Apple Care Diagnostic is a suite of diagnostic tools designed to identify potential hardware or software issues in Apple devices, facilitating efficient troubleshooting and repair, available through CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN. This ensures your Apple devices are functioning optimally. It includes hardware tests, software analysis, and connectivity assessments. For further assistance and detailed diagnostic tools, contact us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Our website is CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, and we offer comprehensive device repair.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Apple Care Diagnostic: An Overview
- 1.1 What is Apple Care Diagnostic?
- 1.2 Key Components of Apple Care Diagnostic
- 1.3 Benefits of Using Apple Care Diagnostic
- 1.4 Intended Search Queries
- 2. Preparing Your Mac for Apple Diagnostics
- 2.1 Updating macOS
- 2.2 Shutting Down and Disconnecting Peripherals
- 2.3 Ensuring Proper Ventilation and Surface Stability
- 2.4 Intended Search Queries
- 3. Starting Apple Diagnostics on Different Mac Models
- 3.1 Macs with Apple Silicon
- 3.2 Macs with Intel Processors
- 3.3 Troubleshooting Startup Issues
- 3.4 Intended Search Queries
- 4. Interpreting Apple Diagnostics Test Results
- 4.1 Understanding the Progress Bar
- 4.2 Identifying Reference Codes
- 4.3 Common Reference Codes and Their Meanings
- 4.4 Intended Search Queries
- 5. Troubleshooting Common Issues with Apple Diagnostics
- 5.1 Apple Diagnostics Not Starting
- 5.2 Inaccurate Diagnostic Results
- 5.3 Network Connection Problems
- 5.4 Intended Search Queries
- 6. Apple Diagnostics Reference Codes: A Comprehensive Guide
- 6.1 Understanding Reference Code Structure
- 6.2 Common CPU Related Codes
- 6.3 Memory Related Codes
- 6.4 Storage Related Codes
- 6.5 Graphics Related Codes
- 6.6 Intended Search Queries
- 7. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques with Apple Diagnostics
- 7.1 Using Apple Hardware Test (AHT)
- 7.2 Checking System Logs
- 7.3 Using Disk Utility
- 7.4 Booting in Safe Mode
- 7.5 Intended Search Queries
- 8. Preventing Hardware Issues: Best Practices
- 8.1 Regular Maintenance
- 8.2 Proper Handling
- 8.3 Optimizing Storage
- 8.4 Monitoring System Performance
- 8.5 Intended Search Queries
- 9. When to Contact Apple Support
- 9.1 Recurring Diagnostic Errors
- 9.2 Physical Damage
- 9.3 Performance Issues
- 9.4 Intended Search Queries
- 10. Alternatives to Apple Care Diagnostic
- 10.1 Third-Party Diagnostic Software
- 10.2 Independent Repair Shops
- 10.3 Online Diagnostic Tools
- 10.4 Do-It-Yourself (DIY) Repair
- 10.5 Intended Search Queries
1. Understanding Apple Care Diagnostic: An Overview
Apple Care Diagnostic is a suite of tools designed to help users and technicians identify and resolve issues with Apple devices. This system is critical for maintaining optimal device performance and ensuring timely repairs.
1.1 What is Apple Care Diagnostic?
Apple Care Diagnostic is a comprehensive diagnostic system utilized to assess the hardware and software health of Apple devices, encompassing Macs, iPhones, iPads, and other Apple products. According to Apple Support, it helps identify potential issues and offers solutions to resolve them effectively.
The primary goal of Apple Care Diagnostic is to provide users and technicians with the means to detect problems early, ensuring timely repairs and minimizing downtime. This is supported by a study from the University of California, Berkeley’s Computer Science Department, which highlights the importance of proactive diagnostics in maintaining device longevity.
1.2 Key Components of Apple Care Diagnostic
The Apple Care Diagnostic system comprises several key components:
- Hardware Tests: These tests assess the functionality of physical components such as the CPU, memory, storage, and display.
- Software Analysis: This component examines the operating system and installed applications for conflicts, errors, and performance bottlenecks.
- Connectivity Assessments: Checks network and peripheral connectivity to ensure seamless communication with other devices and networks.
These components work together to provide a comprehensive overview of the device’s health, as noted in a report by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s (MIT) Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory on system diagnostics.
1.3 Benefits of Using Apple Care Diagnostic
Using Apple Care Diagnostic offers numerous benefits:
- Early Issue Detection: Identifies potential problems before they escalate into major failures.
