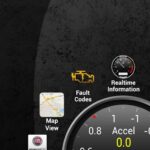
Cell Phone Car Diagnostic tools are revolutionizing vehicle maintenance, offering accessibility and convenience. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN equips you with the knowledge to leverage these tools effectively. By understanding their capabilities and limitations, you can accurately diagnose issues and perform necessary repairs or seek professional help. Discover the freedom of mobile auto diagnostics, empowering you with immediate vehicle insights and promoting informed decisions with the help of CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN. Explore vehicle health monitoring, automotive diagnostic apps and OBD2 scanner apps for iPhone.
Contents
- 1. What is Cell Phone Car Diagnostic?
- 1.1. Core Functions
- 1.2. Hardware Requirements
- 1.3. Benefits of Using Cell Phone Car Diagnostic
- 2. Understanding OBD2 and Its Importance
- 2.1. History and Evolution of OBD
- 2.2. Key Components of the OBD2 System
- 2.3. How OBD2 Works
- 2.4. OBD2 Modes
- 2.5. Impact on Vehicle Maintenance and Repair
- 3. Choosing the Right OBD2 Adapter
- 3.1. Types of OBD2 Adapters
- 3.2. Key Features to Consider
- 3.3. Recommended OBD2 Adapter Brands
- 3.4. Avoiding Cheap Clones
- 3.5. Evaluating Adapter Performance
- 4. Selecting the Right Cell Phone Car Diagnostic App
- 4.1. Popular Diagnostic Apps for iOS and Android
- 4.2. Key Features to Look For
- 4.3. Free vs. Paid Apps
- 4.4. User Interface and Experience
- 4.5. Updates and Support
- 5. Connecting Your Cell Phone to Your Car
- 5.1. Step-by-Step Guide
- 5.2. Troubleshooting Connection Issues
- 5.3. Security Considerations
- 6. Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 6.1. Understanding DTC Structure
- 6.2. Common DTCs and Their Meanings
- 6.3. Using Online Resources to Look Up DTCs
- 6.4. Clearing DTCs
- 6.5. When to Seek Professional Help
- 7. Monitoring Real-Time Sensor Data
- 7.1. Key Sensors to Monitor
- 7.2. Interpreting Sensor Readings
- 7.3. Identifying Potential Problems
- 7.4. Creating Custom Dashboards
- 8. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- 8.1. Mode 06 Testing
- 8.2. Freeze Frame Data
- 8.3. Data Logging and Analysis
- 8.4. Custom PID Support
- 9. Safety Precautions and Best Practices
- 9.1. Avoiding Damage to Your Vehicle
- 9.2. Protecting Your Personal Information
- 9.3. Driving Safely While Diagnosing
- 10. Real-World Applications and Case Studies
- 10.1. Diagnosing a Misfire
- 10.2. Identifying a Vacuum Leak
- 10.3. Troubleshooting Emission Problems
- 10.4. Monitoring Fuel Efficiency
- 11. The Future of Cell Phone Car Diagnostic
- 11.1. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
- 11.2. Enhanced Vehicle Connectivity
- 11.3. Expansion of Supported Vehicles and Systems
- 11.4. The Role of CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 13. Actionable Steps to Get Started
- 14. Call to Action
1. What is Cell Phone Car Diagnostic?
Cell phone car diagnostic involves utilizing your smartphone or tablet with a compatible OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) adapter to read data from your vehicle’s computer. Think of it as having a mechanic’s diagnostic tool right in your pocket. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 systems have been standard on all cars and light trucks sold in the U.S. since 1996, providing a wealth of information about your vehicle’s health.
1.1. Core Functions
Cell phone car diagnostic tools allow you to:
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Identify the cause of the check engine light.
- Clear DTCs: Reset the check engine light after repairs.
- View Real-time Sensor Data: Monitor engine performance, such as coolant temperature, RPM, and fuel trim.
- Perform Emission Readiness Tests: Determine if your vehicle will pass an emissions test.
- Access Vehicle Information: Retrieve VIN, calibration IDs, and other vehicle-specific information.
1.2. Hardware Requirements
To perform cell phone car diagnostic, you’ll need two key components:
- OBD2 Adapter: A device that plugs into your vehicle’s OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard. These adapters communicate with your smartphone via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- Diagnostic App: A software application installed on your smartphone or tablet that interprets the data from the OBD2 adapter.
