Are There Any Manufacturer-specific OBD-II Codes? Yes, manufacturer-specific OBD-II codes exist and they are crucial for diagnosing vehicle problems, as they provide more detailed information than generic codes, which helps you pinpoint the exact issue affecting your car, truck, or SUV. Knowing about these codes can save you time and money by leading to quicker and more accurate repairs. At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we help you decipher these codes. We will equip you with the right tools and knowledge to address your auto repair needs. Let’s explore powertrain malfunctions, body control systems, and emission control problems.
1. Understanding OBD-II Codes
OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) codes are standardized alphanumeric codes used to identify malfunctions in a vehicle’s various systems. These codes are generated by the vehicle’s onboard computer when it detects an issue. Understanding these codes is vital for effective vehicle maintenance and repair.
1.1 What are OBD-II Codes?
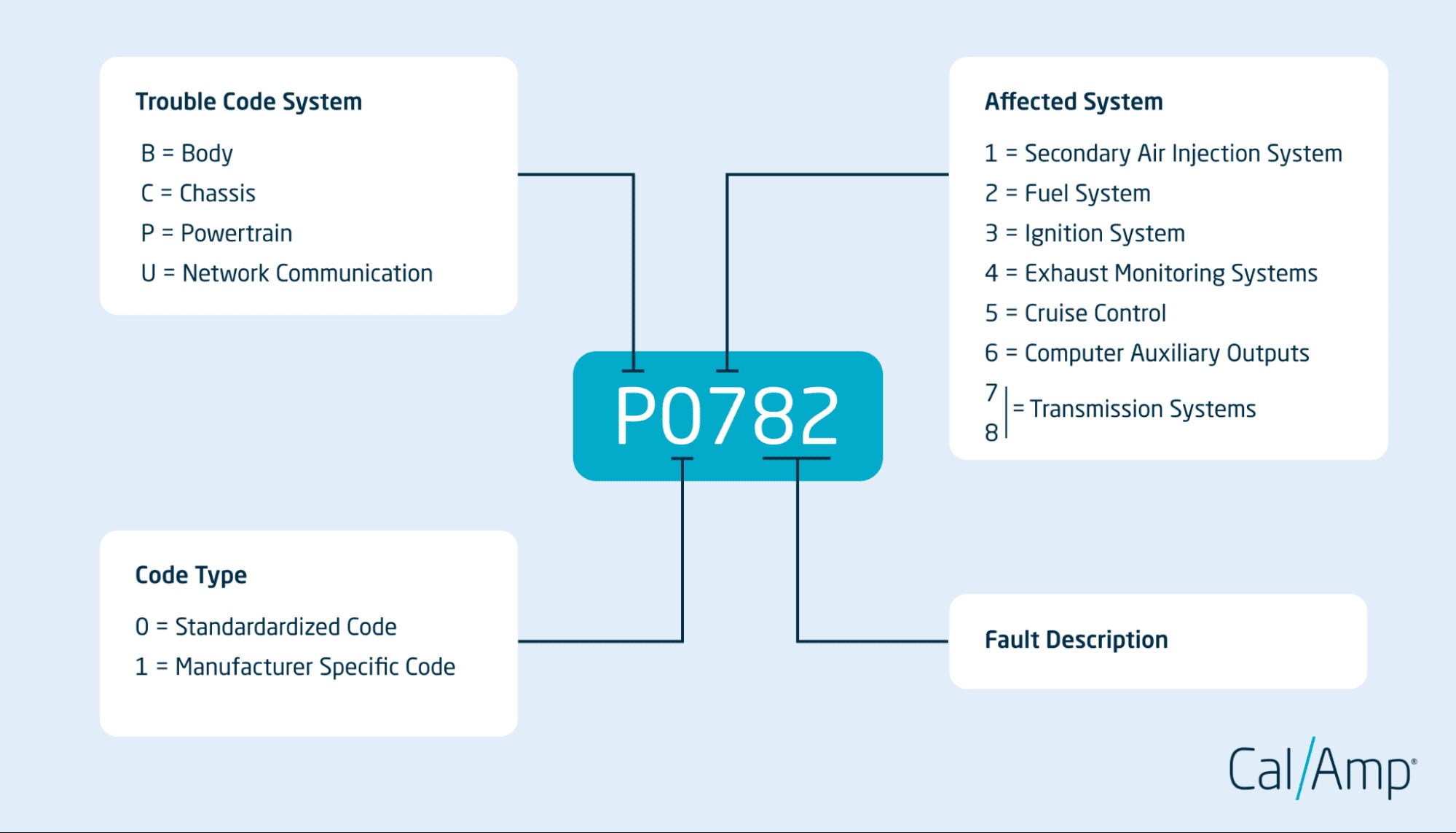
OBD-II codes are essentially diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that your vehicle’s computer uses to communicate issues it detects. These codes are standardized across all vehicles sold in the United States since 1996, ensuring a consistent method for identifying problems. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the standardization of OBD-II codes has greatly improved vehicle diagnostics and repair processes.
