The OBD2 port is a standardized interface found in virtually every car manufactured after 1996, mandated for monitoring emissions, mileage, speed, and other vital vehicle data. Looking for reliable auto repair tools? CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is the place to be. This article will delve into the OBD2 port, exploring its functions, capabilities, and the various devices and applications it supports.
Contents
- 1. What is an OBD2 Port and Why Is It Important?
- 1.1. What is the primary function of the OBD2 port?
- 1.2. Where is the OBD2 port located in a car?
- 1.3. Why was the OBD2 port mandated in 1996?
- 1.4. What types of data can be accessed through the OBD2 port?
- 1.5. What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner?
- 2. What is the difference between OBD1 and OBD2?
- 2.1. What were the main limitations of OBD1 systems?
- 2.2. How did OBD2 standardize vehicle diagnostics?
- 2.3. What are the five basic signal protocols used in OBD2 systems?
- 2.4. Which pins are used for ground and power in OBD2 protocols?
- 2.5. How did the standardization of OBD2 improve vehicle diagnostics?
- 3. How does the OBD2 Port Work?
- 3.1. What are Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)?
- 3.2. How can an OBD2 scan tool read diagnostic trouble codes?
- 3.3. What information is provided by an OBD2 scan tool?
- 3.4. Why is the standardized pinout important for OBD2 scan tools?
- 3.5. Can you clear error codes using an OBD2 scan tool?
- 4. What Devices Can Be Connected to the OBD2 Port?
- 4.1. What are the different types of OBD2 scanners available?
- 4.2. How do GPS trackers utilize the OBD2 port?
- 4.3. What are the benefits of using a GPS tracker connected to the OBD2 port?
- 4.4. Can the OBD2 port be used for vehicle tuning or ECU remapping?
- 4.5. What are the risks associated with ECU remapping via the OBD2 port?
- 5. What are Some Mobile OBD2 Scanner Apps?
- 5.1. How do mobile OBD2 scanner apps work?
- 5.2. What types of data can be monitored using these apps?
- 5.3. What are some of the popular mobile OBD2 scanner apps available?
- 5.4. What are the advantages of using a mobile OBD2 scanner app?
- 5.5. Are there any limitations to using mobile OBD2 scanner apps?
- 6. Recommended OBD2 Scanners
- 6.1. Veepeak Mini WiFi OBD II Scanner
- 6.2. BAFX Products OBDII Code Reader and Scan Tool
- 6.3. Veepeak OBDCheck BLE Bluetooth OBD II Scanner
- 6.4. BlueDriver Pro OBD2 Bluetooth Scan Tool
- 6.5. OBDLink MX+ OBD2 Bluetooth Scanner
- 7. Other Uses for the OBD2 Port
- 7.1. Can the OBD2 port be used to track a vehicle’s location?
- 7.2. What are the benefits of using the OBD2 port for vehicle tracking?
- 7.3. What are the security implications of connecting devices to the OBD2 port?
- 7.4. Can the OBD2 port be used to improve fuel efficiency?
- 7.5. What are some advanced uses for the OBD2 port?
- 8. What Are the Common Issues With OBD2 Ports?
- 8.1. Damaged or Broken Ports
- 8.2. Corrosion
- 8.3. Software Incompatibilities
- 8.4. Power Issues
- 8.5. Communication Errors
- 9. OBD2 Port Security and Privacy Concerns
- 9.1. What are the potential security risks associated with the OBD2 port?
- 9.2. How can these security risks be mitigated?
- 9.3. What privacy concerns are associated with OBD2 data?
- 9.4. How can you protect your privacy when using OBD2 devices and apps?
- 9.5. What regulations are in place to protect OBD2 data?
- 10. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
- 10.1. Why choose CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for your automotive needs?
- 10.2. What types of products and information are available on CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN?
- 10.3. How can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN help you find the right OBD2 scanner for your needs?
- 10.4. How can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN help you save money on car repairs?
- 10.5. How can you contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for assistance?