1.3. Benefits of Using Cell Phone Car Diagnostic
Using cell phone car diagnostic tools offers numerous advantages:
- Cost Savings: Diagnose and potentially fix minor issues yourself, avoiding expensive trips to the mechanic.
- Convenience: Perform diagnostics anytime, anywhere.
- Informed Decision-Making: Understand your vehicle’s condition before taking it to a mechanic, preventing unnecessary repairs.
- Vehicle Health Monitoring: Track performance and identify potential problems early.
- Customization: Customize dashboards and monitor specific parameters relevant to your vehicle.
2. Understanding OBD2 and Its Importance
OBD2 is a standardized system that provides access to data from your vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU). It’s like having a direct line to your car’s brain.
2.1. History and Evolution of OBD
The first OBD systems were introduced in the late 1960s, but they were not standardized. OBD-II was standardized in the mid-1990s, and compliance became mandatory in 1996 in the United States. This standardization ensures that any OBD2-compliant scanner can read data from any OBD2-compliant vehicle, regardless of the manufacturer.
2.2. Key Components of the OBD2 System
- OBD2 Port: The physical connector in your vehicle, usually located under the dashboard.
- ECU (Engine Control Unit): The vehicle’s computer that monitors and controls various engine parameters.
- Sensors: Devices that measure various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and oxygen levels.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Standardized codes that identify specific problems detected by the ECU.
2.3. How OBD2 Works
The OBD2 system works by constantly monitoring various sensors throughout your vehicle. When a sensor reading falls outside of the acceptable range, the ECU stores a DTC and illuminates the check engine light. A diagnostic tool can then read these DTCs to identify the problem area.
2.4. OBD2 Modes
OBD2 systems operate in various modes, each providing specific types of data. Some key modes include:
- Mode 01: Shows current data.
- Mode 03: Shows stored DTCs.
- Mode 04: Clears DTCs and resets the check engine light.
- Mode 06: Shows on-board monitoring test results.
- Mode 07: Shows pending DTCs detected during the current or last driving cycle.
- Mode 09: Shows vehicle information.
2.5. Impact on Vehicle Maintenance and Repair
OBD2 has revolutionized vehicle maintenance by providing mechanics and vehicle owners with a wealth of diagnostic information. This allows for faster and more accurate diagnoses, reducing repair costs and downtime. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), the use of OBD2 scanners has significantly improved the efficiency and accuracy of vehicle repairs.
3. Choosing the Right OBD2 Adapter
Selecting the right OBD2 adapter is crucial for a seamless cell phone car diagnostic experience.
3.1. Types of OBD2 Adapters
- Bluetooth Adapters: These adapters connect wirelessly to your smartphone via Bluetooth. They are generally more affordable and easier to set up.
- Wi-Fi Adapters: Wi-Fi adapters also connect wirelessly but may offer a more stable connection in some cases. They are often preferred for use with iOS devices due to Bluetooth limitations.
- USB Adapters: These adapters connect directly to your laptop or computer via USB. While not ideal for cell phone use, they can be useful for more advanced diagnostics.
3.2. Key Features to Consider
- Compatibility: Ensure the adapter is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model, as well as your smartphone’s operating system (iOS or Android).
- Protocol Support: The adapter should support all OBD2 protocols, including CAN, ISO, PWM, and VPW.
- Speed: A faster adapter will provide real-time data more quickly, which is essential for accurate diagnostics.
- Security: Choose an adapter with robust security features to protect your vehicle’s data from unauthorized access.
- User Reviews: Read reviews from other users to get an idea of the adapter’s reliability and performance.
3.3. Recommended OBD2 Adapter Brands
Several reputable brands offer high-quality OBD2 adapters:
- OBDLink: Known for their fast and reliable adapters, OBDLink offers a range of options for both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity.
- BlueDriver: BlueDriver adapters are praised for their user-friendly app and comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Veepeak: Veepeak offers affordable and reliable adapters that are compatible with a wide range of vehicles and diagnostic apps.
