Car Diagnostic Pc Software is essential for modern automotive repair, offering capabilities to quickly identify and resolve vehicle issues. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides detailed information to help technicians and shop owners find the best solutions. Dive into our guide to explore how the right diagnostic software can revolutionize your repair process, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Contents
- 1. What is Car Diagnostic PC Software?
- 1.1. Why is Car Diagnostic PC Software Important?
- 1.2. Who Benefits from Car Diagnostic PC Software?
- 1.3. What are the Key Features of Car Diagnostic PC Software?
- 2. Understanding the Different Types of Car Diagnostic PC Software
- 2.1. OEM Diagnostic Software
- 2.2. Aftermarket Diagnostic Software
- 2.3. Cloud-Based Diagnostic Software
- 3. Key Features to Look for in Car Diagnostic PC Software
- 3.1. Vehicle Coverage
- 3.2. Diagnostic Functions
- 3.3. User Interface and Ease of Use
- 3.4. Data Logging and Reporting
- 3.5. Update Frequency and Support
- 3.6. Bi-Directional Control Capabilities
- 4. Top Car Diagnostic PC Software Options
- 4.1. OBDwiz
- 4.2. AutoEnginuity ScanTool
- 4.3. Snap-on Diagnostic Software
- 5. How to Choose the Right Car Diagnostic PC Software
- 5.1. Assess Your Needs
- 5.2. Set a Budget
- 5.3. Evaluate Vehicle Coverage and Compatibility
- 5.4. Consider Diagnostic Functions
- 5.5. Assess User Interface and Ease of Use
- 5.6. Check for Data Logging and Reporting
- 5.7. Evaluate Update Frequency and Support
- 6. Step-by-Step Guide to Using Car Diagnostic PC Software
- 6.1. Connect the Diagnostic Tool
- 6.2. Launch the Software and Select Vehicle Information
- 6.3. Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 6.4. Interpret the DTCs
- 6.5. View Live Data
- 6.6. Perform Bi-Directional Tests
- 6.7. Analyze the Data and Perform Repairs
- 6.8. Generate a Report
- 7. Maintenance and Updates for Car Diagnostic PC Software
- 7.1. Regularly Update the Software
- 7.2. Keep Your PC Clean and Optimized
- 7.3. Back Up Your Data
- 7.4. Calibrate Your Diagnostic Tool
- 7.5. Protect Your Equipment
- 8. Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
- 8.1. Software Won’t Connect to Vehicle
- 8.2. Inaccurate Data Readings
- 8.3. Software Freezes or Crashes
- 8.4. Trouble Codes Not Displaying
- 9. The Future of Car Diagnostic PC Software
- 9.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 9.2. Internet of Things (IoT)
- 9.3. Augmented Reality (AR)
- 10. FAQs About Car Diagnostic PC Software
- 10.1. What is OBD-II and Why is it Important?
- 10.2. Can I Use Car Diagnostic PC Software on Any Vehicle?
- 10.3. What is the Difference Between OEM and Aftermarket Diagnostic Software?
- 10.4. How Often Should I Update My Car Diagnostic PC Software?
- 10.5. What is Bi-Directional Control and Why is it Important?
- 10.6. What are PIDs and How are They Used in Car Diagnostics?
- 10.7. How Do I Interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)?
- 10.8. What is Freeze Frame Data and How is it Useful?
- 10.9. Can I Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Myself?
- 10.10. Where Can I Get Technical Support for My Car Diagnostic PC Software?
1. What is Car Diagnostic PC Software?
Car diagnostic PC software is a specialized tool that connects to a vehicle’s onboard computer system (ECU) to read and interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), sensor data, and other vital information. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), the use of diagnostic software can reduce diagnostic time by up to 60%. This software allows technicians to quickly identify problems, understand their root causes, and perform necessary repairs with precision. It’s like having an expert mechanic available for every vehicle that enters your shop.
1.1. Why is Car Diagnostic PC Software Important?
Car diagnostic PC software is important because it enables automotive technicians to accurately and efficiently diagnose vehicle issues. Modern vehicles are equipped with complex electronic systems. A report by the Auto Care Association indicates that electronics account for over 40% of the cost of new vehicles, highlighting the increasing complexity. Diagnostic software provides real-time data and detailed insights, ensuring accurate diagnoses. This accuracy reduces the likelihood of misdiagnosis, saving both time and money.
1.2. Who Benefits from Car Diagnostic PC Software?
Car diagnostic PC software benefits various professionals and enthusiasts:
- Automotive Technicians: Enhances diagnostic accuracy and speed, leading to faster repairs.
- Service Advisors: Improves communication with customers by providing clear explanations of vehicle issues.
- Shop Owners/Managers: Increases shop efficiency, reduces downtime, and improves customer satisfaction, boosting profitability.
- Car Enthusiasts: Allows personal vehicle maintenance and monitoring, saving money on professional diagnostics.
1.3. What are the Key Features of Car Diagnostic PC Software?
The key features of car diagnostic PC software include:
- DTC Reading and Clearing: Reads and clears diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) to identify and resolve issues.