1. What is an OBD2 Port and Why Is It Important?
An OBD2 port, or On-Board Diagnostics II port, is a standardized 16-pin interface in most vehicles manufactured since 1996. This port allows access to the vehicle’s computer, monitoring data like emissions, engine performance, and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 was mandated to ensure vehicles meet emissions standards. The OBD2 port is crucial for mechanics and car owners alike, offering insights into a vehicle’s health and performance.
1.1. What is the primary function of the OBD2 port?
The primary function of the OBD2 port is to provide access to a vehicle’s onboard computer system for diagnostics and monitoring. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the OBD2 standard was developed to provide a standardized way to access vehicle data. This includes reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitoring emissions-related data, and accessing real-time sensor data.
1.2. Where is the OBD2 port located in a car?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side of the vehicle. The exact location can vary slightly depending on the make and model of the car, but it is usually within easy reach.
1.3. Why was the OBD2 port mandated in 1996?
The OBD2 port was mandated in 1996 in the United States as part of the Clean Air Act amendments. According to the EPA, the mandate aimed to standardize vehicle diagnostics, making it easier to monitor and reduce vehicle emissions.
1.4. What types of data can be accessed through the OBD2 port?
Through the OBD2 port, you can access various types of data, including:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Real-time sensor data (e.g., engine temperature, fuel rate)
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
- Emissions-related data
1.5. What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner?
Using an OBD2 scanner offers several benefits, including:
- Early detection of potential issues: By reading DTCs and monitoring real-time data, you can identify problems before they become major repairs.
- Cost savings: Diagnosing issues yourself can save money on diagnostic fees at a mechanic.
- Improved vehicle performance: Monitoring data like fuel efficiency can help you optimize your driving habits.
- Enhanced understanding of your vehicle: Using an OBD2 scanner can give you a better understanding of how your car works.
2. What is the difference between OBD1 and OBD2?
OBD1 (On-Board Diagnostics I) was the predecessor to OBD2 and had several limitations. According to a study by the California Air Resources Board (CARB) in 1988, OBD1 systems were manufacturer-specific, meaning each carmaker used different connectors and protocols. OBD2, introduced in the mid-1990s, standardized these systems, ensuring compatibility across different makes and models.
2.1. What were the main limitations of OBD1 systems?
OBD1 systems had several limitations:
- Manufacturer-specific: Each manufacturer used different connectors and protocols.
- Limited data: OBD1 systems provided limited access to vehicle data.
- Inconsistent diagnostic codes: Diagnostic codes varied between manufacturers, making it difficult to interpret them.
2.2. How did OBD2 standardize vehicle diagnostics?
OBD2 standardized vehicle diagnostics by:
- Standardized connector: Requiring all vehicles to use a standard 16-pin connector.
- Standardized protocols: Defining common communication protocols for accessing vehicle data.
- Standardized diagnostic codes: Establishing a set of standard diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
2.3. What are the five basic signal protocols used in OBD2 systems?
The five basic signal protocols used in OBD2 systems are:
- SAE J1850 PWM: Used in Ford vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW: Used in General Motors vehicles.
- ISO9141-2: Used in Chrysler and some European/Asian vehicles.
- ISO14230-4 (KWP2000): Used in various American, European, and Japanese brands.
- ISO 15765 CAN: Used on all vehicles manufactured after 2008.
2.4. Which pins are used for ground and power in OBD2 protocols?
Pins 4 and 5 are used for ground connections, and pin 16 is used for power from the car’s battery in all OBD2 protocols.
2.5. How did the standardization of OBD2 improve vehicle diagnostics?
The standardization of OBD2 improved vehicle diagnostics by making it easier to:
- Access vehicle data: Mechanics could use a single scan tool to access data from different vehicles.
- Interpret diagnostic codes: Standardized DTCs made it easier to diagnose problems.
- Reduce emissions: Standardized monitoring helped ensure vehicles met emissions standards.
3. How does the OBD2 Port Work?
The OBD2 port works by providing access to the vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU), which stores Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). According to Bosch Automotive Handbook, special scanners connect to this port, reading codes and providing detailed explanations of faults. Less expensive scanners may only provide a numeric code, which can be looked up in a manual or service website.
3.1. What are Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)?
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes stored in the vehicle’s computer system that indicate a problem or malfunction. According to the SAE J2012 standard, DTCs are standardized across different manufacturers. These codes help mechanics and car owners identify specific issues, such as a faulty oxygen sensor or a misfiring engine.