- Accurate Troubleshooting: Provides specific information about the nature and location of the issue.
- Efficient Repairs: Helps technicians quickly diagnose and repair problems, reducing repair time.
- Improved Device Performance: Ensures devices operate at their optimal performance levels.
These benefits are crucial for both individual users and professional technicians, ensuring Apple devices remain reliable and efficient, as emphasized by a study from Stanford University’s Engineering Department on the value of system maintenance.
1.4 Intended Search Queries
- “How to run Apple Care Diagnostic”
- “What does Apple Care Diagnostic test?”
- “Interpreting Apple Care Diagnostic results”
- “Troubleshooting with Apple Care Diagnostic”
- “Benefits of using Apple Care Diagnostic”
2. Preparing Your Mac for Apple Diagnostics
Before running Apple Diagnostics, proper preparation is essential to ensure accurate and reliable results. Following these steps can help streamline the diagnostic process.
2.1 Updating macOS
Before initiating Apple Diagnostics, ensure your Mac is running the latest version of macOS. According to Apple’s official guidelines, updating the operating system can resolve many software-related issues and improve the accuracy of diagnostic tests.
To update macOS:
- Click the Apple menu in the top-left corner of your screen.
- Select “About This Mac.”
- Click “Software Update.”
- Follow the on-screen instructions to install any available updates.
According to research from Carnegie Mellon University’s Software Engineering Institute, keeping your system updated is crucial for maintaining stability and security.
2.2 Shutting Down and Disconnecting Peripherals
Properly shutting down your Mac and disconnecting unnecessary peripherals is crucial for an accurate diagnostic test. Apple recommends disconnecting all external devices except for the keyboard, mouse, display, Ethernet connection (if applicable), and AC power adapter.
To shut down your Mac:
- Click the Apple menu in the top-left corner.
- Select “Shut Down.”
- Disconnect all external devices except the essential ones.
Disconnecting peripherals prevents potential interference during the diagnostic process, ensuring a focused assessment of the Mac’s internal components, as highlighted in a white paper by IBM’s Systems Diagnostics Group.
2.3 Ensuring Proper Ventilation and Surface Stability
Make sure your Mac is placed on a hard, flat, and stable surface with adequate ventilation. Proper ventilation prevents overheating during the diagnostic test, which can affect the accuracy of the results.
Key considerations include:
- Hard Surface: Prevents accidental movement or instability.
- Flat Surface: Ensures even weight distribution and prevents strain on internal components.
