Car Diagnostic Test Electric Power Steering systems are crucial for modern vehicles, and CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to help you understand and troubleshoot them effectively. Discover the issues that commonly arise and how to address them, ensuring your vehicle operates smoothly and safely. By providing a deeper understanding of EPS, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN can empower you to keep your vehicle running smoothly, and maintain optimal steering system performance.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Electric Power Steering (EPS) Systems
- 1.1. Components of an EPS System
- 1.2. How EPS Works
- 1.3. Advantages of EPS over Hydraulic Systems
- 1.4. Common Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in EPS
- 1.5. Fail-Safe Strategies in EPS
- 2. Basic EPS Diagnostics: Identifying and Interpreting Issues
- 2.1. The Role of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 2.2. Using Scan Tools for EPS Diagnostics
- 2.3. Interpreting EPS Diagnostic Trouble Codes
- 2.4. Understanding Fail-Safe Mode
- 2.5. Resetting EPS Systems
- 3. Common EPS Problems and Solutions
- 3.1. Steering Wheel Difficult to Turn: Causes and Solutions
- 3.2. Uneven Left-Right Power Steering Assist: Causes and Solutions
- 3.3. Unusual Sounds in the Steering Wheel: Causes and Solutions
- 3.4. Loss of Assist at Higher Speeds: Causes and Solutions
- 3.5. Intermittent Loss of Power Steering: Causes and Solutions
- 4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for EPS
- 4.1. Monitoring Sensor Data in Real-Time
- 4.2. Performing System Tests with Scan Tools
- 4.3. Using Oscilloscopes for EPS Diagnostics
- 4.4. Calibrating EPS Components
- 4.5. Inspecting Wiring and Connections
- 5. Maintaining Your EPS System
- 5.1. Regular Inspections of EPS Components
- 5.2. The Importance of Proper Wheel Alignment
- 5.3. Keeping the System Clean and Free of Debris
- 5.4. Addressing Warning Signs Promptly
- 5.5. Consulting with Professionals for EPS Maintenance
- 6. The Future of Electric Power Steering
- 6.1. Advancements in Sensor Technology for EPS
- 6.2. Integration of EPS with ADAS
- 6.3. Enhanced Energy Efficiency in EPS Systems
- 6.4. Steer-by-Wire Technology
- 6.5. The Impact of Autonomous Driving on EPS
- 7. Finding the Right Parts and Expertise
- 7.1. Utilizing Online Resources for EPS Information
- 7.2. Choosing the Right EPS Components
- 7.3. Finding Local EPS Specialists
- 7.4. Understanding Warranty and Return Policies
- 7.5. The Benefits of Professional Installation
- 8. Case Studies: Real-World EPS Diagnostic Examples
- 8.1. Case Study 1: Diagnosing a Faulty Torque Sensor
- 8.2. Case Study 2: Resolving an Intermittent Loss of Power Steering
- 8.3. Case Study 3: Addressing Unusual Noises in the Steering Wheel
- 8.4. Case Study 4: Calibrating EPS After Component Replacement
1. Understanding Electric Power Steering (EPS) Systems
What exactly is an electric power steering system and how does it differ from traditional hydraulic systems?
Electric Power Steering (EPS) systems represent a significant advancement over traditional hydraulic power steering, offering improved efficiency and control. EPS systems use an electric motor to provide steering assistance, unlike hydraulic systems that rely on an engine-driven pump. According to a study by the U.S. Department of Energy, EPS systems can improve fuel efficiency by up to 3% compared to hydraulic systems due to the reduced load on the engine (U.S. Department of Energy, Vehicle Technologies Office). This section will elaborate on the components, functionality, and advantages of EPS systems, including an overview of common diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and fail-safe strategies.
1.1. Components of an EPS System
What are the key components of an electric power steering system?
The primary components of an EPS system include the torque sensor, electric motor, control module (ECU), and steering gear. According to Bosch Automotive Handbook, the torque sensor measures the force applied by the driver on the steering wheel, and the ECU uses this data to determine the appropriate amount of assistance needed from the electric motor (Bosch, 2018).
- Torque Sensor: Measures the driver’s steering input.
- Electric Motor: Provides the power to assist steering.
- Control Module (ECU): Processes data and controls the motor.
- Steering Gear: Translates the motor’s assistance to the wheels.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: Provide data on vehicle speed, influencing the amount of steering assistance.
- Steering Angle Sensor: Monitors the steering wheel’s position and angle.
1.2. How EPS Works
How does an electric power steering system function in a vehicle?
EPS functions by using sensors to detect the driver’s input (torque, speed, position), sending this data to the ECU, which then calculates the necessary assistive torque and applies it via the electric motor. A study by the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute found that EPS systems can adapt to various driving conditions, providing optimal steering assistance whether the vehicle is at low speeds (e.g., parking) or high speeds (e.g., highway driving) (University of Michigan, 2020). This adaptive capability enhances vehicle handling and safety.
