Are There Any OBD-II Codes Related To The Braking System? Yes, there are OBD-II codes specifically related to the braking system, which can indicate issues with components like the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), brake sensors, or hydraulic systems; you can find valuable information about these codes and their implications at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN. Understanding these codes helps diagnose brake problems early, ensuring vehicle safety and preventing costly repairs; knowing how to interpret these codes and what actions to take can significantly improve your vehicle maintenance. Early issue detection is key.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD-II Codes and Your Vehicle’s Braking System
- 2. Common OBD-II Codes Related to the Braking System
- 2.1. C0031 – Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- 2.2. C0040 – Brake Pedal Switch A Circuit Malfunction
- 2.3. C0051 – Brake Pressure Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- 2.4. C1214 – System Relay Contact Circuit Open
- 2.5. C1235 – Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Open or Shorted
- 3. Diagnosing and Addressing OBD-II Brake Codes
- 3.1. Use an OBD-II Scanner
- 3.2. Research the Code
- 3.3. Inspect Related Components
- 3.4. Perform Necessary Repairs or Replacements
- 3.5. Clear the Code and Test the System
- 4. Maintaining Your Braking System to Prevent OBD-II Codes
- 4.1. Regular Inspections
- 4.2. Maintain Brake Fluid
- 4.3. Replace Worn Brake Pads and Rotors
- 4.4. ABS Maintenance
- 5. Tools and Equipment for Diagnosing Brake Issues
- 5.1. OBD-II Scanner
- 5.2. Brake Pad Thickness Gauge
- 5.3. Rotor Runout Gauge
- 5.4. Brake Fluid Tester
- 5.5. Basic Hand Tools
- 6. When to Consult a Professional Mechanic
- 6.1. Uncomfortable Performing Repairs
- 6.2. Serious OBD-II Codes
- 6.3. Uncertain Diagnosis
- 7. Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for Automotive Information
- 7.1. Detailed Information on OBD-II Codes
- 7.2. Expert Advice and Guides
- 7.3. Tool Recommendations
- 8. Real-Life Examples of OBD-II Brake Code Issues
- 8.1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
- 8.2. Brake Pedal Switch Failure
- 8.3. Brake Pressure Sensor Issue
- 9. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Brake Systems
- 9.1. Oscilloscope Analysis
- 9.2. Hydraulic Pressure Testing
- 9.3. ABS Module Testing
- 10. Future Trends in Brake System Diagnostics
- 10.1. AI-Powered Diagnostics
- 10.2. Remote Diagnostics
- 10.3. Enhanced Sensor Technology
- Summary
- Call to Action
- FAQ: OBD-II Codes and Brake Systems
- 1. What does it mean when my ABS light is on?
- 2. Can I drive with the ABS light on?
- 3. How do I reset the ABS light?
- 4. What is a wheel speed sensor and why is it important?
- 5. How often should I replace my brake pads?
- 6. What is brake fluid and why does it need to be maintained?
- 7. How do I check the brake fluid level?
- 8. What is the difference between ABS and regular brakes?
- 9. Can I replace brake pads myself?
- 10. How do I know if my brake rotors need to be replaced?
Understanding OBD-II codes is crucial for vehicle maintenance and repair, and CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is your reliable resource for comprehensive insights into automotive diagnostics, repair tools, and expert advice. Explore our website for in-depth guides and resources that simplify complex automotive issues, enhance your diagnostic skills, and ensure your vehicle operates at peak performance with advanced diagnostic and automotive maintenance. With our expert advice, you’ll easily find and maintain your vehicle.
