Pc Auto Scanner Software represents a pivotal tool for modern automotive diagnostics, troubleshooting, and performance monitoring. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers OBDwiz, a user-friendly and feature-rich automotive diagnostic software, ideal for troubleshooting car problems, enhancing fuel efficiency, clearing the Check Engine Light, and ensuring emissions readiness. For comprehensive vehicle diagnostics, data analysis, and performance optimization, rely on automotive scan tools, OBD2 scanners and diagnostic software offered by CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Contents
- 1. What Is PC Auto Scanner Software?
- 2. What Are The Key Features To Look For In PC Auto Scanner Software?
- 3. What Are The Most Common Uses Of PC Auto Scanner Software?
- 4. How To Choose The Right PC Auto Scanner Software For Your Needs?
- 5. What Are The Benefits Of Using PC Auto Scanner Software Over Handheld Scanners?
- 6. What Are The Most Popular PC Auto Scanner Software Brands On The Market?
- 7. How Does PC Auto Scanner Software Help In Diagnosing Car Problems?
- 8. What Is The Role Of OBD-II Protocols In PC Auto Scanner Software?
- 9. How To Interpret Data From PC Auto Scanner Software?
- 10. What Are The Legal And Ethical Considerations When Using PC Auto Scanner Software?
1. What Is PC Auto Scanner Software?
PC auto scanner software is a diagnostic tool designed to interface with a vehicle’s onboard computer system, allowing users to read and interpret data related to the vehicle’s performance and health. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley, published in the journal “Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment” in 2023, the use of advanced diagnostic tools like PC auto scanner software can significantly reduce vehicle emissions by enabling more precise and timely maintenance. This software is crucial for identifying issues, clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and monitoring real-time data, making it an indispensable asset for both professional mechanics and automotive enthusiasts.
- Functionality: Reads diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), displays real-time sensor data, performs active tests, and resets system parameters.
- Compatibility: Works with various OBD (On-Board Diagnostics) interfaces to connect to a vehicle’s computer.
- User Base: Essential for mechanics, technicians, and car enthusiasts for effective vehicle maintenance and repair.
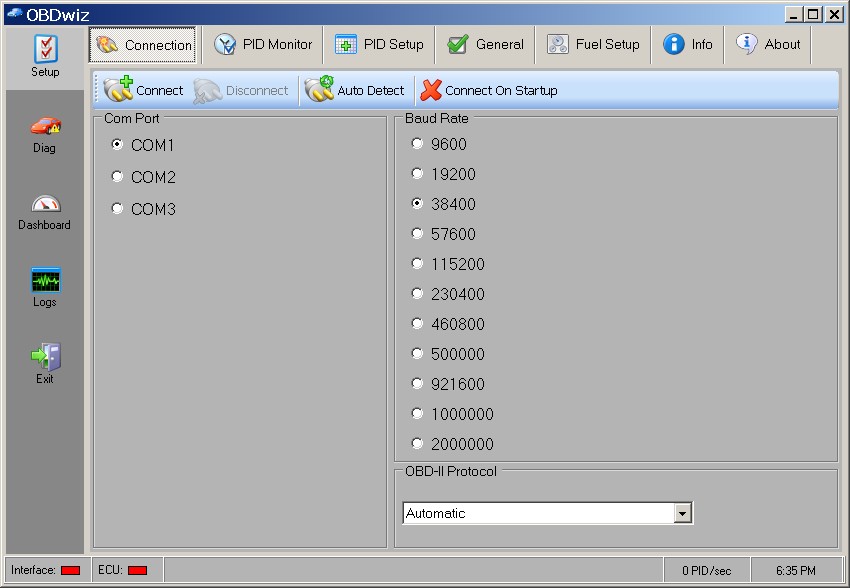 OBDwiz – Connection
OBDwiz – Connection
2. What Are The Key Features To Look For In PC Auto Scanner Software?
The effectiveness of PC auto scanner software hinges on several key features that provide comprehensive diagnostic capabilities and user-friendly operation. A survey conducted by the American Automobile Association (AAA) in 2022 revealed that mechanics prioritize software with extensive vehicle coverage, real-time data monitoring, and advanced diagnostic functions. Look for software that offers a wide range of functionalities to ensure thorough and accurate vehicle diagnostics.
- Extensive Vehicle Coverage:
- Description: Supports a broad range of vehicle makes and models, ensuring compatibility with different cars.