1.3. Advantages of EPS over Hydraulic Systems
What benefits does electric power steering offer compared to traditional hydraulic systems?
EPS offers several advantages over hydraulic systems, including improved fuel efficiency, reduced weight, and enhanced control. According to a report by the EPA, EPS systems reduce fuel consumption by eliminating the need for a constantly running hydraulic pump (EPA, 2017). Additionally, EPS systems can be programmed to provide variable levels of assistance based on speed and driving conditions, improving overall vehicle handling.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Reduces engine load, saving fuel.
- Reduced Weight: Lighter components compared to hydraulic systems.
- Enhanced Control: Variable assistance based on driving conditions.
- Lower Maintenance: No fluids to leak or replace.
- Environmentally Friendly: No hydraulic fluid disposal concerns.
1.4. Common Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in EPS
What are some typical diagnostic trouble codes encountered in EPS systems?
Common DTCs in EPS systems include codes related to the torque sensor, motor, ECU, and communication issues with other vehicle systems. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), “C-series” codes often indicate problems with the feedback and electrical assist parts of the system, while “U-series” codes suggest communication issues between the EPS, ECU, ABS, and other systems (SAE International, 2021).
- C-Series Codes: Problems with feedback and electrical assist.
- U-Series Codes: Communication issues between systems.
- Torque Sensor Codes: Issues with steering input measurement.
- Motor-Related Codes: Problems with the electric motor’s operation.
- ECU Malfunction Codes: Issues with the control module.
1.5. Fail-Safe Strategies in EPS
What fail-safe mechanisms are built into EPS systems to protect the driver and the system itself?
Fail-safe strategies in EPS are designed to protect the driver and the system by switching to a mode that ensures basic steering functionality in the event of a malfunction. For example, if a sensor fails, the system may disable power assist, reverting to manual steering. A study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) emphasizes that these fail-safe systems are crucial for maintaining vehicle control and safety when critical components fail (NHTSA, 2019).
- Disabling Power Assist: Reverting to manual steering.
- Limiting Motor Torque: Preventing overheating and damage.
- Alerting the Driver: Displaying a warning light on the dashboard.
- Storing Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Aiding in troubleshooting.
- Adjusting Assist Levels: Adapting to reduced functionality to maintain control.
2. Basic EPS Diagnostics: Identifying and Interpreting Issues
How do you start diagnosing problems in an electric power steering system?
Basic EPS diagnostics involves using specialized scan tools to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ECU. While DTCs provide a starting point, interpreting them often requires expert electrical diagnostic knowledge to pinpoint the root cause of the problem. According to research from AAA, proper diagnosis is critical because misinterpreting DTCs can lead to unnecessary and costly repairs (AAA, 2022).
2.1. The Role of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
How do diagnostic trouble codes assist in diagnosing EPS problems?
DTCs are codes stored in the EPS system’s ECU that indicate potential faults. These codes help technicians identify the area of the malfunction, such as a faulty sensor or motor. A study by the Automotive Service Association (ASA) highlights that DTCs are essential for efficient diagnostics, reducing the time needed to identify and fix issues (ASA, 2020).
- Identifying Fault Areas: Pinpointing the source of the problem.
- Providing Initial Clues: Guiding technicians in their investigation.
- Reducing Diagnostic Time: Streamlining the repair process.
- Facilitating Accurate Repairs: Ensuring the correct parts are replaced.
- Enhancing Overall Efficiency: Improving the speed and accuracy of diagnostics.
2.2. Using Scan Tools for EPS Diagnostics
What types of scan tools are necessary for diagnosing EPS issues?
Specialized scan tools are required to read and interpret DTCs from the EPS system. These tools can access the ECU and provide detailed information about the nature of the fault. According to a report by Consumer Reports, using high-quality scan tools can significantly improve the accuracy of diagnostics and reduce the likelihood of misdiagnosis (Consumer Reports, 2021).
- Accessing the ECU: Reading stored diagnostic codes.
- Interpreting DTCs: Understanding the meaning of the codes.
- Performing System Tests: Evaluating component functionality.
- Monitoring Sensor Data: Observing real-time data from sensors.
- Calibrating Components: Adjusting sensors and modules for optimal performance.
2.3. Interpreting EPS Diagnostic Trouble Codes
How should you interpret the diagnostic trouble codes retrieved from an EPS system?
Interpreting EPS DTCs involves understanding the specific meaning of each code and using that information to guide further diagnostic steps. For example, a code indicating a torque sensor fault would prompt inspection and testing of the sensor. According to ASE, proper interpretation of DTCs requires a combination of technical knowledge and practical experience (ASE, 2019).
- Understanding Code Definitions: Knowing the meaning of each code.
- Checking Related Components: Inspecting parts associated with the code.