1. Understanding OBD-II Codes and Your Vehicle’s Braking System
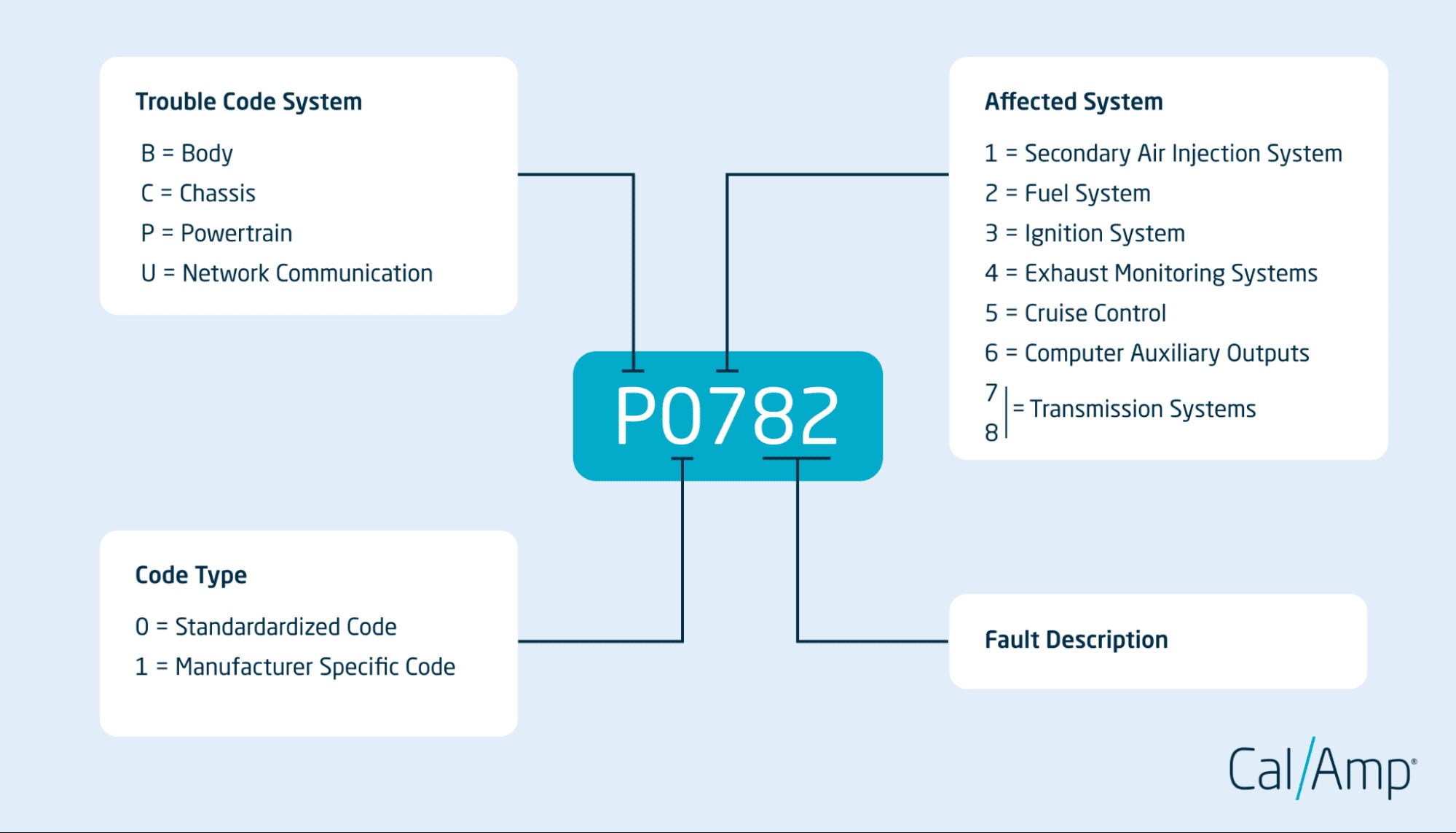
What are OBD-II codes and how do they relate to my vehicle’s braking system? OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) codes are standardized codes used to diagnose issues within a vehicle, and yes, some specifically relate to the braking system; these codes can pinpoint problems within the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), brake sensors, hydraulic systems, and other critical components. These codes play a crucial role in identifying and addressing potential braking issues to maintain vehicle safety and prevent accidents.
OBD-II codes are essential for diagnosing a wide range of automotive issues, and knowing which ones pertain to your brakes can be life-saving. For example, codes in the C000 to C0200 range often indicate problems with the ABS, such as a faulty wheel speed sensor or a malfunctioning hydraulic pump, according to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). The braking system is vital for vehicle safety, and any malfunction can significantly increase the risk of accidents, as noted in a 2018 study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). Therefore, understanding and addressing these codes promptly is essential.
These codes help mechanics and vehicle owners identify problems by providing a standardized way to access information about the vehicle’s systems. By using an OBD-II scanner, you can retrieve these codes and use them to diagnose and fix the problem. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers extensive resources to help you interpret these codes and find the right tools for your diagnostic needs.
2. Common OBD-II Codes Related to the Braking System
What are some common OBD-II codes that I might encounter related to my braking system? Several OBD-II codes are commonly associated with braking system issues, including codes related to the ABS, wheel speed sensors, brake pressure sensors, and hydraulic control units; these codes provide specific information about the nature and location of the problem within the braking system. Understanding these common codes can help you quickly identify and address potential braking issues.
