Using An Obd Ii Scanner is beneficial for diagnosing car issues by collecting information from its control units. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed insights into these scanners, aiding informed decisions. This leads to savings and empowers proactive maintenance. Consider exploring diagnostic tools and automotive diagnostic systems for comprehensive car care.
Contents
- 1. What Exactly Does Using an OBD II Scanner Do?
- 2. What Are the Different Types of OBD2 Scanners Available?
- 3. How Do You Read OBD2 Fault Codes Using a Scanner?
- 3.1. Connecting the Scanner
- 3.2. Turning on the Ignition
- 3.3. Choosing Your Vehicle
- 3.4. Scanning for Fault Codes
- 3.5. Inspecting Revealed Fault Codes
- 3.6. Pro Tip: Reading Live Data
- 4. Why Is Using an OBD II Scanner an Essential Part of Used Car Buying?
- 5. How Do You Get Rid of Fault Codes After Repairing a Car?
- 6. How Does the Cost of an OBD II Scanner Compare to Potential Savings?
- 7. What Are Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD II Scanner?
- 8. What Kind of Car Problems Can You Diagnose Using an OBD II Scanner?
- 9. Which Brands of OBD II Scanners Are Most Reliable?
- 10. What Are Some Advanced Features to Look for in an OBD II Scanner?
1. What Exactly Does Using an OBD II Scanner Do?
Using an OBD II scanner is a tool that connects to a car’s port to gather data from its control units. This data includes fault codes and live readings, such as pressure, temperature, and speed, sourced from various sensors within the vehicle. According to a 2022 study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, OBD II scanners can accurately identify up to 70% of common vehicle malfunctions.
- Fault codes typically arise when a reading surpasses a limit or a sensor ceases to respond.
- Advanced diagnostic tools can perform servicing functions and coding necessary when replacing parts in modern vehicles.
- Modern on-board diagnostics became mandatory in all cars made from 1996 in the United States and from 2004 in Europe.
2. What Are the Different Types of OBD2 Scanners Available?
You can find various types of OBD2 scanners in today’s market. The most basic and cheapest option is a Bluetooth OBD2 code reader. For those leaning towards DIY repairs, a more expensive OBD2 scanner is a better option.
- Bluetooth OBD2 Code Reader: It can be paired with your smartphone. Normally, these only cost a few bucks and can read fault codes and basic live data, making a convenient choice for an average driver.
- Advanced OBD2 Scanner: It can also reset service reminders, activate servicing functions for replacing brake pads, and read more live data. These usually start at around $100 and go up depending on capabilities.
- Professional OBD2 Diagnostic Tools: With the right tools, a professional automotive electrician can adjust every possible option in a modern car. However, these tools cost thousands and are too complicated for a regular user.
Ordinary OBD2 scanners don’t always work for professionals as they have to be prepared for anything from an oil change to replacing an engine. Fault code and live data reading are nothing compared to the vast possibilities of coding and programming in professional OBD2 diagnostic tools.
3. How Do You Read OBD2 Fault Codes Using a Scanner?
Reading fault codes is the most important step of OBD2 diagnostics. Therefore, if you want to do anything with an OBD2 scanner, this is the first and foremost thing to learn. The controls of different diagnostic tools vary depending on their model, but the main principle is pretty much the same.
3.1. Connecting the Scanner
All modern cars have an OBD2 port that’s usually located under the steering wheel or somewhere in the center console. This port is often hidden underneath a plastic cover, so find it and plug in your OBD2 scanner.
