The best car diagnostic app to monitor your O2 sensor is one that offers real-time data, comprehensive diagnostics, and user-friendly interface. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides detailed insights and resources to help you choose the perfect app for your needs, ensuring optimal vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. With advanced diagnostic capabilities, you can easily monitor your car’s health and performance metrics.
Contents
- 1. Why Use a Car Diagnostic App to Monitor Your O2 Sensor?
- 2. Understanding the O2 Sensor: Functions and Importance
- 3. Key Features to Look for in a Car Diagnostic App
- 4. Top Car Diagnostic Apps for Monitoring O2 Sensors
- 4.1. OBDLink
- 4.2. Torque Pro
- 4.3. Carly
- 4.4. Dr. Prius/Dr. Hybrid
- 4.5. BlueDriver
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide: Monitoring Your O2 Sensor with a Car Diagnostic App
- 6. Interpreting O2 Sensor Data
- 7. Tips for Maintaining Your O2 Sensor
- 8. Common Problems and Troubleshooting
- 9. The Future of Car Diagnostics: What’s Next?
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why Use a Car Diagnostic App to Monitor Your O2 Sensor?
Monitoring your O2 sensor with a car diagnostic app offers numerous benefits. It allows you to track your vehicle’s performance, identify potential issues early, and ensure your car is running efficiently.
- Early Problem Detection: Car diagnostic apps enable you to identify problems with your O2 sensor before they escalate into more significant issues. By monitoring real-time data, you can catch irregularities early.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: A faulty O2 sensor can lead to poor fuel economy. Diagnostic apps help you ensure your O2 sensor is functioning correctly, optimizing fuel consumption.
- Reduced Emissions: A properly functioning O2 sensor helps reduce harmful emissions. Monitoring it with an app ensures your vehicle is environmentally friendly.
- Cost Savings: Early detection and timely repairs prevent costly future repairs, saving you money in the long run.
- Real-Time Data: Car diagnostic apps provide real-time data on your O2 sensor’s performance, allowing you to make informed decisions about your vehicle’s maintenance.
- Convenience: With a diagnostic app, you can monitor your O2 sensor from anywhere, at any time, without needing to visit a mechanic.
 Car Diagnostic App Interface
Car Diagnostic App Interface
2. Understanding the O2 Sensor: Functions and Importance
The O2 sensor, or oxygen sensor, is a critical component of your vehicle’s emission control system. It measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases and sends this data to the engine control unit (ECU).
- Function: The primary function of the O2 sensor is to monitor the oxygen levels in the exhaust. This information helps the ECU adjust the air-fuel mixture to ensure optimal combustion.
- Location: O2 sensors are typically located in the exhaust manifold, before and after the catalytic converter. Some vehicles may have multiple O2 sensors for more precise monitoring.
- Types: There are two main types of O2 sensors:
- Zirconia Sensors: These are the most common type and generate their own voltage based on the oxygen difference between the exhaust and ambient air.
- Titania Sensors: These sensors change resistance based on oxygen levels and require an external voltage source.
- Importance:
- Fuel Efficiency: By ensuring the correct air-fuel mixture, the O2 sensor helps maximize fuel efficiency.
- Emission Control: It helps reduce harmful emissions, ensuring the vehicle complies with environmental regulations.
- Engine Performance: A properly functioning O2 sensor ensures the engine runs smoothly and efficiently.
- Symptoms of a Faulty O2 Sensor:
- Poor Fuel Economy: One of the most common symptoms.
- Rough Idling: The engine may idle unevenly.
- Check Engine Light: This light often illuminates when the O2 sensor malfunctions.
- Failed Emission Test: High emissions during testing.
- Hesitation or Stalling: The engine may hesitate or stall during acceleration.
- Black Smoke from Exhaust: Indicates a rich air-fuel mixture.
According to a study by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), faulty O2 sensors can decrease fuel efficiency by as much as 40% and significantly increase vehicle emissions.
3. Key Features to Look for in a Car Diagnostic App
When selecting a car diagnostic app to monitor your O2 sensor, consider these essential features:
- Real-Time Data Monitoring:
- Description: The app should provide real-time data on O2 sensor readings, allowing you to see how the sensor is performing under various driving conditions.
- Benefit: Helps you quickly identify any irregularities or sudden changes in the sensor’s output.