3.2. How can an OBD2 scan tool read diagnostic trouble codes?
An OBD2 scan tool can read diagnostic trouble codes by connecting to the OBD2 port and communicating with the vehicle’s ECU. The scan tool sends a request for DTCs, and the ECU responds with a list of codes.
3.3. What information is provided by an OBD2 scan tool?
An OBD2 scan tool can provide various types of information, including:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Identifies specific problems or malfunctions.
- Real-time sensor data: Displays live data from various sensors, such as engine temperature and fuel rate.
- Freeze frame data: Records sensor data at the moment a DTC was triggered.
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): Identifies the vehicle.
3.4. Why is the standardized pinout important for OBD2 scan tools?
The standardized pinout is important because it ensures that any OBD2 scan tool can connect to any OBD2-compliant vehicle. This standardization allows mechanics and car owners to use a single scan tool for different makes and models.
3.5. Can you clear error codes using an OBD2 scan tool?
Yes, you can clear error codes using an OBD2 scan tool. After diagnosing and repairing the issue, clearing the error codes resets the check engine light and allows the vehicle to run without the error indication. However, it’s important to note that if the underlying problem is not resolved, the error code will likely reappear.
4. What Devices Can Be Connected to the OBD2 Port?
Various devices can be connected to the OBD2 port, including scan tools for reading DTCs, GPS trackers for vehicle location, and devices for tuning the vehicle’s ECU.
4.1. What are the different types of OBD2 scanners available?
There are several types of OBD2 scanners available:
- Basic code readers: These scanners provide only the DTC and a brief description.
- Mid-range scanners: These scanners offer additional features, such as real-time data and freeze frame data.
- Advanced scanners: These scanners provide advanced diagnostics, bidirectional control, and access to manufacturer-specific data.
- Wireless scanners: These scanners connect to your smartphone or laptop via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
4.2. How do GPS trackers utilize the OBD2 port?
GPS trackers utilize the OBD2 port for power and to access vehicle data, such as speed and location. According to a study by ABI Research in 2020, GPS trackers connected to the OBD2 port can provide valuable insights into driving behavior and vehicle usage.
4.3. What are the benefits of using a GPS tracker connected to the OBD2 port?
The benefits of using a GPS tracker connected to the OBD2 port include:
- Real-time location tracking: Allows you to monitor the vehicle’s location in real-time.
- Geofencing: Allows you to set up virtual boundaries and receive alerts when the vehicle enters or exits these areas.
- Driving behavior monitoring: Provides data on driving habits, such as speeding, hard braking, and acceleration.
- Vehicle health monitoring: Accesses vehicle data, such as battery voltage and engine temperature.
- Theft recovery: Helps locate the vehicle in case of theft.
4.4. Can the OBD2 port be used for vehicle tuning or ECU remapping?
Yes, the OBD2 port can be used for vehicle tuning or ECU remapping. According to a report by Grand View Research in 2021, ECU tuning involves modifying the software in the vehicle’s computer to improve performance, fuel efficiency, or other parameters.
4.5. What are the risks associated with ECU remapping via the OBD2 port?
The risks associated with ECU remapping via the OBD2 port include:
- Voiding the vehicle’s warranty: Modifying the ECU can void the manufacturer’s warranty.
- Damaging the engine: Incorrect tuning can lead to engine damage.
- Emissions violations: Modifying the ECU can result in the vehicle failing emissions tests.
- Reduced fuel efficiency: Poorly optimized tuning can reduce fuel efficiency.