Here are some common OBD-II codes related to braking systems:
2.1. C0031 – Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction
What does the C0031 code mean and what are its symptoms? The C0031 code indicates a malfunction in the right front wheel speed sensor circuit, which is critical for the ABS to function correctly; symptoms can include ABS light illumination, traction control issues, and reduced braking performance. This code typically arises when the sensor fails to send accurate speed data to the vehicle’s computer, affecting braking efficiency.
 Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor
The wheel speed sensor plays a vital role in determining when to activate the ABS. A malfunctioning sensor can lead to the ABS not engaging when needed or engaging unnecessarily, which can compromise vehicle control. According to Bosch Automotive Handbook, wheel speed sensors use a magnetic encoder ring and a Hall-effect sensor to measure wheel speed accurately. A problem within this circuit can arise from physical damage, corrosion, or electrical faults. Replacing the sensor or repairing the wiring harness are common solutions.
2.2. C0040 – Brake Pedal Switch A Circuit Malfunction
What does the C0040 code signify and how does it affect my vehicle? The C0040 code indicates a malfunction in the brake pedal switch A circuit, which detects when the brake pedal is pressed; this issue can lead to problems with cruise control, brake lights, and ABS functionality. Addressing this code promptly is essential to ensure these systems operate correctly.
The brake pedal switch is crucial for activating the brake lights and disengaging cruise control when the brakes are applied. The switch also sends a signal to the ABS and traction control systems. According to a report by the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB), a malfunctioning brake pedal switch can cause delayed braking response, increasing the risk of rear-end collisions. Common causes include a faulty switch, wiring issues, or problems with the brake light bulbs.
2.3. C0051 – Brake Pressure Sensor Circuit Malfunction
What does the C0051 code indicate and what are the potential consequences? The C0051 code signals a malfunction in the brake pressure sensor circuit, which monitors the pressure within the braking system; this issue can lead to inaccurate readings and affect the performance of the ABS and stability control systems. This can cause the vehicle to miscalculate the braking force required, reducing overall safety.
The brake pressure sensor provides critical data to the vehicle’s computer, helping it determine the correct amount of braking force needed. A faulty sensor can lead to the ABS engaging unnecessarily or not engaging when required. According to a study by the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute, accurate brake pressure readings are essential for the optimal performance of modern braking systems. Common causes of this code include sensor failure, wiring problems, or hydraulic issues in the brake lines.
2.4. C1214 – System Relay Contact Circuit Open
What does the C1214 code mean and what issues can it cause? The C1214 code indicates an open circuit in the system relay contact circuit, which is vital for the proper functioning of the ABS; this issue can result in the ABS not working at all, leading to reduced braking effectiveness. It’s important to address this code to ensure that the ABS is operational, particularly in emergency braking situations.
The system relay is responsible for providing power to the ABS module. If there is an open circuit, the ABS will not function, leaving the vehicle without anti-lock capabilities. According to an article in Automotive Engineering International, the ABS relies on a consistent and reliable power supply to operate correctly. Common causes include a faulty relay, wiring issues, or problems with the ABS module itself.
2.5. C1235 – Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Open or Shorted
What does the C1235 code signify and how does it impact vehicle safety? The C1235 code indicates an open or shorted circuit in the rear wheel speed sensor circuit, which is crucial for the ABS and traction control systems; this issue can lead to these systems not functioning correctly, potentially affecting vehicle stability and braking performance. Addressing this code is important for maintaining safe driving conditions.
The rear wheel speed sensors, like their front counterparts, provide vital data for the ABS and traction control systems. An open or shorted circuit can prevent accurate speed readings, causing these systems to malfunction. According to a study by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), properly functioning ABS and traction control systems can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, especially in adverse weather conditions. Common causes include damaged wiring, corrosion, or sensor failure.
3. Diagnosing and Addressing OBD-II Brake Codes
How do I diagnose and address OBD-II brake codes effectively? To diagnose and address OBD-II brake codes, you need to use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the code, research the code to understand the potential issues, inspect the related components, and perform necessary repairs or replacements; taking a systematic approach ensures accurate diagnosis and effective resolution of braking system problems. This ensures that you are correctly diagnosing and addressing the issues.
Here’s a step-by-step approach to diagnosing and addressing OBD-II brake codes:
3.1. Use an OBD-II Scanner
How does an OBD-II scanner help in diagnosing brake codes? An OBD-II scanner is essential for retrieving the specific code that indicates a problem within the braking system; this code provides a starting point for diagnosing the issue and determining the necessary repairs. Without the scanner, identifying the problem can be time-consuming and inaccurate.