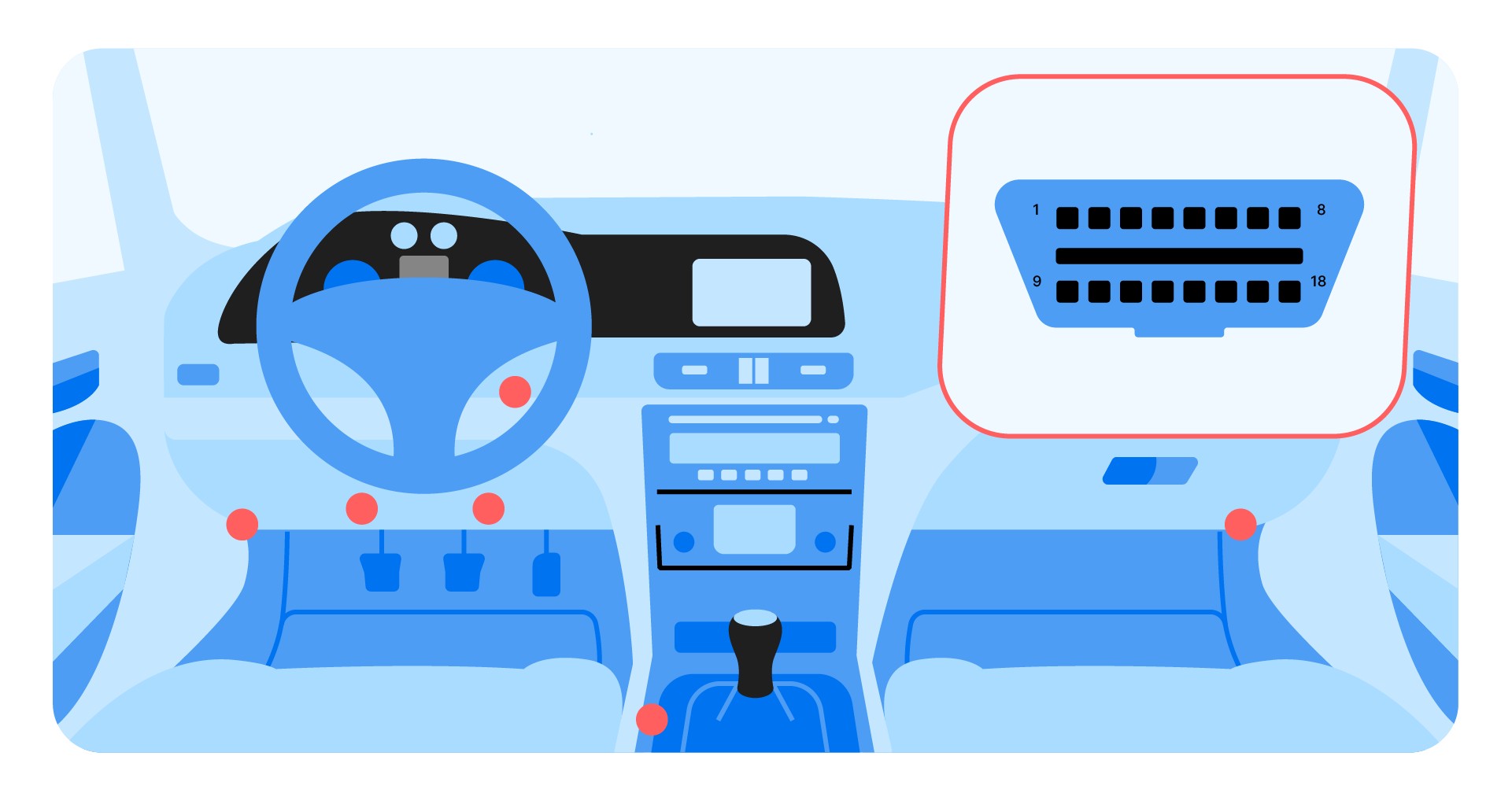 OBD2 scanner port location
OBD2 scanner port location
Modern scanners and code readers use Bluetooth instead of wires, so make sure it’s connected.
3.2. Turning on the Ignition
You can’t perform computer diagnostics on a car if the ignition isn’t on, so turn on the ignition before scanning. Turn off the headlights, radio, and AC to reduce electricity consumption to a minimum. Most vehicles allow you to scan for fault codes when the engine’s running. Fault codes are stored and won’t disappear until you clear them, but starting the engine is convenient when looking at live data because of various readings.