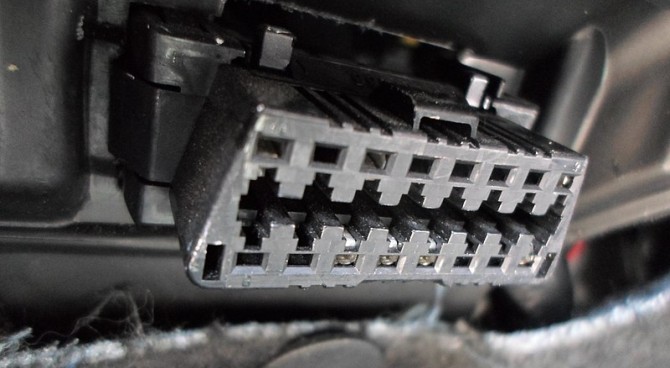 OBD-II port
OBD-II port
5. What are Some Mobile OBD2 Scanner Apps?
Mobile OBD2 scanner apps have become increasingly popular, offering a convenient way to monitor vehicle parameters and diagnose issues. According to a 2022 report by Global Market Insights, the market for automotive diagnostic tools is expected to grow significantly, driven by the increasing adoption of mobile OBD2 scanners. These apps use a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi adapter connected to the OBD2 port to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
5.1. How do mobile OBD2 scanner apps work?
Mobile OBD2 scanner apps work by connecting to an OBD2 adapter plugged into the vehicle’s OBD2 port. The adapter communicates with the vehicle’s ECU and transmits data to the app via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
5.2. What types of data can be monitored using these apps?
Using these apps, you can monitor various types of data, including:
- Engine temperature
- Fuel rate
- O2 sensor voltages
- Battery voltage level
- Engine runtime
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
5.3. What are some of the popular mobile OBD2 scanner apps available?
Some popular mobile OBD2 scanner apps include:
- Torque Pro
- OBD Car Doctor
- DashCommand
- BimmerCode (for BMW vehicles)
- BimmerLink (for BMW vehicles)
- ScanMaster
5.4. What are the advantages of using a mobile OBD2 scanner app?
The advantages of using a mobile OBD2 scanner app include:
- Convenience: Allows you to monitor vehicle data using your smartphone or tablet.
- Cost-effectiveness: Mobile apps are often more affordable than dedicated scan tools.
- Real-time data: Provides real-time access to vehicle data.
- Portability: Easy to carry and use in different vehicles.
5.5. Are there any limitations to using mobile OBD2 scanner apps?
Yes, there are some limitations to using mobile OBD2 scanner apps:
- Adapter compatibility: Requires a compatible OBD2 adapter.
- App compatibility: Not all apps are compatible with all vehicles.
- Limited advanced features: Mobile apps may not offer the same advanced features as dedicated scan tools.
- Security concerns: Potential security risks associated with connecting to the vehicle’s computer via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
6. Recommended OBD2 Scanners
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner depends on your needs and budget. Here are a few recommended scanners catering to different requirements:
6.1. Veepeak Mini WiFi OBD II Scanner
The Veepeak Mini WiFi OBD II Scanner is a budget-friendly option for Android users. It connects via Wi-Fi and works with apps like Torque Pro and OBD Car Doctor. According to customer reviews on Amazon, it’s praised for its ease of use and reliable performance.
6.2. BAFX Products OBDII Code Reader and Scan Tool
The BAFX Products OBDII Code Reader and Scan Tool is a wireless OBD reader that transforms your iOS device into an advanced diagnostic tool. It allows you to monitor real-time parameters and is praised for its compatibility and performance.
6.3. Veepeak OBDCheck BLE Bluetooth OBD II Scanner
The Veepeak OBDCheck BLE Bluetooth OBD II Scanner is a slightly more advanced device for both Android and iOS devices. It supports Bluetooth 4.0 and works with various software, including Torque, BimmerCode, and ScanMaster.
6.4. BlueDriver Pro OBD2 Bluetooth Scan Tool
The BlueDriver Pro OBD2 Bluetooth Scan Tool is a professional-grade scanner that works with both Android and iOS devices. It offers advanced features like reading and clearing basic and advanced error codes, live data, and repair reports.
6.5. OBDLink MX+ OBD2 Bluetooth Scanner
The OBDLink MX+ OBD2 Bluetooth Scanner is a high-end option that provides access to real-time data and enhanced support for various vehicle brands. It allows you to display, graph, and log hundreds of real-time parameters.
 veepeak obd-ii scanner
veepeak obd-ii scanner
7. Other Uses for the OBD2 Port
Besides diagnostics, the OBD2 port can be used for various other purposes, such as vehicle tracking and performance tuning.
