How to use an OBD2 scanner? An OBD2 scanner is your car’s health monitor, providing insights into its performance and potential issues; CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers in-depth information on these diagnostic tools, helping you interpret fault codes and live data. By mastering OBD2 scanner usage, you empower yourself with car diagnostic skills and vehicle maintenance knowledge. Learn the ins and outs of automotive diagnostics and diagnostic trouble codes with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Contents
- 1. What Is An OBD2 Scanner and How Does It Work?
- 2. What Are the Different Types of OBD2 Scanners Available?
- 3. How Do I Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner for My Needs?
- 4. Where Is the OBD2 Port Located in My Car?
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use an OBD2 Scanner
- 6. Understanding and Interpreting OBD2 Fault Codes
- 7. What Is Live Data and How Can It Help with Diagnosis?
- 8. Can I Clear OBD2 Fault Codes Myself?
- 9. What Are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10. Advanced Functions of OBD2 Scanners: Beyond Basic Code Reading
- 11. How to Use OBD2 Scanner for Used Car Inspection
- 12. Maintaining Your OBD2 Scanner: Tips for Longevity
- 13. Where to Buy a Reliable OBD2 Scanner?
- 14. The Future of OBD2 Technology: What’s Next?
- 15. FAQ: Common Questions About Using OBD2 Scanners
1. What Is An OBD2 Scanner and How Does It Work?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool that connects to a vehicle’s onboard computer system to retrieve data about its performance and identify potential problems. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) in 2022, using OBD2 scanners can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40%. This powerful tool, when properly utilized, can save you time and money by allowing you to identify and address issues early.
- The OBD2 scanner connects to the vehicle’s diagnostic port, typically located under the dashboard.
- Once connected, the scanner communicates with the vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU) and other control modules to retrieve data.
- The scanner displays diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), which indicate specific problems within the vehicle’s systems.
- It also provides access to live data streams, allowing you to monitor various parameters such as engine temperature, RPM, and sensor readings in real-time.
2. What Are the Different Types of OBD2 Scanners Available?
There are several types of OBD2 scanners, each with its own features and capabilities, catering to different user needs and budgets.
- Basic Code Readers: These are the most affordable and simplest OBD2 scanners, typically used for reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). They are suitable for basic troubleshooting and identifying common issues. Prices range from $20 to $50.
- Mid-Range Scanners: These scanners offer more advanced features such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, and the ability to perform some basic tests. They are suitable for DIYers and car enthusiasts who want more detailed information about their vehicle’s performance. Prices range from $50 to $200.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These are the most advanced and expensive OBD2 scanners, offering a wide range of features such as bi-directional control, advanced diagnostics, and programming capabilities. They are typically used by professional mechanics and technicians. Prices range from $200 to $1000+.
- Smartphone-Based Scanners: These scanners consist of a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi adapter that plugs into the OBD2 port and communicates with a smartphone app. They offer a convenient and affordable way to access OBD2 data, with features similar to mid-range scanners. Prices range from $20 to $100.
3. How Do I Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner for My Needs?
Choosing the right OBD2 scanner depends on your specific needs, budget, and technical expertise. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- Your budget: OBD2 scanners range in price from around $20 to over $1,000. Determine how much you are willing to spend before you start shopping.
- Your needs: What do you want to use the OBD2 scanner for? If you just want to read and clear codes, a basic code reader will suffice. If you want more advanced features, such as live data streaming and bi-directional control, you will need a more expensive scanner.
- Your technical expertise: How comfortable are you working on cars? If you are a beginner, you may want to start with a basic code reader and gradually upgrade to a more advanced scanner as you gain experience.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the OBD2 scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Features: Consider the features that are important to you, such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, bi-directional control, and the ability to perform advanced tests.
- Ease of Use: Choose an OBD2 scanner that is easy to use and has a clear, intuitive interface.
4. Where Is the OBD2 Port Located in My Car?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side of the vehicle. However, the exact location may vary depending on the make and model of the car. Here are some common locations:
- Under the steering wheel column
- Near the center console
- Inside the glove compartment
- Behind a small access panel
Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the exact location of the OBD2 port.