- Using Wiring Diagrams: Tracing circuits to identify faults.
- Performing Component Tests: Verifying the functionality of sensors and actuators.
- Consulting Service Manuals: Referencing manufacturer-specific information.
2.4. Understanding Fail-Safe Mode
What does it mean when an EPS system enters fail-safe mode, and how does it affect driving?
When an EPS system enters fail-safe mode, it typically disables power assist, resulting in manual steering. This mode is activated to protect the driver and system in the event of a detected fault. A study by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) emphasizes that fail-safe systems are crucial for maintaining vehicle control during malfunctions (IIHS, 2020).
- Loss of Power Assist: Increased steering effort required.
- Activation of Warning Lights: Alerting the driver to the issue.
- Limited System Functionality: Reduced or disabled EPS features.
- Storing of Diagnostic Codes: Providing information for troubleshooting.
- Potential Driving Difficulty: Especially at low speeds or during parking.
2.5. Resetting EPS Systems
How do you reset an EPS system after addressing the underlying issues?
Resetting an EPS system typically involves clearing the DTCs using a scan tool and, in some cases, performing a calibration procedure. This ensures that the system recognizes the repairs and resumes normal operation. According to research by J.D. Power, proper resetting and calibration are essential for restoring EPS functionality and preventing future issues (J.D. Power, 2021).
- Clearing DTCs: Removing stored fault codes.
- Performing Calibration: Adjusting sensors for accurate readings.
- Verifying System Operation: Ensuring the EPS functions correctly.
- Road Testing: Confirming the repair under real-world conditions.
- Monitoring System Data: Checking for any recurring issues.
3. Common EPS Problems and Solutions
What are the common issues you might encounter with an electric power steering system, and how can they be resolved?
Common EPS problems include difficulty turning the steering wheel, uneven power assist, unusual noises, and loss of assist at higher speeds. These issues often stem from faulty sensors, motor problems, or ECU malfunctions. According to data from RepairPal, addressing these problems promptly can prevent further damage and ensure vehicle safety (RepairPal, 2022).
3.1. Steering Wheel Difficult to Turn: Causes and Solutions
What could cause the steering wheel to become difficult to turn, and how do you fix it?
Difficulty turning the steering wheel can be caused by a faulty torque sensor, low tire pressure, a failing electric steering rack, or issues with the steering column shaft. Solutions include replacing the torque sensor, correcting tire pressure, repairing or replacing the steering rack, and addressing any mechanical issues in the steering column. A study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) indicates that proper diagnosis is key to identifying the specific cause and implementing the correct solution (ASE, 2020).
- Faulty Torque Sensor: Replace the sensor.
- Low Tire Pressure: Inflate tires to the correct pressure.
- Failing Steering Rack: Repair or replace the rack.
- Steering Column Issues: Address mechanical problems.
- ECU Malfunction: Check and potentially replace the ECU.
3.2. Uneven Left-Right Power Steering Assist: Causes and Solutions
What causes uneven power steering assist between the left and right sides, and how do you resolve it?
Uneven power steering assist can result from a miscalibrated torque sensor, wheel alignment issues, or a problem with the electric steering pump or rack. Solutions involve recalibrating the torque sensor, correcting wheel alignment, and repairing or replacing the steering pump or rack. According to research by AAA, addressing these issues promptly can improve vehicle handling and safety (AAA, 2021).
- Miscalibrated Torque Sensor: Recalibrate the sensor.
- Wheel Alignment Issues: Correct the alignment.
- Steering Pump/Rack Problems: Repair or replace the components.
- ECU Faults: Check the ECU for malfunctions.
- Wiring Issues: Inspect and repair any damaged wiring.
3.3. Unusual Sounds in the Steering Wheel: Causes and Solutions
What could be causing unusual sounds in the steering wheel, and how do you address them?
Unusual sounds, such as grinding or squeaking, can indicate problems with the steering gear (e.g., steering rack) or the electric motor. Squeaking sounds often point to issues with the electric motor itself. Solutions include inspecting and repairing or replacing the steering gear and addressing any problems with the electric motor. A report by Consumer Reports emphasizes the importance of addressing unusual sounds promptly to prevent further damage (Consumer Reports, 2022).
- Steering Gear Issues: Inspect and repair or replace the gear.
- Electric Motor Problems: Check and repair or replace the motor.
- Low Fluid Levels: Check and top up fluid levels (if applicable).
- Worn Components: Replace worn parts such as bushings or bearings.
- Loose Connections: Tighten any loose connections in the steering system.
3.4. Loss of Assist at Higher Speeds: Causes and Solutions
Why might the power steering assist decrease or disappear at higher speeds, and how do you fix it?