- Comprehensive Diagnostics:
- Description: Look for apps that offer in-depth diagnostic capabilities, including the ability to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Benefit: Enables you to identify the specific issue and take appropriate action.
- O2 Sensor-Specific Tests:
- Description: The app should have specific tests designed to evaluate the performance of the O2 sensor, such as response time and voltage range tests.
- Benefit: Provides a detailed assessment of the sensor’s health.
- Data Logging and Analysis:
- Description: The ability to log data over time and analyze trends can be invaluable in diagnosing intermittent issues.
- Benefit: Helps you track the sensor’s performance and identify patterns that may indicate a problem.
- User-Friendly Interface:
- Description: An intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface is crucial for ease of use.
- Benefit: Makes it simple to access the information you need and perform diagnostic tests.
- Compatibility:
- Description: Ensure the app is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Benefit: Guarantees accurate and reliable data.
- Connectivity:
- Description: The app should seamlessly connect to your OBD-II scanner via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- Benefit: Ensures a stable and reliable connection for real-time data transmission.
- Reporting:
- Description: The app should generate detailed reports that you can save, print, or share with a mechanic.
- Benefit: Facilitates communication and ensures everyone is on the same page regarding the vehicle’s condition.
- Customer Support:
- Description: Reliable customer support is essential for troubleshooting any issues you may encounter.
- Benefit: Provides assistance when you need it, ensuring a smooth experience.
4. Top Car Diagnostic Apps for Monitoring O2 Sensors
Here are some of the top car diagnostic apps available, each with features that make them suitable for monitoring O2 sensors:
4.1. OBDLink
Overview: The OBDLink app is known for its enhanced diagnostics and access to additional vehicle modules and parameters not included in the SAE OBD-II standard.
- Key Features:
- Enhanced OEM add-ons for specific vehicle manufacturers.
- Access to ABS, SRS, and TPMS codes.
- Real-time data monitoring.
- User-friendly interface.
- Pros:
- Comprehensive diagnostics.
- Wide vehicle compatibility.
- Exclusive add-ons for GM, Honda, Acura, Hyundai, and Kia with OBDLink MX+ adapter.
- Cons:
- Enhanced OEM add-ons primarily available for North American vehicles.
- Some features require the OBDLink MX+ adapter.
 OBDLink App Interface
OBDLink App Interface
4.2. Torque Pro
Overview: Torque Pro is a popular app among car enthusiasts for its extensive customization options and real-time data display.
- Key Features:
- Customizable dashboards.
- Real-time O2 sensor data.
- DTC reading and clearing.
- GPS tracking.
- Plugin support for extended functionality.
- Pros:
- Highly customizable.
- Extensive data logging capabilities.
- Affordable.
- Cons:
- Requires some technical knowledge to set up.
- Interface can be overwhelming for beginners.
4.3. Carly
Overview: Carly is a user-friendly app that offers advanced diagnostics and coding options for specific car brands like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Volkswagen.
- Key Features:
- Advanced diagnostics for specific car brands.
- Coding capabilities for customizing vehicle settings.
- Real-time data monitoring.
- Digital garage feature for storing vehicle information.
- Pros:
- Specifically designed for certain car brands.
- Offers coding options.
- User-friendly interface.
- Cons:
- Limited to specific car brands.
- Some features require a subscription.
4.4. Dr. Prius/Dr. Hybrid
Overview: Designed specifically for hybrid vehicles, Dr. Prius (or Dr. Hybrid for other brands) offers detailed diagnostics for the hybrid system, including the O2 sensor.
- Key Features:
- Hybrid system diagnostics.
- Battery health check.
- Real-time data monitoring.
- O2 sensor-specific tests.
- Pros:
- Specialized for hybrid vehicles.
- Detailed battery health information.
- User-friendly interface.
- Cons:
- Limited to hybrid vehicles.
4.5. BlueDriver
Overview: BlueDriver is known for its comprehensive diagnostics and access to repair reports generated by certified mechanics.
- Key Features:
- Comprehensive diagnostics.
- Access to repair reports.
- Real-time data monitoring.
- User-friendly interface.
- Pros:
- Access to professional repair information.
- Easy to use.
- Wide vehicle compatibility.
- Cons:
- Requires the BlueDriver Bluetooth scan tool.
- Some features require a subscription.