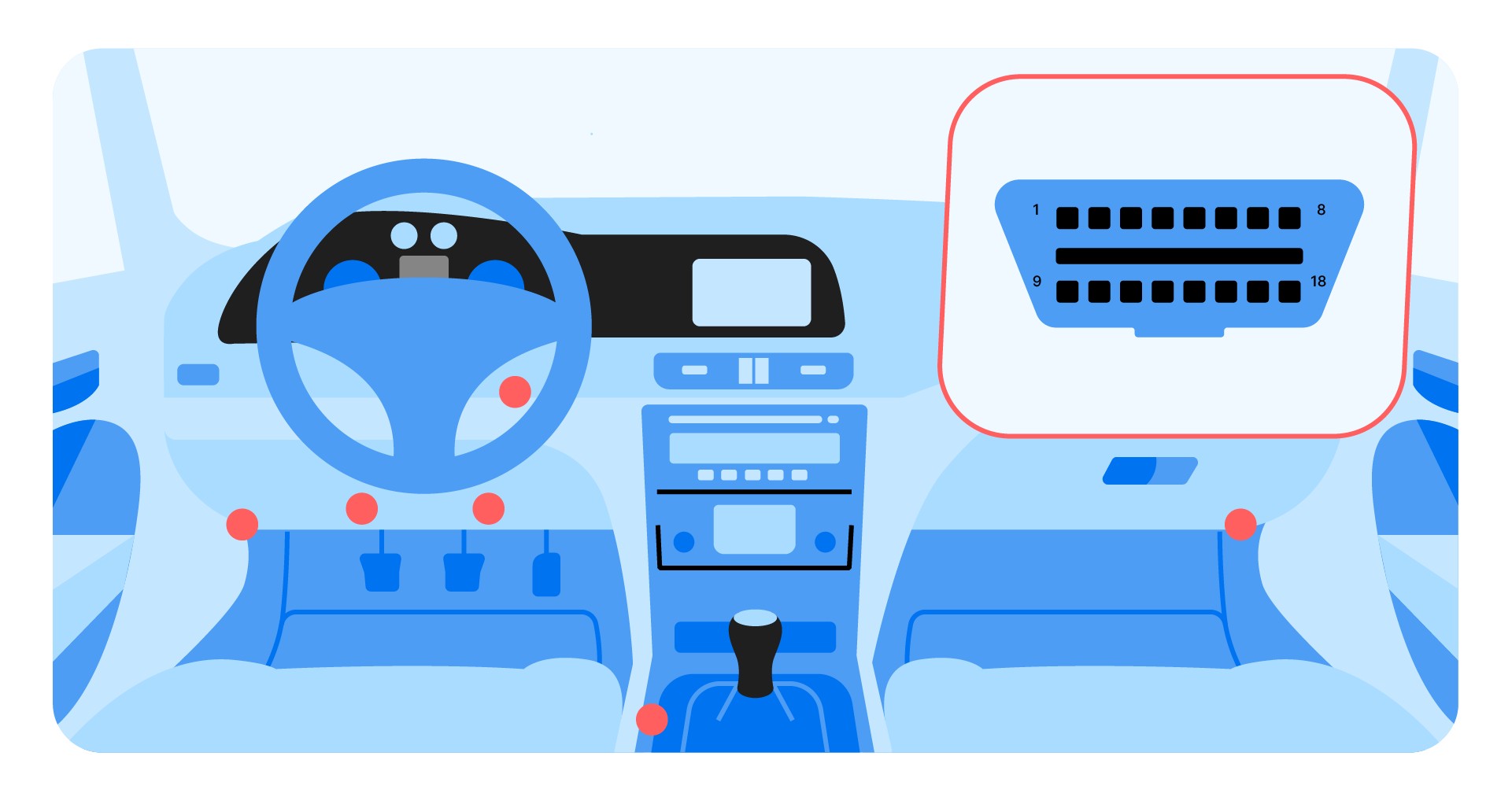 OBD2 scanner port location
OBD2 scanner port location
5. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use an OBD2 Scanner
Using an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process, but it’s essential to follow the steps carefully to ensure accurate results.
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port in your vehicle, usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the port. Ensure it’s securely plugged in.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Power on the Scanner: The scanner should power on automatically. If not, press the power button.
- Select Vehicle Information: Enter your vehicle’s make, model, and year into the scanner. Some scanners can automatically detect this information.
- Read Codes: Select the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option on the scanner.
- Interpret Codes: The scanner will display any stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). Consult the scanner’s manual or a reliable online resource to interpret the codes.
- View Live Data (Optional): If your scanner supports live data, you can view real-time information about your vehicle’s performance.
- Clear Codes (Optional): If you have addressed the underlying issue, you can clear the codes using the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option.
- Disconnect the Scanner: Once you are finished, disconnect the scanner from the OBD2 port.