- Real-Time Data Streaming: Provides live sensor data for comprehensive vehicle monitoring.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures data snapshots when a DTC is set, aiding in pinpointing the problem.
- Bi-Directional Control: Enables active testing of components to verify functionality.
- Vehicle Information Display: Shows important vehicle data like VIN, calibration ID, and ECU information.
- Reporting and Data Logging: Generates detailed diagnostic reports and logs data for analysis.
- Customizable Dashboards: Allows users to create personalized displays for monitoring specific parameters.
 OBDwiz Custom Dashboards
OBDwiz Custom Dashboards
2. Understanding the Different Types of Car Diagnostic PC Software
Understanding the different types of car diagnostic PC software is crucial for selecting the right tool for your needs. These tools range from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic systems.
2.1. OEM Diagnostic Software
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) diagnostic software is designed by vehicle manufacturers for their specific makes and models. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), OEM software provides the most comprehensive diagnostic capabilities for a particular brand.
- Pros:
- Comprehensive Coverage: Provides in-depth diagnostics for specific vehicle brands.
- Advanced Functions: Supports advanced functions like ECU programming and module calibration.
- Up-to-Date Information: Includes the latest updates and technical service bulletins (TSBs).
- Cons:
- High Cost: Can be expensive, requiring subscriptions and specialized hardware.
- Limited Compatibility: Only works with specific vehicle brands.
- Complexity: May require extensive training to use effectively.
2.2. Aftermarket Diagnostic Software
Aftermarket diagnostic software is developed by third-party companies and offers broader compatibility across various vehicle makes and models. A report by IBISWorld indicates that the aftermarket automotive software industry is growing, driven by the increasing complexity of vehicles.
- Pros:
- Wide Compatibility: Supports a wide range of vehicle makes and models.
- Cost-Effective: Generally more affordable than OEM software.
- User-Friendly Interface: Often designed with ease of use in mind.
- Cons:
- Limited Functionality: May not offer the same depth of diagnostics as OEM software.
- Variable Quality: Quality can vary significantly between different brands.
- Update Dependency: Requires regular updates to maintain compatibility with new vehicles.
2.3. Cloud-Based Diagnostic Software
Cloud-based diagnostic software stores data and runs applications on remote servers, offering accessibility from various devices. A study by Grand View Research projects significant growth in the cloud-based automotive diagnostic market, driven by increasing demand for remote diagnostics and data analytics.
- Pros:
- Accessibility: Can be accessed from any device with an internet connection.
- Automatic Updates: Software updates are automatically installed.
- Data Storage: Diagnostic data is stored securely in the cloud.
- Cons:
- Internet Dependency: Requires a stable internet connection.
- Security Concerns: Potential security risks associated with cloud data storage.
- Subscription Costs: Typically involves ongoing subscription fees.
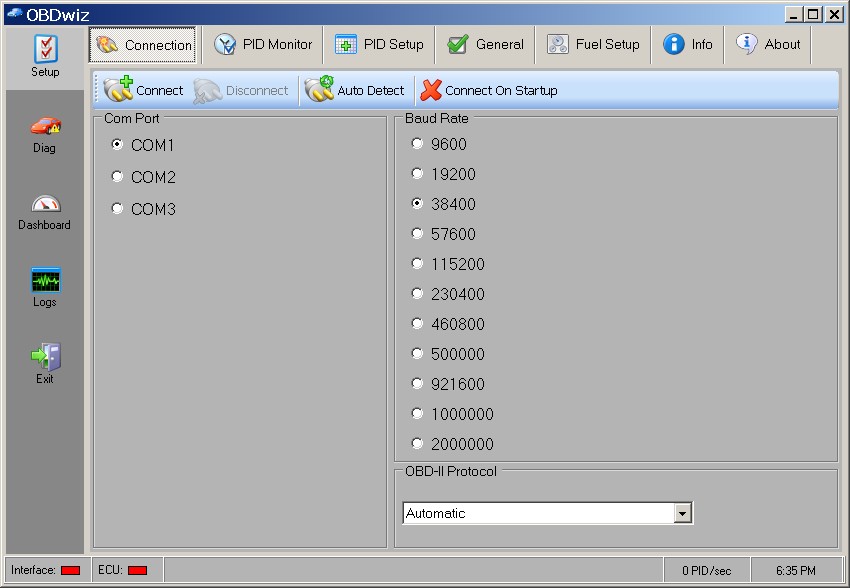 OBDwiz Connection Tab
OBDwiz Connection Tab
3. Key Features to Look for in Car Diagnostic PC Software
When selecting car diagnostic PC software, several key features can significantly impact its usability and effectiveness. Focus on these features to ensure you choose the best tool for your needs.
3.1. Vehicle Coverage
Vehicle coverage refers to the range of makes and models that the software supports. According to a report by the Auto Care Association, shops that service a wide range of vehicles need diagnostic tools with extensive coverage.
- Importance: Ensures you can diagnose a variety of vehicles that come into your shop.