1.2 How OBD-II Codes Work
When a vehicle’s computer detects a problem, it stores a corresponding OBD-II code. This code can be retrieved using an OBD-II scanner, which connects to the vehicle’s diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard. The scanner reads the code, providing information about the nature and location of the problem.
For instance, if the engine misfires, the computer will detect this and generate a code such as P0300, indicating a random or multiple cylinder misfire. The mechanic can then use this information to diagnose the cause of the misfire, such as faulty spark plugs or a malfunctioning ignition coil.
1.3 The Importance of OBD-II Codes
OBD-II codes are crucial for several reasons:
- Accurate Diagnostics: They provide specific information about the problem, reducing guesswork and saving time.
- Preventative Maintenance: Identifying issues early can prevent more significant and costly repairs down the road.
- Compliance: Ensuring your vehicle meets emissions standards is essential for legal compliance and environmental responsibility.
Knowing how to interpret and address OBD-II codes can help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
2. Generic vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes
OBD-II codes are divided into two main categories: generic codes and manufacturer-specific codes. Understanding the difference between these two types of codes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and repair.
2.1 Generic OBD-II Codes
Generic OBD-II codes, also known as SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) codes, are standardized across all vehicle makes and models. These codes cover common issues that can occur in any vehicle, regardless of its manufacturer.
- Purpose: Generic codes are designed to provide a basic level of diagnostic information that is consistent across all vehicles.
- Range: These codes typically fall within the range of P0000 to P0999, B0000 to B0999, C0000 to C0999, and U0000 to U0999.
- Examples:
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
2.2 Manufacturer-Specific OBD-II Codes
Manufacturer-specific OBD-II codes are unique to each vehicle manufacturer. These codes provide more detailed information about issues that are specific to a particular make or model.
- Purpose: Manufacturer-specific codes allow for more precise diagnostics by addressing issues that are unique to a specific vehicle’s design or components.
- Range: These codes typically fall within the range of P1000 to P1999, B1000 to B1999, C1000 to C1999, and U1000 to U1999.
- Examples:
- P1138 (Audi/VW): Exhaust Gas Correction Behind Catalyst, Bank 1
- P1504 (Ford): Idle Air Control Circuit Malfunction
- P1630 (BMW): Injector Circuit Cylinder 1
2.3 Key Differences
| Feature | Generic OBD-II Codes | Manufacturer-Specific OBD-II Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Standardization | Standardized across all makes and models | Unique to each vehicle manufacturer |
| Detail Level | Provides basic diagnostic information | Offers more detailed and precise diagnostic information |
| Code Range | P0000-P0999, B0000-B0999, C0000-C0999, U0000-U0999 | P1000-P1999, B1000-B1999, C1000-C1999, U1000-U1999 |
| Diagnostic Scope | Covers common issues applicable to any vehicle | Addresses issues specific to a particular vehicle’s design or components |
| Repair Guidance | Provides a general direction for troubleshooting | Offers more specific guidance for targeted repairs |
| Applicability | Applicable to all OBD-II compliant vehicles | Applicable only to the specific make and model |
| Ease of Interpretation | Easier to interpret due to their widespread use | May require access to manufacturer-specific diagnostic tools and information |
2.4 Why Manufacturer-Specific Codes Matter
Manufacturer-specific codes are essential for accurate diagnostics because they provide a level of detail that generic codes cannot match. For instance, a generic code might indicate a problem with the fuel system, while a manufacturer-specific code can pinpoint the exact component within the fuel system that is malfunctioning.
3. Examples of Manufacturer-Specific Codes
To illustrate the importance of manufacturer-specific codes, let’s look at some examples from different automakers.
3.1 Ford
-
P1000: OBD-II Monitor Testing Incomplete
- Description: Indicates that the OBD-II system has not completed all of its diagnostic tests.