6. Understanding and Interpreting OBD2 Fault Codes
OBD2 fault codes, also known as diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), are alphanumeric codes that indicate specific problems within a vehicle’s systems. Understanding these codes is crucial for diagnosing and repairing vehicle issues. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), OBD2 codes are standardized across all vehicles manufactured since 1996, making it easier to identify and address problems.
-
Code Structure: OBD2 codes consist of five characters: a letter followed by four numbers.
- The letter indicates the system where the fault occurred:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission, etc.)
- B: Body (airbags, lights, etc.)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension, etc.)
- U: Network (communication systems)
- The first number indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- The remaining three numbers indicate the specific fault.
- The letter indicates the system where the fault occurred:
-
Common OBD2 Codes: Some common OBD2 codes include:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty MAF sensor, fuel pump issue |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, O2 sensor issue |
| P0401 | Insufficient EGR Flow | Faulty EGR valve, clogged EGR passages |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issue |
- Interpreting Codes: Consult the OBD2 scanner’s manual or a reliable online resource to interpret the meaning of each code.
- Further Diagnosis: OBD2 codes provide a starting point for diagnosis. Further testing and inspection may be necessary to pinpoint the exact cause of the problem.
7. What Is Live Data and How Can It Help with Diagnosis?
Live data, also known as real-time data or sensor data, refers to the continuous stream of information from various sensors and components within a vehicle’s systems. This data can be accessed using an OBD2 scanner and provides valuable insights into the vehicle’s performance and potential issues. According to a study by Bosch in 2021, analyzing live data can improve diagnostic accuracy by up to 30%.
-
Parameters: Live data includes a wide range of parameters, such as:
- Engine speed (RPM)
- Engine temperature
- Oxygen sensor readings
- Fuel trim values
- Mass airflow (MAF) sensor readings
- Throttle position
- Vehicle speed
-
Benefits of Live Data:
- Pinpointing Intermittent Problems: Live data can help identify intermittent problems that may not trigger a diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
- Verifying Sensor Readings: Live data allows you to verify that sensors are functioning correctly and providing accurate readings.
- Assessing System Performance: Live data can provide insights into the overall performance of various systems, such as the engine, transmission, and fuel system.
- Troubleshooting Complex Issues: Live data can be used to troubleshoot complex issues by monitoring multiple parameters simultaneously and identifying correlations.
-
Example: If you are experiencing a lack of power, you can use live data to monitor the MAF sensor readings, fuel trim values, and throttle position to identify potential causes.
-
Analyzing Live Data: Analyzing live data requires some technical knowledge and experience. Consult the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online resource for guidance.
 OBD2 scanner
OBD2 scanner
8. Can I Clear OBD2 Fault Codes Myself?
Yes, you can clear OBD2 fault codes yourself using an OBD2 scanner. However, it’s important to understand the implications of clearing codes and to do so responsibly.
- Clearing Codes: Clearing codes erases the stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the vehicle’s computer system.
- When to Clear Codes: You should only clear codes after you have identified and addressed the underlying issue that caused the code to be set.
- Consequences of Clearing Codes Without Repairing the Issue:
- The code will likely return if the underlying issue is not resolved.
- Clearing codes can mask symptoms and make it more difficult to diagnose the problem in the future.
- Clearing codes may also reset certain system settings, which can affect vehicle performance.
- How to Clear Codes:
- Connect the OBD2 scanner to the vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Turn on the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Select the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option on the scanner.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to confirm the code clearing process.
- After Clearing Codes: After clearing codes, it’s recommended to drive the vehicle for a while to see if the codes return. If the codes reappear, it indicates that the underlying issue has not been resolved.
9. What Are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner?
Using an OBD2 scanner is generally straightforward, but there are some common mistakes that you should avoid to ensure accurate results and prevent potential problems.
- Not Researching Codes Before Clearing: Always research the meaning of a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) before clearing it. Clearing codes without understanding the underlying issue can mask symptoms and make it more difficult to diagnose the problem in the future.
- Ignoring Live Data: Don’t rely solely on DTCs. Live data provides valuable insights into the vehicle’s performance and can help you pinpoint intermittent problems that may not trigger a code.
- Using an Incompatible Scanner: Ensure that the OBD2 scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Using an incompatible scanner can result in inaccurate readings or even damage to the vehicle’s computer system.
- Forgetting to Turn on the Ignition: The ignition must be turned on to the “ON” position without starting the engine for the OBD2 scanner to communicate with the vehicle’s computer system.
- Not Consulting the Vehicle’s Service Manual: The vehicle’s service manual provides valuable information about the vehicle’s systems and components. Consult the manual for guidance on interpreting codes and troubleshooting problems.