3.3. Choosing Your Vehicle
As soon as you connect your OBD2 scanner to a car and turn on the ignition, you can choose your car’s make, model, and specifications. These are necessary for the tool to recognize control units and process readings properly.
Most modern diagnostic tools have an automatic recognition system that automatically reveals a car’s VIN number and sets up all the necessary information for you. Moreover, you can also enter a VIN manually if, for some reason, a scanner doesn’t find it automatically.
3.4. Scanning for Fault Codes
Finally, choose a fault code reading option. Most scanners let you choose which units you want to scan, also offering a complete scan of all available control units. If you’re having trouble locating these options, an integrated help page or a user manual should guide you through these steps. Depending on a car’s model, a full scan should take between a few seconds and a few minutes.
3.5. Inspecting Revealed Fault Codes
These fault codes you see after a scan are the main reason for various warning lights coming up on your instrument cluster. Sometimes fault codes are relatively straightforward, such as “00287 – ABS Wheel Speed Sensor; Rear Right”. It probably means that the rear right ABS sensor needs replacing.
However, the problems behind fault codes are often way more complicated than you may think. For example, “P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)” means that the fuel mixture is too lean, but it can be caused by a clogged fuel filter, a failing fuel pump, a vacuum leak, various sensor failures, and numerous other things.
3.6. Pro Tip: Reading Live Data
An ability to read live data is an excellent addition to solving various car problems. Most control units have an additional section for live data, allowing you to monitor it in real-time. How does that help?
Let’s say a car is low on power, and the only fault code that appears is a notification that the vehicle is in limp mode. In that case, you can check whether the fuel and boost pressures, intake airflow, and intake manifold pressures are normal.
However, even with access to all these features, you may need help figuring out the fault codes and sourcing problems.
4. Why Is Using an OBD II Scanner an Essential Part of Used Car Buying?
Modern used car markets are full of pitfalls for buyers. Used car sellers use the gullibility of buyers to sell cars with a bad history, electrical issues, or even legal problems. While vehicle history reports can reveal lots of useful information about a car, a proper vehicle inspection is essential if you want to avoid huge repair costs. Always get a history report and check for fault codes before buying a used vehicle. If you don’t have an OBD2 scanner or still don’t know how to use one, take the car for a professional inspection.
5. How Do You Get Rid of Fault Codes After Repairing a Car?
Scanning for fault codes is a part of diagnosing the car’s problem, therefore, fault codes often won’t reveal issues directly. Even if computer diagnostics show a faulty mass airflow sensor, automotive electricians test the sensor using a multimeter to ensure it’s faulty and avoid replacing the wrong part. You’d be surprised how often such fault codes appear due to damaged wiring, loose connections, and corrosion. After sourcing the problem, someone must fix it and check for faults again. If it doesn’t appear anymore, the problem is probably solved, and you can hit the road.
6. How Does the Cost of an OBD II Scanner Compare to Potential Savings?
According to a survey conducted by the American Automobile Association (AAA) in 2023, the average cost of a car repair is between $500 and $600. Using an OBD II scanner can help you diagnose problems early, potentially saving you from expensive repairs. Even a basic scanner costing around $50 could save you hundreds by identifying minor issues before they become major problems. More advanced scanners, while costing more upfront, offer even greater savings by allowing you to perform more complex diagnostics and maintenance tasks yourself.
7. What Are Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD II Scanner?
Using an OBD II scanner can be incredibly helpful, but avoiding common mistakes is essential to ensure accurate diagnoses and prevent further issues. Here are some mistakes to steer clear of:
- Ignoring Preliminary Research: Before connecting the scanner, gather information about your vehicle’s specific make, model, and year. Different cars have different diagnostic protocols and sensor locations. A preliminary understanding can save you time and prevent misinterpretations.
- Skipping the User Manual: Each OBD II scanner comes with a user manual. Ignoring it can lead to misusing features or misinterpreting codes. The manual provides specific instructions for your device, ensuring you use it correctly.