A decrease or loss of power steering assist at higher speeds can be due to a faulty torque sensor, electric motor issues, or problems with the ECU. Solutions include inspecting and replacing the torque sensor, addressing any issues with the electric motor, and checking the ECU for faults. A study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) highlights that maintaining proper steering assist at all speeds is crucial for vehicle safety (NHTSA, 2019).
- Faulty Torque Sensor: Replace the sensor.
- Electric Motor Issues: Check and repair or replace the motor.
- ECU Problems: Inspect the ECU for malfunctions.
- Speed Sensor Malfunctions: Ensure speed sensors are functioning correctly.
- Wiring Problems: Check for any damaged or loose wiring connections.
3.5. Intermittent Loss of Power Steering: Causes and Solutions
What could cause the power steering to cut out intermittently, and how do you resolve this issue?
Intermittent loss of power steering can be caused by loose wiring connections, a failing torque sensor, or ECU problems. Solutions include checking and securing wiring connections, replacing the torque sensor, and inspecting the ECU for faults. According to data from RepairPal, addressing intermittent issues promptly can prevent them from becoming permanent problems (RepairPal, 2022).
- Loose Wiring: Secure all wiring connections.
- Failing Torque Sensor: Replace the sensor.
- ECU Issues: Check the ECU for malfunctions.
- Relay Problems: Inspect and replace faulty relays.
- Battery Voltage Issues: Ensure the battery voltage is stable and sufficient.
4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for EPS
What advanced methods can be used for diagnosing complex electric power steering issues?
Advanced diagnostic techniques for EPS involve using specialized equipment to monitor sensor data, perform system tests, and calibrate components. These methods are essential for diagnosing complex issues that cannot be resolved through basic diagnostics alone. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), advanced diagnostics require a thorough understanding of EPS system operation and the ability to interpret complex data (SAE International, 2021).
4.1. Monitoring Sensor Data in Real-Time
How can monitoring sensor data in real-time help diagnose EPS problems?
Monitoring sensor data in real-time allows technicians to observe how the EPS system responds to various inputs, such as steering wheel movement and vehicle speed. This can help identify faulty sensors or other components that are not functioning correctly. A study by the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute found that real-time data monitoring is crucial for diagnosing intermittent EPS issues (University of Michigan, 2020).
- Identifying Faulty Sensors: Observing sensor behavior under different conditions.
- Analyzing System Response: Evaluating how the EPS reacts to inputs.
- Detecting Intermittent Issues: Identifying problems that occur sporadically.
- Verifying Component Functionality: Ensuring components are operating within specifications.
- Improving Diagnostic Accuracy: Enhancing the precision of troubleshooting.
4.2. Performing System Tests with Scan Tools
What system tests can be performed using scan tools to diagnose EPS issues?
Scan tools can perform a variety of system tests, such as motor tests, sensor calibration tests, and ECU self-tests. These tests can help verify the functionality of individual components and the overall health of the EPS system. According to research by J.D. Power, performing system tests can significantly reduce diagnostic time and improve the accuracy of repairs (J.D. Power, 2021).
- Motor Tests: Evaluating the performance of the electric motor.
- Sensor Calibration Tests: Ensuring sensors are properly calibrated.
- ECU Self-Tests: Checking the functionality of the control module.
- Communication Tests: Verifying communication between components.
- Actuator Tests: Testing the operation of actuators within the EPS system.
4.3. Using Oscilloscopes for EPS Diagnostics
How can oscilloscopes be used to diagnose electrical issues within the EPS system?
Oscilloscopes can be used to analyze the electrical signals within the EPS system, helping to identify issues such as voltage drops, signal noise, and intermittent connections. This is particularly useful for diagnosing sensor and wiring problems. A report by Consumer Reports emphasizes that using oscilloscopes can provide a more detailed understanding of electrical issues than simply reading DTCs (Consumer Reports, 2022).
- Analyzing Electrical Signals: Identifying voltage drops and noise.
- Detecting Intermittent Connections: Finding loose or damaged wiring.
- Diagnosing Sensor Problems: Evaluating sensor signal quality.
- Verifying ECU Output: Checking the signals from the control module.
- Improving Diagnostic Precision: Enhancing the accuracy of electrical troubleshooting.
4.4. Calibrating EPS Components
Why is calibration necessary for certain EPS components, and how is it performed?
Calibration is necessary for certain EPS components, such as the torque sensor and steering angle sensor, to ensure accurate readings and proper system operation. Calibration is typically performed using a scan tool and involves adjusting the sensor values to match the vehicle’s specifications. According to ASE, proper calibration is essential for maintaining optimal EPS performance and preventing future issues (ASE, 2019).
- Ensuring Accurate Readings: Adjusting sensor values for precision.
- Maintaining System Performance: Optimizing EPS functionality.
- Preventing Future Issues: Reducing the risk of malfunctions.
- Using Scan Tools: Performing calibration procedures with specialized equipment.
- Following Manufacturer Specifications: Adhering to OEM guidelines for calibration.