- Carista: Offers advanced diagnostics and customization options for VW, Audi, Skoda, Seat, BMW, Mini and Toyota, Lexus, Scion vehicles
3.4. Avoiding Cheap Clones
Beware of cheap OBD2 adapters sold online, especially those marked as version 2.1. These adapters often have poor build quality, unreliable performance, and may even damage your vehicle’s ECU. It’s best to invest in a reputable brand to ensure a safe and effective diagnostic experience. As noted in a warning from Car Scanner ELM OBD2, some cheap clones can cause unstable engine operation, connection loss, and increased data lag.
3.5. Evaluating Adapter Performance
To evaluate the performance of an OBD2 adapter, consider the following factors:
- Connection Stability: Does the adapter maintain a stable connection with your smartphone and vehicle?
- Data Transfer Rate: How quickly does the adapter transmit data from the vehicle to your smartphone?
- Error Rate: Does the adapter accurately read and interpret DTCs and sensor data?
- Ease of Use: Is the adapter easy to set up and use with your chosen diagnostic app?
4. Selecting the Right Cell Phone Car Diagnostic App
Choosing the right diagnostic app is just as important as selecting the right OBD2 adapter. The app is your interface to your vehicle’s data, so it should be user-friendly, feature-rich, and compatible with your adapter and vehicle.
4.1. Popular Diagnostic Apps for iOS and Android
- Torque Pro (Android): A popular and feature-rich app for Android devices, Torque Pro offers real-time data, DTC reading and clearing, and customizable dashboards.
- OBD Fusion (iOS and Android): OBD Fusion is a versatile app that supports a wide range of vehicles and adapters. It offers real-time data, DTC diagnostics, and advanced features such as data logging and graphing.
- Car Scanner ELM OBD2 (iOS and Android): Car Scanner ELM OBD2 is known for its extensive database of DTC codes and its ability to access manufacturer-specific data.
- BlueDriver (iOS and Android): The BlueDriver app is designed to work with BlueDriver’s proprietary OBD2 adapter. It offers comprehensive diagnostics, including DTC reading and clearing, enhanced diagnostics for specific makes and models, and repair reports.
4.2. Key Features to Look For
- DTC Reading and Clearing: The app should be able to read and clear DTCs, as well as provide detailed descriptions of the codes.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: The app should display real-time data from various sensors, such as coolant temperature, RPM, and fuel trim.
- Customizable Dashboards: The app should allow you to create custom dashboards to monitor the parameters that are most important to you.
- Data Logging and Graphing: The app should be able to log data and create graphs to track vehicle performance over time.
- Emission Readiness Tests: The app should perform emission readiness tests to determine if your vehicle will pass an emissions test.
- Vehicle Information Retrieval: The app should be able to retrieve vehicle information such as VIN, calibration IDs, and ECU information.
- User-Friendly Interface: The app should be easy to navigate and use, even for beginners.
- Compatibility: Ensure the app is compatible with your OBD2 adapter and your vehicle’s make and model.
4.3. Free vs. Paid Apps
Many diagnostic apps offer both free and paid versions. Free versions typically provide basic functionality, such as DTC reading and clearing, while paid versions offer advanced features such as data logging, graphing, and enhanced diagnostics. Consider your needs and budget when choosing between a free and paid app.
4.4. User Interface and Experience
The user interface and experience of a diagnostic app can greatly impact its usability. Look for an app with a clean, intuitive interface that is easy to navigate. The app should also provide clear and concise information about DTCs and sensor data.
4.5. Updates and Support
Choose an app that is regularly updated with new features, bug fixes, and vehicle compatibility updates. The app developer should also provide good customer support in case you encounter any issues.
5. Connecting Your Cell Phone to Your Car
Connecting your cell phone to your car via an OBD2 adapter is a straightforward process.
5.1. Step-by-Step Guide
- Locate the OBD2 Port: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard, near the steering column.
- Plug in the OBD2 Adapter: Plug the OBD2 adapter into the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Pair the Adapter with Your Smartphone:
- Bluetooth Adapters: Go to your smartphone’s Bluetooth settings and search for the OBD2 adapter. Select the adapter and enter the pairing code if prompted (usually “1234” or “0000”).
- Wi-Fi Adapters: Go to your smartphone’s Wi-Fi settings and connect to the Wi-Fi network broadcast by the OBD2 adapter.
- Launch the Diagnostic App: Open your chosen diagnostic app on your smartphone.
- Connect to the Adapter: Within the app, go to the settings menu and select the OBD2 adapter from the list of available devices.