- Possible Causes: Recent battery disconnection, recent code clearing, or incomplete drive cycles.
-
P1131: Lack of HO2S Switch Sensor Indicates Lean Bank 1
- Description: Indicates that the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) on Bank 1 is not switching properly, suggesting a lean condition.
- Possible Causes: Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, or fuel delivery issues.
3.2 GM (General Motors)
-
P1689: Delivered Torque Signal Circuit
- Description: Indicates a problem with the delivered torque signal circuit, which is used by the engine control module (ECM) to manage engine performance.
- Possible Causes: Faulty sensor, wiring issues, or ECM malfunction.
-
P1174: Fuel Trim Learn
- Description: Indicates a problem with the fuel trim learning process, which helps the ECM adjust fuel delivery for optimal performance.
- Possible Causes: Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, or fuel injector issues.
3.3 Toyota
-
P1349: VVT System Malfunction (Bank 1)
- Description: Indicates a malfunction in the variable valve timing (VVT) system on Bank 1, which controls the timing of the intake and exhaust valves.
- Possible Causes: Faulty VVT solenoid, oil control valve issues, or mechanical problems with the VVT system.
-
P1656: Open Circuit of VVT System (Bank 1)
- Description: Indicates an open circuit in the VVT system on Bank 1, which can prevent the system from functioning correctly.
- Possible Causes: Wiring issues, faulty VVT solenoid, or damaged connectors.
3.4 BMW
-
P1520: Camshaft Position Actuator ‘A’ Circuit Open (Bank 1)
- Description: Indicates an open circuit in the camshaft position actuator ‘A’ circuit on Bank 1, which is used to control the position of the camshaft.
- Possible Causes: Wiring issues, faulty actuator, or damaged connectors.
-
P1083: Fuel Control Mixture Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
- Description: Indicates that the fuel mixture is too lean on Bank 1, as detected by the upstream oxygen sensor.
- Possible Causes: Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, or fuel delivery issues.
3.5 Audi/Volkswagen
-
P1136: Fuel Trim: System Lean (Bank 1)
- Description: Indicates that the fuel trim is too lean on Bank 1, meaning the engine is not getting enough fuel.
- Possible Causes: Vacuum leaks, faulty MAF sensor, or fuel delivery issues.
-
P1545: Throttle Valve Control System Malfunction
- Description: Indicates a malfunction in the throttle valve control system, which controls the amount of air entering the engine.
- Possible Causes: Faulty throttle position sensor, wiring issues, or throttle body problems.
These examples illustrate how manufacturer-specific codes can provide precise information about the nature and location of a problem, leading to more efficient and accurate repairs.
4. Accessing Manufacturer-Specific Code Information
Accessing manufacturer-specific code information is essential for accurate diagnostics and repairs. Several resources are available to help you retrieve and interpret these codes.
4.1 OBD-II Scanners
OBD-II scanners are essential tools for retrieving diagnostic trouble codes from your vehicle’s computer. While basic scanners can read both generic and manufacturer-specific codes, advanced scanners offer additional features that can be particularly useful.
- Basic Scanners: These scanners can read and clear codes, providing a basic level of diagnostic information.
- Advanced Scanners: These scanners offer enhanced features such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, and bidirectional control, allowing for more in-depth diagnostics.
4.2 Online Databases
Several online databases provide information about OBD-II codes, including manufacturer-specific codes. These databases can be valuable resources for looking up code definitions and potential causes.
- OBD-Codes.com: A comprehensive database of OBD-II codes, including generic and manufacturer-specific codes.
- AutoCodes.com: Offers detailed information about OBD-II codes, including potential causes, symptoms, and troubleshooting tips.
4.3 Repair Manuals
Repair manuals provide detailed information about your vehicle’s systems, including diagnostic procedures and code definitions. These manuals are available for specific makes and models, making them a valuable resource for accessing manufacturer-specific information.
- Haynes Repair Manuals: Offer step-by-step instructions and diagrams for various repair procedures.
- Chilton Repair Manuals: Provide comprehensive coverage of vehicle systems, including diagnostic information and code definitions.
4.4 Professional Diagnostic Tools
Professional diagnostic tools, such as those used by mechanics and technicians, offer advanced features and access to manufacturer-specific data. These tools can be expensive but provide the most comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Snap-on Scanners: Known for their advanced features and comprehensive coverage of vehicle makes and models.
