Veterinary Point Of Care Diagnostics are defined as diagnostic tests performed near or at the site of an animal, providing rapid results that can lead to immediate changes in the animal’s care. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is committed to providing comprehensive information on these diagnostics, enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of animal healthcare. This article explores the different types of veterinary diagnostics, their applications, and benefits, focusing on advancements in veterinary medicine and diagnostic solutions.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Veterinary Point Of Care Diagnostics
- 1.1. The Evolution Of Veterinary Poct
- 1.2. Settings For Veterinary Poct
- 2. Antigen-Based Assays In Veterinary Diagnostics
- 2.1. Lateral Flow Assays (LFA)
- 2.2. Snap Assay Technology
- 2.3. Avian Diagnostics
- 3. Antibody-Based Assays In Veterinary Medicine
- 3.1. Limitations Of Antibody Assays
- 3.2. Comparison Of Commercial Pocts
- 3.3. Applications In Livestock
- 4. Nucleic Acid-Based Assays In Veterinary Poct
- 4.1. Isothermal Amplification
- 4.2. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (Lamp)
- 4.3. Pcr-Based Poct
- 5. Poct In Wild And Exotic Animals
- 5.1. Challenges In Developing Wild Animal Pocts
- 5.2. Examples Of Wild Animal Pocts
- 6. Quality Assurance And Quality Control In Veterinary Poct
- 6.1. Woah Validation Standards
- 6.2. Asvcp Guidelines
- 7. Advantages And Disadvantages Of Veterinary Poct
- 7.1. Advantages
- 7.2. Disadvantages
- 8. Concluding Remarks And Future Directions
- 8.1. Emerging Technologies
- 8.2. Multiplex Pocts
- 9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 9.1. What Are The Main Types Of Veterinary Point Of Care Diagnostics Available?
- 9.2. How Accurate Are Point-Of-Care Tests In Veterinary Medicine?
- 9.3. What Diseases Can Be Diagnosed Using Veterinary Poct?
- 9.4. Are Veterinary Point-Of-Care Tests Affordable For Most Pet Owners?
- 9.5. How Do I Ensure The Quality Of Veterinary Poct Results?
- 9.6. Where Can I Find Reliable Veterinary Point-Of-Care Diagnostic Products?
- 9.7. What Are The Benefits Of Using Lateral Flow Assays In Veterinary Diagnostics?
- 9.8. How Is Isothermal Amplification Used In Veterinary Poct?
- 9.9. What Are The Challenges In Developing Pocts For Wild And Exotic Animals?
- 9.10. What Is The Role Of Woah In Veterinary Diagnostic Validation?
- Unlock Precision In Animal Care With CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- Ready To Enhance Your Animal Care Practices?
1. Understanding Veterinary Point Of Care Diagnostics
Veterinary point of care diagnostics refers to tests conducted close to the animal, allowing for quick results and immediate clinical decisions. This method is also known as pen-side, animal-side, or farm-side testing. Rapid veterinary diagnostics ensures timely interventions, especially crucial in managing animal health in various settings.
1.1. The Evolution Of Veterinary Poct
The concept of point-of-care testing began in human medicine in 1984 with self-monitored blood glucose tests for diabetes. According to Google Trends, the term “point-of-care test” has seen a steady increase in searches, indicating growing interest and adoption. In veterinary medicine, this has translated to significant advancements in rapid diagnostic solutions for various animal diseases.
1.2. Settings For Veterinary Poct
Point-of-care testing can occur in various locations. In human medicine, this includes patient homes, clinics, emergency care facilities, and public places like airports. For animals, testing may take place on farms, in veterinary hospitals, or at a veterinarian’s office. These settings require efficient and reliable animal health monitoring tools to ensure accurate and timely diagnoses.
2. Antigen-Based Assays In Veterinary Diagnostics
Antigen-based assays are immunoassays used to test for animal diseases and monitor animal health. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) are widely used due to their ease of development, use, and validation, making them a key component of veterinary rapid diagnostics.
2.1. Lateral Flow Assays (LFA)
Lateral flow assays are popular in veterinary point of care diagnostics because they are easy to use and provide quick results. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the lateral flow assay market is expected to grow significantly due to its simplicity and scalability. Lateral flow assays are used to detect various pathogens and conditions in animals.