5. Step-by-Step Guide: Monitoring Your O2 Sensor with a Car Diagnostic App
Follow these steps to monitor your O2 sensor using a car diagnostic app:
- Purchase an OBD-II Scanner:
- Choose a scanner that is compatible with your car and the diagnostic app you plan to use. Popular options include OBDLink MX+, BlueDriver, and generic Bluetooth OBD-II scanners.
- Download and Install the Diagnostic App:
- Download the app from the App Store (iOS) or Google Play Store (Android). Install it on your smartphone or tablet.
- Connect the OBD-II Scanner:
- Plug the OBD-II scanner into the OBD-II port in your car. This port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Pair the Scanner with Your Device:
- Turn on your car’s ignition (but don’t start the engine).
- Enable Bluetooth on your smartphone or tablet.
- Open the diagnostic app and follow the instructions to pair with the OBD-II scanner.
- Start Monitoring Your O2 Sensor:
- Once connected, navigate to the real-time data or sensor monitoring section of the app.
- Select the O2 sensor data parameters to monitor. These may be labeled as “O2 Sensor Voltage,” “O2 Sensor Current,” or similar.
- Start your engine and observe the O2 sensor readings as you drive or idle.
- Analyze the Data:
- Monitor the O2 sensor readings for any irregularities. The voltage should fluctuate as the engine runs, indicating the sensor is working.
- If the readings are consistently high or low, or if the sensor response is slow, it may indicate a problem.
- Run Diagnostic Tests:
- Use the app to run specific diagnostic tests on the O2 sensor, if available. These tests can help determine if the sensor is functioning within the specified parameters.
- Read and Clear DTCs:
- If the app detects any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the O2 sensor, read the codes to understand the issue.
- After addressing the problem, clear the DTCs using the app.
- Generate Reports:
- Use the app to generate reports of your O2 sensor data and diagnostic tests. Save or share these reports with your mechanic for further analysis.
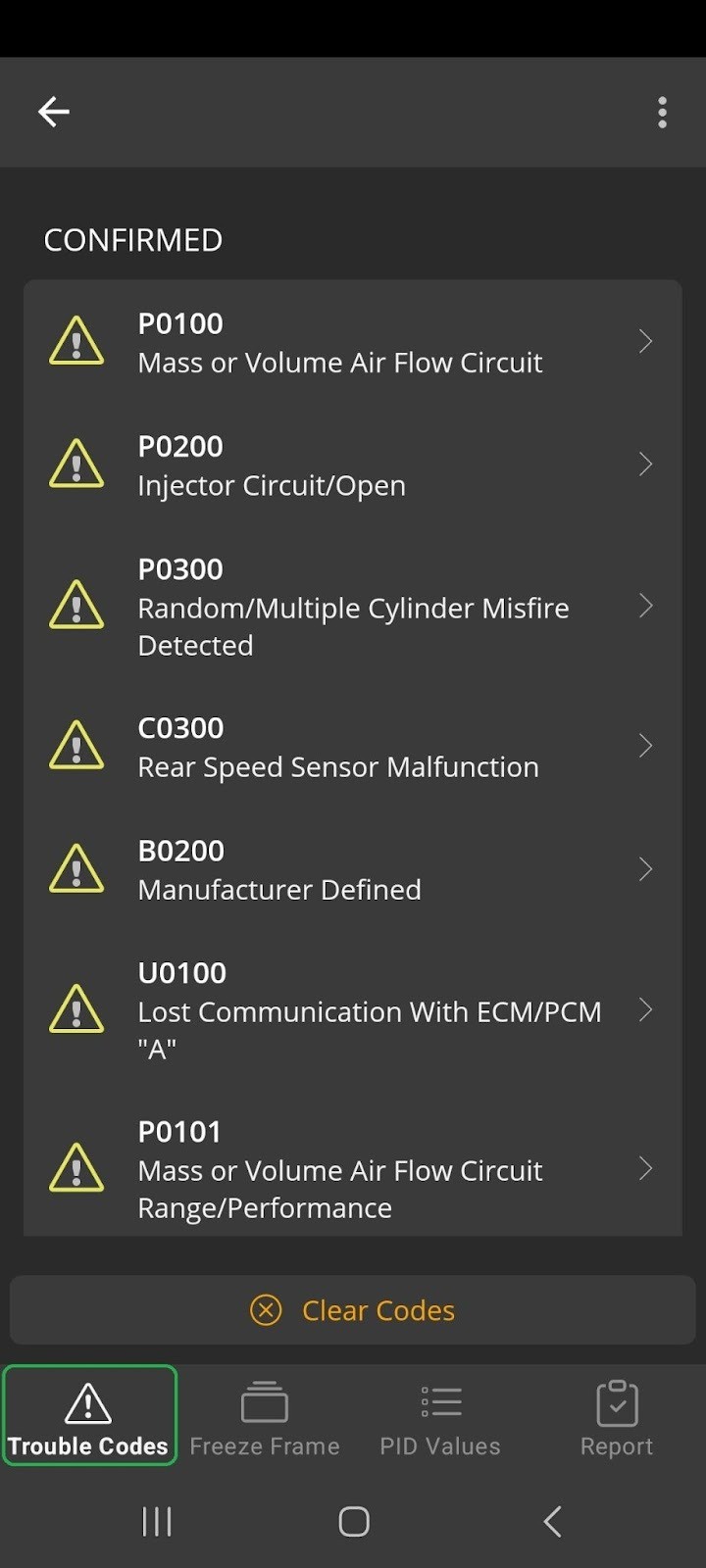 Trouble Codes Display on Diagnostic App
Trouble Codes Display on Diagnostic App
6. Interpreting O2 Sensor Data
Understanding the data provided by your car diagnostic app is crucial for identifying potential issues with your O2 sensor. Here’s how to interpret common O2 sensor readings:
- O2 Sensor Voltage:
- Normal Range: Typically, O2 sensor voltage ranges from 0.1 to 0.9 volts.
- Low Voltage (0.1-0.3V): Indicates a lean condition (too much oxygen).