- Autel Scanners: Offer a range of diagnostic capabilities, including code reading, live data streaming, and bidirectional control.
4.5 Manufacturer Websites
Some vehicle manufacturers provide access to diagnostic information through their websites or subscription services. These resources can be valuable for accessing the most up-to-date and accurate information about manufacturer-specific codes.
- GM Techlink: Provides technical information and diagnostic tips for GM vehicles.
- Ford Technical Resources: Offers access to diagnostic information and repair procedures for Ford vehicles.
5. Interpreting Manufacturer-Specific Codes
Interpreting manufacturer-specific codes requires a systematic approach and access to the right resources. Here are some tips for effectively interpreting these codes:
5.1 Use the Correct Resources
Ensure you are using resources that are specific to your vehicle’s make and model. Generic code definitions may not be accurate for manufacturer-specific codes.
5.2 Understand the Code Structure
Familiarize yourself with the structure of OBD-II codes, including the meaning of each digit and letter. This will help you narrow down the potential causes of the problem.
5.3 Consider the Symptoms
Pay attention to any symptoms your vehicle is exhibiting, such as rough idling, poor acceleration, or unusual noises. These symptoms can provide valuable clues about the nature of the problem.
5.4 Check for Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs)
Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) are issued by vehicle manufacturers to provide information about common problems and recommended repair procedures. Checking for TSBs related to your vehicle’s make, model, and OBD-II code can provide valuable insights.
5.5 Seek Professional Assistance
If you are unsure about how to interpret a manufacturer-specific code or diagnose the underlying problem, seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or technician.
6. Common Issues Indicated by Manufacturer-Specific Codes
Manufacturer-specific codes can indicate a wide range of issues, depending on the vehicle’s make, model, and systems. Here are some common issues that are often indicated by these codes:
6.1 Powertrain Issues
- Engine Misfires: Codes related to engine misfires can indicate problems with the ignition system, fuel system, or engine components.
- Fuel System Problems: Codes related to the fuel system can indicate issues with fuel injectors, fuel pumps, or fuel pressure regulators.
- Transmission Problems: Codes related to the transmission can indicate issues with shift solenoids, transmission sensors, or internal transmission components.
6.2 Body Issues
- Airbag System Problems: Codes related to the airbag system can indicate issues with airbag sensors, airbag modules, or wiring.
- Lighting System Problems: Codes related to the lighting system can indicate issues with headlights, taillights, or turn signals.
- Climate Control Problems: Codes related to the climate control system can indicate issues with the AC compressor, blower motor, or temperature sensors.
6.3 Chassis Issues
- ABS Problems: Codes related to the anti-lock braking system (ABS) can indicate issues with wheel speed sensors, ABS modules, or hydraulic components.
- Suspension Problems: Codes related to the suspension system can indicate issues with shocks, struts, or air suspension components.
- Steering Problems: Codes related to the steering system can indicate issues with power steering pumps, steering sensors, or steering gears.
6.4 Network Communication Issues
- CAN Bus Problems: Codes related to the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus can indicate issues with communication between different vehicle modules.
- Module Communication Problems: Codes related to module communication can indicate issues with specific modules, such as the engine control module (ECM) or transmission control module (TCM).
7. The Role of CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN in OBD-II Diagnostics
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is dedicated to providing comprehensive information and resources for automotive diagnostics, including OBD-II codes. We understand the importance of accurate and reliable information when it comes to vehicle maintenance and repair.
7.1 Comprehensive Database
Our website features a comprehensive database of OBD-II codes, including both generic and manufacturer-specific codes. This database is regularly updated to ensure that you have access to the most accurate and up-to-date information.
7.2 Expert Guidance
We provide expert guidance on how to interpret OBD-II codes and diagnose vehicle problems. Our team of experienced automotive technicians and mechanics is dedicated to helping you understand the complexities of OBD-II diagnostics.
7.3 Product Recommendations
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers product recommendations for OBD-II scanners and diagnostic tools. We carefully select and review products to ensure that you have access to the best tools for your diagnostic needs.
7.4 Educational Resources
We provide a wide range of educational resources, including articles, videos, and tutorials, to help you learn about OBD-II diagnostics. Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge and skills you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
7.5 Community Support
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a community forum where you can connect with other vehicle owners and enthusiasts. This forum provides a platform for sharing information, asking questions, and getting support from fellow members.
