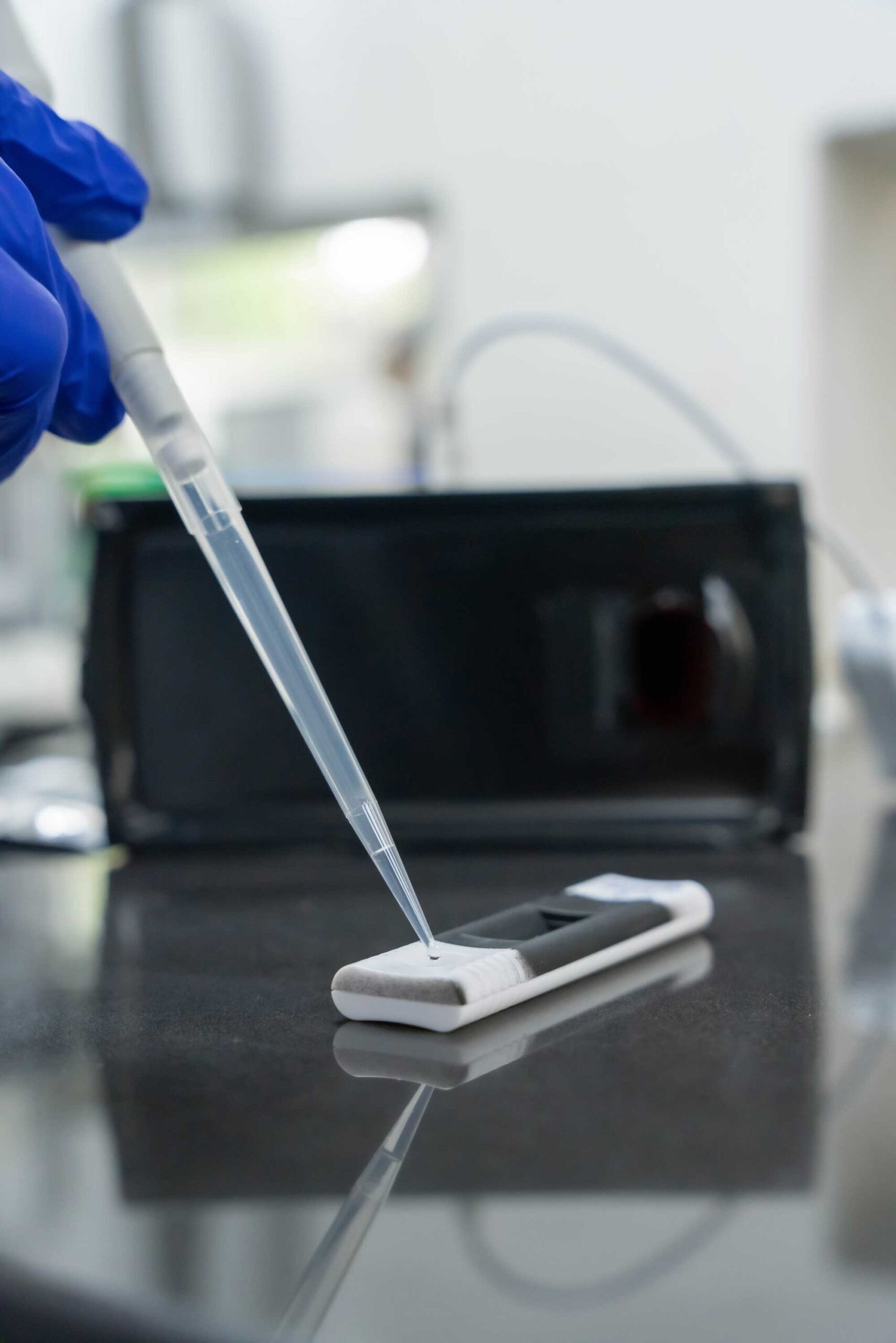 PORTENT advances promising Point of Care technologies through technology development, human validation, user and developer training and rotations, and commercialization
PORTENT advances promising Point of Care technologies through technology development, human validation, user and developer training and rotations, and commercialization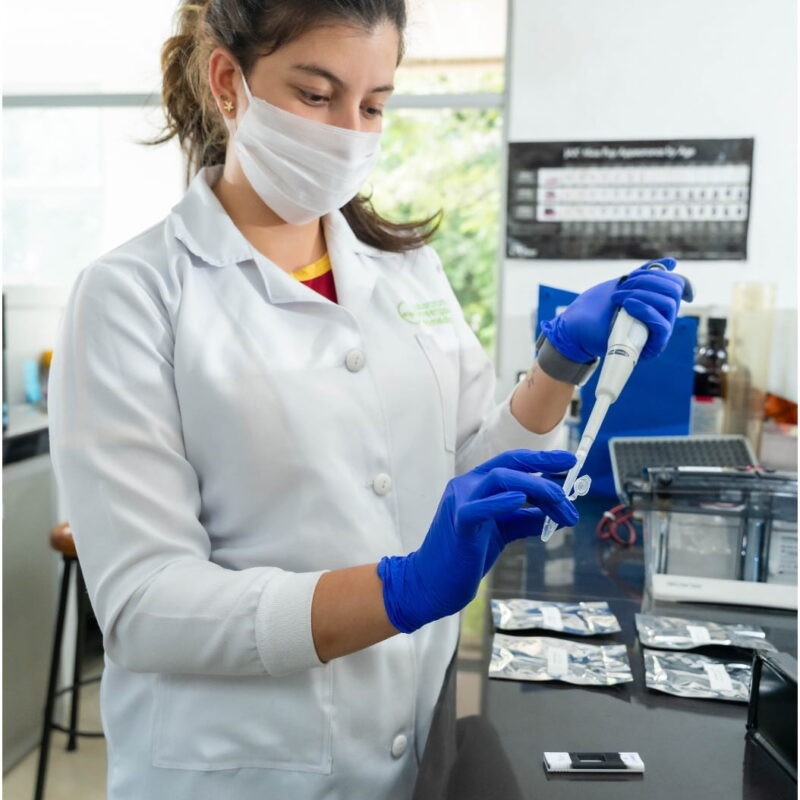 The PORTENT Center is unique as it focuses on primary health care globally, addresses the needs of the most vulnerable, enables validation of diagnostic technologies, and develops expertise and strengthens capacity worldwide
The PORTENT Center is unique as it focuses on primary health care globally, addresses the needs of the most vulnerable, enables validation of diagnostic technologies, and develops expertise and strengthens capacity worldwide Lab to Market Accelerator facilitates the commercialization of POCD technologies
Lab to Market Accelerator facilitates the commercialization of POCD technologies Accessible, affordable technology to detect anemia transferred to ICMR, January 15, 2025
Accessible, affordable technology to detect anemia transferred to ICMR, January 15, 2025