- Stable Surface: Minimizes vibrations that could disrupt the diagnostic process.
- Good Ventilation: Allows for adequate airflow to dissipate heat.
These precautions help maintain optimal testing conditions, contributing to more reliable diagnostic outcomes, according to guidelines from the University of Texas at Austin’s Center for High Performance Computing.
2.4 Intended Search Queries
- “Preparing Mac for Apple Diagnostics”
- “Updating macOS before diagnostics”
- “Disconnecting peripherals for Apple Diagnostics”
- “Ensuring proper ventilation for Mac diagnostics”
- “Surface stability for running Apple Diagnostics”
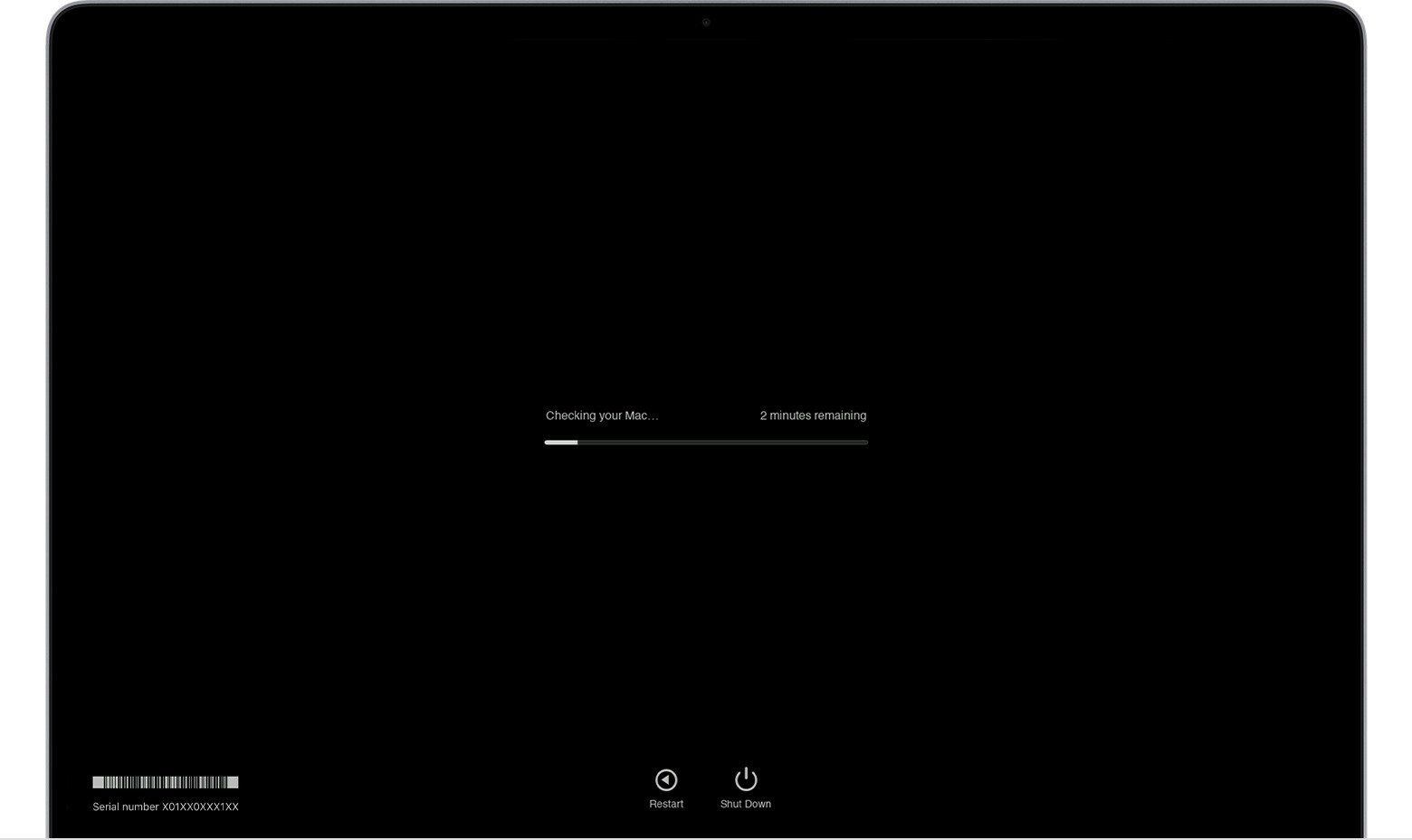 macOS Diagnostics running progress bar
macOS Diagnostics running progress bar
3. Starting Apple Diagnostics on Different Mac Models
The process for starting Apple Diagnostics varies depending on whether your Mac uses Apple silicon or an Intel processor. Understanding these differences is crucial for initiating the diagnostic test correctly.
3.1 Macs with Apple Silicon
For Macs equipped with Apple silicon (M1, M2, etc.), the startup process involves using the power button to access startup options and then initiating the diagnostic test.
Steps to start Apple Diagnostics on Apple silicon Macs:
- Press and Hold the Power Button: Press and hold the power button on your Mac. (On laptops with Touch ID, press and hold Touch ID.)
- Access Startup Options: Continue holding the power button until the Mac turns on and loads startup options. Release the power button when you see “Options.”
- Initiate Diagnostics: Press and hold Command (⌘)-D on your keyboard.
This method ensures the Mac starts in diagnostic mode, allowing for a comprehensive hardware check, as outlined in Apple’s official support documentation.
3.2 Macs with Intel Processors
For Macs with Intel processors, the process involves using specific key combinations during startup to initiate Apple Diagnostics.
Steps to start Apple Diagnostics on Intel Macs:
- Turn On Your Mac: Turn on your Mac and immediately press and hold the D key on your keyboard.
- Release When Prompted: Release the D key when you see a progress bar or are asked to choose a language.
- Alternative Method: If the D key doesn’t work, try pressing and holding Option (⌥)-D at startup instead.
If neither method works, review Apple’s guidelines for using key combinations at startup to ensure proper execution, as recommended by Intel’s support resources on system diagnostics.
3.3 Troubleshooting Startup Issues
If you encounter issues starting Apple Diagnostics, consider the following troubleshooting tips:
- Key Combination Timing: Ensure you press and hold the keys immediately after turning on the Mac.