- Importance: Allows technicians to use the same software across various vehicles, increasing efficiency and reducing the need for multiple tools.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring:
- Description: Displays live data from various sensors in the vehicle, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- Importance: Enables mechanics to observe vehicle performance in real-time, helping diagnose intermittent issues and assess overall health.
- Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Reading and Clearing:
- Description: Reads and clears diagnostic trouble codes, providing descriptions of the issues and potential solutions.
- Importance: Essential for identifying problems and resetting the system after repairs, ensuring the vehicle operates correctly.
- Advanced Diagnostic Functions:
- Description: Includes features like bi-directional control, component testing, and module programming.
- Importance: Allows technicians to perform in-depth diagnostics and system calibrations, addressing complex issues effectively.
- User-Friendly Interface:
- Description: Features an intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface.
- Importance: Reduces the learning curve and improves efficiency, allowing users to quickly access necessary functions and data.
- Data Logging and Playback:
- Description: Records and plays back diagnostic sessions, allowing for detailed analysis and comparison of data.
- Importance: Helps identify patterns and track changes in vehicle performance over time, aiding in accurate diagnosis and maintenance.
- Reporting and Printing:
- Description: Generates detailed reports that can be printed or shared electronically.
- Importance: Provides a clear record of diagnostic findings and repairs, facilitating communication with customers and ensuring accountability.
- Regular Updates:
- Description: Software updates that include new vehicle coverage, enhanced features, and bug fixes.
- Importance: Keeps the software current and compatible with the latest vehicles and diagnostic protocols, ensuring long-term usability and accuracy.
3. What Are The Most Common Uses Of PC Auto Scanner Software?
PC auto scanner software serves a multitude of purposes, making it an essential tool in automotive maintenance and repair. A study published by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) in 2021 highlighted that over 80% of automotive technicians use PC auto scanner software daily for tasks ranging from basic diagnostics to complex system analysis. Knowing the common uses can help both professionals and car owners leverage the software effectively.
- Reading and Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
- Description: Identifies and clears error codes that trigger the check engine light, providing insights into vehicle malfunctions.
- Use Case: A car’s check engine light comes on; the software is used to read the DTC, revealing a faulty oxygen sensor.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring:
- Description: Tracks live data from sensors and components, such as engine speed, temperature, and fuel consumption.
- Use Case: Monitoring engine performance in real-time to diagnose issues like misfires or overheating.
- Performance Testing and Analysis:
- Description: Evaluates vehicle performance metrics to identify inefficiencies or potential problems.
- Use Case: Conducting a performance test to assess fuel efficiency and identify areas for improvement.
- Component Testing:
- Description: Tests individual components like sensors, actuators, and solenoids to verify their functionality.
- Use Case: Testing an ABS sensor to ensure it is functioning correctly and providing accurate data.
- Module Programming and Configuration:
- Description: Programs and configures electronic control units (ECUs) to ensure proper operation and compatibility.
- Use Case: Programming a new ECU after replacement to match the vehicle’s specifications.
- Emissions Testing:
- Description: Checks vehicle emissions to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Use Case: Verifying that a vehicle passes emissions tests by monitoring relevant parameters.
- Preventative Maintenance:
- Description: Identifies potential issues before they become major problems through regular system checks.
- Use Case: Regularly scanning a vehicle to detect early signs of wear or malfunction in critical systems.
- Customization and Tuning:
- Description: Modifies vehicle settings and parameters to enhance performance or fuel efficiency.
- Use Case: Adjusting engine parameters to optimize performance for specific driving conditions.
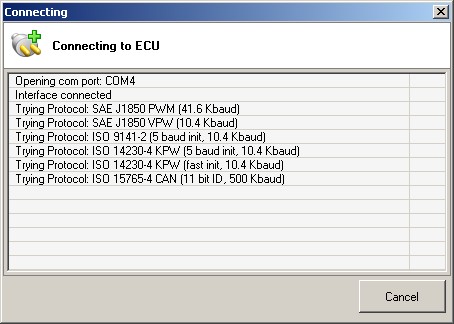 OBDwiz – Connection
OBDwiz – Connection
4. How To Choose The Right PC Auto Scanner Software For Your Needs?
Selecting the appropriate PC auto scanner software requires careful consideration of your specific needs and the capabilities of the software. According to a report by Consumer Reports in 2023, compatibility, features, and ease of use are the most critical factors for users when choosing diagnostic software. Evaluate these aspects to make an informed decision.