- Considerations: Check the software’s vehicle compatibility list to ensure it covers the makes and models you frequently service.
- Example: Software that supports both domestic, Asian, and European vehicles provides broader coverage.
3.2. Diagnostic Functions
Diagnostic functions include the software’s ability to read and clear DTCs, perform bi-directional tests, and access live data. A study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) highlights the importance of advanced diagnostic functions for accurate troubleshooting.
- Importance: Enables comprehensive vehicle diagnostics and accurate identification of issues.
- Considerations: Look for software that offers a wide range of diagnostic functions, including ABS, SRS, and transmission diagnostics.
- Example: Bi-directional control allows you to activate components like fuel injectors or relays to verify their functionality.
3.3. User Interface and Ease of Use
The user interface (UI) should be intuitive and easy to navigate. A user-friendly interface can significantly reduce diagnostic time and minimize errors.
- Importance: Simplifies the diagnostic process and reduces the learning curve.
- Considerations: Look for software with clear menus, easy-to-read data displays, and customizable dashboards.
- Example: Software with a touchscreen-friendly interface and customizable layouts enhances usability.
3.4. Data Logging and Reporting
Data logging and reporting features allow you to record diagnostic data for later analysis and generate reports for customers. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, data-driven insights are crucial for improving automotive repair processes.
- Importance: Facilitates in-depth analysis and provides documentation for repairs.
- Considerations: Ensure the software can log data in a standard format (e.g., CSV) and generate detailed reports with vehicle information, DTCs, and diagnostic findings.
- Example: The ability to plot multiple engine parameters on the same screen or log them for playback in a spreadsheet program enhances data analysis.
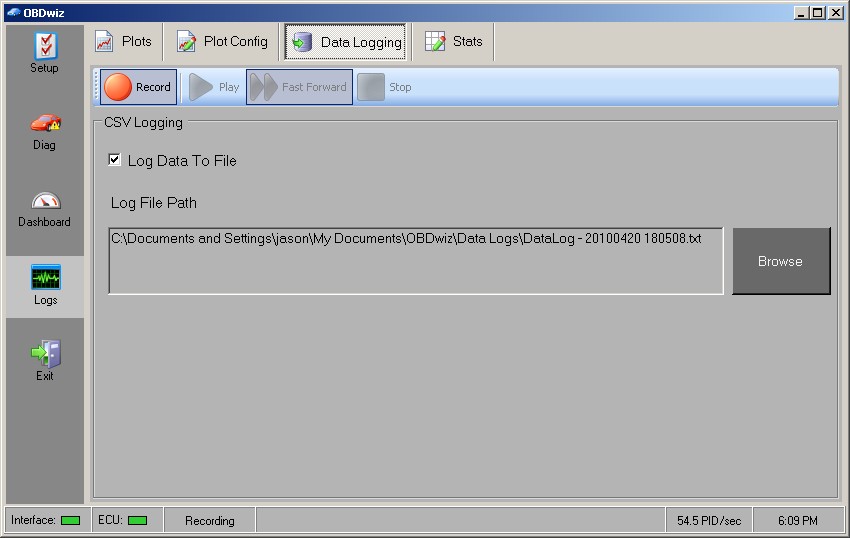 OBDwiz Data Logging
OBDwiz Data Logging
3.5. Update Frequency and Support
Regular software updates are essential to maintain compatibility with new vehicles and access the latest diagnostic information. Reliable technical support is also crucial for resolving any issues that may arise.
- Importance: Keeps the software current and ensures you can diagnose the latest vehicles.
- Considerations: Check the update frequency and the availability of technical support.
- Example: Software that offers free, unlimited updates and comprehensive technical support ensures long-term usability.
3.6. Bi-Directional Control Capabilities
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s control modules to test components and systems. This is essential for accurate diagnostics and verifying repairs.
- Importance: Enables active testing of components, verifying their functionality and ensuring proper operation.
- Considerations: Look for software that supports a wide range of bi-directional tests, such as injector activation, ABS pump cycling, and EVAP system testing.
- Example: Activating the fuel pump relay to verify its operation or commanding the EGR valve to open and close.
4. Top Car Diagnostic PC Software Options
Choosing the right car diagnostic PC software can significantly improve your diagnostic capabilities and efficiency. Here are some of the top options available:
4.1. OBDwiz
OBDwiz is a comprehensive automotive diagnostic software included with every ScanTool.net PC-based scan tool. It’s known for its user-friendly interface and robust features.
- Key Features:
- Compatible with all PC-based scan tools from ScanTool.net.
- Supports all OBD-II compliant vehicles, including EOBD and JOBD.
- Customizable dashboards and real-time plotting of PID values.
- Data logging to CSV format and diagnostic trouble code reading and clearing.
- Displays vehicle information, including VIN number and calibration ID.
- Pros:
- Easy to install and use.
- Packed with features for comprehensive diagnostics.
- Offers free, unlimited updates.
- Cons:
- Primarily designed for use with ScanTool.net scan tools.