- Advantages Of LFA: Easy to manufacture, scalable, simple to use, and results are easy to read.
- Applications In Veterinary Medicine: Detecting canine parvovirus, Ehrlichia, Giardia, Lyme disease, feline leukemia, Cryptococcus, and feline immunodeficiency.
2.2. Snap Assay Technology
SNAP assays are in-clinic devices performing ELISA steps in a timed, sequential manner with minimal user interaction. IDEXX Laboratories Inc. developed this technology, which is widely used for detecting heartworm antigens and other infectious diseases.
2.3. Avian Diagnostics
Several antigen-based tests are available for detecting influenza A virus in chickens, ducks, turkeys, and geese. These tests, often adapted from human applications, include FluDirect Avian (Zoetis) and Sofia Influenza A+B (Quidel Corporation, CA). These veterinary diagnostics are essential for controlling avian diseases and maintaining flock health.
3. Antibody-Based Assays In Veterinary Medicine
Antibody-based assays detect antibodies against pathogens causing animal diseases and are used for both disease surveillance and diagnosis. Commercial kits are available for in-clinic testing, aiding in rapid veterinary diagnostics.
3.1. Limitations Of Antibody Assays
A significant limitation of antibody-based tests is their inability to differentiate between responses to vaccination and natural exposure. However, some assays, like the FIV antibody POCT “Witness” by Zoetis, can distinguish between these responses, offering more precise diagnostic information.
3.2. Comparison Of Commercial Pocts
Bergmann et al. (2020) compared four commercial POCTs for detecting canine parvovirus (CPV) antibodies, including ImmunoComb Canine VacciCheck ELISA (Biogal Galed Labs) and TiterCHEK CDV/CPV ELISA (Zoetis). The study found all four POCTs reliable, with FASTest showing the highest sensitivity and CanTiCheck the highest specificity.
3.3. Applications In Livestock
In cattle, milk tests for Brucella antibodies have been developed using chemiluminescence immunosensors. These tests, more sensitive than conventional ELISA, use silane-benzophenone as a coupling agent with killed Brucella to detect anti-Brucella IgG antibodies. This technology improves animal health monitoring in livestock.
4. Nucleic Acid-Based Assays In Veterinary Poct
Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) are used as POCTs in both small and large animal diagnostics. Manufacturers like Fluxergy LLC (Irvine, CA) and Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA) offer commercial tests.
4.1. Isothermal Amplification
Isothermal amplification is an ideal technique for POCT because it occurs at a constant temperature, simplifying the instrumentation. This process significantly reduces test run times compared to conventional PCR. Examples include helicase-dependent amplification (HDA) and recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA).
4.2. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (Lamp)
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification is a commonly used platform in POCT. Gunther et al. (2018) compared two reaction mixes for detecting feline coronavirus (FCoV), finding both reliable as POCTs but less sensitive than RT-PCR.
4.3. Pcr-Based Poct
Fluxergy developed a PCR-based POCT for detecting Streptococcus equi subspecies equi. Compared to RT-PCR, this POCT had 89% sensitivity and 100% specificity. This technology offers a reliable method for rapid diagnostics in equine health.
5. Poct In Wild And Exotic Animals
There is a growing need for POCTs to detect pathogens in wild and exotic animals for early disease diagnosis. According to the World Health Organization, about 75% of emerging infectious diseases are zoonotic, highlighting the importance of wildlife disease monitoring.
5.1. Challenges In Developing Wild Animal Pocts
Developing and validating POCTs for wild animals faces several challenges, including:
- Lack of information on wildlife physiology and pathogen behavior.
- Regulatory and logistic considerations for specimen collection.
- Incomplete data on sampled animals or species.
- Sampling difficulties.
5.2. Examples Of Wild Animal Pocts
Tomaszewicz Brown et al. (2020) developed a quantitative RT-PCR assay for detecting canine distemper virus (CDV) from wildlife using a handheld platform. Additionally, Veerasami et al. (2018) created a point-of-care tuberculosis diagnostic kit for detecting antibodies in wild animals.
6. Quality Assurance And Quality Control In Veterinary Poct
The rapid influx of POCT devices and methods requires stringent quality control measures. These tests are not always held to the same standards as regular laboratory diagnostics, leading to concerns about result accuracy.