- Misinterpreting Freeze Frame Data: Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions when a DTC was set. Misinterpreting this data can lead to incorrect diagnoses.
- Overlooking Wiring and Connections: Faulty wiring and loose connections can cause a variety of problems and trigger false DTCs. Always inspect wiring and connections before replacing parts.
10. Advanced Functions of OBD2 Scanners: Beyond Basic Code Reading
Modern OBD2 scanners offer a range of advanced functions that go beyond basic code reading, providing more in-depth diagnostic capabilities. These functions are typically found in mid-range and professional-grade scanners and can be invaluable for diagnosing complex issues.
- Bi-Directional Control: This function allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer system to activate or deactivate certain components, such as the fuel pump, injectors, or cooling fans. This can be useful for testing components and troubleshooting problems.
- Actuation Tests: These tests allow you to activate specific components to verify their functionality. For example, you can activate the ABS pump to check for proper operation.
- Programming and Coding: Some advanced scanners allow you to program and code certain modules, such as the ECU or transmission control module (TCM). This is typically used for replacing modules or updating software.
- Key Programming: Some scanners can program new keys for vehicles with immobilizer systems.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Some scanners offer advanced diagnostic capabilities, such as the ability to perform compression tests, cylinder balance tests, and relative compression tests.
- Adaptation Reset: This function allows you to reset certain adaptation values after replacing a component, such as the throttle body or mass airflow sensor.
- Service Resets: Many scanners offer service reset functions, such as oil reset, brake pad reset, and TPMS reset.
- OBD1 Support: Some scanners can also read and clear codes from older OBD1 vehicles.
11. How to Use OBD2 Scanner for Used Car Inspection
An OBD2 scanner is an essential tool for inspecting used cars before making a purchase. It can help you identify hidden problems that may not be immediately apparent, potentially saving you thousands of dollars in repair costs. According to a report by the National Automobile Dealers Association (NADA) in 2023, approximately 5% of used cars have hidden issues that can be detected with an OBD2 scanner.
- Check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Connect the OBD2 scanner to the vehicle’s OBD2 port and scan for any stored DTCs.
- Research the Codes: Research the meaning of any DTCs that are found. Some codes may indicate minor issues, while others may indicate more serious problems.
- Check for Cleared Codes: Some unscrupulous sellers may clear the codes just before you inspect the car. Check the scanner’s freeze frame data to see when the codes were last cleared. If the codes were recently cleared, it may be a red flag.
- Inspect Live Data: Inspect live data to monitor the performance of various systems, such as the engine, transmission, and fuel system. Look for any abnormal readings or fluctuations.
- Perform Actuation Tests: If the scanner supports actuation tests, perform some basic tests to verify the functionality of certain components, such as the cooling fans, fuel pump, and injectors.
- Compare Readings to Specifications: Compare the scanner’s readings to the vehicle’s specifications. The vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online resource can provide these specifications.
- Consider a Professional Inspection: If you are not comfortable performing a thorough inspection yourself, consider taking the car to a professional mechanic for a pre-purchase inspection.
12. Maintaining Your OBD2 Scanner: Tips for Longevity
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and accurate performance of your OBD2 scanner. Here are some tips for maintaining your scanner:
- Store the Scanner in a Safe Place: When not in use, store the scanner in a clean, dry, and safe place to protect it from damage.
- Protect the Cable: Avoid bending or twisting the cable excessively, as this can damage the wires inside.
- Keep the Connectors Clean: Keep the connectors clean and free of dirt and debris. Use a soft cloth to clean the connectors if necessary.
- Update the Software: Keep the scanner’s software up to date to ensure that it has the latest features and bug fixes.
- Handle with Care: Avoid dropping or mishandling the scanner, as this can damage the internal components.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Do not expose the scanner to extreme temperatures, as this can damage the display and other components.
- Replace Batteries When Necessary: If your scanner uses batteries, replace them when they are low to ensure proper operation.
- Read the Manual: Read the scanner’s manual to learn about specific maintenance recommendations.
13. Where to Buy a Reliable OBD2 Scanner?
Purchasing a reliable OBD2 scanner is crucial for accurate diagnostics and effective vehicle maintenance. Here are some reputable sources where you can buy OBD2 scanners:
- CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN: Offers a wide selection of OBD2 scanners from trusted brands, catering to various needs and budgets. Our website provides detailed product information and customer reviews to help you make an informed decision.
- Automotive Parts Stores: Major automotive parts stores like AutoZone, Advance Auto Parts, and O’Reilly Auto Parts carry a variety of OBD2 scanners. They often have knowledgeable staff who can assist you in choosing the right scanner for your needs.