- Pricing: Included with ScanTool.net PC-based scan tools.
- Why Choose OBDwiz?: OBDwiz is a great choice for those who already own or plan to purchase a ScanTool.net scan tool. Its ease of use and comprehensive features make it suitable for both beginners and experienced technicians.
4.2. AutoEnginuity ScanTool
AutoEnginuity ScanTool is a powerful PC-based diagnostic tool known for its extensive vehicle coverage and advanced capabilities.
- Key Features:
- Extensive vehicle coverage, supporting a wide range of makes and models.
- Advanced diagnostic functions, including bi-directional controls and system tests.
- Customizable interface and data logging capabilities.
- Available enhanced interfaces for specific vehicle brands.
- Pros:
- Comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Wide vehicle coverage.
- Detailed reporting and data analysis.
- Cons:
- Higher cost compared to some other options.
- May require additional enhanced interfaces for specific functions.
- Pricing: Varies depending on the vehicle coverage and enhanced interfaces selected.
- Why Choose AutoEnginuity ScanTool?: AutoEnginuity ScanTool is ideal for professional technicians who need a versatile and powerful diagnostic tool with extensive vehicle coverage.
4.3. Snap-on Diagnostic Software
Snap-on is a well-known brand in the automotive industry, and their diagnostic software is highly regarded for its performance and reliability.
- Key Features:
- Comprehensive vehicle coverage and advanced diagnostic functions.
- User-friendly interface with intuitive navigation.
- Integrated access to technical information and repair procedures.
- Regular software updates to support new vehicles and features.
- Pros:
- Trusted brand with a reputation for quality.
- Powerful diagnostic capabilities.
- Excellent technical support and training resources.
- Cons:
- High cost.
- Requires a Snap-on diagnostic scan tool.
- Pricing: Requires purchase of a Snap-on diagnostic scan tool and subscription to software updates.
- Why Choose Snap-on Diagnostic Software?: Snap-on diagnostic software is a top choice for professional technicians who demand the best performance and reliability. Its integration with Snap-on scan tools and access to technical information make it a comprehensive diagnostic solution.
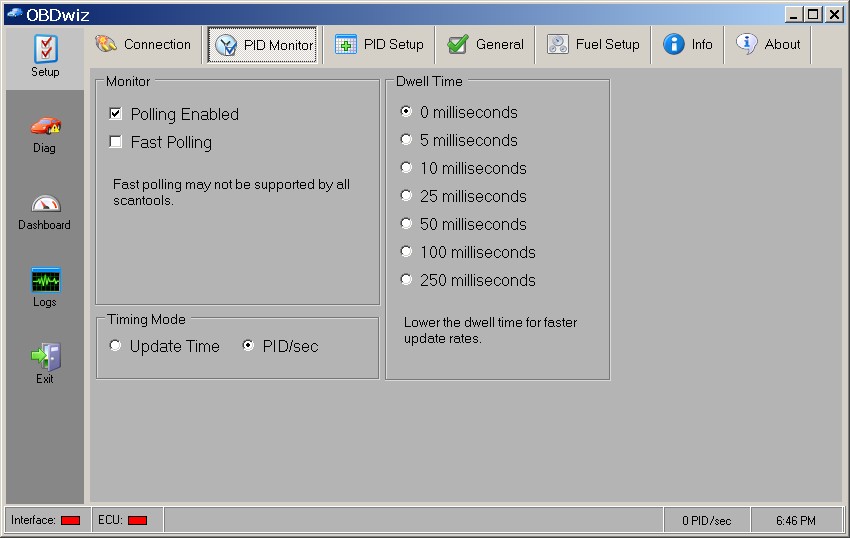 OBDwiz PID Monitor
OBDwiz PID Monitor
5. How to Choose the Right Car Diagnostic PC Software
Choosing the right car diagnostic PC software involves evaluating your specific needs, budget, and the types of vehicles you service. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make the best decision.
5.1. Assess Your Needs
Start by identifying your diagnostic needs.
- Considerations:
- Types of Vehicles: Determine the makes and models you service most frequently.
- Diagnostic Requirements: Identify the diagnostic functions you need, such as reading and clearing DTCs, bi-directional controls, and advanced system testing.
- User Skill Level: Evaluate your technical expertise and choose software that matches your skill level.
- Example: If you specialize in European vehicles, you’ll need software with extensive coverage for brands like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Audi.
5.2. Set a Budget
Establish a budget for your diagnostic software. Prices can range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand, depending on the features and vehicle coverage.
- Considerations:
- Initial Cost: Consider the upfront cost of the software and any required hardware.
- Subscription Fees: Factor in ongoing subscription fees for software updates and support.
- Return on Investment: Evaluate the potential return on investment by considering how the software will improve efficiency and reduce diagnostic time.
- Example: A shop owner might invest in a higher-priced diagnostic system if it significantly reduces diagnostic time and increases customer satisfaction.
5.3. Evaluate Vehicle Coverage and Compatibility
Ensure the software covers the makes and models you service.