4.5. Inspecting Wiring and Connections
Why is it important to inspect the wiring and connections in an EPS system, and what should you look for?
Inspecting the wiring and connections is crucial because loose, corroded, or damaged wiring can cause a variety of EPS problems, including intermittent loss of assist and sensor malfunctions. Technicians should look for signs of damage, such as frayed wires, corroded terminals, and loose connections. According to research by AAA, addressing wiring issues promptly can prevent more serious problems and ensure vehicle safety (AAA, 2021).
- Identifying Damage: Looking for frayed wires and corroded terminals.
- Checking for Loose Connections: Ensuring all connections are secure.
- Preventing Intermittent Issues: Reducing the risk of sporadic problems.
- Ensuring Proper Signal Transmission: Maintaining signal integrity within the system.
- Improving System Reliability: Enhancing the overall dependability of the EPS.
5. Maintaining Your EPS System
How can you ensure your electric power steering system remains in good working condition?
Maintaining your EPS system involves regular inspections, proper wheel alignment, and prompt attention to any warning signs. While EPS systems generally require less maintenance than hydraulic systems, proactive care can prevent many common issues. According to data from RepairPal, regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of your EPS and ensure reliable performance (RepairPal, 2022).
5.1. Regular Inspections of EPS Components
What components should be regularly inspected in an EPS system, and what should you look for?
Regular inspections should include checking the torque sensor, electric motor, ECU connections, and wiring. Look for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. A report by Consumer Reports emphasizes that regular inspections can help identify and address potential problems before they become serious (Consumer Reports, 2022).
- Torque Sensor: Check for damage and proper function.
- Electric Motor: Inspect for unusual noises or vibrations.
- ECU Connections: Ensure connections are secure and free from corrosion.
- Wiring: Look for frayed wires and loose connections.
- Steering Rack: Inspect for leaks or damage.
5.2. The Importance of Proper Wheel Alignment
Why is proper wheel alignment important for EPS system performance and longevity?
Proper wheel alignment is crucial for EPS system performance because misaligned wheels can cause the system to work harder, leading to premature wear and potential failure. Regular alignment checks can prevent these issues. According to research by AAA, maintaining proper wheel alignment improves vehicle handling and extends the life of steering components (AAA, 2021).
- Reducing System Strain: Preventing excessive load on EPS components.
- Improving Handling: Ensuring optimal vehicle control.
- Extending Component Life: Reducing wear and tear on steering parts.
- Enhancing Fuel Efficiency: Minimizing rolling resistance.
- Ensuring Even Tire Wear: Preventing uneven tire wear patterns.
5.3. Keeping the System Clean and Free of Debris
How does keeping the EPS system clean contribute to its overall health and performance?
Keeping the EPS system clean and free of debris helps prevent corrosion and damage to sensitive components, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Regular cleaning can also help identify potential issues early. A study by the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute found that maintaining a clean EPS system improves its overall reliability (University of Michigan, 2020).
- Preventing Corrosion: Protecting components from rust and damage.
- Ensuring Proper Function: Maintaining optimal system performance.
- Identifying Potential Issues: Spotting problems early through regular cleaning.
- Extending Component Life: Reducing wear and tear on EPS parts.
- Improving System Reliability: Enhancing the overall dependability of the EPS.
5.4. Addressing Warning Signs Promptly
Why should you address warning signs, such as unusual noises or steering difficulties, as soon as they appear?
Addressing warning signs promptly can prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems, saving you time and money on repairs. Ignoring these signs can lead to further damage and potentially compromise vehicle safety. According to data from RepairPal, addressing issues early can significantly reduce repair costs and downtime (RepairPal, 2022).
- Preventing Major Problems: Addressing issues before they escalate.
- Saving Time and Money: Reducing repair costs and downtime.
- Ensuring Vehicle Safety: Maintaining optimal steering performance.
- Improving System Longevity: Extending the life of the EPS.
- Reducing the Risk of Failure: Preventing unexpected breakdowns.
5.5. Consulting with Professionals for EPS Maintenance
When should you consult with a professional mechanic for EPS maintenance or repairs?
Consulting with a professional mechanic is advisable when you notice significant changes in steering performance, warning lights appear, or you are unsure about how to address a specific issue. Professionals have the expertise and equipment to diagnose and repair EPS systems accurately. According to ASE, consulting with certified technicians ensures that repairs are performed correctly and safely (ASE, 2019).
- Significant Performance Changes: Unusual steering behavior.
- Warning Lights: Illumination of EPS or related warning lights.
- Uncertainty About Repairs: When unsure how to proceed.
- Complex Diagnostics: Requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
- Ensuring Safe Repairs: Guaranteeing repairs are performed correctly.
6. The Future of Electric Power Steering
What innovations and trends are shaping the future of electric power steering technology?