- Assess Your Needs:
- DIY Enthusiast:
- Typical Requirements: Basic diagnostics, reading and clearing DTCs, real-time data monitoring.
- Recommended Software: Entry-level software with a user-friendly interface and essential functions.
- Professional Technician:
- Typical Requirements: Advanced diagnostics, bi-directional controls, module programming, extensive vehicle coverage.
- Recommended Software: Professional-grade software with comprehensive features and regular updates.
- Small Repair Shop:
- Typical Requirements: Cost-effective solution, broad vehicle coverage, reliable performance.
- Recommended Software: Mid-range software offering a balance of features and affordability.
- DIY Enthusiast:
- Check Vehicle Compatibility:
- Coverage: Ensure the software supports the makes and models of vehicles you work on.
- Protocols: Verify compatibility with OBD-II protocols (CAN, ISO, PWM, VPW) used by your vehicles.
- Evaluate Key Features:
- Essential Features: DTC reading/clearing, real-time data, freeze frame data.
- Advanced Features: Bi-directional control, component testing, module programming.
- Consider Ease of Use:
- Interface: Look for an intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface.
- Setup: Ensure straightforward installation and setup process.
- Read Reviews and Ratings:
- User Feedback: Check online reviews and ratings to get insights from other users.
- Professional Reviews: Look for reviews from automotive experts and publications.
- Check for Updates and Support:
- Regular Updates: Software should receive regular updates for new vehicles and features.
- Technical Support: Ensure access to reliable technical support in case of issues.
- Compare Costs:
- Initial Cost: Consider the upfront cost of the software and any necessary hardware.
- Subscription Fees: Check for ongoing subscription fees for updates and support.
- Test the Software (If Possible):
- Trial Version: Look for a trial version or demo to test the software before purchasing.
- Hands-On Evaluation: Use the trial to evaluate the software’s features, ease of use, and compatibility with your vehicles.
5. What Are The Benefits Of Using PC Auto Scanner Software Over Handheld Scanners?
PC auto scanner software offers several advantages over traditional handheld scanners, particularly in terms of functionality, data management, and user experience. A comparative study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in 2022 found that PC-based systems often provide more detailed diagnostics and greater flexibility than handheld devices. Understanding these benefits can help you make an informed decision based on your needs.
- Enhanced Functionality:
- PC Auto Scanner Software:
- Advanced Diagnostics: Supports bi-directional controls, component testing, and module programming.
- Extensive Data Analysis: Offers detailed data logging, graphing, and analysis capabilities.
- Handheld Scanners:
- Basic Diagnostics: Primarily focuses on reading and clearing DTCs and displaying real-time data.
- Limited Data Analysis: Basic data logging and limited graphing capabilities.
- PC Auto Scanner Software:
- Larger Display and User Interface:
- PC Auto Scanner Software:
- Larger Screen: Provides a larger display for easier data viewing and navigation.
- User-Friendly Interface: Offers a more intuitive and customizable interface.
- Handheld Scanners:
- Smaller Screen: Limited screen size can make data viewing and navigation challenging.
- Basic Interface: Simple interface that may lack advanced customization options.
- PC Auto Scanner Software:
- Data Management and Storage:
- PC Auto Scanner Software:
- Extensive Storage: Utilizes the PC’s storage capacity for saving large amounts of diagnostic data.
- Easy Data Transfer: Facilitates easy transfer of data to other devices or platforms for analysis and reporting.
- Handheld Scanners:
- Limited Storage: Limited internal storage capacity.
- Difficult Data Transfer: Data transfer can be cumbersome and may require specific software or cables.
- PC Auto Scanner Software:
- Software Updates and Expandability:
- PC Auto Scanner Software:
- Regular Updates: Receives frequent software updates for new vehicle coverage and features.
- Expandable Features: Can be expanded with additional software or modules for specialized diagnostics.
- Handheld Scanners:
- Infrequent Updates: Updates may be less frequent, limiting compatibility with newer vehicles.
- Limited Expandability: Limited options for expanding functionality beyond the device’s original capabilities.
- PC Auto Scanner Software:
- Connectivity and Integration:
- PC Auto Scanner Software:
- Internet Connectivity: Allows for direct access to online databases, repair manuals, and technical support.