- Start Diagnosing: Once the app is connected to the adapter, you can start reading DTCs, viewing real-time data, and performing other diagnostic functions.
5.2. Troubleshooting Connection Issues
If you encounter connection issues, try the following:
- Ensure the Adapter is Properly Plugged In: Make sure the OBD2 adapter is securely plugged into the OBD2 port.
- Verify Bluetooth/Wi-Fi Connection: Ensure your smartphone is properly connected to the OBD2 adapter via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- Check Adapter Compatibility: Verify that the OBD2 adapter is compatible with your vehicle and smartphone.
- Restart Your Smartphone and Adapter: Sometimes, simply restarting your smartphone and OBD2 adapter can resolve connection issues.
- Update the Diagnostic App: Make sure you have the latest version of the diagnostic app installed on your smartphone.
- Contact Support: If you’re still having trouble, contact the adapter manufacturer or app developer for support.
5.3. Security Considerations
When using an OBD2 adapter, it’s important to be aware of security risks. Some OBD2 adapters may be vulnerable to hacking, which could allow unauthorized access to your vehicle’s systems. To protect your vehicle, choose an adapter from a reputable brand with robust security features, and keep your diagnostic app up to date.
6. Reading and Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Reading and interpreting DTCs is a fundamental aspect of cell phone car diagnostic. DTCs are standardized codes that identify specific problems detected by your vehicle’s ECU.
6.1. Understanding DTC Structure
DTCs consist of five characters:
- First Character: Indicates the system affected:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (airbags, power windows)
- C: Chassis (ABS, suspension)
- U: Network (communication between ECUs)
- Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: Generic (standardized across all manufacturers)
- 1: Manufacturer-specific
- Third Character: Indicates the specific subsystem affected:
- 1: Fuel and air metering
- 2: Fuel and air metering (injector circuit)
- 3: Ignition system
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls
- 5: Vehicle speed control and idle control system
- 6: Computer output system
- 7: Transmission
- 8: Transmission
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Indicate the specific fault within the subsystem.
6.2. Common DTCs and Their Meanings
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
- P0301: Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
6.3. Using Online Resources to Look Up DTCs
Many online resources can help you look up DTCs and their meanings. Some popular resources include:
- OBD-Codes.com: A comprehensive database of OBD2 codes with detailed descriptions, possible causes, and troubleshooting tips.
- AutoCodes.com: Another comprehensive database of OBD2 codes with detailed descriptions and troubleshooting tips.
- Your Vehicle’s Repair Manual: Your vehicle’s repair manual may contain a list of DTCs and their meanings.
6.4. Clearing DTCs
After you have identified and repaired the problem that caused a DTC, you can clear the code using your diagnostic app. To clear a DTC, go to the DTC menu in your app and select the “Clear Codes” option. Keep in mind that clearing a DTC will also reset your vehicle’s emission readiness monitors, so you may need to drive your vehicle for a while before it will pass an emissions test.
6.5. When to Seek Professional Help
While cell phone car diagnostic tools can be useful for diagnosing and fixing minor issues, it’s important to know when to seek professional help. If you’re not comfortable working on your vehicle, or if the DTC indicates a serious problem, it’s best to take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic.
7. Monitoring Real-Time Sensor Data
Monitoring real-time sensor data is another powerful feature of cell phone car diagnostic tools. Real-time data allows you to see how your vehicle’s various systems are performing in real-time, which can help you identify potential problems before they cause a DTC.
7.1. Key Sensors to Monitor
- Coolant Temperature: Indicates the temperature of your engine coolant.
- RPM: Indicates the engine’s revolutions per minute.
- Fuel Trim: Indicates how much the ECU is adjusting the fuel mixture to compensate for lean or rich conditions.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Indicates the oxygen content in the exhaust gas.
- Mass Air Flow (MAF): Indicates the amount of air entering the engine.
- Throttle Position: Indicates the position of the throttle plate.
- Vehicle Speed: Indicates the vehicle’s speed.
7.2. Interpreting Sensor Readings
Interpreting sensor readings requires some knowledge of how your vehicle’s systems work. For example, a high coolant temperature could indicate a problem with the cooling system, while a high fuel trim value could indicate a vacuum leak. Consult your vehicle’s repair manual or online resources to learn more about interpreting sensor readings.