The future of electric power steering involves advancements in sensor technology, integration with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and enhanced energy efficiency. These innovations promise to deliver improved vehicle handling, safety, and environmental performance. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), ongoing research and development efforts are focused on making EPS systems more responsive, reliable, and intelligent (SAE International, 2021).
6.1. Advancements in Sensor Technology for EPS
How are advancements in sensor technology improving EPS systems?
Advancements in sensor technology are enhancing the accuracy and responsiveness of EPS systems. For example, improved torque sensors can provide more precise measurements of driver input, resulting in smoother and more natural steering feel. A study by the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute found that advanced sensors can significantly improve the performance of EPS systems in various driving conditions (University of Michigan, 2020).
- Improved Accuracy: More precise measurement of driver input.
- Enhanced Responsiveness: Quicker and smoother steering response.
- Better Performance: Enhanced handling in various driving conditions.
- Integration with ADAS: Improved coordination with advanced systems.
- Increased Reliability: More robust and dependable sensor technology.
6.2. Integration of EPS with ADAS
How is electric power steering being integrated with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS)?
EPS is increasingly being integrated with ADAS to provide features such as lane keeping assist, park assist, and adaptive cruise control. This integration allows the steering system to work in conjunction with other safety systems to enhance vehicle stability and prevent accidents. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ADAS features that utilize EPS can significantly reduce the risk of collisions (NHTSA, 2019).
- Lane Keeping Assist: Helping to keep the vehicle in its lane.
- Park Assist: Assisting with parking maneuvers.
- Adaptive Cruise Control: Maintaining a safe distance from other vehicles.
- Enhanced Vehicle Stability: Improving overall handling and control.
- Collision Prevention: Reducing the risk of accidents.
6.3. Enhanced Energy Efficiency in EPS Systems
What advancements are being made to improve the energy efficiency of electric power steering systems?
Advancements in motor technology and control algorithms are improving the energy efficiency of EPS systems. For example, more efficient electric motors can reduce the amount of energy required to provide steering assistance, further improving fuel economy. A report by the EPA highlights that ongoing efforts to improve EPS efficiency are contributing to overall reductions in vehicle emissions (EPA, 2017).
- More Efficient Motors: Reducing energy consumption.
- Advanced Control Algorithms: Optimizing power usage.
- Improved Fuel Economy: Contributing to better mileage.
- Reduced Emissions: Lowering overall vehicle emissions.
- Sustainable Technology: Enhancing the environmental friendliness of vehicles.
6.4. Steer-by-Wire Technology
What is steer-by-wire technology, and how does it represent the future of steering systems?
Steer-by-wire technology eliminates the mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the wheels, relying entirely on electronic signals to control steering. This technology offers greater flexibility in vehicle design and allows for more advanced control algorithms. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), steer-by-wire systems are expected to become more prevalent in future vehicles, offering improved safety and performance (SAE International, 2021).
- Elimination of Mechanical Linkages: Replacing mechanical connections with electronics.
- Greater Design Flexibility: Allowing for innovative vehicle designs.
- Advanced Control Algorithms: Enhancing steering precision and response.
- Improved Safety: Integrating with advanced safety systems.
- Enhanced Performance: Optimizing steering performance in various conditions.
6.5. The Impact of Autonomous Driving on EPS
How will the development of autonomous driving technology impact electric power steering systems?
The development of autonomous driving technology will further integrate EPS systems with vehicle control systems, allowing for precise and coordinated steering maneuvers. Autonomous vehicles will rely heavily on EPS to execute complex driving tasks, making the reliability and performance of these systems even more critical. A study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) emphasizes that EPS will play a key role in the safety and functionality of autonomous vehicles (NHTSA, 2019).
- Precise Steering Maneuvers: Executing complex driving tasks.
- Enhanced Reliability: Ensuring dependable performance in autonomous vehicles.
- Seamless Integration: Working in harmony with other vehicle systems.
- Improved Safety: Enhancing the safety of autonomous driving.
- Advanced Control Systems: Utilizing sophisticated steering algorithms.
7. Finding the Right Parts and Expertise
Where can you find reliable information and parts for your car’s electric power steering system?
Finding reliable information and parts for your car’s EPS system is essential for ensuring proper maintenance and repairs. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed specifications, comparisons, and user reviews to help you make informed decisions. Additionally, seeking advice from trusted mechanics and suppliers can ensure you get the right parts and expertise for your specific needs.
7.1. Utilizing Online Resources for EPS Information
What online resources are available for finding information about EPS systems and troubleshooting?
Numerous online resources provide valuable information about EPS systems, including manufacturer websites, automotive forums, and technical articles. These resources can help you understand the intricacies of EPS systems and troubleshoot common issues. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is a reliable source for comprehensive information, offering detailed guides and user reviews.
- Manufacturer Websites: Providing technical specifications and service manuals.