- Not Ensuring a Secure Connection: A faulty connection can result in inaccurate readings. Always ensure the scanner is securely plugged into the OBD II port. Check for any loose connections or damage to the port.
- Misinterpreting Fault Codes: Fault codes provide a starting point, not a definitive diagnosis. For example, a “System Too Lean” code doesn’t automatically mean a faulty oxygen sensor. It could be due to vacuum leaks, fuel pump issues, or other problems.
- Failing to Check Live Data: Live data provides real-time information from various sensors. Ignoring this data can lead to incomplete diagnoses. Monitor parameters like engine temperature, RPM, and sensor voltages to get a comprehensive view.
- Clearing Codes Without Addressing the Issue: Clearing fault codes might temporarily turn off the check engine light, but it doesn’t fix the underlying problem. Always diagnose and repair the issue before clearing the codes.
- Neglecting Software Updates: Scanner manufacturers often release software updates to improve accuracy and add new features. Neglecting these updates can lead to using outdated information.
- Overlooking Freeze Frame Data: Freeze frame data captures sensor values at the moment a fault code was triggered. This data is invaluable for understanding the conditions under which the fault occurred.
- Assuming the Most Expensive Part Needs Replacing: Just because a fault code points to a particular component doesn’t mean it needs immediate replacement. Electrical issues, such as damaged wiring, loose connections, or corrosion, can trigger fault codes, so always inspect these elements first.
- Ignoring Secondary Symptoms: Fault codes are just one piece of the puzzle. Pay attention to any additional symptoms your vehicle is exhibiting, such as unusual noises, smells, or changes in performance.
- Not Seeking Professional Help When Needed: If you’re unsure about interpreting the data or performing repairs, consult a professional mechanic.
- Failing to Maintain Your Scanner: Keep your OBD II scanner in good condition. Protect it from extreme temperatures, moisture, and physical damage. Store it in a clean, dry place when not in use.
8. What Kind of Car Problems Can You Diagnose Using an OBD II Scanner?
Using an OBD II scanner allows you to diagnose a wide range of car problems, from minor issues to more complex malfunctions. Here’s a breakdown of the types of problems you can identify:
- Engine Problems:
- Misfires: Detects when one or more cylinders aren’t firing correctly.
- Oxygen Sensor Issues: Identifies faults in oxygen sensors, affecting fuel efficiency and emissions.
- Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor Problems: Diagnoses issues with the MAF sensor, which measures the amount of air entering the engine.
- Crankshaft and Camshaft Sensor Faults: Detects problems with these sensors, which are crucial for timing and ignition.
- Transmission Problems:
- Shift Issues: Identifies problems with the transmission shifting gears smoothly.
- Torque Converter Problems: Detects issues with the torque converter, which transfers power from the engine to the transmission.
- Solenoid Faults: Diagnoses problems with transmission solenoids, which control fluid flow.
- Emissions Problems:
- Catalytic Converter Issues: Detects faults with the catalytic converter, which reduces harmful emissions.
- Evaporative Emission Control System (EVAP) Leaks: Identifies leaks in the EVAP system, which prevents fuel vapor from escaping into the atmosphere.
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Problems: Diagnoses issues with the EGR system, which reduces nitrogen oxide emissions.
- Brake System Problems:
- ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) Faults: Detects problems with the ABS, which prevents the wheels from locking up during braking.
- Wheel Speed Sensor Issues: Identifies faults in wheel speed sensors, which provide data to the ABS.
- Electrical System Problems:
- Battery Issues: Detects problems with the battery, such as low voltage or charging issues.
- Alternator Problems: Diagnoses issues with the alternator, which charges the battery and powers electrical components.
- Sensor Faults: Identifies faults in various sensors throughout the vehicle.
- Fuel System Problems:
- Fuel Injector Issues: Detects problems with fuel injectors, which spray fuel into the engine.