8. Steps to Take When You Encounter a Manufacturer-Specific Code
When you encounter a manufacturer-specific code, it’s important to take a systematic approach to diagnosis and repair. Here are the steps you should follow:
8.1 Record the Code
Use an OBD-II scanner to record the code and any associated data, such as freeze frame data. This information can be valuable for troubleshooting.
8.2 Research the Code
Use online databases, repair manuals, or manufacturer websites to research the code and understand its definition and potential causes.
8.3 Inspect the Vehicle
Inspect the vehicle for any obvious symptoms, such as leaks, damage, or worn components. Pay attention to any unusual noises or smells.
8.4 Test the Components
Use diagnostic tools, such as multimeters and scan tools, to test the components that are related to the code. Follow the diagnostic procedures outlined in the repair manual or manufacturer’s website.
8.5 Repair or Replace the Components
Repair or replace any faulty components, following the recommended repair procedures.
8.6 Clear the Code
After completing the repairs, clear the code using an OBD-II scanner.
8.7 Test the Vehicle
Test the vehicle to ensure that the problem has been resolved and that no new codes have been generated.
9. Preventing OBD-II Codes
Preventing OBD-II codes is essential for maintaining the health and longevity of your vehicle. Here are some tips for preventing these codes:
9.1 Regular Maintenance
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, including oil changes, fluid flushes, and filter replacements.
9.2 Use Quality Fluids
Use high-quality fluids that meet or exceed the manufacturer’s specifications.
9.3 Monitor Vehicle Performance
Pay attention to any changes in your vehicle’s performance, such as decreased fuel economy, rough idling, or unusual noises.
9.4 Address Problems Promptly
Address any problems as soon as they are detected to prevent them from escalating into more significant issues.
9.5 Drive Responsibly
Avoid aggressive driving habits, such as hard acceleration and braking, which can put unnecessary stress on your vehicle’s components.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
10.1 What is the difference between a generic and a manufacturer-specific OBD-II code?
Generic OBD-II codes are standardized across all vehicles, while manufacturer-specific codes are unique to each vehicle manufacturer and provide more detailed information.
10.2 How can I find the definition of a manufacturer-specific OBD-II code?
You can find the definition of a manufacturer-specific OBD-II code by using online databases, repair manuals, or manufacturer websites.
10.3 Do I need a special OBD-II scanner to read manufacturer-specific codes?
Most OBD-II scanners can read both generic and manufacturer-specific codes, but advanced scanners offer additional features that can be particularly useful for diagnosing manufacturer-specific issues.
10.4 Can I fix a problem indicated by a manufacturer-specific code myself?
Whether you can fix a problem yourself depends on your mechanical skills and the complexity of the issue. Some repairs may require specialized tools or knowledge, in which case it’s best to seek professional assistance.
10.5 What should I do if I’m not sure how to interpret a manufacturer-specific code?
If you’re not sure how to interpret a manufacturer-specific code, seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or technician.
10.6 Are manufacturer-specific codes more serious than generic codes?
Not necessarily. The severity of a code depends on the nature of the problem, not whether it’s generic or manufacturer-specific.
10.7 How often should I scan my vehicle for OBD-II codes?
You should scan your vehicle for OBD-II codes whenever the check engine light comes on or if you notice any changes in your vehicle’s performance.
10.8 Can clearing an OBD-II code fix the underlying problem?
No, clearing an OBD-II code will not fix the underlying problem. It will only turn off the check engine light. The problem will likely return if the underlying issue is not addressed.
10.9 Where can I buy an OBD-II scanner?
You can buy an OBD-II scanner from automotive parts stores, online retailers, or tool suppliers.
10.10 How can I prevent OBD-II codes from appearing in my vehicle?
You can prevent OBD-II codes from appearing in your vehicle by following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, using quality fluids, monitoring vehicle performance, and addressing problems promptly.
Manufacturer-specific OBD-II codes are essential for accurate vehicle diagnostics and repairs. By understanding these codes and knowing how to interpret them, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we’re here to provide you with the information and resources you need to tackle any diagnostic challenge. Whether you need to access technical service bulletins, or decode a network communication code, we are here to help you.
 OBD-II Scanner
OBD-II Scanner
Need assistance with manufacturer-specific OBD-II codes? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert advice and product recommendations. Our team is ready to help you diagnose and resolve any vehicle issue. Reach out to us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN. Let us help you keep your vehicle running at its best.