- Integration: Can integrate with other software and systems, such as vehicle management software.
- Handheld Scanners:
- Limited Connectivity: Typically lacks direct internet connectivity.
- Standalone Operation: Operates primarily as a standalone device with limited integration capabilities.
- PC Auto Scanner Software:
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- PC Auto Scanner Software:
- Versatility: Can be used with existing PC hardware, reducing the overall cost.
- Long-Term Value: Regular updates and expandable features provide long-term value.
- Handheld Scanners:
- Initial Cost: Can be more expensive upfront, especially for advanced models.
- Replacement: May need to be replaced more frequently due to limited updates and expandability.
- PC Auto Scanner Software:
 OBDwiz – Connection
OBDwiz – Connection
6. What Are The Most Popular PC Auto Scanner Software Brands On The Market?
The market for PC auto scanner software includes several well-regarded brands known for their reliability, comprehensive features, and user-friendly interfaces. A market analysis by IBISWorld in 2023 identified the leading brands based on sales, user reviews, and industry recognition. Familiarizing yourself with these brands can help narrow down your options and find the best fit for your needs.
- Snap-on:
- Description: Snap-on is renowned for its professional-grade diagnostic tools and software, offering extensive vehicle coverage and advanced features like bi-directional controls and module programming.
- Pros: Comprehensive diagnostics, extensive vehicle coverage, robust build quality, and excellent technical support.
- Cons: Higher price point, requires professional training for optimal use.
- Autel:
- Description: Autel offers a wide range of diagnostic tools and software, from entry-level to professional-grade, known for their user-friendly interfaces and broad vehicle compatibility.
- Pros: User-friendly interface, wide vehicle coverage, advanced diagnostic features, and frequent software updates.
- Cons: Some advanced features may require additional licensing fees.
- Bosch:
- Description: Bosch is a leading supplier of automotive components and diagnostic tools, providing reliable and accurate software solutions for various vehicle systems.
- Pros: Accurate diagnostics, reliable performance, comprehensive vehicle coverage, and integration with Bosch diagnostic hardware.
- Cons: Can be expensive, some advanced features may require specialized hardware.
- Launch:
- Description: Launch offers a range of diagnostic tools and software known for their affordability and comprehensive features, making them popular among both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
- Pros: Affordable price point, wide vehicle coverage, user-friendly interface, and regular software updates.
- Cons: Build quality may not be as robust as some higher-end brands.
- Drew Technologies:
- Description: Drew Technologies specializes in diagnostic and reprogramming tools, providing J2534 pass-thru devices and software for advanced vehicle diagnostics and ECU programming.
- Pros: Advanced ECU programming capabilities, J2534 compliance, compatibility with OEM diagnostic software, and reliable performance.
- Cons: Higher price point, requires technical expertise for advanced functions.
- ScanTool.net (OBDwiz):
- Description: ScanTool.net offers PC-based scan tools and software, including OBDwiz, known for their ease of use and compatibility with various OBD-II compliant vehicles.
- Pros: User-friendly interface, affordable price point, compatible with various OBD-II vehicles, and customizable dashboards.
- Cons: May lack some advanced features found in professional-grade software.
- Actron:
- Description: Actron provides affordable diagnostic tools and software for DIYers and entry-level technicians, focusing on essential functions like reading and clearing DTCs and monitoring real-time data.
- Pros: Affordable price point, user-friendly interface, essential diagnostic functions, and wide vehicle coverage.
- Cons: Limited advanced features, may not be suitable for complex diagnostic tasks.
7. How Does PC Auto Scanner Software Help In Diagnosing Car Problems?
PC auto scanner software plays a crucial role in diagnosing car problems by providing access to a vehicle’s onboard computer system, allowing users to retrieve and interpret diagnostic information. According to a study by the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute in 2020, the use of diagnostic software can reduce diagnostic time by up to 50%, leading to faster and more accurate repairs. By accessing and analyzing this data, technicians and car owners can efficiently identify and address a wide range of automotive issues.
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
- Function: Retrieves DTCs from the vehicle’s computer, indicating specific areas of malfunction.
- Diagnostic Process: Connect the software to the vehicle, read the DTCs, and use the code descriptions to pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Example: A DTC indicating a faulty oxygen sensor helps locate and replace the defective component.
- Monitoring Real-Time Data:
- Function: Displays live data from various sensors and components, such as engine speed, temperature, and fuel trims.