6.1. Woah Validation Standards
The World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH) provides official validation and certification for animal diagnostic tests, including POCT. However, registration is not mandatory in most countries, affecting the quality and reliability of available tests.
6.2. Asvcp Guidelines
The American Society for Veterinary Clinical Pathology (ASVCP) developed quality assurance guidelines for veterinary POCT in 2013. These guidelines emphasize a formalized approach to POCT, written policies, operator training, and accurate reporting of results.
7. Advantages And Disadvantages Of Veterinary Poct
Veterinary POCT offers several benefits but also presents certain drawbacks. Understanding these aspects is crucial for effective implementation.
7.1. Advantages
- Convenience: Tests can be performed at the pen-side, beneficial for rural farmers with limited access to veterinary services.
- Faster Turnaround Time: Enables quick, evidence-based decisions on treatment and disease management.
- Early Detection: Helps mitigate and minimize negative outcomes.
- Ease Of Use: Most POCTs are user-friendly, requiring minimal training.
7.2. Disadvantages
- Poor Quality Control: Includes insufficient validation, lack of controls, and low-throughput designs.
- Affordability: Cost-effectiveness is a significant factor, especially in food animal disease diagnosis.
- Complexity: Lack of simplicity and portability can deter widespread acceptance.
8. Concluding Remarks And Future Directions
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the development of POCT technologies. Miniaturized isothermal amplification tests, lateral flow assays, and nanoparticle-based assays have become more accessible, reflecting advancements in veterinary rapid diagnostics.
8.1. Emerging Technologies
Advanced technologies such as high-performing biosensors, CRISPR/Cas technology, and paper fluidic devices are increasingly used in animal disease diagnostics. Smartphone-based POCTs are also gaining traction, supported by growing research in this area.
8.2. Multiplex Pocts
Multiplex POCTs, which diagnose diseases using a syndromic approach, offer a cost-effective and rapid method for therapeutic and control decisions. Combining multiplexing with artificial intelligence and machine learning can create more powerful and sophisticated POCT platforms for animal and human disease diagnostics.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
9.1. What Are The Main Types Of Veterinary Point Of Care Diagnostics Available?
Veterinary point of care diagnostics include antigen-based assays, antibody-based assays, and nucleic acid-based assays.
9.2. How Accurate Are Point-Of-Care Tests In Veterinary Medicine?
The accuracy of point-of-care tests varies. Nucleic acid-based tests generally have high sensitivity and specificity, while antigen and antibody-based tests may have lower accuracy but are easier to use.
9.3. What Diseases Can Be Diagnosed Using Veterinary Poct?
Veterinary POCT can diagnose a wide range of diseases, including canine parvovirus, feline leukemia, avian influenza, and bovine viral diarrhea.
9.4. Are Veterinary Point-Of-Care Tests Affordable For Most Pet Owners?
The affordability of veterinary point-of-care tests depends on the specific test and the region. Some tests may be more cost-effective than traditional laboratory tests, while others may be more expensive.
9.5. How Do I Ensure The Quality Of Veterinary Poct Results?
To ensure the quality of veterinary POCT results, follow established quality assurance guidelines, use written policies, train operators, and ensure accurate reporting of results.
9.6. Where Can I Find Reliable Veterinary Point-Of-Care Diagnostic Products?
Reliable veterinary point-of-care diagnostic products can be found through reputable manufacturers and distributors. Check the WOAH registry for validated diagnostic kits.
9.7. What Are The Benefits Of Using Lateral Flow Assays In Veterinary Diagnostics?
Lateral flow assays are easy to manufacture, scalable, simple to use, and provide easy-to-read results, making them suitable for various environments and applications.
9.8. How Is Isothermal Amplification Used In Veterinary Poct?
Isothermal amplification is used in veterinary POCT because it occurs at a constant temperature, simplifying the instrumentation and reducing test run times compared to conventional PCR.
9.9. What Are The Challenges In Developing Pocts For Wild And Exotic Animals?
Challenges include lack of information on wildlife physiology, regulatory considerations, incomplete data on sampled animals, and sampling difficulties.
9.10. What Is The Role Of Woah In Veterinary Diagnostic Validation?
The World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH) provides official validation and certification for animal diagnostic tests, ensuring quality and reliability.