7.3. Identifying Potential Problems
By monitoring real-time sensor data, you can identify potential problems before they cause a DTC. For example, a gradual increase in coolant temperature over time could indicate a developing problem with the cooling system, while erratic oxygen sensor readings could indicate a problem with the oxygen sensors.
7.4. Creating Custom Dashboards
Most diagnostic apps allow you to create custom dashboards to monitor the parameters that are most important to you. This can be useful for tracking vehicle performance, identifying potential problems, and diagnosing issues.
8. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
In addition to reading DTCs and monitoring real-time data, cell phone car diagnostic tools can also be used for more advanced diagnostic techniques.
8.1. Mode 06 Testing
Mode 06 testing allows you to access the results of on-board diagnostic tests performed by your vehicle’s ECU. These tests can provide valuable information about the performance of various systems, such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and evaporative emissions system.
8.2. Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures sensor readings at the moment a DTC is stored. This can be useful for troubleshooting intermittent problems or diagnosing issues that are difficult to reproduce.
8.3. Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging allows you to record sensor data over time, which can be useful for tracking vehicle performance, identifying potential problems, and diagnosing issues. Many diagnostic apps also provide graphing tools to help you analyze the data.
8.4. Custom PID Support
Some diagnostic apps support custom PIDs (Parameter IDs), which allow you to access manufacturer-specific data that is not available through the standard OBD2 interface. This can be useful for diagnosing issues with specific makes and models of vehicles.
9. Safety Precautions and Best Practices
When using cell phone car diagnostic tools, it’s important to follow safety precautions and best practices to avoid damaging your vehicle or injuring yourself.
9.1. Avoiding Damage to Your Vehicle
- Use a Reputable OBD2 Adapter: Avoid cheap OBD2 adapters that may damage your vehicle’s ECU.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Follow the instructions in your diagnostic app and your vehicle’s repair manual carefully.
- Don’t Clear Codes Without Understanding the Problem: Clearing DTCs without understanding the underlying problem can mask symptoms and make it more difficult to diagnose issues in the future.
- Be Careful When Working Under the Hood: Be careful when working under the hood of your vehicle to avoid burns, electrical shocks, and other injuries.
9.2. Protecting Your Personal Information
- Choose a Secure OBD2 Adapter: Choose an OBD2 adapter with robust security features to protect your vehicle’s data from unauthorized access.
- Keep Your Diagnostic App Up to Date: Keep your diagnostic app up to date with the latest security patches.
- Be Careful When Sharing Data: Be careful when sharing data from your diagnostic app, as it may contain personal information about your vehicle and driving habits.
9.3. Driving Safely While Diagnosing
- Don’t Drive While Using Your Smartphone: It’s dangerous to drive while using your smartphone. If you need to monitor real-time data while driving, have a passenger operate the diagnostic app.
- Pull Over if You Need to Investigate a Problem: If you notice a problem while driving, pull over to a safe location before investigating.
10. Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Cell phone car diagnostic tools can be used in a variety of real-world applications to diagnose and fix vehicle problems.
10.1. Diagnosing a Misfire
A misfire occurs when one or more cylinders in your engine fails to fire properly. This can cause rough idling, poor acceleration, and reduced fuel economy. Cell phone car diagnostic tools can be used to diagnose a misfire by reading DTCs such as P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected) and P0301-P0306 (Cylinder 1-6 Misfire Detected). By monitoring real-time data such as RPM and oxygen sensor readings, you can further pinpoint the cause of the misfire.
10.2. Identifying a Vacuum Leak
A vacuum leak occurs when air enters the engine through an unintended source, such as a cracked hose or a faulty gasket. This can cause lean conditions, rough idling, and poor performance. Cell phone car diagnostic tools can be used to identify a vacuum leak by monitoring real-time data such as fuel trim values. A high fuel trim value indicates that the ECU is adding extra fuel to compensate for a lean condition, which could be caused by a vacuum leak.
10.3. Troubleshooting Emission Problems
Emission problems can cause your vehicle to fail an emissions test. Cell phone car diagnostic tools can be used to troubleshoot emission problems by reading DTCs related to the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and evaporative emissions system. By performing emission readiness tests, you can determine if your vehicle will pass an emissions test.