An OBD-II scanner connects to your vehicle’s diagnostic port, usually located under the dashboard. It reads the codes stored in the vehicle’s computer and displays them, allowing you to identify the specific issue. According to Popular Mechanics, using an OBD-II scanner is the first step in any diagnostic process. Several scanners are available, from basic models that only read codes to advanced versions that offer real-time data and diagnostic functions.
3.2. Research the Code
Why is it important to research the OBD-II code I’ve retrieved? Researching the OBD-II code is crucial to understand the potential causes, symptoms, and solutions associated with the specific issue in the braking system; this knowledge helps you make informed decisions about the necessary repairs. This will ensure that you understand the problem and the solutions to it.
After retrieving the code, it’s important to research its meaning and potential causes. Websites like CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, repair manuals, and online forums can provide valuable information. For example, a code indicating a faulty wheel speed sensor could be caused by a damaged sensor, wiring issues, or a problem with the ABS module. Knowing the potential causes helps you narrow down the possible solutions.
3.3. Inspect Related Components
What components should I inspect when addressing OBD-II brake codes? When addressing OBD-II brake codes, inspect the components related to the code, such as sensors, wiring, connectors, and hydraulic components; this thorough inspection helps identify the root cause of the problem and ensures that all affected parts are addressed. If you only address some of the parts you might have a recurring issue.
 Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Depending on the code, inspect the relevant components for damage, corrosion, or wear. For example, if the code indicates a problem with a wheel speed sensor, check the sensor for physical damage and inspect the wiring and connectors for corrosion or breaks. If the code relates to the hydraulic system, check for leaks or damaged lines. According to a guide by the Automotive Service Association (ASA), a visual inspection is a critical step in diagnosing automotive issues.
3.4. Perform Necessary Repairs or Replacements
What types of repairs or replacements might be necessary to resolve OBD-II brake codes? Depending on the diagnosis, repairs or replacements may include replacing faulty sensors, repairing damaged wiring, replacing hydraulic components, or addressing issues with the ABS module; performing these repairs correctly is crucial for restoring the braking system to proper working condition. This makes sure that your vehicle functions properly again.
Based on your inspection, perform the necessary repairs or replacements. This might involve replacing a faulty wheel speed sensor, repairing damaged wiring, or replacing a malfunctioning ABS module. Always use high-quality replacement parts that meet or exceed the original manufacturer’s specifications. According to a report by Consumer Reports, using high-quality parts can improve the reliability and longevity of repairs.
3.5. Clear the Code and Test the System
Why is it important to clear the OBD-II code and test the braking system after repairs? Clearing the OBD-II code and testing the braking system after repairs is essential to ensure that the problem has been resolved and that the system is functioning correctly; this step confirms the effectiveness of the repairs and helps prevent future issues. This verifies the issue has been solved.
After completing the repairs, use the OBD-II scanner to clear the code from the vehicle’s computer. Then, test the braking system to ensure it is functioning correctly. This might involve performing a test drive and monitoring the ABS and traction control systems. If the code reappears, it indicates that there is still an underlying issue that needs to be addressed.
4. Maintaining Your Braking System to Prevent OBD-II Codes
How can I maintain my braking system to prevent OBD-II codes from appearing? To prevent OBD-II codes related to the braking system, perform regular inspections, maintain brake fluid, replace worn brake pads and rotors, and ensure proper ABS maintenance; proactive maintenance helps prevent issues before they trigger OBD-II codes, ensuring reliable braking performance.
Preventative maintenance is key to avoiding OBD-II codes and maintaining the health of your braking system. Here are some essential maintenance tasks:
4.1. Regular Inspections
Why are regular inspections important for maintaining my braking system? Regular inspections are crucial for identifying potential issues early, such as worn brake pads, leaks, or damaged components; addressing these issues promptly can prevent them from escalating and triggering OBD-II codes. Early detection is key in preventing costly repairs.
Regularly inspect your braking system for signs of wear or damage. This includes checking the brake pads for thickness, inspecting the rotors for cracks or warping, and looking for leaks in the hydraulic lines. According to a maintenance guide by AAA, regular inspections can help identify problems before they become major issues.
4.2. Maintain Brake Fluid
How do I properly maintain the brake fluid in my vehicle? Maintaining brake fluid involves checking its level, ensuring it is free from contamination, and flushing the system as recommended by the manufacturer; this helps ensure proper hydraulic pressure and prevents corrosion within the braking system. This will keep your brakes working properly.
Brake fluid is essential for the proper functioning of your braking system. Check the fluid level regularly and ensure it is within the recommended range. Brake fluid can absorb moisture over time, which can lead to corrosion and reduced braking performance. Flush the brake fluid every two to three years, or as recommended by the manufacturer, to remove any contaminants and maintain optimal performance.