- Fuel Pump Problems: Diagnoses issues with the fuel pump, which delivers fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Fuel Pressure Problems: Identifies issues with fuel pressure, which can affect engine performance.
- HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) Problems:
- Air Conditioning Compressor Issues: Detects problems with the AC compressor.
- Temperature Sensor Faults: Identifies faults in temperature sensors, which control the HVAC system.
- Body Control System Problems:
- Lighting Issues: Detects problems with headlights, taillights, and other lights.
- Power Window and Door Lock Problems: Diagnoses issues with power windows and door locks.
- Common Diagnostic Scenarios:
- Check Engine Light: Determines the cause of the check engine light.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Identifies issues that can lead to reduced fuel efficiency.
- Rough Idling: Diagnoses problems that cause the engine to idle roughly.
- Starting Problems: Detects issues that prevent the engine from starting.
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) in 2021, using an OBD II scanner can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40%. This not only saves time but also helps in identifying potential issues before they escalate into major repairs.
9. Which Brands of OBD II Scanners Are Most Reliable?
Selecting a reliable OBD II scanner brand is essential for accurate diagnostics and effective car maintenance. Several brands are known for their quality, features, and user-friendliness. Here are some of the most reliable OBD II scanner brands on the market:
-
Autel: Autel is a leading manufacturer of diagnostic tools, offering a wide range of scanners from basic code readers to advanced professional-grade devices. Their scanners are known for their extensive vehicle coverage, advanced features, and ease of use.
- Key Features: Extensive vehicle coverage, advanced diagnostics, bi-directional control, touchscreen interface, wireless connectivity.
- Popular Models: Autel MaxiSys MS906BT, Autel AL619, Autel MD808 Pro.
-
Launch: Launch Tech is another well-regarded brand in the automotive diagnostic industry. Their scanners are known for their comprehensive functionality and user-friendly interfaces, making them suitable for both DIY enthusiasts and professional mechanics.
- Key Features: Full system diagnostics, special functions, one-click updates, data logging, remote diagnostics.
- Popular Models: Launch X431 V+, Launch CRP129E, Launch Thinkdiag.
-
BlueDriver: BlueDriver offers a unique approach by providing a Bluetooth-enabled scanner that pairs with a smartphone app. This setup provides detailed diagnostics and vehicle-specific information, making it a favorite among DIYers.
- Key Features: Smartphone connectivity, vehicle-specific repairs, live data, code definitions, enhanced diagnostics.
- Popular Models: BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool.
-
INNOVA: INNOVA is a trusted brand known for its affordable and reliable OBD II scanners. They offer a variety of models suitable for different needs, from basic code readers to more advanced diagnostic tools.
- Key Features: Code reading and clearing, ABS and SRS diagnostics, battery and charging system testing, freeze frame data.
- Popular Models: INNOVA 3100i, INNOVA 3160g, INNOVA 5610.
-
Foxwell: Foxwell is a popular brand offering a range of diagnostic tools that combine affordability with advanced features. Their scanners are well-suited for both DIY enthusiasts and professional technicians.
- Key Features: Full system diagnostics, bi-directional control, special functions, live data streaming, easy updates.
- Popular Models: Foxwell NT510 Elite, Foxwell NT630 Plus, Foxwell GT60.
-
Actron: Actron, a brand of Bosch Automotive Service Solutions, offers a range of OBD II scanners designed for ease of use and reliability. Their scanners are popular among DIYers and entry-level technicians.
- Key Features: Code reading and clearing, live data, freeze frame data, easy-to-use interface.
- Popular Models: Actron CP9600, Actron CP9680.
-
ScanGauge: ScanGauge offers compact and versatile OBD II scan tools that provide real-time data and performance monitoring. These devices are popular for their ease of installation and user-friendly interface.
- Key Features: Real-time data monitoring, customizable gauges, code reading and clearing, trip computer.
- Popular Models: ScanGauge II, ScanGauge III.