- Considerations:
- Vehicle Compatibility List: Check the software’s vehicle compatibility list to ensure it supports the vehicles you work on.
- OBD-II Compliance: Verify that the software is compatible with OBD-II standards.
- Specialty Vehicles: If you work on specialty vehicles like hybrids or EVs, ensure the software supports these vehicles.
- Example: A technician working on a variety of vehicles will need software with broad vehicle coverage, including domestic, Asian, and European models.
5.4. Consider Diagnostic Functions
Ensure the software offers the diagnostic functions you need.
- Considerations:
- Basic Functions: Ensure the software can read and clear DTCs, display live data, and access freeze frame information.
- Advanced Functions: Look for software with bi-directional controls, system tests, and ECU programming capabilities.
- Specific System Diagnostics: Ensure the software supports diagnostics for specific systems, such as ABS, SRS, and transmission.
- Example: A technician specializing in engine performance will need software with advanced functions for fuel system diagnostics, ignition system testing, and emissions control.
5.5. Assess User Interface and Ease of Use
Choose software with an intuitive and user-friendly interface.
- Considerations:
- Menu Navigation: Look for software with clear menus and easy navigation.
- Data Display: Ensure the software displays data in a clear and easy-to-understand format.
- Customization Options: Consider software that allows you to customize the interface and create personalized dashboards.
- Example: A technician who is new to diagnostic software will benefit from an intuitive interface with step-by-step instructions and helpful prompts.
5.6. Check for Data Logging and Reporting
Ensure the software can log data and generate reports for analysis and customer communication.
- Considerations:
- Data Logging Format: Ensure the software can log data in a standard format like CSV.
- Reporting Capabilities: Look for software that can generate detailed reports with vehicle information, DTCs, and diagnostic findings.
- Report Customization: Consider software that allows you to customize reports with your shop’s logo and contact information.
- Example: A shop owner can use data logging and reporting to track diagnostic trends, identify common issues, and improve repair processes.
5.7. Evaluate Update Frequency and Support
Check the frequency of software updates and the availability of technical support.
- Considerations:
- Update Frequency: Look for software with regular updates to support new vehicles and features.
- Technical Support: Ensure the vendor offers reliable technical support through phone, email, or online resources.
- Training Resources: Consider software that includes training resources like tutorials, videos, and user manuals.
- Example: A technician working on new vehicles will need software with frequent updates to stay current with the latest diagnostic information and repair procedures.
6. Step-by-Step Guide to Using Car Diagnostic PC Software
Using car diagnostic PC software effectively involves a systematic approach to ensure accurate and efficient diagnostics. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get the most out of your diagnostic tool.
6.1. Connect the Diagnostic Tool
- Step 1: Locate the OBD-II port in the vehicle. It is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Step 2: Plug the diagnostic tool into the OBD-II port.
- Step 3: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position, but do not start the engine.
6.2. Launch the Software and Select Vehicle Information
- Step 1: Open the car diagnostic PC software on your computer.
- Step 2: Select the vehicle make, model, and year from the software’s menu.
- Step 3: Verify the vehicle information to ensure it is correct.
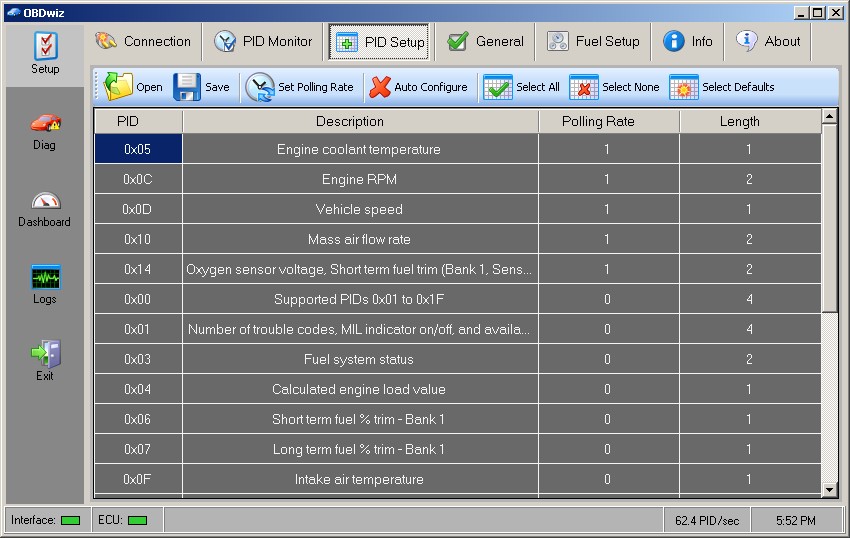 OBDwiz PID Setup
OBDwiz PID Setup
6.3. Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Step 1: Navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” section of the software.
- Step 2: Initiate the code reading process. The software will communicate with the vehicle’s computer and display any stored DTCs.
- Step 3: Record the DTCs and their descriptions for further analysis.
6.4. Interpret the DTCs
- Step 1: Consult the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online database to understand the meaning of each DTC.