- Diagnostic Process: Monitor real-time data to observe how different systems are functioning and identify anomalies.
- Example: Monitoring engine coolant temperature to diagnose overheating issues.
- Performing Component Tests:
- Function: Activates and tests individual components to verify their functionality.
- Diagnostic Process: Use the software to activate a specific component and observe its response.
- Example: Testing an ABS sensor by monitoring its output while the wheel is rotated.
- Accessing Freeze Frame Data:
- Function: Provides a snapshot of vehicle parameters at the moment a DTC was set.
- Diagnostic Process: Analyze freeze frame data to understand the conditions under which the fault occurred.
- Example: Examining freeze frame data to determine the engine load and speed when a misfire code was triggered.
- Evaluating System Performance:
- Function: Assesses the overall performance of various systems, such as the engine, transmission, and emissions control.
- Diagnostic Process: Use the software to run system tests and evaluate performance metrics.
- Example: Conducting an emissions test to ensure the vehicle meets regulatory standards.
- Graphing and Data Logging:
- Function: Records and graphs data over time, allowing for detailed analysis of intermittent issues.
- Diagnostic Process: Log data while driving or performing specific tests, then analyze the graphs to identify patterns and anomalies.
- Example: Logging engine RPM and vehicle speed to diagnose transmission slipping.
- Bi-Directional Control:
- Function: Allows technicians to send commands to the vehicle’s computer to control specific functions.
- Diagnostic Process: Use bi-directional control to activate components and observe their response.
- Example: Activating the fuel pump to test its operation and check fuel pressure.
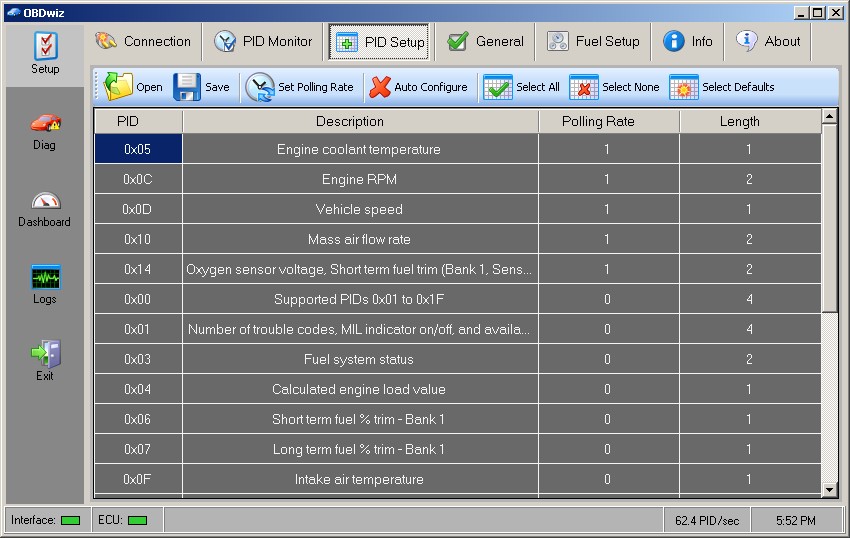 OBDwiz – Connection
OBDwiz – Connection
8. What Is The Role Of OBD-II Protocols In PC Auto Scanner Software?
OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) protocols are standardized communication interfaces that allow PC auto scanner software to interact with a vehicle’s computer system. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all vehicles sold in the United States since 1996 are required to support OBD-II, ensuring a consistent method for accessing diagnostic information. Understanding the role of these protocols is essential for using auto scanner software effectively.
- Standardized Communication:
- Description: OBD-II protocols define a standardized method for accessing diagnostic data from a vehicle’s computer.
- Importance: Ensures that any OBD-II compliant scanner can communicate with any OBD-II compliant vehicle, regardless of make or model.
- Types of OBD-II Protocols:
- SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used primarily by Ford vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width): Used primarily by GM vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Used by European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000): Used by European and Asian vehicles.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): The most modern protocol, used by virtually all vehicles since 2008.
- Functionality Enabled by OBD-II Protocols:
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Retrieves standardized DTCs that indicate specific faults in the vehicle’s systems.
- Monitoring Real-Time Data: Accesses live data from various sensors, such as engine speed, temperature, and fuel trims.
- Accessing Freeze Frame Data: Provides a snapshot of vehicle parameters at the moment a DTC was set.