10.4. Monitoring Fuel Efficiency
Cell phone car diagnostic tools can be used to monitor fuel efficiency by tracking real-time data such as fuel consumption, vehicle speed, and engine load. By analyzing this data, you can identify factors that are affecting your fuel economy, such as aggressive driving habits or a malfunctioning sensor.
11. The Future of Cell Phone Car Diagnostic
The future of cell phone car diagnostic is bright, with new technologies and features constantly being developed.
11.1. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are being integrated into diagnostic apps to provide more accurate and personalized diagnostics. These technologies can analyze sensor data, DTCs, and other information to identify potential problems and recommend repairs.
11.2. Enhanced Vehicle Connectivity
As vehicles become more connected, cell phone car diagnostic tools will be able to access even more data and perform more advanced diagnostics. This could include remote diagnostics, over-the-air updates, and predictive maintenance.
11.3. Expansion of Supported Vehicles and Systems
Cell phone car diagnostic tools are expanding to support a wider range of vehicles and systems, including electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
11.4. The Role of CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is committed to providing you with the latest information and resources on cell phone car diagnostic tools. We offer detailed product reviews, how-to guides, and expert advice to help you choose the right tools and use them effectively. We also provide a forum for users to share their experiences and ask questions.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
12.1. What is the best cell phone car diagnostic tool?
The best cell phone car diagnostic tool depends on your needs and budget. Some popular options include OBDLink MX+, BlueDriver, and Veepeak OBDCheck BLE. Consider factors such as compatibility, features, and user reviews when making your decision.
12.2. Is cell phone car diagnostic safe for my vehicle?
Yes, cell phone car diagnostic is generally safe for your vehicle, provided you use a reputable OBD2 adapter and follow safety precautions. Avoid cheap adapters that may damage your vehicle’s ECU.
12.3. Can cell phone car diagnostic replace a professional mechanic?
Cell phone car diagnostic can be a useful tool for diagnosing and fixing minor issues, but it cannot replace a professional mechanic. If you’re not comfortable working on your vehicle, or if the DTC indicates a serious problem, it’s best to take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic.
12.4. What is the check engine light?
The check engine light is a warning light on your dashboard that indicates a problem with your vehicle’s engine or emissions system.
12.5. What does a DTC mean?
A DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Code) is a standardized code that identifies a specific problem detected by your vehicle’s ECU.
12.6. How do I clear a DTC?
You can clear a DTC using your diagnostic app. Go to the DTC menu in your app and select the “Clear Codes” option.
12.7. What is real-time data?
Real-time data is data from your vehicle’s sensors that is displayed in real-time. This can be useful for monitoring vehicle performance and identifying potential problems.
12.8. What is freeze frame data?
Freeze frame data captures sensor readings at the moment a DTC is stored. This can be useful for troubleshooting intermittent problems.
12.9. What is Mode 06 testing?
Mode 06 testing allows you to access the results of on-board diagnostic tests performed by your vehicle’s ECU.
12.10. Where can I buy a cell phone car diagnostic tool?
You can buy cell phone car diagnostic tools online from retailers such as Amazon, or from auto parts stores such as AutoZone and Advance Auto Parts.
13. Actionable Steps to Get Started
Ready to start using cell phone car diagnostic tools? Here are some actionable steps to get started:
- Research and Choose an OBD2 Adapter: Consider factors such as compatibility, features, and user reviews.
- Select a Diagnostic App: Choose an app that is compatible with your adapter and vehicle, and that offers the features you need.
- Connect Your Cell Phone to Your Car: Follow the step-by-step guide in this article to connect your cell phone to your car via the OBD2 adapter.
- Read and Interpret DTCs: Use your diagnostic app to read DTCs and identify any problems with your vehicle.
- Monitor Real-Time Sensor Data: Monitor real-time sensor data to track vehicle performance and identify potential problems.
- Seek Professional Help When Needed: If you’re not comfortable working on your vehicle, or if the DTC indicates a serious problem, take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic.
14. Call to Action
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s health? At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges you face in finding reliable auto parts and tools, comparing prices, and ensuring durability. That’s why we’re here to help.
Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert advice and assistance in selecting the right auto parts and tools for your needs.
Address: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
Let us assist you in finding the best solutions for your auto repair needs, ensuring you get quality, reliability, and value. We offer detailed information on auto parts specifications, tool comparisons, user reviews, and reputable suppliers. Contact us now and experience the CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN difference.