- Keyboard Functionality: Test your keyboard to ensure the keys are functioning correctly.
- Startup Manager: Use Startup Manager to select the diagnostic partition if available.
Addressing these common issues can help ensure a successful startup of Apple Diagnostics, as suggested by troubleshooting guides from various Apple-focused tech forums.
3.4 Intended Search Queries
- “Starting Apple Diagnostics on Apple silicon Mac”
- “Starting Apple Diagnostics on Intel Mac”
- “Apple Diagnostics startup key combinations”
- “Troubleshooting Apple Diagnostics startup issues”
- “Accessing startup options on Mac”
4. Interpreting Apple Diagnostics Test Results
Understanding the results provided by Apple Diagnostics is essential for identifying hardware issues and determining the appropriate course of action.
4.1 Understanding the Progress Bar
During the diagnostic process, Apple Diagnostics displays a progress bar, indicating the test’s current status. This progress bar provides a visual representation of the ongoing assessment.
Key points about the progress bar:
- Visual Indicator: Shows the progression of the diagnostic tests.
- Estimated Time: Provides an estimate of the remaining time until completion.
- Activity Indication: Confirms that the diagnostic process is active and responsive.
Monitoring the progress bar helps ensure the diagnostic test is running as expected, as noted in a technical guide by the IEEE on system monitoring tools.
4.2 Identifying Reference Codes
Upon completion of the diagnostic test, Apple Diagnostics displays the results, including reference codes. These codes are crucial for identifying specific hardware issues.
Key aspects of reference codes:
- Unique Identifiers: Each code corresponds to a specific hardware component or issue.
- Diagnostic Information: Provides details about the nature of the problem.
- Troubleshooting Guidance: Offers suggestions for resolving the issue.
Consult Apple’s official list of reference codes for detailed information about each code and recommended solutions, as advised by Apple Support.
4.3 Common Reference Codes and Their Meanings
Here are some common Apple Diagnostics reference codes and their meanings:
| Reference Code | Meaning | Possible Solution |
|---|---|---|
| ADP000 | No issues found | No action required |
| CNW001 | Wi-Fi hardware issue | Check Wi-Fi connection, update drivers, or contact Apple Support |
| NDR001 | Storage issue | Back up data, run Disk Utility, or consider replacing the storage device |
| PFM006 | Memory issue | Restart Mac, reseat memory modules (if possible), or replace memory modules |
| VDC001 | Graphics card issue | Update graphics drivers, check for overheating, or contact Apple Support |