- Online Retailers: Online retailers like Amazon and eBay offer a vast selection of OBD2 scanners. However, it’s important to read reviews carefully and choose reputable sellers to avoid purchasing counterfeit or unreliable products.
- Professional Tool Suppliers: Professional tool suppliers like Snap-on and Mac Tools offer high-quality OBD2 scanners designed for professional technicians. These scanners are typically more expensive but offer advanced features and durability.
When choosing an OBD2 scanner, consider the following factors:
- Brand Reputation: Choose a scanner from a reputable brand known for quality and reliability.
- Features: Select a scanner with the features you need for your specific diagnostic tasks.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Warranty: Look for a scanner with a good warranty to protect your investment.
- Customer Reviews: Read customer reviews to get an idea of the scanner’s performance and reliability.
14. The Future of OBD2 Technology: What’s Next?
OBD2 technology is constantly evolving to meet the demands of modern vehicles and the changing automotive landscape. Here are some of the trends and developments that are shaping the future of OBD2 technology:
- Enhanced Diagnostics: Future OBD2 systems will offer more advanced diagnostic capabilities, such as the ability to diagnose problems with hybrid and electric vehicles.
- Wireless Connectivity: Wireless OBD2 scanners are becoming increasingly popular, offering greater convenience and flexibility.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Cloud-based diagnostic platforms are emerging, allowing technicians to access vehicle data and diagnostic information remotely.
- Integration with Mobile Devices: OBD2 scanners are increasingly being integrated with mobile devices, allowing users to access vehicle data and diagnostic information on their smartphones and tablets.
- Cybersecurity: As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity is becoming a major concern. Future OBD2 systems will need to be designed with robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access and tampering.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to develop more advanced diagnostic tools that can automatically identify and diagnose problems.
- Predictive Maintenance: OBD2 data is being used to develop predictive maintenance systems that can anticipate potential problems before they occur.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostics are becoming increasingly common, allowing technicians to diagnose and repair vehicles remotely.
15. FAQ: Common Questions About Using OBD2 Scanners
Here are some frequently asked questions about using OBD2 scanners:
- Q: Will an OBD2 scanner work on any car?
- A: OBD2 scanners are compatible with most cars manufactured since 1996 in the United States and 2004 in Europe. However, it’s always a good idea to check the scanner’s compatibility with your vehicle’s make, model, and year before purchasing.
- Q: Can an OBD2 scanner fix my car?
- A: An OBD2 scanner can help you diagnose problems with your car, but it cannot fix them. You will need to repair the underlying issue to resolve the problem.
- Q: How do I know which OBD2 scanner is right for me?
- A: Choosing the right OBD2 scanner depends on your specific needs, budget, and technical expertise. Consider the factors discussed in Section 3 of this article.
- Q: Can I use an OBD2 scanner to pass an emissions test?
- A: An OBD2 scanner can help you identify problems that may cause your car to fail an emissions test, but it cannot guarantee that your car will pass.
- Q: Is it safe to clear OBD2 codes myself?
- A: It is generally safe to clear OBD2 codes yourself, but it’s important to understand the implications of clearing codes and to do so responsibly.
- Q: How often should I use an OBD2 scanner on my car?
- A: You should use an OBD2 scanner whenever you notice a warning light on your dashboard or experience any unusual symptoms with your car.
- Q: Can an OBD2 scanner damage my car?
- A: It is unlikely that an OBD2 scanner will damage your car if used correctly. However, using an incompatible scanner or misinterpreting the data can potentially cause problems.
- Q: Are there any free OBD2 scanner apps?
- A: Yes, there are several free OBD2 scanner apps available for smartphones. However, these apps typically offer limited functionality and may not be as accurate as dedicated OBD2 scanners.
- Q: Where can I find a list of OBD2 codes and their meanings?
- A: You can find a list of OBD2 codes and their meanings in the scanner’s manual or online resources like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) website.
- Q: What does it mean when an OBD2 scanner says “No Codes Found”?
- A: “No Codes Found” means that the scanner did not detect any stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) in the vehicle’s computer system. This does not necessarily mean that there are no problems with the car, as some issues may not trigger a code.
By understanding how to use an OBD2 scanner, you can take control of your vehicle’s maintenance and make informed decisions about repairs. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a novice car owner, an OBD2 scanner is an invaluable tool for keeping your vehicle running smoothly.
Are you looking for reliable and accurate OBD2 scanners or other auto repair tools? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States or Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 and let our experts help you find the perfect tools for your needs.