- High Voltage (0.6-0.9V): Indicates a rich condition (too little oxygen).
- Fluctuations: The voltage should fluctuate rapidly between the lean and rich conditions as the ECU adjusts the air-fuel mixture.
- Normal Range: Typically, O2 sensor voltage ranges from 0.1 to 0.9 volts.
- O2 Sensor Response Time:
- Definition: The time it takes for the O2 sensor to switch from lean to rich or vice versa.
- Normal Response: A healthy O2 sensor should switch quickly (within a few hundred milliseconds).
- Slow Response: A slow response time indicates a failing sensor.
- Air-Fuel Ratio (AFR):
- Ideal AFR: The ideal air-fuel ratio is 14.7:1 (stoichiometric).
- Reading: Diagnostic apps may display the AFR or lambda value (where lambda = 1 represents the stoichiometric ratio).
- Interpretation:
- AFR > 14.7:1 (Lambda > 1): Indicates a lean condition.
- AFR < 14.7:1 (Lambda < 1): Indicates a rich condition.
- Short-Term Fuel Trim (STFT) and Long-Term Fuel Trim (LTFT):
- Definition: These values indicate how much the ECU is adjusting the air-fuel mixture to compensate for deviations from the ideal AFR.
- Normal Range: Ideally, STFT and LTFT should be close to 0%.
- Interpretation:
- Positive Values: The ECU is adding fuel (compensating for a lean condition).
- Negative Values: The ECU is reducing fuel (compensating for a rich condition).
- High Values (±10% or more): Indicate a significant problem.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
- Common O2 Sensor DTCs:
- P0130-P0167: O2 Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1).
- P0172: System Too Rich (Bank 1).
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1).
- Action: Research the specific DTC to understand the problem and take appropriate action.
- Common O2 Sensor DTCs:
A study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) found that accurate interpretation of O2 sensor data can reduce diagnostic time by up to 50%.
7. Tips for Maintaining Your O2 Sensor
Proper maintenance can extend the life of your O2 sensor and ensure optimal performance. Here are some tips:
- Regular Inspections:
- Frequency: Check the O2 sensor data regularly using a car diagnostic app.
- Purpose: Identify potential issues early.
- Use High-Quality Fuel:
- Reason: Low-quality fuel can contain additives that contaminate the O2 sensor.
- Recommendation: Use fuel from reputable sources.
- Address Engine Issues Promptly:
- Reason: Issues like oil leaks or coolant leaks can damage the O2 sensor.
- Action: Fix any engine problems as soon as they arise.
- Avoid Over-Oiling Air Filters:
- Reason: Excess oil can contaminate the O2 sensor.