Unlock Precision In Animal Care With CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
Are you seeking reliable and detailed information on veterinary point of care diagnostics? At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer comprehensive resources to help you make informed decisions about animal health. Whether you’re a veterinarian, a farm owner, or a pet enthusiast, our website provides the insights you need.
Ready To Enhance Your Animal Care Practices?
Don’t navigate the complexities of veterinary diagnostics alone. Contact us today for expert guidance and personalized advice on selecting the right diagnostic tools for your needs. Reach out via:
- Address: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States.
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880.
- Website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
Let CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in ensuring the health and well-being of your animals. Contact us now and discover how we can help you achieve excellence in animal care.
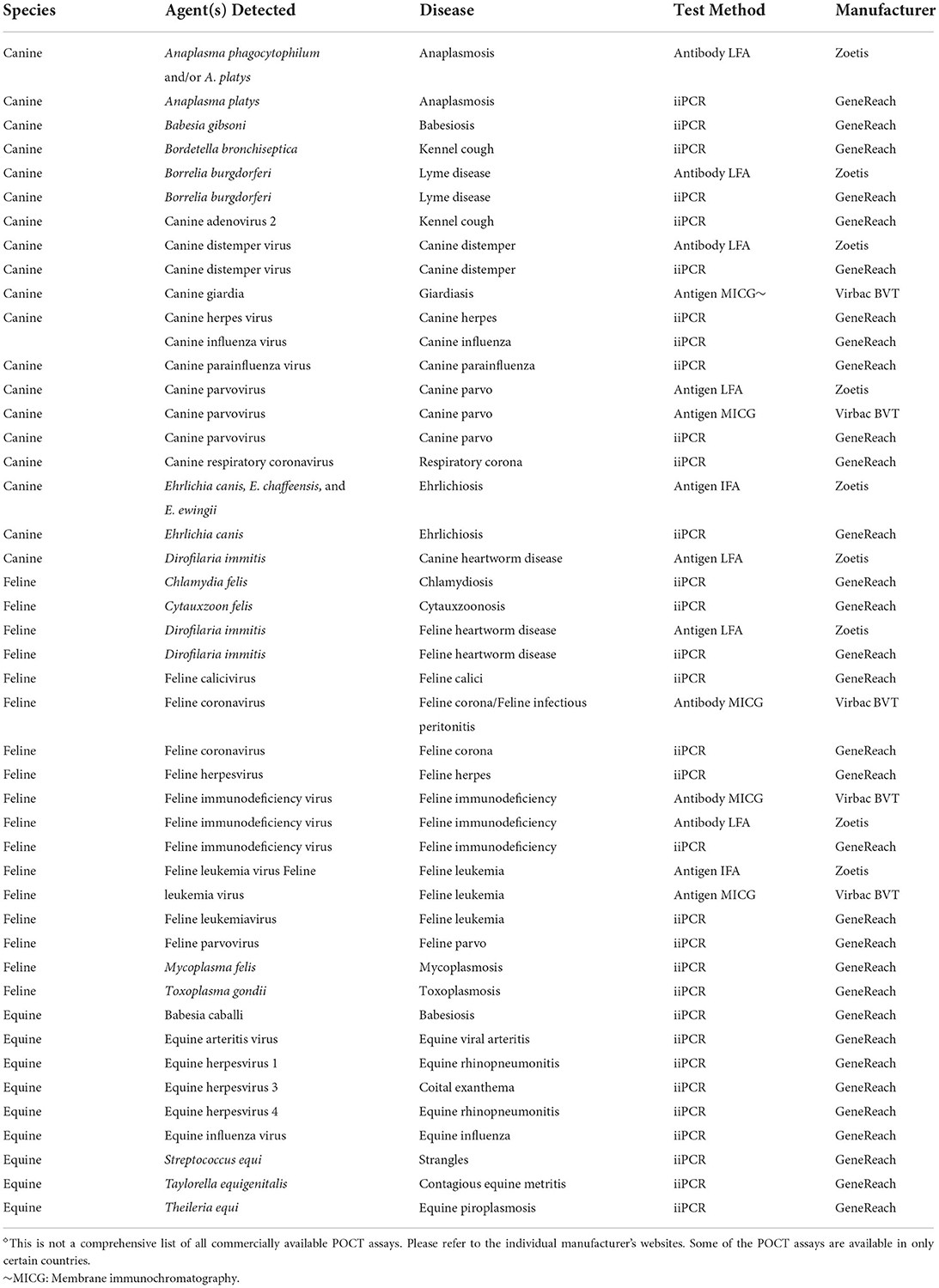 Veterinary Point of Care Diagnostics
Veterinary Point of Care Diagnostics
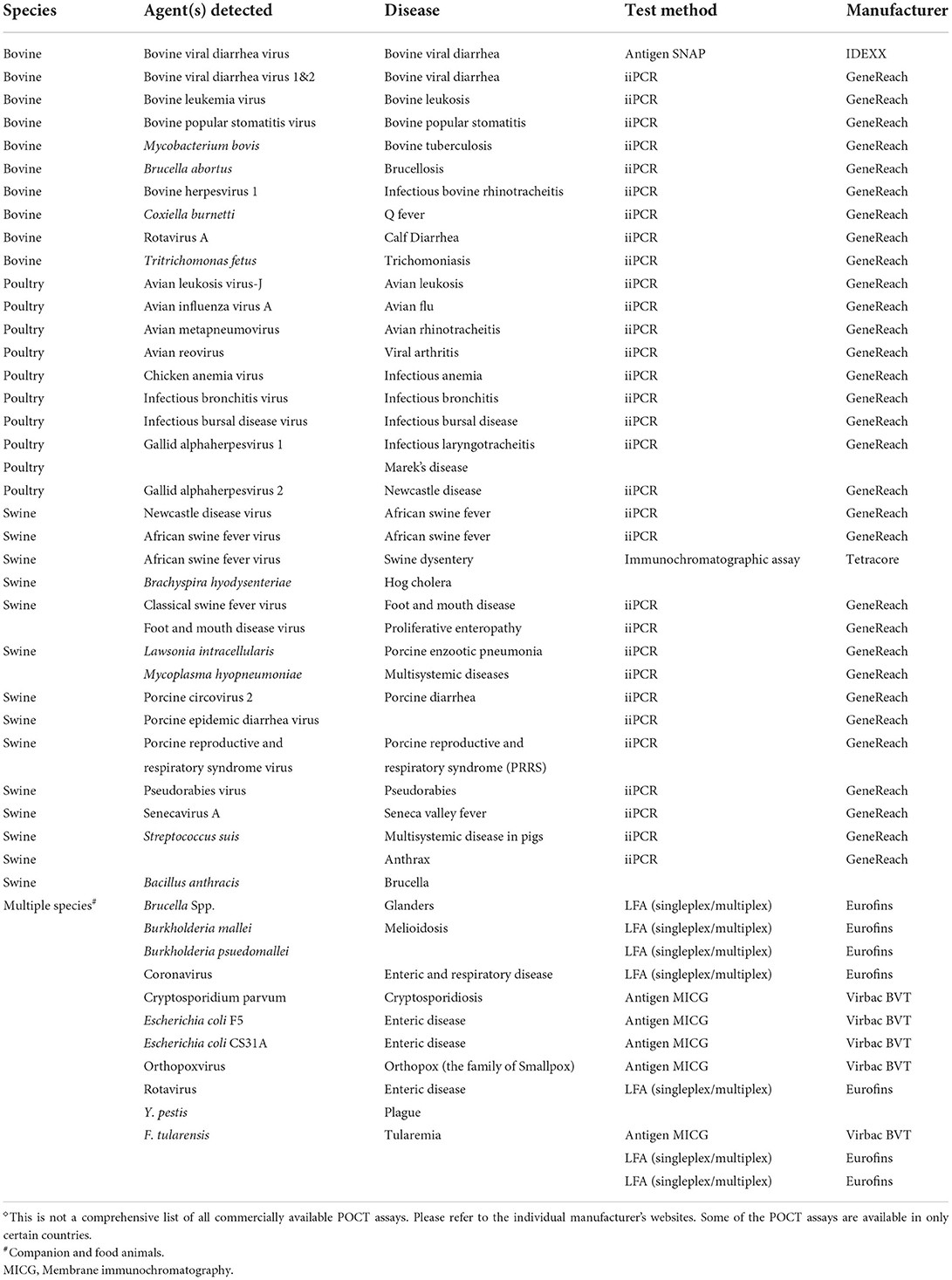 Companion Animal Diagnostics
Companion Animal Diagnostics