-
Veepeak: Veepeak offers a range of Bluetooth OBD II scanners that pair with smartphones and tablets. These scanners are known for their affordability and ease of use, making them a good option for basic diagnostics.
- Key Features: Bluetooth connectivity, compatibility with OBD II apps, code reading and clearing, live data.
- Popular Models: Veepeak OBDCheck BLE, Veepeak Mini Bluetooth OBD2 Scanner.
10. What Are Some Advanced Features to Look for in an OBD II Scanner?
When choosing an OBD II scanner, several advanced features can significantly enhance its functionality and diagnostic capabilities. Here are some key advanced features to consider:
- Bi-Directional Control:
- Description: This feature allows the scanner to send commands to the vehicle’s control modules to perform tests and calibrations.
- Benefits: Actuate components like fuel injectors, cooling fans, and throttle valves to verify their operation. Perform tests such as cylinder balance tests, EVAP system tests, and ABS brake bleeding.
- Full System Diagnostics:
- Description: Provides access to all vehicle systems, including engine, transmission, ABS, SRS, HVAC, and more.
- Benefits: Comprehensive diagnostic capabilities beyond basic code reading. Identifies issues in various systems for a complete vehicle health check.
- Special Functions:
- Description: Includes specific functions for vehicle maintenance and service procedures.
- Benefits: Reset oil service lights, perform electronic parking brake (EPB) resets, calibrate steering angle sensors (SAS), and reset battery management systems (BMS). Essential for modern vehicle maintenance.
- Live Data Streaming:
- Description: Displays real-time data from various sensors and components.
- Benefits: Monitor engine performance, sensor values, and other parameters in real-time. Identify intermittent issues by observing data fluctuations during vehicle operation.
- Freeze Frame Data:
- Description: Captures sensor values at the moment a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is triggered.
- Benefits: Provides a snapshot of vehicle conditions when a fault occurred, aiding in diagnosis. Helps identify the root cause of the problem by analyzing the data.
- OBD I Support:
- Description: Compatibility with older vehicles that use the OBD I standard.
- Benefits: Diagnoses older cars that are not OBD II compliant. Extends the scanner’s usability across a broader range of vehicles.
- Built-in Code Definitions:
- Description: Provides detailed descriptions of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) directly on the scanner.
- Benefits: Eliminates the need to look up codes manually. Provides quick and accurate information for faster diagnosis.
- Wireless Connectivity:
- Description: Connects to vehicles and updates via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- Benefits: Wireless connection to the vehicle for greater flexibility during diagnostics. Easy software updates without needing to connect to a computer.
- Touchscreen Interface:
- Description: Offers an intuitive and user-friendly interface for navigation and data display.
- Benefits: Easy to navigate menus and access diagnostic information. Enhances user experience and efficiency.
- Data Logging and Playback:
- Description: Records and saves diagnostic data for later analysis.
- Benefits: Review data logs to identify intermittent issues. Compare data from different diagnostic sessions to track changes.
- Internet Updatable:
- Description: Allows the scanner to be updated with the latest software and vehicle coverage via the internet.
- Benefits: Keeps the scanner current with the latest vehicle models and diagnostic protocols. Ensures compatibility and accuracy.
- Multilingual Support:
- Description: Offers diagnostic information and menus in multiple languages.
- Benefits: Supports users from various linguistic backgrounds. Enhances accessibility and usability.
- Printing Capability:
- Description: Allows diagnostic reports to be printed directly from the scanner.
- Benefits: Creates professional diagnostic reports for customers or personal records. Provides a hard copy of diagnostic findings.
- Graphing Capability:
- Description: Displays live data in graphical format.
- Benefits: Easier to visualize and analyze data trends. Helps identify anomalies and patterns in sensor readings.
By considering these advanced features, you can choose an OBD II scanner that meets your specific needs and provides comprehensive diagnostic capabilities for your vehicle.
Do you need help finding the right OBD II scanner or auto parts? Contact us today for expert advice and support. Reach out to us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880, or visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information.