4.3. Replace Worn Brake Pads and Rotors
When should I replace my brake pads and rotors? Replace worn brake pads and rotors when they reach the minimum thickness specified by the manufacturer, or if they show signs of damage such as cracks or excessive wear; replacing these components ensures proper braking performance and prevents damage to other parts of the system. It’s better to be safe and replace them before issues occur.
Brake pads and rotors wear down over time and need to be replaced periodically. Check the thickness of the brake pads regularly and replace them when they reach the minimum specified thickness. Rotors should also be inspected for damage and replaced if necessary. According to a report by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), replacing worn brake pads and rotors is essential for maintaining optimal braking performance.
4.4. ABS Maintenance
What specific maintenance steps are required for the ABS? ABS maintenance involves checking the ABS sensors, ensuring they are clean and properly connected, and verifying that the ABS module is functioning correctly; proper ABS maintenance ensures that this critical safety system operates reliably. It’s better to be safe than sorry when it comes to ABS maintenance.
The ABS is a critical safety system that requires regular maintenance. Check the ABS sensors to ensure they are clean and properly connected. If you suspect a problem with the ABS module, have it inspected by a qualified mechanic. Proper ABS maintenance ensures that the system will function correctly in emergency braking situations.
5. Tools and Equipment for Diagnosing Brake Issues
What tools and equipment do I need to diagnose brake issues effectively? To diagnose brake issues effectively, you need an OBD-II scanner, brake pad thickness gauge, rotor runout gauge, brake fluid tester, and basic hand tools; having these tools ensures accurate diagnosis and efficient repair of braking system problems.
Having the right tools and equipment is essential for diagnosing brake issues and performing necessary repairs. Here are some essential tools:
5.1. OBD-II Scanner
Why is an OBD-II scanner a must-have tool for brake diagnostics? An OBD-II scanner is essential for retrieving diagnostic trouble codes, providing a starting point for diagnosing brake issues; without a scanner, identifying the root cause of brake problems can be difficult and time-consuming. It’s the first tool you should reach for.
As mentioned earlier, an OBD-II scanner is essential for retrieving diagnostic trouble codes. Choose a scanner that is compatible with your vehicle and offers the features you need, such as real-time data and advanced diagnostic functions. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a variety of OBD-II scanners to suit different needs and budgets.
5.2. Brake Pad Thickness Gauge
How does a brake pad thickness gauge help in brake maintenance? A brake pad thickness gauge allows you to accurately measure the thickness of brake pads, helping you determine when they need to be replaced; this tool prevents excessive wear and damage to the rotors, ensuring safe braking performance. Regular measurement is key.
A brake pad thickness gauge is a simple but essential tool for measuring the thickness of brake pads. This tool allows you to accurately determine when the brake pads need to be replaced, preventing damage to the rotors and ensuring safe braking performance. According to a guide by the Car Care Council, checking brake pad thickness is a critical part of regular brake maintenance.
5.3. Rotor Runout Gauge
What does a rotor runout gauge measure and why is it important? A rotor runout gauge measures the lateral runout of brake rotors, which indicates whether they are warped or damaged; this tool helps identify rotor issues that can cause vibration and poor braking performance. Warped rotors can be dangerous.
A rotor runout gauge measures the lateral runout of brake rotors. Excessive runout can cause vibration and poor braking performance. This tool helps you identify rotors that are warped or damaged and need to be replaced. According to a guide by StopTech, a leading manufacturer of braking systems, measuring rotor runout is essential for diagnosing brake problems.
5.4. Brake Fluid Tester
How does a brake fluid tester contribute to brake system maintenance? A brake fluid tester measures the moisture content in brake fluid, helping you determine when it needs to be flushed; this tool prevents corrosion and ensures optimal braking performance by maintaining the quality of the brake fluid. Maintaining fluid quality is essential.
A brake fluid tester measures the moisture content in brake fluid. As brake fluid absorbs moisture over time, it can lead to corrosion and reduced braking performance. This tool helps you determine when the brake fluid needs to be flushed. According to a guide by Bosch, brake fluid should be tested regularly and replaced when the moisture content exceeds a certain level.
5.5. Basic Hand Tools
What basic hand tools are essential for brake repairs? Basic hand tools such as wrenches, sockets, screwdrivers, and pliers are essential for performing brake repairs; these tools allow you to disassemble and reassemble brake components efficiently and safely. Having a good set of tools can help you with any repair.