- Recommendation: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions when oiling air filters.
- Replace O2 Sensors as Recommended:
- Interval: Replace O2 sensors every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the manufacturer’s recommendation.
- Benefit: Ensures optimal performance and fuel efficiency.
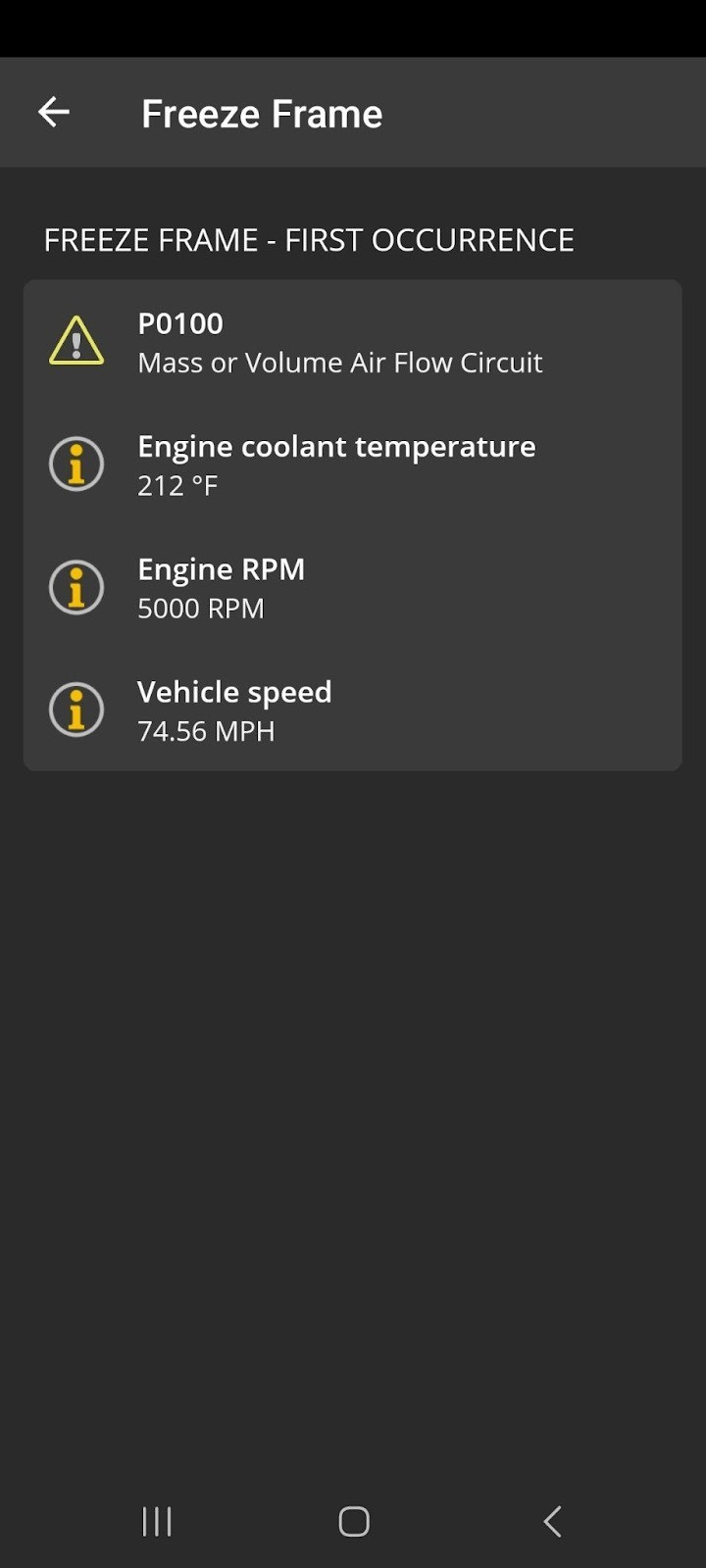 Freeze Frame Data on Diagnostic App
Freeze Frame Data on Diagnostic App
8. Common Problems and Troubleshooting
Even with regular maintenance, O2 sensors can experience problems. Here are some common issues and how to troubleshoot them:
- Contamination:
- Cause: Oil, coolant, or fuel additives can contaminate the O2 sensor.