7.1. Can the OBD2 port be used to track a vehicle’s location?
Yes, the OBD2 port can be used to track a vehicle’s location using a GPS tracker. These devices plug into the OBD2 port and transmit location data to a monitoring service.
7.2. What are the benefits of using the OBD2 port for vehicle tracking?
The benefits of using the OBD2 port for vehicle tracking include:
- Easy installation: GPS trackers can be easily plugged into the OBD2 port without requiring complex wiring.
- Power source: The OBD2 port provides a reliable power source for the GPS tracker.
- Vehicle data: Some GPS trackers can access vehicle data, such as speed and mileage, through the OBD2 port.
7.3. What are the security implications of connecting devices to the OBD2 port?
Connecting devices to the OBD2 port can pose security risks, as it provides access to the vehicle’s computer system. According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in 2016, unauthorized access to the OBD2 port could potentially allow hackers to control vehicle functions.
7.4. Can the OBD2 port be used to improve fuel efficiency?
Yes, the OBD2 port can be used to improve fuel efficiency by monitoring fuel consumption and adjusting driving habits. Some OBD2 devices and apps provide real-time feedback on fuel efficiency, helping drivers optimize their driving.
7.5. What are some advanced uses for the OBD2 port?
Some advanced uses for the OBD2 port include:
- Remote diagnostics: Allows mechanics to remotely diagnose vehicle problems.
- Usage-based insurance: Tracks driving behavior for insurance purposes.
- Fleet management: Monitors vehicle location and performance for fleet management.
- Custom tuning: Modifies engine parameters for improved performance.
8. What Are the Common Issues With OBD2 Ports?
While the OBD2 port is a robust and standardized interface, it’s not immune to issues. Here are some common problems you might encounter:
8.1. Damaged or Broken Ports
Physical damage is a frequent issue. The port can be broken or the pins can be bent, preventing proper connection with scanners or other devices.
Solution: A damaged port often requires professional repair or replacement. Avoid forcing connectors into the port.
8.2. Corrosion
Corrosion can build up on the pins, especially in older vehicles or those exposed to moisture. This can impede connectivity and data transfer.
Solution: Clean the pins with a specialized electronic contact cleaner. Ensure the area is dry before reconnecting any devices.
8.3. Software Incompatibilities
Not all scanners or apps are compatible with every vehicle. Software incompatibilities can lead to errors or an inability to read data.
Solution: Check the compatibility of the scanner or app with your vehicle’s make and model. Update software regularly.
8.4. Power Issues
The OBD2 port requires a stable power supply. Power-related issues can cause scanners to fail or produce inaccurate readings.
Solution: Check the vehicle’s battery and electrical system. Ensure the port is receiving the correct voltage.
8.5. Communication Errors
Sometimes, the scanner might fail to communicate with the vehicle’s ECU, resulting in error messages or no data.
Solution: Verify that the vehicle’s ignition is on. Try a different scanner or app to rule out software issues. Check the vehicle’s ECU for any underlying problems.
9. OBD2 Port Security and Privacy Concerns
While the OBD2 port provides numerous benefits, it also introduces potential security and privacy risks. According to a report by the Automotive Information Sharing and Analysis Center (Auto-ISAC) in 2020, securing vehicle connectivity is a top priority for the automotive industry.
9.1. What are the potential security risks associated with the OBD2 port?
The potential security risks associated with the OBD2 port include:
- Unauthorized access: Hackers could potentially gain unauthorized access to the vehicle’s computer system through the OBD2 port.
- Malware injection: Malware could be injected into the vehicle’s computer system via compromised OBD2 devices or apps.
- Data theft: Sensitive vehicle data, such as location and driving behavior, could be stolen.
- Vehicle control: In extreme cases, hackers could potentially gain control of vehicle functions, such as steering and braking.
9.2. How can these security risks be mitigated?
These security risks can be mitigated by:
- Using trusted OBD2 devices and apps: Only use devices and apps from reputable vendors.
- Keeping software updated: Regularly update the software on your OBD2 devices and apps to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Monitoring OBD2 port activity: Be vigilant for any unusual activity or unauthorized access to the OBD2 port.