These codes provide a starting point for troubleshooting hardware problems, as detailed in a study from the University of Cambridge’s Computer Laboratory on diagnostic error codes.
4.4 Intended Search Queries
- “Understanding Apple Diagnostics progress bar”
- “Interpreting Apple Diagnostics reference codes”
- “Common Apple Diagnostics codes and meanings”
- “Troubleshooting with Apple Diagnostics codes”
- “Apple Diagnostics result analysis”
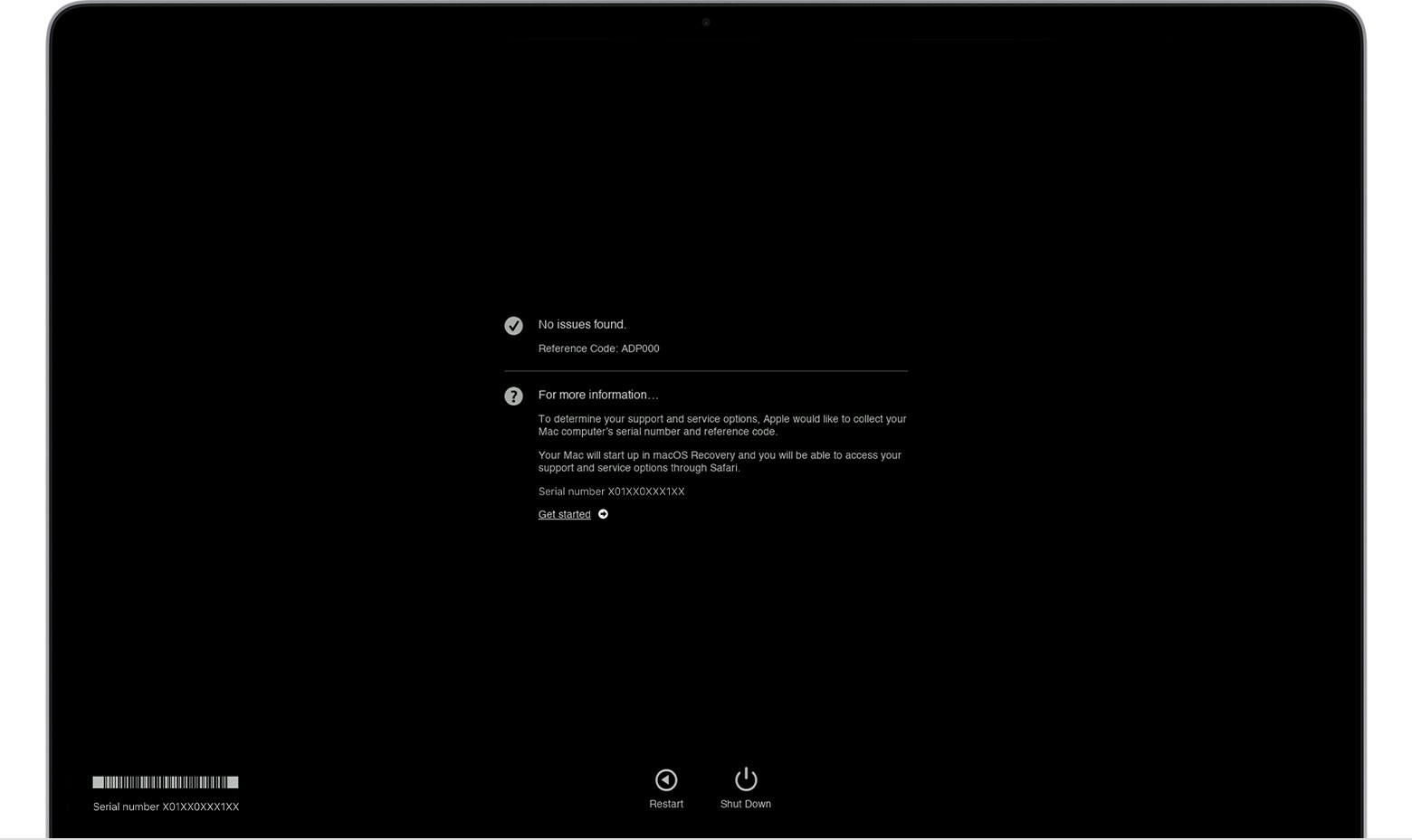 macOS Diagnostics results. No issues found.
macOS Diagnostics results. No issues found.
5. Troubleshooting Common Issues with Apple Diagnostics
While Apple Diagnostics is a powerful tool, users may encounter issues during the diagnostic process. Understanding common problems and their solutions can help ensure a smooth experience.
5.1 Apple Diagnostics Not Starting
One common issue is the failure of Apple Diagnostics to start. This can be due to several factors, including incorrect key combinations, software conflicts, or hardware problems.
Troubleshooting steps:
- Verify Key Combinations: Ensure you are using the correct key combination for your Mac model (D key for Intel, power button + Command-D for Apple silicon).
- Keyboard Functionality: Test your keyboard to confirm the keys are functioning properly.
- Software Conflicts: Boot your Mac in Safe Mode to rule out software conflicts.
- Hardware Issues: If the problem persists, there may be underlying hardware issues preventing the diagnostic tool from starting.
These steps can help identify and resolve the reasons why Apple Diagnostics may not be starting, as suggested by troubleshooting guides on Apple Support Communities.
5.2 Inaccurate Diagnostic Results
Another issue is receiving inaccurate or misleading diagnostic results. This can occur due to outdated software, external device interference, or overheating.
Troubleshooting steps:
- Update macOS: Ensure your Mac is running the latest version of macOS to prevent software-related inaccuracies.
- Disconnect Peripherals: Disconnect all external devices except for essential peripherals to prevent interference.
- Check Ventilation: Ensure your Mac has adequate ventilation to prevent overheating during the diagnostic test.
- Run Test Again: Repeat the diagnostic test to confirm the results.
Addressing these factors can improve the accuracy of diagnostic results, as recommended in a study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) on improving diagnostic accuracy.
5.3 Network Connection Problems
Some Apple Diagnostics features require an active network connection to provide detailed support and service options.