- Step 2: Identify the potential causes of each DTC based on its description and related symptoms.
- Step 3: Prioritize the DTCs based on their severity and relevance to the vehicle’s symptoms.
6.5. View Live Data
- Step 1: Navigate to the “Live Data” or “Real-Time Data” section of the software.
- Step 2: Select the parameters you want to monitor, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and fuel trim.
- Step 3: Observe the live data while the engine is running. Look for any abnormal readings or fluctuations.
6.6. Perform Bi-Directional Tests
- Step 1: Navigate to the “Bi-Directional Controls” or “Active Tests” section of the software.
- Step 2: Select the component or system you want to test, such as the fuel pump, EGR valve, or ABS pump.
- Step 3: Follow the software’s instructions to activate the component and observe its response.
6.7. Analyze the Data and Perform Repairs
- Step 1: Analyze the DTCs, live data, and bi-directional test results to pinpoint the cause of the vehicle’s problem.
- Step 2: Perform the necessary repairs, such as replacing faulty sensors, repairing damaged wiring, or cleaning clogged components.
- Step 3: Clear the DTCs and retest the vehicle to ensure the problem has been resolved.
6.8. Generate a Report
- Step 1: Navigate to the “Reporting” section of the software.
- Step 2: Select the diagnostic data you want to include in the report, such as DTCs, live data snapshots, and repair notes.
- Step 3: Generate the report and save it as a PDF or other suitable format.
- Step 4: Provide the report to the customer, along with a clear explanation of the vehicle’s problem and the repairs performed.
7. Maintenance and Updates for Car Diagnostic PC Software
Maintaining your car diagnostic PC software is essential for ensuring its accuracy, reliability, and compatibility with new vehicles. Regular updates and proper maintenance can help you avoid diagnostic errors and keep your tool running smoothly.
7.1. Regularly Update the Software
- Importance: Software updates provide the latest vehicle coverage, diagnostic functions, and bug fixes.
- How to Update:
- Enable automatic updates in the software settings.
- Check for updates manually on a regular basis.
- Download and install updates as soon as they are available.
- Example: Keeping your software updated ensures you can diagnose the latest vehicle models and access new diagnostic procedures.
7.2. Keep Your PC Clean and Optimized
- Importance: A clean and optimized PC ensures the diagnostic software runs smoothly and efficiently.
- How to Maintain:
- Remove unnecessary files and programs.
- Run a virus scan regularly.
- Defragment the hard drive.
- Ensure sufficient RAM and storage space.
- Example: Removing unnecessary programs and files can improve the performance of your diagnostic software and reduce the risk of crashes or errors.
7.3. Back Up Your Data
- Importance: Backing up your data protects against data loss due to hardware failures or software issues.
- How to Back Up:
- Create regular backups of your diagnostic data and software settings.
- Store backups on an external hard drive or in the cloud.
- Test your backups to ensure they are working correctly.
- Example: Backing up your data ensures you can quickly restore your diagnostic software and data in case of a computer crash or other unexpected event.
7.4. Calibrate Your Diagnostic Tool
- Importance: Calibrating your diagnostic tool ensures its accuracy and reliability.
- How to Calibrate:
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration.
- Use a certified calibration service if necessary.
- Keep records of all calibration activities.
- Example: Calibrating your diagnostic tool ensures it provides accurate readings and minimizes the risk of misdiagnosis.
7.5. Protect Your Equipment
- Importance: Protecting your diagnostic equipment prevents damage and extends its lifespan.
- How to Protect:
- Store your diagnostic tool in a safe and dry place.
- Use a protective case or cover when transporting the tool.
- Avoid exposing the tool to extreme temperatures or humidity.
- Example: Storing your diagnostic tool in a protective case prevents damage from impacts, dust, and moisture.
8. Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Even with the best car diagnostic PC software, you may encounter issues from time to time. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting tips to help you resolve them quickly.
8.1. Software Won’t Connect to Vehicle
- Possible Causes:
- Incorrect COM port selection.
- Faulty OBD-II cable.
- Vehicle not OBD-II compliant.
- Ignition not turned on.
- Troubleshooting Tips:
- Verify the correct COM port is selected in the software settings.
- Check the OBD-II cable for damage and ensure it is securely connected.
- Confirm the vehicle is OBD-II compliant.
- Ensure the ignition is turned on, but the engine is not running.
- Example: If the software fails to connect, double-check the COM port settings and try a different OBD-II cable.
8.2. Inaccurate Data Readings
- Possible Causes:
- Faulty sensor.
- Incorrect vehicle information selected.
- Software not calibrated.
- Troubleshooting Tips:
- Verify the sensor is functioning correctly using a multimeter or other testing equipment.
- Ensure the correct vehicle make, model, and year are selected in the software.
- Calibrate the diagnostic tool according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Example: If you suspect inaccurate data readings, verify the sensor’s output and recalibrate the diagnostic tool.