In addition to specialized tools, you will also need a set of basic hand tools for performing brake repairs. This includes wrenches, sockets, screwdrivers, pliers, and a torque wrench for tightening bolts to the correct specifications. Having a good set of tools will make the job easier and ensure that the repairs are done correctly.
6. When to Consult a Professional Mechanic
When should I consult a professional mechanic for brake issues? Consult a professional mechanic for brake issues if you are uncomfortable performing repairs yourself, if the OBD-II code indicates a serious problem, or if you are unsure about the diagnosis; a professional can provide expert diagnosis and ensure that the braking system is repaired correctly. It’s better to be safe than sorry, so consult a professional if you have any doubts.
While many brake issues can be diagnosed and repaired at home, there are times when it’s best to consult a professional mechanic. Here are some situations when you should seek professional help:
6.1. Uncomfortable Performing Repairs
When should I defer brake repairs to a professional due to my own limitations? If you are uncomfortable performing brake repairs yourself, it is best to consult a professional mechanic; attempting repairs beyond your skill level can lead to mistakes and compromise the safety of your vehicle. Safety should always be the top priority.
If you are not comfortable performing brake repairs yourself, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic. Brake repairs can be complex and require specialized knowledge and tools. Attempting repairs beyond your skill level can lead to mistakes and compromise the safety of your vehicle.
6.2. Serious OBD-II Codes
What types of OBD-II codes warrant immediate professional attention? If the OBD-II code indicates a serious problem, such as ABS malfunction or hydraulic system failure, consult a professional mechanic immediately; these issues can significantly compromise the safety of your vehicle and require expert diagnosis and repair. These issues require professional attention to ensure safety.
If the OBD-II code indicates a serious problem, such as an ABS malfunction or hydraulic system failure, consult a professional mechanic immediately. These issues can significantly compromise the safety of your vehicle and require expert diagnosis and repair.
6.3. Uncertain Diagnosis
What should I do if I am unsure about the diagnosis of a brake issue? If you are unsure about the diagnosis of a brake issue, consult a professional mechanic; they can perform a thorough inspection and provide an accurate diagnosis, ensuring that the correct repairs are performed. An accurate diagnosis can help prevent future problems.
If you are unsure about the diagnosis of a brake issue, consult a professional mechanic. They have the expertise and equipment to perform a thorough inspection and provide an accurate diagnosis. Getting a professional diagnosis can prevent you from wasting time and money on unnecessary repairs.
7. Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for Automotive Information
How can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN help me with automotive information and repairs? CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides detailed information, expert advice, and tool recommendations to help you diagnose and repair automotive issues effectively; our resources empower you to maintain your vehicle with confidence and ensure its optimal performance.
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources to help you with automotive information and repairs. Here are some of the benefits of using our website:
7.1. Detailed Information on OBD-II Codes
What kind of information can I find about OBD-II codes on CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN? CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides detailed information on various OBD-II codes, including their causes, symptoms, and potential solutions; this resource helps you understand the meaning of each code and take appropriate action.
Our website provides detailed information on various OBD-II codes, including their causes, symptoms, and potential solutions. Whether you’re dealing with a brake issue, an engine problem, or any other automotive issue, our resources can help you understand the meaning of the code and take appropriate action.
7.2. Expert Advice and Guides
What kind of expert advice and guides does CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offer? CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers expert advice and guides on various automotive topics, providing step-by-step instructions and tips for diagnosing and repairing common issues; these resources help you perform repairs with confidence and ensure the job is done correctly.
We offer expert advice and guides on various automotive topics. Our step-by-step instructions and tips can help you diagnose and repair common issues, from brake problems to engine maintenance. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional mechanic, our resources can help you perform repairs with confidence.
7.3. Tool Recommendations
How does CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN help me choose the right tools for automotive repairs? CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides recommendations for the best tools and equipment for automotive repairs, helping you choose the right tools for your needs and budget; our reviews and comparisons ensure you invest in quality tools that will last.
We provide recommendations for the best tools and equipment for automotive repairs. Our reviews and comparisons can help you choose the right tools for your needs and budget. Whether you’re looking for an OBD-II scanner, a brake pad thickness gauge, or a complete set of hand tools, we can help you find the best options.
8. Real-Life Examples of OBD-II Brake Code Issues
Can you share some real-life examples of how OBD-II brake codes manifested and were resolved? Yes, there are numerous examples where OBD-II brake codes have helped diagnose and resolve critical issues, such as a faulty wheel speed sensor causing ABS malfunction, a brake pedal switch failure affecting cruise control, and a brake pressure sensor issue impacting stability control; these examples illustrate the practical importance of understanding and addressing OBD-II brake codes.