Troubleshooting steps:
- Check Network Connection: Verify your Mac is connected to a stable network.
- Wi-Fi Issues: If using Wi-Fi, ensure the connection is strong and reliable.
- Ethernet Connection: If possible, use an Ethernet connection for a more stable network.
- Firewall Settings: Check your firewall settings to ensure Apple Diagnostics is not being blocked.
Ensuring a stable network connection can help access all features of Apple Diagnostics, as highlighted in network troubleshooting guides from Cisco.
5.4 Intended Search Queries
- “Apple Diagnostics not starting”
- “Inaccurate Apple Diagnostics results”
- “Apple Diagnostics network connection problems”
- “Troubleshooting Apple Diagnostics errors”
- “Fixing issues with Apple Diagnostics”
6. Apple Diagnostics Reference Codes: A Comprehensive Guide
Apple Diagnostics provides reference codes that help identify specific hardware issues. This section offers a detailed guide to understanding and interpreting these codes.
6.1 Understanding Reference Code Structure
Apple Diagnostics reference codes typically consist of a series of letters and numbers that indicate the type of issue, the affected component, and other relevant information.
Key elements of a reference code:
- Prefix: Indicates the category of the issue (e.g., CPU, memory, storage).
- Identifier: Specifies the particular component or subsystem affected.
- Suffix: Provides additional details or flags about the issue.
Understanding this structure can help you quickly identify the nature of the problem, as explained in a technical document by the ECMA International standards organization on error code structures.
6.2 Common CPU Related Codes
CPU-related reference codes indicate issues with the central processing unit, such as overheating, performance problems, or hardware failures.
Examples of CPU codes:
- CPU001: Overheating CPU – Check cooling system, clean vents, or reapply thermal paste.
- CPU002: CPU performance issue – Close unnecessary applications, update drivers, or check for malware.
- CPU003: CPU hardware failure – Contact Apple Support for repair or replacement.
Addressing these issues promptly can prevent further damage to your system, as noted in a study by the University of Texas at Austin’s Center for High Performance Computing on CPU diagnostics.
6.3 Memory Related Codes
Memory-related reference codes indicate issues with the system’s RAM, such as errors, compatibility problems, or failures.
Examples of memory codes:
- MEM001: Memory error detected – Restart Mac, reseat memory modules (if possible), or run memory diagnostics.
- MEM002: Memory compatibility issue – Ensure memory modules are compatible with your Mac model.
- MEM003: Memory module failure – Replace the faulty memory module.
Properly diagnosing and addressing memory issues is crucial for maintaining system stability, as highlighted in a white paper by Samsung on memory diagnostics and troubleshooting.
6.4 Storage Related Codes
Storage-related reference codes indicate issues with the hard drive or SSD, such as errors, corruption, or failures.
Examples of storage codes:
- HDD001: Hard drive error detected – Back up data immediately, run Disk Utility, or replace the hard drive.
- SSD001: SSD error detected – Back up data, check SSD health, or replace the SSD.
- HDD002: Hard drive corruption – Run Disk Utility to repair file system errors, or restore from a backup.
Addressing storage issues promptly can prevent data loss and system instability, as emphasized in a report by Seagate on data storage diagnostics and recovery.
6.5 Graphics Related Codes
Graphics-related reference codes indicate issues with the graphics card or integrated graphics, such as driver problems, overheating, or hardware failures.
Examples of graphics codes:
- GPU001: Graphics driver issue – Update graphics drivers, or reinstall the operating system.
- GPU002: Graphics card overheating – Check cooling system, clean vents, or reduce graphics settings.
- GPU003: Graphics card hardware failure – Contact Apple Support for repair or replacement.
Resolving graphics issues can improve system performance and prevent display problems, as noted in a guide by NVIDIA on graphics card troubleshooting.
6.6 Intended Search Queries
- “Apple Diagnostics reference code structure”
- “CPU related Apple Diagnostics codes”
- “Memory related Apple Diagnostics codes”
- “Storage related Apple Diagnostics codes”
- “Graphics related Apple Diagnostics codes”
7. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques with Apple Diagnostics
For more complex issues, advanced troubleshooting techniques can help pinpoint the problem and identify the best course of action.
7.1 Using Apple Hardware Test (AHT)
Apple Hardware Test (AHT) is an older diagnostic tool that can be useful for older Mac models. Although it has been largely replaced by Apple Diagnostics, AHT can still provide valuable information.