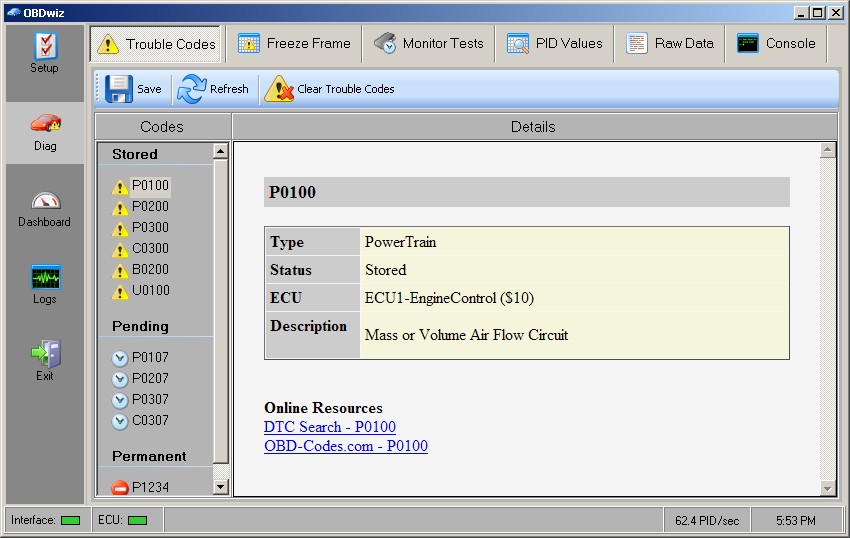 OBDwiz Trouble Codes Tab
OBDwiz Trouble Codes Tab
8.3. Software Freezes or Crashes
- Possible Causes:
- Insufficient system resources.
- Corrupted software files.
- Conflicting software.
- Troubleshooting Tips:
- Close unnecessary programs to free up system resources.
- Reinstall the diagnostic software.
- Check for conflicting software and remove it.
- Example: If the software frequently freezes or crashes, try closing other programs and reinstalling the diagnostic software.
8.4. Trouble Codes Not Displaying
- Possible Causes:
- No trouble codes stored in the vehicle’s computer.
- Software not compatible with the vehicle.
- Faulty connection.
- Troubleshooting Tips:
- Verify there are no active trouble codes in the vehicle by checking the instrument panel.
- Ensure the software is compatible with the vehicle make, model, and year.
- Check the OBD-II cable and connection.
- Example: If no trouble codes are displaying, verify the vehicle’s computer has stored codes and check the software’s compatibility.
9. The Future of Car Diagnostic PC Software
The future of car diagnostic PC software is set to be shaped by several key trends, including advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and augmented reality (AR). These technologies promise to enhance diagnostic capabilities, improve efficiency, and transform the way automotive repairs are performed.
9.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Impact: AI can analyze vast amounts of diagnostic data to identify patterns, predict failures, and provide technicians with targeted repair recommendations. According to a report by PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC), AI is expected to significantly impact the automotive industry, with applications ranging from predictive maintenance to autonomous driving.
- Benefits:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can predict potential failures based on historical data, allowing technicians to perform proactive maintenance and prevent breakdowns.
- Automated Diagnostics: AI can automate the diagnostic process, reducing diagnostic time and improving accuracy.
- Expert Systems: AI-powered expert systems can provide technicians with step-by-step repair instructions and troubleshooting guidance.
- Example: AI algorithms can analyze sensor data to detect anomalies and predict when a component is likely to fail, allowing technicians to replace it before it causes a breakdown.
9.2. Internet of Things (IoT)
- Impact: The IoT enables vehicles to communicate with diagnostic tools, cloud-based servers, and other devices, providing real-time data and remote diagnostic capabilities. A report by McKinsey & Company highlights the growing importance of connected car technologies, including remote diagnostics and over-the-air (OTA) updates.
- Benefits:
- Remote Diagnostics: Technicians can remotely diagnose vehicles, reducing the need for on-site visits and improving customer convenience.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Software updates and patches can be delivered wirelessly, eliminating the need for manual updates.
- Data Sharing: Vehicles can share diagnostic data with manufacturers and service providers, enabling continuous improvement and proactive support.
- Example: A technician can remotely diagnose a vehicle’s engine performance while the customer is driving, providing immediate feedback and recommendations.
9.3. Augmented Reality (AR)
- Impact: AR can overlay diagnostic information and repair instructions onto the technician’s view of the vehicle, providing hands-free guidance and improving repair accuracy. According to a report by Deloitte, AR is transforming the automotive industry, with applications ranging from manufacturing to after-sales service.
- Benefits:
- Hands-Free Guidance: AR provides technicians with step-by-step repair instructions directly in their field of vision, allowing them to focus on the task at hand.
- Improved Accuracy: AR overlays diagnostic data onto the vehicle, helping technicians identify the correct components and perform repairs with greater precision.
- Enhanced Training: AR can be used to train technicians on new repair procedures and diagnostic techniques, reducing training time and improving skill levels.
- Example: A technician wearing AR glasses can view a virtual diagram of the engine overlaid onto the actual engine, highlighting the location of specific components and providing step-by-step repair instructions.