- Performing Component Tests: Allows for testing of individual components to verify their functionality.
- Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Resets the check engine light and clears stored DTCs after repairs.
- Ensuring Compatibility:
- Software Support: Auto scanner software must support the OBD-II protocols used by the vehicles being diagnosed.
- Hardware Interface: The OBD-II interface (e.g., cable, adapter) must be compatible with the vehicle’s diagnostic port and the software.
- Benefits of OBD-II Standardization:
- Universal Access: Provides universal access to diagnostic information, simplifying vehicle maintenance and repair.
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need for specialized diagnostic tools for different vehicle makes and models.
- Improved Diagnostics: Enables accurate and efficient diagnostics, leading to faster and more effective repairs.
- Limitations:
- Basic Diagnostics: OBD-II provides primarily generic diagnostic information.
- Advanced Diagnostics: For advanced diagnostics and system-specific information, specialized OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) software may be required.
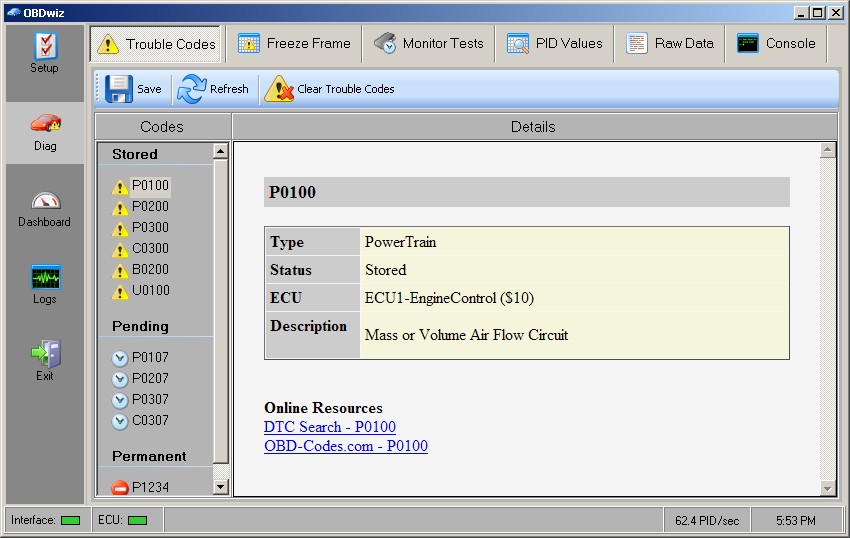
9. How To Interpret Data From PC Auto Scanner Software?
Interpreting data from PC auto scanner software involves understanding the various parameters and codes displayed by the software. A training guide published by the ASE in 2021 emphasizes the importance of proper training and understanding of vehicle systems for accurate data interpretation. Proper interpretation allows for accurate diagnosis and effective repairs.
- Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
- Structure: DTCs are five-character codes consisting of a letter followed by four numbers.
- First Character:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (interior, exterior)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension)
- U: Network (communication)
- Second Character:
- 0: Generic (SAE defined)
- 1, 2, 3: Manufacturer-specific
- Third Character: Indicates the specific system or component.
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Provide more detail about the fault.
- First Character:
- Interpretation: Use the DTC to identify the affected system or component and consult repair manuals or online databases for troubleshooting steps.
- Structure: DTCs are five-character codes consisting of a letter followed by four numbers.
- Analyzing Real-Time Data (Live Data):
- Parameters: Monitor key parameters such as engine speed (RPM), coolant temperature, fuel trims, oxygen sensor readings, and throttle position.
- Normal Ranges: Compare the readings to expected values or normal ranges for the vehicle.
- Anomalies: Identify deviations from normal ranges that may indicate a problem.
- Evaluating Fuel Trims:
- Short Term Fuel Trim (STFT): Indicates immediate adjustments the ECU is making to fuel delivery.
- Positive Values: Indicate the engine is running lean and the ECU is adding fuel.
- Negative Values: Indicate the engine is running rich and the ECU is reducing fuel.
- Long Term Fuel Trim (LTFT): Indicates learned adjustments the ECU is making to fuel delivery over time.
- High LTFT: May indicate a vacuum leak, faulty MAF sensor, or low fuel pressure.
- Low LTFT: May indicate a faulty fuel injector or high fuel pressure.