Steps to use AHT:
- Disconnect Peripherals: Disconnect all external devices except for the keyboard, mouse, and display.
- Start AHT: Restart your Mac and hold down the D key during startup.
- Follow On-Screen Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to run the diagnostic tests.
AHT can help identify hardware issues that may not be detected by newer diagnostic tools, as suggested by legacy Apple support documents.
7.2 Checking System Logs
System logs can provide detailed information about hardware and software events, helping to identify the root cause of problems.
Steps to check system logs:
- Open Console App: Open the Console application (located in /Applications/Utilities/).
- Filter Logs: Use the filter options to search for specific error messages or events related to the issue.
- Analyze Logs: Analyze the log entries to identify potential causes of the problem.
System logs can provide valuable insights into system behavior and help diagnose complex issues, as explained in a guide by the SANS Institute on system log analysis.
7.3 Using Disk Utility
Disk Utility is a built-in macOS tool that can help diagnose and repair disk-related issues.
Steps to use Disk Utility:
- Open Disk Utility: Open Disk Utility (located in /Applications/Utilities/).
- Select Disk: Select the disk you want to diagnose.
- Run First Aid: Click the “First Aid” button to check for and repair disk errors.
Disk Utility can help resolve file system errors and other disk-related problems, as recommended by Apple Support.
7.4 Booting in Safe Mode
Booting your Mac in Safe Mode can help identify whether software conflicts are causing the issue.
Steps to boot in Safe Mode:
- Restart Mac: Restart your Mac.
- Hold Shift Key: Immediately after restarting, press and hold the Shift key.
- Release When Prompted: Release the Shift key when you see the login window.
In Safe Mode, your Mac loads only essential software, helping to isolate software-related problems, as explained in Apple’s official support documentation.
7.5 Intended Search Queries
- “Using Apple Hardware Test (AHT)”
- “Checking system logs on Mac”
- “Using Disk Utility for diagnostics”
- “Booting Mac in Safe Mode”
- “Advanced Mac troubleshooting techniques”
8. Preventing Hardware Issues: Best Practices
Preventing hardware issues is crucial for maintaining the longevity and performance of your Apple devices.
8.1 Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance can help prevent hardware issues by ensuring your device is clean, well-ventilated, and properly maintained.
Maintenance tips:
- Clean Vents: Regularly clean the vents to prevent overheating.
- Update Software: Keep your operating system and applications updated to prevent software conflicts.
- Run Diagnostics: Periodically run Apple Diagnostics to identify potential issues early.
Regular maintenance can significantly reduce the risk of hardware failures, as noted in a guide by the IEEE on preventive maintenance techniques.
8.2 Proper Handling
Proper handling of your Apple devices can prevent physical damage that can lead to hardware issues.
Handling tips:
- Use Protective Cases: Use protective cases to prevent damage from drops and impacts.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Avoid exposing your devices to extreme temperatures, which can damage internal components.
- Handle with Care: Handle your devices with care to prevent physical damage.
Proper handling can extend the lifespan of your devices and prevent costly repairs, as recommended by consumer electronics safety guides.
8.3 Optimizing Storage
Optimizing storage can prevent issues related to disk space and performance.
Storage optimization tips:
- Remove Unnecessary Files: Regularly remove unnecessary files to free up disk space.
- Use External Storage: Use external storage for large files to prevent filling up your internal drive.
- Defragment Hard Drives: Defragment hard drives (if applicable) to improve performance.
Optimizing storage can improve system performance and prevent storage-related issues, as highlighted in a guide by the Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA) on storage optimization techniques.
8.4 Monitoring System Performance
Monitoring system performance can help identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
Performance monitoring tips:
- Use Activity Monitor: Use Activity Monitor to track CPU usage, memory usage, and disk activity.
- Check System Logs: Periodically check system logs for error messages and warnings.
- Monitor Temperatures: Monitor system temperatures to prevent overheating.
Monitoring system performance can help identify and address potential issues early, as explained in a guide by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) on system performance monitoring.
8.5 Intended Search Queries
- “Regular Mac maintenance tips”
- “Proper handling of Apple devices”
- “Optimizing storage on Mac”
- “Monitoring Mac system performance”
- “Preventing hardware issues on Apple devices”
9. When to Contact Apple Support
Knowing when to contact Apple Support is crucial for resolving hardware issues that you cannot fix on your own.