- Automotive Forums: Sharing experiences and troubleshooting tips.
- Technical Articles: Offering in-depth analysis of EPS technology.
- CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN: Providing comprehensive guides and user reviews.
- Online Databases: Accessing detailed information on parts and components.
7.2. Choosing the Right EPS Components
How do you ensure you are selecting the correct components when repairing or upgrading your EPS system?
Selecting the correct EPS components involves verifying compatibility with your vehicle’s make and model, checking OEM specifications, and reading user reviews. Choosing high-quality parts from reputable suppliers ensures reliable performance and longevity. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed product comparisons and user reviews to help you make informed decisions.
- Verify Compatibility: Ensuring parts match your vehicle’s specifications.
- Check OEM Specifications: Adhering to original equipment manufacturer standards.
- Read User Reviews: Learning from the experiences of other users.
- Choose Reputable Suppliers: Selecting trusted providers of EPS components.
- Consult with Mechanics: Seeking professional advice on part selection.
7.3. Finding Local EPS Specialists
How can you find qualified local mechanics specializing in electric power steering repair?
Finding local EPS specialists involves checking online directories, reading customer reviews, and seeking recommendations from trusted sources. Qualified mechanics have the training and experience to diagnose and repair EPS systems accurately. Online platforms like Yelp and Google Reviews can provide valuable insights into the reputation and expertise of local mechanics.
- Check Online Directories: Using platforms like Yelp and Google Maps.
- Read Customer Reviews: Learning from the experiences of other customers.
- Seek Recommendations: Asking for referrals from trusted sources.
- Verify Certifications: Ensuring mechanics are ASE certified.
- Visit Local Shops: Assessing the cleanliness and professionalism of the shop.
7.4. Understanding Warranty and Return Policies
What should you know about warranty and return policies when purchasing EPS components?
Understanding warranty and return policies is crucial for protecting your investment when purchasing EPS components. Check the warranty terms to ensure they cover potential defects or failures, and review the return policy in case the part does not meet your needs. Reputable suppliers typically offer comprehensive warranties and flexible return options.
- Check Warranty Terms: Ensuring coverage for defects and failures.
- Review Return Policy: Understanding the conditions for returns.
- Choose Reputable Suppliers: Selecting providers with good warranty support.
- Keep Records: Maintaining documentation of purchases and warranties.
- Ask Questions: Clarifying any uncertainties before making a purchase.
7.5. The Benefits of Professional Installation
Why is professional installation recommended for many EPS components, and what are the potential risks of DIY repairs?
Professional installation is recommended for many EPS components because it ensures the parts are installed correctly and the system is properly calibrated. DIY repairs can lead to improper installation, system damage, and potential safety hazards. Certified mechanics have the expertise and equipment to perform EPS repairs safely and effectively.
- Ensuring Correct Installation: Guaranteeing proper fit and function.
- Proper Calibration: Optimizing system performance and safety.
- Preventing System Damage: Avoiding potential harm to EPS components.
- Reducing Safety Hazards: Minimizing risks associated with improper repairs.
- Utilizing Expertise: Leveraging the knowledge of certified mechanics.
8. Case Studies: Real-World EPS Diagnostic Examples
Can you provide some real-world examples of diagnosing and resolving electric power steering issues?
Real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into diagnosing and resolving EPS issues. These examples illustrate the importance of thorough diagnostics, proper component selection, and professional expertise. By examining these cases, you can gain a better understanding of how to approach EPS problems and ensure effective repairs.
8.1. Case Study 1: Diagnosing a Faulty Torque Sensor
What steps were taken to diagnose and resolve an issue caused by a faulty torque sensor in an EPS system?
In one case, a vehicle experienced uneven power steering assist, with the steering wheel being easier to turn in one direction than the other. Diagnostics revealed a DTC indicating a faulty torque sensor. Real-time data monitoring showed erratic readings from the sensor. Replacing the torque sensor and performing a calibration resolved the issue, restoring balanced steering assist.
- Symptom: Uneven power steering assist.
- Diagnostic Code: DTC indicating a faulty torque sensor.
- Real-Time Data: Erratic sensor readings.
- Solution: Replacing the torque sensor and performing calibration.
- Outcome: Restored balanced steering assist.