- Securing the vehicle’s network: Protect the vehicle’s network with firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
9.3. What privacy concerns are associated with OBD2 data?
The privacy concerns associated with OBD2 data include:
- Data collection: OBD2 devices and apps may collect and transmit sensitive vehicle data, such as location, driving behavior, and vehicle health information.
- Data sharing: This data may be shared with third parties, such as insurance companies, advertisers, and data brokers.
- Data misuse: The data could be misused for purposes such as targeted advertising, insurance rate discrimination, or even vehicle repossession.
9.4. How can you protect your privacy when using OBD2 devices and apps?
You can protect your privacy by:
- Reviewing privacy policies: Carefully review the privacy policies of OBD2 devices and apps before using them.
- Limiting data sharing: Opt out of data sharing whenever possible.
- Using privacy-focused devices and apps: Choose devices and apps that prioritize user privacy.
- Securing your data: Take steps to protect your data, such as using strong passwords and enabling encryption.
9.5. What regulations are in place to protect OBD2 data?
Regulations in place to protect OBD2 data include:
- The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Gives California residents the right to know what personal information is collected about them, to delete their personal information, and to opt out of the sale of their personal information.
- The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Gives EU residents similar rights regarding their personal data.
- Industry standards: The automotive industry is developing standards and best practices for protecting OBD2 data.
10. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of having access to reliable and accurate information about your vehicle. That’s why we offer a comprehensive range of resources to help you make informed decisions about your car’s maintenance and repair.
10.1. Why choose CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for your automotive needs?
Choosing CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for your automotive needs offers several advantages:
- Expert Information: Access detailed information about various automotive parts, tools, and technologies.
- Comprehensive Comparisons: Compare different products and brands to find the best fit for your needs and budget.
- User Reviews: Read reviews and testimonials from other car owners and mechanics to gain valuable insights.
- Trusted Suppliers: Find reputable suppliers offering competitive prices and high-quality products.
- Expert Support: Receive expert advice and support from our team of automotive professionals.
10.2. What types of products and information are available on CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wide range of products and information, including:
- OBD2 Scanners: Find detailed information and comparisons of various OBD2 scanners.
- Diagnostic Tools: Explore different diagnostic tools for identifying and resolving vehicle issues.
- Auto Parts: Access information about different auto parts, including specifications, brands, and suppliers.
- Repair Guides: Find step-by-step repair guides for common vehicle problems.
- Maintenance Tips: Get tips on how to properly maintain your vehicle and extend its lifespan.
10.3. How can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN help you find the right OBD2 scanner for your needs?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN can help you find the right OBD2 scanner for your needs by:
- Providing detailed product information: Access detailed specifications, features, and benefits of various OBD2 scanners.
- Offering comprehensive comparisons: Compare different scanners side-by-side to identify the best option.
- Providing user reviews: Read reviews from other users to gain insights into the real-world performance of different scanners.
- Offering expert recommendations: Receive personalized recommendations from our team of automotive professionals.
10.4. How can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN help you save money on car repairs?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN can help you save money on car repairs by:
- Providing diagnostic information: Identify the root cause of vehicle problems before taking it to a mechanic.
- Offering repair guides: Perform simple repairs yourself, saving on labor costs.
- Finding affordable parts: Locate reputable suppliers offering competitive prices on auto parts.
- Preventive maintenance tips: Properly maintain your vehicle to prevent costly repairs down the road.
10.5. How can you contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for assistance?
You can contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for assistance via:
- Address: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
By leveraging the resources and expertise available at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can take control of your vehicle’s maintenance and repair, saving time and money.
Understanding the OBD2 port and its capabilities can empower you to take better care of your vehicle. With the right tools and information from CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can diagnose problems, monitor performance, and ensure your car runs smoothly for years to come.
Are you struggling to find the right auto parts or repair tools? Do you need expert advice on diagnosing a vehicle issue? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for personalized assistance. Our team of automotive professionals is ready to help you find the perfect solutions for your needs and budget. We’re located at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, and we’re committed to providing top-notch support and guidance. Don’t wait—reach out now and let us help you keep your vehicle in top condition with quality components and diagnostic assistance!