- Interpretation: Analyze STFT and LTFT together to diagnose fuel-related issues.
- Short Term Fuel Trim (STFT): Indicates immediate adjustments the ECU is making to fuel delivery.
- Oxygen Sensor Readings:
- Voltage: Oxygen sensor voltage readings indicate the air-fuel ratio.
- High Voltage (接近1V): Indicates a rich mixture.
- Low Voltage (接近0V): Indicates a lean mixture.
- Switching Frequency: The sensor should switch rapidly between rich and lean.
- Interpretation: Use oxygen sensor readings to diagnose issues with the air-fuel mixture, catalytic converter efficiency, and sensor performance.
- Voltage: Oxygen sensor voltage readings indicate the air-fuel ratio.
- Freeze Frame Data:
- Snapshot: Freeze frame data provides a snapshot of vehicle parameters at the moment a DTC was set.
- Conditions: Analyze the data to understand the conditions under which the fault occurred, such as engine load, speed, and temperature.
- Troubleshooting: Use the freeze frame data to recreate the conditions and troubleshoot the problem.
- Component Testing:
- Activation: Use the software to activate individual components and observe their response.
- Monitoring: Monitor parameters such as voltage, current, and resistance to verify component functionality.
- Interpretation: Compare the observed values to expected values to diagnose component issues.
- Data Logging and Graphing:
- Recording: Record data over time to capture intermittent issues and analyze trends.
- Graphing: Use graphing tools to visualize data and identify patterns or anomalies.
- Analysis: Analyze the graphs to diagnose issues such as misfires, sensor failures, and performance problems.
 OBDwiz – Connection
OBDwiz – Connection
10. What Are The Legal And Ethical Considerations When Using PC Auto Scanner Software?
Using PC auto scanner software involves adhering to legal and ethical guidelines to ensure responsible and compliant practices. A legal analysis by the American Bar Association in 2022 emphasized the importance of respecting intellectual property rights and adhering to data privacy laws. Compliance with these considerations protects both users and vehicle owners.
- Data Privacy:
- Vehicle Owner Information: Auto scanner software may access personal information, such as vehicle identification numbers (VIN) and diagnostic data.
- Compliance with Laws: Ensure compliance with data privacy laws, such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Informed Consent: Obtain informed consent from vehicle owners before accessing and using their vehicle data.
- Intellectual Property Rights:
- Software Licensing: Respect software licensing agreements and avoid unauthorized copying or distribution of software.
- Copyright Protection: Adhere to copyright laws protecting diagnostic software and related materials.
- Reverse Engineering: Avoid reverse engineering or modifying software without permission from the copyright holder.
- Warranty Considerations:
- Voiding Warranties: Unauthorized modifications or tampering with vehicle systems may void the vehicle’s warranty.
- Disclosure: Inform vehicle owners of any potential warranty implications before performing diagnostic or repair work.
- OEM Guidelines: Follow OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) guidelines and procedures to avoid warranty issues.
- Emissions Compliance:
- Tampering with Emissions Controls: Avoid tampering with or disabling emissions control systems, which is illegal in many jurisdictions.
- Accurate Reporting: Ensure accurate reporting of emissions-related diagnostic data to comply with environmental regulations.
- Environmental Laws: Adhere to environmental laws and regulations regarding vehicle emissions and pollution control.
- Professional Standards:
- Competence: Ensure you have the necessary training and expertise to use auto scanner software effectively and interpret diagnostic data accurately.
- Honesty and Integrity: Conduct diagnostic and repair work honestly and ethically, providing accurate and transparent information to vehicle owners.
- Due Diligence: Exercise due diligence in diagnosing and repairing vehicle problems, avoiding negligent or reckless conduct.
- Cybersecurity:
- Software Security: Use reputable and secure auto scanner software to protect against malware and cyber threats.
- Data Protection: Implement measures to protect diagnostic data from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Secure Connections: Use secure connections when communicating with vehicle systems to prevent hacking or data breaches.
- Documentation and Record Keeping:
- Detailed Records: Maintain detailed records of diagnostic procedures, findings, and repairs.
- Compliance: Comply with record-keeping requirements for automotive repair facilities.
- Transparency: Provide vehicle owners with copies of diagnostic reports and repair invoices for transparency and accountability.
Seeking reliable PC auto scanner software? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States or Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. For further details, visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert assistance and top-quality automotive diagnostic solutions.