- Symptoms: Slow response, inaccurate readings.
- Troubleshooting:
- Inspect the sensor for visible contamination.
- Check for oil or coolant leaks.
- Replace the sensor if necessary.
- Electrical Issues:
- Cause: Damaged wiring, loose connections, or grounding problems.
- Symptoms: Intermittent readings, no signal.
- Troubleshooting:
- Inspect the wiring and connectors for damage.
- Ensure the sensor is properly grounded.
- Use a multimeter to check for voltage and continuity.
- Sensor Failure:
- Cause: Natural wear and tear, age.
- Symptoms: No signal, consistently high or low readings.
- Troubleshooting:
- Use a diagnostic app to check for DTCs.
- Replace the sensor.
- Exhaust Leaks:
- Cause: Leaks in the exhaust system near the O2 sensor.
- Symptoms: Inaccurate readings, lean condition.
- Troubleshooting:
- Inspect the exhaust system for leaks.
- Repair or replace damaged exhaust components.
According to a survey by AAA, electrical issues are the most common cause of O2 sensor failure, accounting for approximately 40% of all cases.
9. The Future of Car Diagnostics: What’s Next?
The field of car diagnostics is continually evolving. Here are some trends to watch for:
- AI-Powered Diagnostics:
- Description: Artificial intelligence (AI) is being integrated into diagnostic apps to provide more accurate and personalized recommendations.
- Benefits: AI can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential issues.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics:
- Description: Cloud-based diagnostic platforms allow for remote monitoring and analysis of vehicle data.
- Benefits: Mechanics can access real-time data and provide remote assistance.
- Enhanced Sensor Technology:
- Description: New and improved sensor technologies are being developed to provide more accurate and reliable data.
- Benefits: Improved accuracy leads to better diagnostics and maintenance decisions.
- Integration with Smart Devices:
- Description: Car diagnostic apps are increasingly integrated with smart devices like smartwatches and home assistants.
- Benefits: Provides convenient access to vehicle data and diagnostic information.
- Predictive Maintenance:
- Description: Diagnostic systems are being developed to predict when maintenance will be required.
- Benefits: Reduces downtime and prevents costly repairs.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is an O2 sensor and what does it do?
An O2 sensor measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. It helps the ECU adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
2. How do I know if my O2 sensor is bad?
Symptoms of a bad O2 sensor include poor fuel economy, rough idling, a check engine light, failed emission test, hesitation or stalling, and black smoke from the exhaust.
3. Can I replace an O2 sensor myself?
Yes, you can replace an O2 sensor yourself if you have basic mechanical skills. However, it’s essential to use the correct tools and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
4. How often should I replace my O2 sensor?
Replace O2 sensors every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the manufacturer’s recommendation.
5. Will a bad O2 sensor affect my gas mileage?
Yes, a bad O2 sensor can significantly reduce your gas mileage by causing the engine to run with an improper air-fuel mixture.
6. Can a car diagnostic app clear O2 sensor codes?
Yes, many car diagnostic apps can read and clear O2 sensor codes after you have addressed the underlying issue.
7. What is the normal voltage range for an O2 sensor?
The normal voltage range for an O2 sensor is typically between 0.1 and 0.9 volts.
8. What is the difference between upstream and downstream O2 sensors?
Upstream O2 sensors are located before the catalytic converter and measure the air-fuel mixture entering the engine. Downstream O2 sensors are located after the catalytic converter and monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
9. Can exhaust leaks affect O2 sensor readings?
Yes, exhaust leaks can cause inaccurate O2 sensor readings, leading to a lean condition.
10. Where can I buy a reliable car diagnostic app and OBD-II scanner?
You can find reliable car diagnostic apps on the App Store (iOS) and Google Play Store (Android). OBD-II scanners can be purchased from automotive parts stores, online retailers like Amazon, and directly from manufacturers like OBDLink.
Monitoring your O2 sensor with a car diagnostic app is a proactive way to maintain your vehicle’s performance, fuel efficiency, and environmental impact. By understanding the function of the O2 sensor, selecting the right diagnostic app, and interpreting the data correctly, you can ensure your car runs smoothly and efficiently.
For more detailed information and access to a wide range of automotive tools and resources, visit CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Need help selecting the right car diagnostic app and OBD-II scanner for your needs? Contact us today for expert advice and support.
Address: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN