The 2013 Tesla Model S TPMS (Tire Pressure Monitoring System) sensor replacement involves specific procedures to ensure proper functionality and safety, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to guide you through the crucial steps for successful TPMS sensor replacement and relearn. Understanding the TPMS system type, frequency, and necessary tools enhances the repair process, leading to optimal vehicle performance and safety standards.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the 2013 Tesla Model S TPMS System
- 2. Identifying TPMS Sensor Options
- 3. Determining TPMS Frequency
- 4. Selecting the Correct TPMS Tool
- 5. Understanding the Relearn Procedure
- 5.1 Auto Relearn Procedure (2012-2016 Tesla Model S)
- 5.2 Auto Relearn Procedure (2017-2019 Tesla Model S)
- 6. Troubleshooting Tips
- 7. Common Issues and How to Resolve Them
- 7.1 Sensor Not Registering
- 7.2 Incorrect Tire Pressure Readings
- 7.3 TPMS Warning Light Remains On
- 7.4 Interference
- 7.5 TPMS Module Issues
- 8. Maintenance Tips to Prolong TPMS Sensor Life
- 8.1 Regular Tire Maintenance
- 8.2 Proper Installation and Handling
- 8.3 Environmental Considerations
- 8.4 Periodic Checks and Inspections
- 9. Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for TPMS Information
- 9.1 Detailed Information
- 9.2 Technical Specifications
- 9.3 User Reviews
- 9.4 Product Comparisons
- 9.5 Expert Advice
- 9.6 Up-to-Date Information
- 9.7 Troubleshooting Guides
- 9.8 Wide Range of Products
- 9.9 Easy Navigation
- 9.10 Cost Savings
- 10. Cost Analysis of TPMS Sensor Replacement
- 10.1 Cost Factors
- 10.2 Estimated Costs
- 10.3 Cost-Saving Strategies
- 10.4 Long-Term Savings
- 11. Key Considerations for Choosing TPMS Sensors
- 11.1 Compatibility
- 11.2 Quality and Durability
- 11.3 Brand Reputation
- 11.4 Ease of Installation and Programming
- 11.5 Features and Functionality
- 11.6 Cost-Effectiveness
- 11.7 Certification and Compliance
- 12. Using Diagnostic Tools for TPMS Issues
- 12.1 Types of Diagnostic Tools
- 12.2 Common TPMS Diagnostic Codes
- 12.3 How to Diagnose TPMS Issues
- 12.4 Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
- 12.5 Benefits of Using Diagnostic Tools
- 13. Auto Repair Technicians’ Perspectives on TPMS Sensor Replacements
- 13.1 Common Challenges Faced
- 13.2 Best Practices for TPMS Sensor Replacement
- 13.3 Essential Tools and Equipment
- 13.4 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 13.5 Tips for Efficient TPMS Service
- 14. Industry Insights and Statistics
- 14.1 Market Trends
- 14.2 Regulatory Landscape
- 14.3 TPMS Replacement Rates
- 14.4 Economic Impact
- 14.5 Future Outlook
- 15. Step-by-Step Guide for DIY TPMS Sensor Replacement
- 15.1 Preparation
- 15.2 Removal of Old TPMS Sensor
- 15.3 Installation of New TPMS Sensor
- 15.4 TPMS Relearn Procedure
- 15.5 Final Checks
- 16. Innovations in TPMS Technology
- 16.1 Direct TPMS (dTPMS)
- 16.2 Indirect TPMS (iTPMS)
- 16.3 Next-Generation TPMS Features
- 16.4 Impact on Vehicle Performance
- 16.5 Future Trends
- 17. Glossary of TPMS Terms
- 17.1 Basic TPMS Terms
- 17.2 Sensor-Related Terms
- 17.3 Diagnostic and Service Terms
- 17.4 Tire-Related Terms
- 17.5 Additional Terms
- 18. How CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Supports Automotive Technicians
- 18.1 Access to Comprehensive Information
- 18.2 Training and Educational Resources
- 18.3 Diagnostic Tools and Equipment
- 18.4 Troubleshooting Guides and Tips
- 18.5 Community and Networking
- 18.6 Cost-Saving Solutions
- 18.7 Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
1. Understanding the 2013 Tesla Model S TPMS System
For a 2013 Tesla Model S, a direct TPMS system is utilized. This system features sensors installed inside the wheels that transmit tire pressure data to the vehicle’s ECU (Electronic Control Unit) via radio frequency (RF) technology. In the event that the tire pressure is low, the TPMS sensor communicates this information, activating a warning on the dashboard to alert the driver.
- Direct TPMS: This system has TPMS sensors inside the wheels to communicate tire pressure data to the vehicle’s ECU through RF technology.
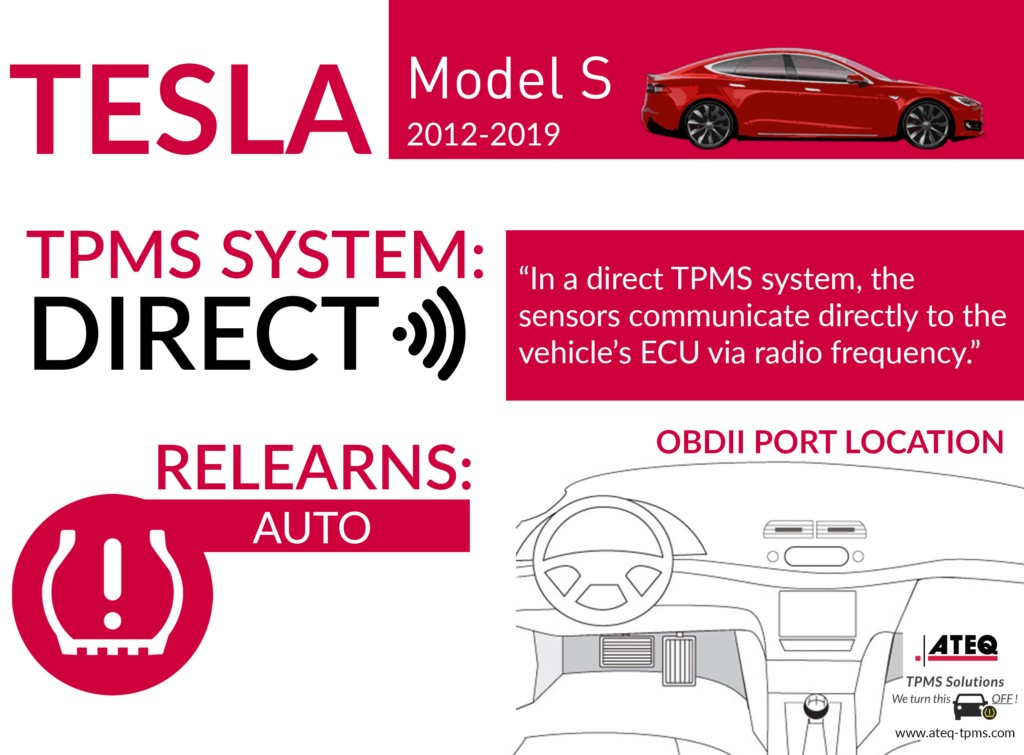 Tesla Model S Infographic
Tesla Model S Infographic
2. Identifying TPMS Sensor Options
Several options are available when replacing TPMS sensors in a 2013 Tesla Model S, including OE (Original Equipment), programmable, configurable, hybrid, and OE-type (one-to-one) sensors. These sensors can be programmed and configured using tools like the VT56, VT46, and VT36 TPMS tools, ensuring compatibility and proper function with the vehicle’s system.
- OE Sensors: Manufactured by the original equipment manufacturer to ensure perfect fit and function.
- Programmable Sensors: Versatile sensors that can be programmed to match various vehicle models.
- Configurable Sensors: Sensors that can be configured with specific vehicle information.
- Hybrid Sensors: Combine features of both programmable and OE sensors.
- OE-Type Sensors: Designed to replicate the performance and functionality of OE sensors.
3. Determining TPMS Frequency
The 2013 Tesla Model S TPMS operates on a specific radio frequency to communicate tire pressure data. Knowing the correct frequency is crucial for selecting compatible replacement sensors and ensuring accurate communication between the sensors and the vehicle’s ECU.
- Frequency: 433MHz.
4. Selecting the Correct TPMS Tool
To properly service and relearn the TPMS system, the correct TPMS tool is essential. Tools like the VT56 and VT46 are capable of displaying step-by-step relearn procedures specific to Tesla models, ensuring that the new sensors are correctly recognized and integrated into the vehicle’s system.
- VT56 and VT46: These tools offer step-by-step relearn procedures for Tesla models.
5. Understanding the Relearn Procedure
The relearn procedure is a critical step in the TPMS sensor replacement process. It involves teaching the vehicle’s ECU to recognize the new TPMS sensors. For the 2013 Tesla Model S, an auto relearn procedure is used. This process allows the vehicle to automatically detect and register the new sensors without manual programming.
- Auto Relearn: The vehicle automatically detects and registers new sensors.
5.1 Auto Relearn Procedure (2012-2016 Tesla Model S)
The auto relearn procedure for Tesla Model S models manufactured between 2012 and 2016 involves specific steps to ensure the TPMS sensors are correctly reset:
- Installation: Ensure TPMS sensors are properly installed in the wheels.
- Tire Pressure: Adjust the tire pressure to the values specified on the tire placard.
- Ignition: Turn the ignition ON.
- Wheel/Tire Pressure Monitor: Access the WHEEL/TIRE PRESSURE MONITOR through the vehicle’s interface.
- Tire Size Selection: Select the correct tire size, either 19″ or 21″.
- Reset: Tap the RESET button and follow the on-screen instructions in the dialog box.
- Driving: Drive the vehicle over 25 MPH for approximately 10 minutes to reset the TPMS sensors.
- Note: This function should not be used to clear existing TPMS warnings.
5.2 Auto Relearn Procedure (2017-2019 Tesla Model S)
For Tesla Model S models manufactured between 2017 and 2019, the auto relearn procedure is slightly different:
- Installation: Ensure TPMS sensors are properly installed.
- Tire Pressure: Adjust tire pressure to the values on the tire placard.
- Driving: Drive the vehicle until the system detects a change in TPMS and displays the prompt: “RESET sensors: We have detected new wheels on your car.”
- Tire Size Selection: Select the appropriate tire size.
- Reset: Tap the RESET button and follow the instructions in the dialog box.
- Driving: Drive over 25 MPH for about 3 minutes. The pressure should then be displayed on the dashboard.
- Note: This function should not be used to clear TPMS warnings.
6. Troubleshooting Tips
When performing TPMS sensor replacement on a 2013 Tesla Model S, several troubleshooting tips can help ensure a smooth and successful process:
- Wheel Size Selection: Ensure the correct wheel size is selected in the vehicle’s settings. The vehicle uses this information to set the correct “Recommended Cold Pressure (RCP)” target values.
- Incorrect Wheel Size: If the wheel size is selected incorrectly, the vehicle may display incorrect tire pressure warnings. To correct this, exit the vehicle, close all doors and the rear trunk, wait for the touch-screen to go black, re-enter the vehicle, and select the correct tire size before resetting again.
- Clearing Warnings: Do not attempt to reset the TPMS sensors to clear tire pressure warnings, as disabling TPMS warning systems is illegal.
- Original Specifications: Use tires that match the original specifications indicated on the tire placard, as incorrect tires can affect vehicle performance.
- Relearn Time: The auto relearn process can take up to 20 minutes of driving.
7. Common Issues and How to Resolve Them
7.1 Sensor Not Registering
Issue: New TPMS sensor is installed, but the vehicle does not recognize it.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Verify Sensor Compatibility: Ensure the sensor is compatible with the 2013 Tesla Model S.
- Check Sensor Activation: Use a TPMS tool to ensure the sensor is active and transmitting a signal.
- Relearn Procedure: Redo the relearn procedure, ensuring each step is followed correctly.
- Tool Compatibility: Make sure the TPMS tool is updated with the latest software.
7.2 Incorrect Tire Pressure Readings
Issue: The vehicle displays incorrect tire pressure readings after sensor replacement.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Verify Tire Pressure: Manually check the tire pressure to ensure it matches the recommended pressure.
- Sensor Calibration: Some sensors may require calibration. Check if the sensor has a calibration procedure.
- Wheel Size Setting: Confirm that the correct wheel size is selected in the vehicle’s settings.
- Sensor Quality: If using aftermarket sensors, ensure they are of high quality and from a reputable brand.
7.3 TPMS Warning Light Remains On
Issue: The TPMS warning light stays on even after completing the relearn procedure.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check for Additional Issues: Scan the TPMS system for any additional error codes.
- Inspect Sensors: Inspect the sensors for physical damage or corrosion.
- Battery Life: Check the battery life of the sensors, as old sensors may have weak batteries.
- Wiring and Connections: Inspect the wiring and connections to the TPMS module for any damage or loose connections.
7.4 Interference
Issue: Intermittent or unreliable TPMS readings.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check for Signal Interference: Ensure there are no sources of signal interference, such as electronic devices or aftermarket accessories.
- Sensor Placement: Verify that the sensors are properly installed and positioned within the wheel.
- Antenna Condition: Check the condition of the TPMS antenna and wiring.
- Software Updates: Ensure that the vehicle’s software is up to date.
7.5 TPMS Module Issues
Issue: Problems with the TPMS module itself.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Scan for Codes: Use a diagnostic tool to scan the TPMS module for error codes.
- Check Power and Ground: Verify that the module is receiving proper power and ground.
- Module Replacement: If the module is faulty, it may need to be replaced.
8. Maintenance Tips to Prolong TPMS Sensor Life
8.1 Regular Tire Maintenance
Keep Tires Properly Inflated: Regularly check and maintain the correct tire pressure as recommended by Tesla. Under- or over-inflated tires can cause undue stress on TPMS sensors.
Rotate Tires Regularly: Rotating tires helps ensure even wear and extends the life of both the tires and TPMS sensors.
Inspect Tires Regularly: Check tires for signs of damage or wear, such as cuts, bulges, or uneven tread wear. Addressing tire issues promptly can prevent damage to TPMS sensors.
8.2 Proper Installation and Handling
Use Qualified Technicians: Have TPMS sensors installed and serviced by qualified technicians who are familiar with Tesla vehicles.
Avoid Harsh Chemicals: When cleaning wheels, avoid using harsh chemicals that could damage TPMS sensors.
Be Careful During Tire Changes: Exercise caution during tire changes to avoid damaging the TPMS sensors. Use proper tools and techniques to remove and install tires.
8.3 Environmental Considerations
Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Extreme temperatures can affect TPMS sensor performance and battery life. Try to park in shaded areas during hot weather.
Protect from Corrosion: In areas with road salt or harsh weather conditions, consider using corrosion-resistant TPMS sensors or protective coatings.
8.4 Periodic Checks and Inspections
Check TPMS Sensor Battery Life: TPMS sensors have a limited battery life. Have them checked periodically and replaced as needed.
Inspect Sensor Seals: Check the sensor seals for damage or wear. Replace them as needed to prevent air leaks.
Monitor TPMS Readings: Regularly monitor TPMS readings and address any unusual or inconsistent data promptly.
By following these maintenance tips, you can extend the life of your TPMS sensors and ensure that your TPMS system functions correctly, providing you with timely warnings and helping you maintain optimal tire conditions for safety and efficiency.
9. Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for TPMS Information
When searching for detailed information about TPMS and other automotive parts, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers numerous advantages. The website provides comprehensive details, technical specifications, and user reviews, making it easier to find reliable and effective solutions. Additionally, the platform helps users compare different products, understand their features, and make informed decisions.
9.1 Detailed Information
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides detailed information on TPMS sensors, tools, and procedures, helping users fully understand the specifics of the TPMS system in the 2013 Tesla Model S.
9.2 Technical Specifications
Users can find technical specifications for various TPMS sensors and tools, ensuring they select the correct components for their vehicle.
9.3 User Reviews
The platform includes user reviews and ratings, offering insights into the performance and reliability of different TPMS products.
9.4 Product Comparisons
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN allows users to compare different TPMS sensors and tools, highlighting their features, pros, and cons to aid in decision-making.
9.5 Expert Advice
The website may offer expert advice and recommendations, guiding users through the TPMS replacement process.
9.6 Up-to-Date Information
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN keeps its information up-to-date with the latest TPMS technology and products, ensuring users have access to current and relevant data.
9.7 Troubleshooting Guides
The platform provides troubleshooting guides and tips for resolving common TPMS issues, helping users maintain their systems effectively.
9.8 Wide Range of Products
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN covers a wide range of TPMS sensors and tools from different manufacturers, giving users ample choices.
9.9 Easy Navigation
The website is designed for easy navigation, allowing users to quickly find the information they need.
9.10 Cost Savings
By providing comprehensive information and comparisons, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN helps users make informed decisions, potentially saving them money on unnecessary purchases or incorrect parts.
10. Cost Analysis of TPMS Sensor Replacement
10.1 Cost Factors
Several factors influence the cost of TPMS sensor replacement, including the type of sensor, the brand, and the labor involved. Here’s a breakdown:
Type of Sensor:
- OE (Original Equipment): Typically more expensive due to higher quality and guaranteed compatibility.
- Aftermarket: Can be more affordable but vary in quality and compatibility.
- Programmable: May have a higher upfront cost but can be programmed for multiple vehicles, potentially saving money in the long run.
Brand:
- Premium Brands: Known for reliability and performance but come at a higher price.
- Generic Brands: More budget-friendly but may not offer the same level of quality or durability.
Labor Costs:
- Professional Installation: Ensures proper installation and programming but adds to the overall cost.
- DIY Installation: Can save on labor costs but requires the right tools and knowledge.
10.2 Estimated Costs
Here are some estimated costs for TPMS sensor replacement on a 2013 Tesla Model S:
- OE Sensors: $50 – $150 per sensor
- Aftermarket Sensors: $30 – $100 per sensor
- Programmable Sensors: $40 – $120 per sensor
- Labor Costs: $50 – $150 per hour (depending on the shop and location)
Total Estimated Cost (per wheel):
- OE Sensor + Labor: $100 – $300
- Aftermarket Sensor + Labor: $80 – $250
10.3 Cost-Saving Strategies
To save money on TPMS sensor replacement:
- Shop Around: Compare prices from different suppliers and repair shops.
- Buy in Bulk: If replacing multiple sensors, buying a set can sometimes reduce the cost per sensor.
- DIY Installation: If you have the skills and tools, consider installing the sensors yourself.
- Use Aftermarket Sensors: Opt for reputable aftermarket brands that offer good quality at a lower price than OE sensors.
- Check Warranties: Ensure the sensors come with a warranty to protect against defects.
- Regular Maintenance: Proper tire maintenance can extend the life of TPMS sensors, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
10.4 Long-Term Savings
Investing in quality TPMS sensors and proper installation can lead to long-term savings by:
- Preventing Tire Damage: Maintaining proper tire pressure can prevent premature tire wear and damage.
- Improving Fuel Efficiency: Correctly inflated tires improve fuel efficiency, saving money on gas.
- Ensuring Safety: Reliable TPMS sensors enhance vehicle safety by alerting you to tire pressure issues promptly.
11. Key Considerations for Choosing TPMS Sensors
11.1 Compatibility
Vehicle Specificity: Ensure that the TPMS sensor is specifically designed for the 2013 Tesla Model S. Check the manufacturer’s compatibility list or consult with a professional to verify fitment.
Frequency Match: Confirm that the sensor operates on the correct frequency (433MHz for the 2013 Tesla Model S) to communicate effectively with the vehicle’s TPMS module.
11.2 Quality and Durability
Material Quality: Look for sensors made from high-quality materials that can withstand harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures, moisture, and vibrations.
Battery Life: Check the expected battery life of the sensor. A longer battery life reduces the frequency of replacements.
Warranty: Opt for sensors that come with a warranty, which indicates the manufacturer’s confidence in their product’s durability and reliability.
11.3 Brand Reputation
Established Brands: Choose sensors from well-known and reputable brands in the automotive industry. These brands typically have a track record of producing reliable and high-quality products.
Customer Reviews: Read customer reviews and ratings to get insights into the real-world performance and reliability of different TPMS sensors.
11.4 Ease of Installation and Programming
Installation Process: Consider how easy the sensor is to install. Some sensors may require specialized tools or expertise.
Programmability: If using programmable sensors, ensure that the programming process is straightforward and compatible with your TPMS tool.
11.5 Features and Functionality
Real-Time Monitoring: Ensure the sensor provides accurate, real-time tire pressure and temperature readings.
Alert System: Verify that the sensor effectively triggers alerts when tire pressure deviates from the recommended levels.
11.6 Cost-Effectiveness
Initial Cost: Compare the initial cost of different sensors, but also consider the long-term value in terms of durability and reliability.
Maintenance Costs: Factor in any potential maintenance costs, such as the need for frequent replacements or specialized programming.
11.7 Certification and Compliance
Industry Standards: Check if the sensor meets industry standards and certifications, such as those from regulatory bodies.
Legal Compliance: Ensure that the sensor complies with local laws and regulations regarding TPMS systems.
12. Using Diagnostic Tools for TPMS Issues
12.1 Types of Diagnostic Tools
Handheld TPMS Tools:
- Activation Tools: Used to activate and read TPMS sensor data.
- Programming Tools: Allow you to program aftermarket TPMS sensors with vehicle-specific information.
- Relearn Tools: Facilitate the relearn procedure, where the vehicle learns the new TPMS sensor IDs.
OBD II Scanners:
- Code Readers: Read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the TPMS system.
- Advanced Scanners: Offer more in-depth diagnostics, including live data monitoring and system tests.
Specialized Diagnostic Equipment:
- Professional TPMS Diagnostic Stations: Comprehensive tools used by automotive technicians for advanced TPMS diagnostics and repairs.
12.2 Common TPMS Diagnostic Codes
- C0700: Tire Pressure Monitoring System Malfunction
- C0701-C0707: Tire Pressure Sensor Circuit Malfunction (specific to each tire)
- C0750: Tire Pressure Sensor ID Incorrect
- C0755: Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) Sensor Not Detected
12.3 How to Diagnose TPMS Issues
- Visual Inspection: Check the tires for proper inflation, damage, or wear.
- Use a TPMS Tool: Activate each TPMS sensor to read its ID, tire pressure, temperature, and battery status.
- Scan for DTCs: Use an OBD II scanner to check for any diagnostic trouble codes related to the TPMS system.
- Interpret the Data: Analyze the data from the TPMS tool and OBD II scanner to identify the root cause of the issue.
12.4 Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
- Live Data Monitoring: Use a diagnostic tool to monitor live data from the TPMS sensors and module to identify intermittent issues.
- System Tests: Perform system tests, such as sensor tests and communication tests, to verify the functionality of the TPMS components.
- Wiring and Connection Checks: Inspect the wiring and connections to the TPMS sensors and module for any damage or loose connections.
- Module Testing: Test the TPMS module itself to ensure it is functioning correctly.
12.5 Benefits of Using Diagnostic Tools
- Accurate Diagnosis: Pinpoint the exact cause of TPMS issues, reducing guesswork and unnecessary repairs.
- Time Savings: Speed up the diagnostic process, saving time and labor costs.
- Comprehensive Analysis: Provide detailed data and system tests for a thorough analysis of the TPMS system.
- Preventive Maintenance: Identify potential issues before they become major problems, helping to prevent costly repairs down the road.
13. Auto Repair Technicians’ Perspectives on TPMS Sensor Replacements
13.1 Common Challenges Faced
Sensor Compatibility: Ensuring the replacement sensor is compatible with the specific vehicle model and TPMS system.
Corrosion and Damage: Dealing with corroded or damaged sensors that are difficult to remove.
Relearn Procedures: Navigating the relearn procedures required to synchronize new sensors with the vehicle’s computer.
Tool Updates: Keeping TPMS diagnostic and programming tools updated with the latest software and vehicle information.
13.2 Best Practices for TPMS Sensor Replacement
Proper Diagnosis: Thoroughly diagnose the TPMS issue to ensure sensor replacement is necessary.
Use Quality Parts: Choose high-quality replacement sensors from reputable brands.
Follow Procedures: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended procedures for installation, programming, and relearning.
Inspect Components: Inspect related components, such as valve stems and seals, and replace them as needed.
Document Work: Keep detailed records of the work performed, including sensor IDs and relearn procedures.
13.3 Essential Tools and Equipment
TPMS Diagnostic Tool: Used to read sensor data, diagnose issues, and perform relearn procedures.
Sensor Programming Tool: Required for programming aftermarket sensors with vehicle-specific information.
Torque Wrench: Ensures proper tightening of the sensor to prevent leaks and damage.
Valve Stem Tool: Used to remove and install valve stems without damaging the sensor.
13.4 Common Mistakes to Avoid
Skipping the Diagnosis: Replacing sensors without properly diagnosing the TPMS issue.
Using Incorrect Parts: Installing sensors that are not compatible with the vehicle.
Ignoring Relearn Procedures: Failing to perform the relearn procedure, resulting in a TPMS warning light.
Over-Tightening: Over-tightening the sensor, which can damage it and cause leaks.
13.5 Tips for Efficient TPMS Service
Stay Updated: Keep up with the latest TPMS technology and service procedures through training and industry resources.
Organize Parts: Keep TPMS sensors and related components organized for quick access.
Use Time-Saving Tools: Invest in efficient TPMS tools that can speed up the service process.
Communicate with Customers: Clearly communicate the TPMS issue, repair options, and associated costs to the customer.
14. Industry Insights and Statistics
14.1 Market Trends
The TPMS market has been growing due to increasing vehicle production, stringent safety regulations, and rising consumer awareness about tire safety.
Rising Adoption of TPMS: The adoption of TPMS is increasing globally, driven by government mandates and growing awareness of the safety benefits.
Technological Advancements: Advancements in TPMS technology, such as wireless sensors and integration with vehicle telematics systems, are driving market growth.
Growing Aftermarket: The TPMS aftermarket is expanding as vehicles age and require sensor replacements.
14.2 Regulatory Landscape
TPMS is mandated in many countries, including the United States, Canada, and the European Union, to improve vehicle safety.
TREAD Act in the US: The Transportation Recall Enhancement, Accountability, and Documentation (TREAD) Act requires all new vehicles to be equipped with TPMS.
European Regulations: The European Union has mandated TPMS for all new passenger vehicles since 2012.
Impact on Vehicle Safety: Studies have shown that TPMS can significantly reduce the risk of tire-related accidents by alerting drivers to low tire pressure.
14.3 TPMS Replacement Rates
TPMS sensors typically have a lifespan of 5 to 7 years, depending on usage and environmental conditions.
Battery Life: TPMS sensors are battery-powered, and the battery life is a key factor in determining replacement frequency.
Corrosion and Damage: Sensors can also fail due to corrosion, physical damage, or other environmental factors.
Replacement Frequency: The average TPMS replacement rate is around 5% to 10% per year, depending on vehicle age and usage.
14.4 Economic Impact
The TPMS market generates significant revenue for manufacturers, distributors, and service providers.
Market Size: The global TPMS market is estimated to be worth several billion dollars annually.
Job Creation: The TPMS industry supports jobs in manufacturing, sales, service, and research and development.
Economic Benefits: Proper TPMS maintenance can save consumers money by improving fuel efficiency and preventing tire damage.
14.5 Future Outlook
The TPMS market is expected to continue growing in the coming years, driven by increasing vehicle production, stricter safety regulations, and technological advancements.
Integration with ADAS: TPMS is increasingly being integrated with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to provide more comprehensive safety features.
Smart Tires: The development of smart tires with embedded sensors is expected to further enhance TPMS capabilities.
Sustainability: There is a growing focus on developing more sustainable TPMS solutions, such as recyclable sensors and energy-efficient technologies.
15. Step-by-Step Guide for DIY TPMS Sensor Replacement
15.1 Preparation
Gather Tools and Materials:
- New TPMS sensors compatible with your 2013 Tesla Model S
- TPMS diagnostic tool
- Torque wrench
- Jack and jack stands
- Lug wrench
- Valve stem tool
- Tire pressure gauge
- Gloves and safety glasses
Safety Precautions:
- Park your vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake.
- Wear safety glasses and gloves to protect your eyes and hands.
- Follow all safety guidelines when using jacks and other tools.
15.2 Removal of Old TPMS Sensor
- Loosen Lug Nuts: Use the lug wrench to loosen the lug nuts on the wheel you’re working on.
- Jack Up the Vehicle: Place the jack under the vehicle’s frame near the tire you’re removing and raise the vehicle until the tire is off the ground.
- Secure with Jack Stands: Place jack stands under the vehicle’s frame for added safety.
- Remove the Wheel: Finish unscrewing the lug nuts and carefully remove the wheel.
- Deflate the Tire: Use the valve stem tool to remove the valve core and deflate the tire completely.
- Break the Bead: Use a tire bead breaker to separate the tire from the wheel rim. If you don’t have a bead breaker, you can take the wheel to a professional tire shop.
- Remove the Tire: Carefully remove one side of the tire from the rim to access the TPMS sensor.
- Detach the TPMS Sensor: Use the valve stem tool to detach the TPMS sensor from the valve stem.
15.3 Installation of New TPMS Sensor
- Attach the New TPMS Sensor: Use the valve stem tool to attach the new TPMS sensor to the valve stem.
- Re-Mount the Tire: Carefully re-mount the tire onto the wheel rim.
- Inflate the Tire: Inflate the tire to the recommended pressure using the tire pressure gauge.
- Secure the Bead: Ensure the tire bead is properly seated on the rim. You may need to use a tire lubricant to help with this.
- Reinstall the Wheel: Place the wheel back onto the vehicle and tighten the lug nuts by hand.
- Lower the Vehicle: Remove the jack stands and lower the vehicle using the jack.
- Torque Lug Nuts: Use the torque wrench to tighten the lug nuts to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
15.4 TPMS Relearn Procedure
- Turn on the Vehicle: Turn on the vehicle and access the TPMS settings through the infotainment system.
- Initiate Relearn: Follow the on-screen prompts to initiate the TPMS relearn procedure. This may involve driving the vehicle for a certain distance or using a TPMS diagnostic tool.
- Verify Sensor Readings: Once the relearn procedure is complete, verify that the TPMS system is displaying accurate tire pressure readings for all four tires.
15.5 Final Checks
- Check for Leaks: Use a soapy water solution to check for leaks around the valve stem and tire bead.
- Test Drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure the TPMS system is functioning properly.
- Monitor Tire Pressure: Monitor the tire pressure regularly and adjust as needed to maintain optimal performance and safety.
16. Innovations in TPMS Technology
16.1 Direct TPMS (dTPMS)
Working Principle: dTPMS uses sensors mounted inside each tire to directly measure tire pressure and temperature. These sensors transmit data wirelessly to the vehicle’s ECU.
Advantages:
- Accurate, real-time monitoring of tire pressure and temperature.
- Ability to detect gradual pressure loss and rapid deflation.
- Provides specific pressure readings for each tire.
Limitations:
- Higher cost compared to iTPMS due to sensor hardware.
- Requires sensor replacement when batteries deplete (typically every 5-7 years).
- More complex installation and maintenance.
16.2 Indirect TPMS (iTPMS)
Working Principle: iTPMS relies on the vehicle’s anti-lock braking system (ABS) to indirectly monitor tire pressure. It detects changes in tire pressure by analyzing the rotational speed of each wheel.
Advantages:
- Lower cost compared to dTPMS as it doesn’t require additional sensors.
- Simpler to maintain and does not require sensor replacements.
Limitations:
- Less accurate than dTPMS as it relies on indirect measurements.
- May not detect gradual pressure loss as effectively.
- Can be affected by factors like tire wear and road conditions.
16.3 Next-Generation TPMS Features
Integration with ADAS: Next-generation TPMS systems are being integrated with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) to provide more comprehensive safety features.
Remote Monitoring: Some TPMS systems allow remote monitoring of tire pressure and temperature via smartphone apps.
Predictive Maintenance: Advanced TPMS systems can predict potential tire issues and provide alerts to drivers.
16.4 Impact on Vehicle Performance
Improved Fuel Efficiency: Proper tire inflation, as monitored by TPMS, can improve fuel efficiency by reducing rolling resistance.
Extended Tire Life: Maintaining optimal tire pressure can extend tire life and reduce the need for frequent replacements.
Enhanced Safety: TPMS helps prevent tire-related accidents by alerting drivers to low tire pressure and other tire issues.
16.5 Future Trends
Wireless Charging: Future TPMS sensors may incorporate wireless charging technology to extend battery life.
Self-Calibrating Sensors: Development of self-calibrating sensors that automatically adjust for changes in temperature and other factors.
Smart Tires: Integration of TPMS sensors directly into tires to provide more accurate and comprehensive tire data.
By exploring these technological advancements and innovative features, you can better understand the evolving landscape of TPMS technology and its impact on vehicle performance, safety, and maintenance.
17. Glossary of TPMS Terms
Understanding the common terminology associated with Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) is essential for effectively diagnosing, maintaining, and repairing these systems. Here’s a comprehensive glossary of TPMS terms:
17.1 Basic TPMS Terms
TPMS (Tire Pressure Monitoring System): An electronic system designed to monitor the air pressure inside the tires on a vehicle.
Direct TPMS (dTPMS): A TPMS that uses pressure sensors inside each tire to directly measure tire pressure and temperature.
Indirect TPMS (iTPMS): A TPMS that uses the vehicle’s anti-lock braking system (ABS) to indirectly monitor tire pressure by analyzing the rotational speed of each wheel.
ECU (Electronic Control Unit): The vehicle’s central computer that receives and processes data from the TPMS sensors.
OBD II (On-Board Diagnostics II): A standardized system used to diagnose vehicle problems, including TPMS issues.
17.2 Sensor-Related Terms
TPMS Sensor: A device installed in each tire that measures tire pressure and temperature and transmits this data to the vehicle’s ECU.
Sensor ID: A unique identifier for each TPMS sensor, used by the ECU to track and monitor individual sensors.
Sensor Frequency: The radio frequency at which the TPMS sensor communicates with the vehicle’s ECU (e.g., 433MHz).
Valve Stem: The component on the wheel through which air is added to the tire and to which the TPMS sensor is often attached.
Programmable Sensor: An aftermarket TPMS sensor that can be programmed to match the specifications of different vehicles.
17.3 Diagnostic and Service Terms
Relearn Procedure: The process of teaching the vehicle’s ECU to recognize new or replacement TPMS sensors.
TPMS Tool: A handheld device used to activate TPMS sensors, read sensor data, and perform relearn procedures.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC): A code stored in the vehicle’s ECU that indicates a problem with the TPMS or other vehicle systems.
Activation Tool: A TPMS tool used to activate sensors and read their data.
Programming Tool: A TPMS tool used to program aftermarket sensors with vehicle-specific information.
17.4 Tire-Related Terms
Tire Pressure: The amount of air pressure inside the tire, typically measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) or kilopascals (kPa).
Recommended Tire Pressure: The tire pressure recommended by the vehicle manufacturer for optimal performance and safety.
Tire Placard: A label typically located on the driver’s side doorjamb that provides information about the vehicle’s tires, including the recommended tire pressure.
17.5 Additional Terms
Aftermarket Sensor: A TPMS sensor manufactured by a company other than the original vehicle manufacturer.
Original Equipment (OE) Sensor: A TPMS sensor manufactured by the original vehicle manufacturer or an authorized supplier.
Calibration: The process of adjusting the TPMS to ensure accurate pressure readings.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL): A warning light on the dashboard that indicates a problem with the TPMS or other vehicle systems.
18. How CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Supports Automotive Technicians
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN plays a crucial role in supporting automotive technicians by providing a wealth of resources, tools, and information that enhance their knowledge, skills, and efficiency.
18.1 Access to Comprehensive Information
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides access to comprehensive technical specifications, repair procedures, and diagnostic information for a wide range of vehicles, including the 2013 Tesla Model S.
18.2 Training and Educational Resources
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers training materials, tutorials, and educational resources that help automotive technicians stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and best practices.
18.3 Diagnostic Tools and Equipment
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides detailed information and comparisons of various diagnostic tools and equipment, helping technicians select the right tools for their needs.
18.4 Troubleshooting Guides and Tips
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers troubleshooting guides and tips that help technicians diagnose and resolve complex automotive issues efficiently.
18.5 Community and Networking
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides a platform for automotive technicians to connect with peers, share knowledge, and collaborate on challenging projects.
18.6 Cost-Saving Solutions
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN helps automotive technicians find cost-effective solutions by providing information on affordable tools, parts, and repair procedures.
18.7 Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN streamlines the automotive repair process by providing quick access to essential information, reducing downtime and improving productivity.
By leveraging the resources and support offered by CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