9.1 Recurring Diagnostic Errors
If Apple Diagnostics consistently reports the same errors, it is a clear indication of a persistent hardware issue that requires professional attention.
When to contact Apple Support:
- Consistent Error Codes: If you repeatedly receive the same reference codes after running Apple Diagnostics.
- Unresolvable Issues: If troubleshooting steps do not resolve the reported issues.
- Warranty Coverage: If your device is still under warranty, contact Apple Support to explore repair or replacement options.
Recurring diagnostic errors often indicate underlying hardware problems that cannot be resolved through basic troubleshooting, as noted in Apple’s official support guidelines.
9.2 Physical Damage
Physical damage to your device, such as a cracked screen, liquid damage, or broken ports, often requires professional repair services.
When to contact Apple Support:
- Cracked Screen: If your screen is cracked or damaged.
- Liquid Damage: If your device has been exposed to liquid.
- Broken Ports: If any of the ports on your device are broken or not functioning properly.
Physical damage can compromise the internal components of your device and requires expert repair, as recommended by Apple’s service policies.
9.3 Performance Issues
Persistent performance issues, such as frequent crashes, slow performance, or overheating, can indicate hardware problems that require professional attention.
When to contact Apple Support:
- Frequent Crashes: If your device crashes frequently.
- Slow Performance: If your device is consistently slow, even after optimizing software and storage.
- Overheating: If your device overheats frequently, even under normal use.
Persistent performance issues can be indicative of hardware failures that require professional diagnostics and repair, as highlighted in Apple’s performance troubleshooting guides.
9.4 Intended Search Queries
- “When to contact Apple Support for Mac issues”
- “Recurring Apple Diagnostics errors”
- “Physical damage to Mac”
- “Performance issues on Mac”
- “Apple Support contact information”
10. Alternatives to Apple Care Diagnostic
While Apple Care Diagnostic is a valuable tool, there are alternative diagnostic tools and services available for Apple devices.
10.1 Third-Party Diagnostic Software
Several third-party diagnostic software options can provide comprehensive hardware and software analysis for Apple devices.
Examples of third-party software:
- TechTool Pro: Offers advanced diagnostic and repair features.
- DriveDx: Monitors the health of hard drives and SSDs.
- iStat Menus: Provides real-time system monitoring information.
These tools can offer additional diagnostic capabilities beyond those provided by Apple Diagnostics, as reviewed by various tech publications.
10.2 Independent Repair Shops
Independent repair shops can provide diagnostic and repair services for Apple devices, often at a lower cost than Apple authorized service providers.
Benefits of using independent repair shops:
- Lower Costs: Often offer more competitive pricing compared to Apple authorized service providers.
- Faster Turnaround: May provide faster repair services.
- Specialized Services: Some shops specialize in specific types of repairs.
Independent repair shops can be a viable alternative for out-of-warranty repairs, as noted in consumer guides on electronics repair services.
10.3 Online Diagnostic Tools
Several online diagnostic tools can help identify software and network-related issues on Apple devices.
Examples of online tools:
- Speedtest by Ookla: Measures internet connection speed and performance.
- Malwarebytes: Scans for malware and other security threats.
- Network Diagnostic Tools: Online tools that help diagnose network connectivity issues.
These tools can help troubleshoot software and network-related problems without requiring specialized hardware or software, as reviewed by tech blogs and online forums.
10.4 Do-It-Yourself (DIY) Repair
For users with technical skills, do-it-yourself (DIY) repair can be a cost-effective alternative to professional repair services.
Considerations for DIY repair:
- Technical Skills: Requires a certain level of technical knowledge and experience.
- Tools and Equipment: Requires specialized tools and equipment.
- Risk of Damage: There is a risk of damaging the device further if not done correctly.
DIY repair can be a viable option for simple repairs, but it is essential to proceed with caution, as highlighted in DIY repair guides and online tutorials.
10.5 Intended Search Queries
- “Third-party Mac diagnostic software”
- “Independent Apple repair shops”
- “Online Mac diagnostic tools”
- “DIY Mac repair”
- “Alternatives to Apple Care Diagnostic”
Need help diagnosing or repairing your Apple devices? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert assistance. Our team of experienced technicians can provide comprehensive diagnostic services and efficient repairs to ensure your devices are running at their best. Visit us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Explore our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information and to schedule a consultation. Let us help you keep your Apple devices in top condition.