Here are a few real-life examples of how OBD-II brake codes have helped diagnose and resolve critical issues:
8.1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
How did an OBD-II code help diagnose a faulty wheel speed sensor? In one case, an OBD-II code indicating a faulty wheel speed sensor led to the discovery that the ABS was malfunctioning; replacing the sensor restored the ABS to proper working condition, preventing potential accidents.
A driver noticed that their ABS light was on and the ABS was not functioning correctly. Using an OBD-II scanner, they retrieved a code indicating a faulty wheel speed sensor. After replacing the sensor, the ABS light turned off, and the ABS was functioning correctly. This prevented potential accidents by ensuring the ABS would work in emergency braking situations.
8.2. Brake Pedal Switch Failure
How did an OBD-II code pinpoint a brake pedal switch failure affecting cruise control? An OBD-II code indicating a brake pedal switch failure helped identify why the cruise control was not disengaging when the brakes were applied; replacing the switch resolved the issue, ensuring the cruise control system functioned safely.
A driver noticed that their cruise control was not disengaging when they applied the brakes. Using an OBD-II scanner, they retrieved a code indicating a brake pedal switch failure. After replacing the switch, the cruise control system functioned correctly, ensuring that it would disengage safely when the brakes were applied.
8.3. Brake Pressure Sensor Issue
How did an OBD-II code reveal a brake pressure sensor issue impacting stability control? An OBD-II code indicating a brake pressure sensor issue revealed that the stability control system was not functioning correctly; replacing the sensor restored the stability control system, enhancing vehicle safety during challenging driving conditions.
A driver noticed that their stability control system was not functioning correctly, especially during wet conditions. Using an OBD-II scanner, they retrieved a code indicating a brake pressure sensor issue. After replacing the sensor, the stability control system functioned correctly, enhancing vehicle safety during challenging driving conditions.
9. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Brake Systems
What are some advanced diagnostic techniques for brake systems beyond reading OBD-II codes? Beyond reading OBD-II codes, advanced diagnostic techniques for brake systems include using an oscilloscope to analyze sensor signals, performing hydraulic pressure tests, and conducting ABS module testing; these techniques provide deeper insights into the system’s performance and help identify complex issues.
For complex brake issues, advanced diagnostic techniques can provide deeper insights into the system’s performance. Here are some advanced techniques:
9.1. Oscilloscope Analysis
How can an oscilloscope help diagnose brake system issues? An oscilloscope can be used to analyze sensor signals in the brake system, providing a visual representation of the signal patterns; this helps identify intermittent or unusual signals that may indicate a faulty sensor or wiring issue. This provides more accurate results.
An oscilloscope can be used to analyze sensor signals in the brake system. This tool provides a visual representation of the signal patterns, allowing you to identify intermittent or unusual signals that may indicate a faulty sensor or wiring issue. According to Fluke Corporation, a leading manufacturer of oscilloscopes, this technique is invaluable for diagnosing complex electrical problems.
9.2. Hydraulic Pressure Testing
What does hydraulic pressure testing involve and why is it important? Hydraulic pressure testing involves measuring the pressure in the brake lines to identify issues such as leaks, blockages, or a faulty master cylinder; this ensures that the braking system is providing adequate pressure for safe and effective braking. It’s essential to make sure your brakes are working as intended.
Hydraulic pressure testing involves measuring the pressure in the brake lines to identify issues such as leaks, blockages, or a faulty master cylinder. This ensures that the braking system is providing adequate pressure for safe and effective braking. According to a guide by Gates Corporation, a leading manufacturer of automotive parts, hydraulic pressure testing is essential for diagnosing hydraulic brake problems.
9.3. ABS Module Testing
What does ABS module testing involve and what does it reveal? ABS module testing involves using specialized diagnostic tools to test the functionality of the ABS module, ensuring it is communicating correctly with the sensors and controlling the braking system as intended; this helps identify internal module faults that may not be apparent through standard OBD-II codes.
ABS module testing involves using specialized diagnostic tools to test the functionality of the ABS module. This ensures that the module is communicating correctly with the sensors and controlling the braking system as intended. This can help identify internal module faults that may not be apparent through standard OBD-II codes. According to a guide byATE, a leading manufacturer of braking systems, ABS module testing is essential for diagnosing complex ABS problems.
10. Future Trends in Brake System Diagnostics
What are the future trends in brake system diagnostics and how will they impact vehicle maintenance? Future trends in brake system diagnostics include the integration of AI-powered diagnostics, remote diagnostics via connected car technology, and enhanced sensor technology; these advancements will enable more accurate, efficient, and proactive brake system maintenance.