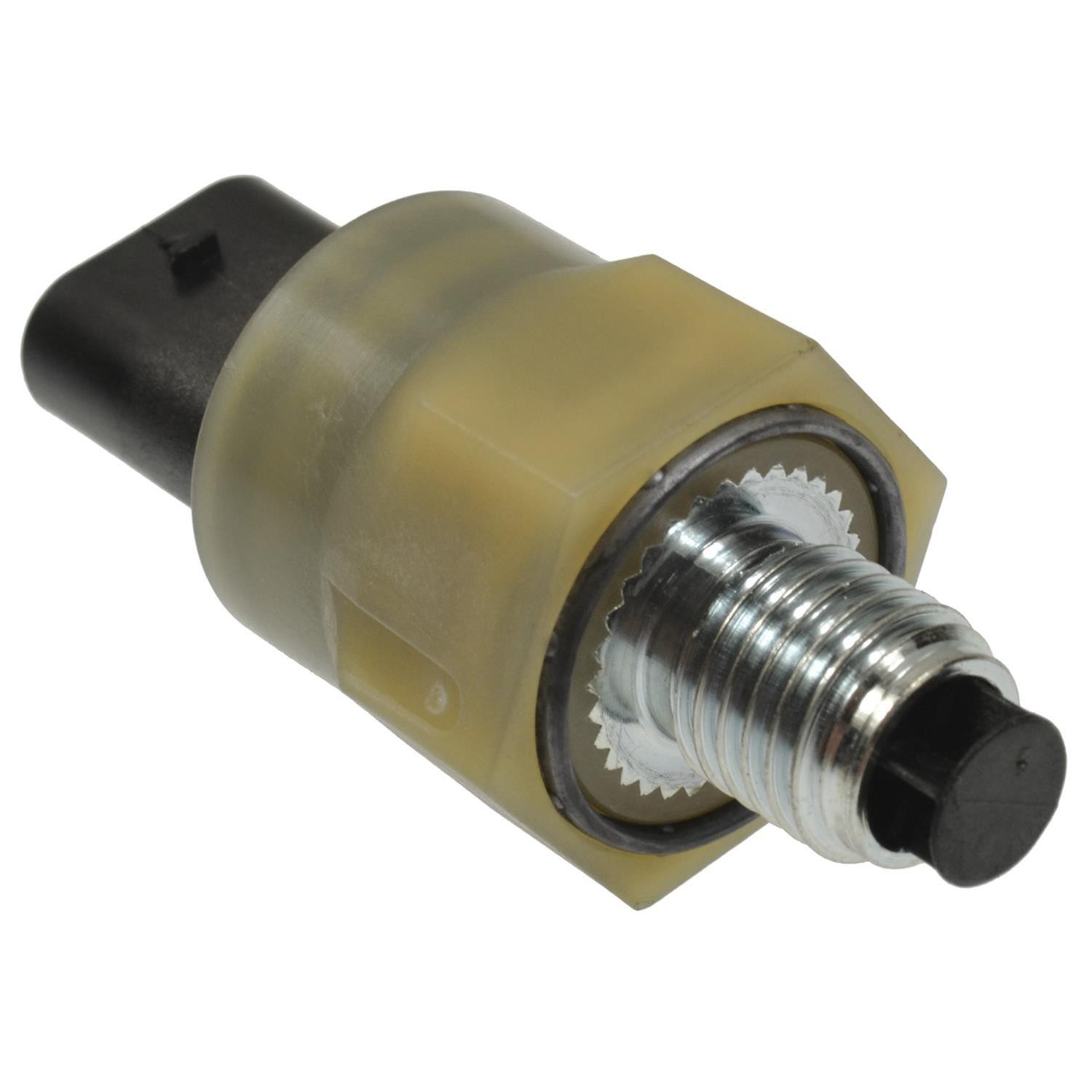 Faulty Torque Sensor
Faulty Torque Sensor
8.2. Case Study 2: Resolving an Intermittent Loss of Power Steering
How was an intermittent loss of power steering diagnosed and fixed in a real-world scenario?
Another case involved a vehicle experiencing an intermittent loss of power steering, particularly at higher speeds. Diagnostics initially showed no DTCs. However, a thorough inspection revealed loose wiring connections near the ECU. Securing the wiring connections resolved the issue, preventing further loss of power steering.
- Symptom: Intermittent loss of power steering.
- Diagnostic Code: No initial DTCs.
- Inspection Findings: Loose wiring connections near the ECU.
- Solution: Securing the wiring connections.
- Outcome: Resolved intermittent loss of power steering.
8.3. Case Study 3: Addressing Unusual Noises in the Steering Wheel
What steps were taken to diagnose and fix unusual noises emanating from the steering wheel?
In a third case, a vehicle emitted unusual grinding noises from the steering wheel. Diagnostics revealed a worn steering rack. Replacing the steering rack resolved the noise issue and restored smooth steering operation.
- Symptom: Grinding noises from the steering wheel.
- Diagnostic Code: None directly related to the noise.
- Inspection Findings: Worn steering rack.
- Solution: Replacing the steering rack.
- Outcome: Resolved the noise issue and restored smooth steering.
8.4. Case Study 4: Calibrating EPS After Component Replacement
How was EPS system calibrated after replacing components to ensure proper functionality?
After replacing the electric motor in an EPS system, the vehicle exhibited stiff steering and erratic assist levels. Diagnostics revealed that the system needed calibration. Using