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is committed to providing the latest information and resources to help you stay ahead in the rapidly evolving field of automotive diagnostics. By embracing these emerging trends, you can enhance your diagnostic capabilities, improve efficiency, and deliver superior service to your customers.
10. FAQs About Car Diagnostic PC Software
Here are some frequently asked questions about car diagnostic PC software to help you better understand these tools and their applications:
10.1. What is OBD-II and Why is it Important?
OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) is a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and diagnose engine and emissions-related problems. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD-II was mandated in all cars and light trucks sold in the United States starting in 1996 to ensure vehicles meet emissions standards.
- Importance: OBD-II provides a standardized way to access diagnostic information, making it easier for technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles.
- Key Features:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Standardized codes that identify specific problems.
- Live Data: Real-time data from sensors and other components.
- Standardized Connector: A 16-pin connector located under the dashboard.
10.2. Can I Use Car Diagnostic PC Software on Any Vehicle?
Car diagnostic PC software is compatible with most vehicles manufactured after 1996 that are OBD-II compliant. However, vehicle coverage can vary depending on the software and the specific makes and models supported.
- Considerations:
- Vehicle Compatibility List: Check the software’s vehicle compatibility list to ensure it supports the vehicles you work on.
- OBD-II Compliance: Verify that the vehicle is OBD-II compliant.
- Specialty Vehicles: If you work on specialty vehicles like hybrids or EVs, ensure the software supports these vehicles.
10.3. What is the Difference Between OEM and Aftermarket Diagnostic Software?
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) diagnostic software is designed by vehicle manufacturers for their specific makes and models, while aftermarket diagnostic software is developed by third-party companies and offers broader compatibility across various vehicle makes and models.
- OEM Software:
- Pros: Comprehensive coverage, advanced functions, up-to-date information.
- Cons: High cost, limited compatibility, complexity.
- Aftermarket Software:
- Pros: Wide compatibility, cost-effective, user-friendly interface.
- Cons: Limited functionality, variable quality, update dependency.
10.4. How Often Should I Update My Car Diagnostic PC Software?
You should update your car diagnostic PC software regularly to maintain compatibility with new vehicles and access the latest diagnostic information.
- Recommendations:
- Enable automatic updates in the software settings.
- Check for updates manually on a regular basis.
- Download and install updates as soon as they are available.
10.5. What is Bi-Directional Control and Why is it Important?
Bi-directional control allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s control modules to test components and systems. This is essential for accurate diagnostics and verifying repairs.
- Importance: Enables active testing of components, verifying their functionality and ensuring proper operation.
- Examples:
- Activating the fuel pump relay to verify its operation.
- Commanding the EGR valve to open and close.
- Cycling the ABS pump to test its performance.
10.6. What are PIDs and How are They Used in Car Diagnostics?
PIDs (Parameter IDs) are codes used to request data from a vehicle’s computer. They allow you to access real-time data from sensors and other components.
- Importance: PIDs provide valuable information for diagnosing vehicle problems.
- Examples:
- Engine RPM (Revolutions Per Minute).
- Coolant Temperature.
- Fuel Trim.
- Throttle Position.
10.7. How Do I Interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)?
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are standardized codes that identify specific problems in a vehicle’s engine and emissions systems. To interpret DTCs:
- Step 1: Record the DTC and its description.
- Step 2: Consult the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online database to understand the meaning of the DTC.
- Step 3: Identify the potential causes of the DTC based on its description and related symptoms.
10.8. What is Freeze Frame Data and How is it Useful?
Freeze Frame data is a snapshot of vehicle parameters at the exact moment a DTC was set. It provides valuable information about the conditions that caused the problem.
- Importance: Freeze Frame data can help you pinpoint the cause of a DTC by providing a context for the problem.
- Examples:
- Engine RPM.
- Coolant Temperature.
- Engine Load.
- Vehicle Speed.
10.9. Can I Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Myself?
Yes, you can clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) using car diagnostic PC software. However, it’s important to understand the implications of clearing DTCs:
- Considerations:
- Clearing DTCs will erase the stored codes and turn off the Check Engine Light.
- The underlying problem may still exist, and the DTC may return if the issue is not resolved.
- Clearing DTCs may also erase valuable Freeze Frame data that can help diagnose the problem.
10.10. Where Can I Get Technical Support for My Car Diagnostic PC Software?
You can get technical support for your car diagnostic PC software from the software vendor or manufacturer.
- Resources:
- Technical Support Website: Check the vendor’s website for FAQs, troubleshooting guides, and contact information.
- Phone Support: Call the vendor’s technical support hotline.
- Email Support: Send an email to the vendor’s support team.
- Online Forums: Participate in online forums and communities to get help from other users.
By understanding these FAQs, you can better utilize car diagnostic PC software to diagnose and repair vehicles effectively.
Don’t let diagnostic challenges slow you down. Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, for expert advice and solutions. Get in touch today and let us help you enhance your diagnostic capabilities.