The future of brake system diagnostics is evolving rapidly with new technologies and innovations. Here are some trends to watch:
10.1. AI-Powered Diagnostics
How will AI-powered diagnostics improve brake system maintenance? AI-powered diagnostics will analyze data from various sensors in real-time, providing more accurate and efficient diagnoses of brake system issues; this technology will help identify potential problems before they become serious, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
AI-powered diagnostics will analyze data from various sensors in real-time, providing more accurate and efficient diagnoses of brake system issues. This technology will help identify potential problems before they become serious, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, AI-powered diagnostics will revolutionize the automotive industry.
10.2. Remote Diagnostics
How will remote diagnostics enhance brake system maintenance? Remote diagnostics via connected car technology will allow mechanics to access vehicle data remotely, enabling them to diagnose brake issues without the need for a physical inspection; this will streamline the diagnostic process and allow for quicker repairs.
Remote diagnostics via connected car technology will allow mechanics to access vehicle data remotely, enabling them to diagnose brake issues without the need for a physical inspection. This will streamline the diagnostic process and allow for quicker repairs. According to a report by Deloitte, connected car technology is transforming the automotive service industry.
10.3. Enhanced Sensor Technology
How will enhanced sensor technology improve brake system diagnostics? Enhanced sensor technology will provide more detailed and accurate data about brake system performance, enabling more precise diagnoses and preventative maintenance; these advanced sensors will detect subtle changes in brake system behavior, allowing for early intervention.
Enhanced sensor technology will provide more detailed and accurate data about brake system performance, enabling more precise diagnoses and preventative maintenance. These advanced sensors will detect subtle changes in brake system behavior, allowing for early intervention. According to a report by Bosch, enhanced sensor technology is driving innovation in automotive diagnostics.
Summary
Understanding OBD-II codes related to the braking system is essential for maintaining vehicle safety and preventing costly repairs. By using an OBD-II scanner, researching the codes, and performing regular maintenance, you can ensure that your braking system is functioning correctly. When in doubt, consult a professional mechanic to ensure that the repairs are done safely and effectively. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is your trusted resource for detailed information, expert advice, and tool recommendations to help you with all your automotive needs.
Call to Action
Ready to ensure your vehicle’s braking system is in top condition? Don’t wait until a minor issue turns into a major problem. Contact us at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert advice, high-quality tools, and comprehensive diagnostic services. Whether you’re dealing with a specific OBD-II code or just want to perform routine maintenance, we’re here to help. Reach out to us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, call us on Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN. Let us help you keep your vehicle safe and reliable. Contact us now and drive with confidence]
FAQ: OBD-II Codes and Brake Systems
1. What does it mean when my ABS light is on?
An illuminated ABS light typically indicates a problem within the anti-lock braking system, which could be due to a faulty wheel speed sensor, a malfunctioning ABS module, or other issues.
2. Can I drive with the ABS light on?
While you can technically drive with the ABS light on, it’s not recommended, as your ABS system may not function properly in an emergency braking situation.
3. How do I reset the ABS light?
To reset the ABS light, you first need to diagnose and fix the underlying issue causing the light to illuminate, then use an OBD-II scanner to clear the code.
4. What is a wheel speed sensor and why is it important?
A wheel speed sensor measures the rotational speed of the wheel and provides this data to the ABS, traction control, and stability control systems, which is essential for their proper functioning.
5. How often should I replace my brake pads?
Brake pads should be replaced when they reach the minimum thickness specified by the manufacturer, typically around 3mm, or if they show signs of damage or wear.
6. What is brake fluid and why does it need to be maintained?
Brake fluid is a hydraulic fluid that transmits pressure from the brake pedal to the brake calipers, and it needs to be maintained to prevent corrosion and ensure optimal braking performance.
7. How do I check the brake fluid level?
You can check the brake fluid level by locating the brake fluid reservoir under the hood and ensuring that the fluid level is within the “min” and “max” markings.
8. What is the difference between ABS and regular brakes?
ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) prevents the wheels from locking up during hard braking, allowing you to maintain steering control, while regular brakes can lock up the wheels, potentially causing a skid.
9. Can I replace brake pads myself?
Yes, you can replace brake pads yourself if you have the necessary tools and experience, but if you’re uncomfortable with the task, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic.
10. How do I know if my brake rotors need to be replaced?
Brake rotors should be replaced if they are below the minimum thickness specified by the manufacturer, or if they show signs of damage such as cracks, warping, or excessive rust.