The P0420 Car Diagnostic Code P0420 signifies a catalyst system efficiency below threshold (Bank 1). Addressing this issue promptly is important for maintaining optimal engine performance, reducing emissions, and preventing potential damage. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides expert insights and solutions to help you navigate this diagnostic code effectively, ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently. Explore comprehensive guides, troubleshooting tips, and recommended tools for resolving P0420, alongside related issues like oxygen sensor malfunction, exhaust system leaks, and catalytic converter health.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the P0420 Code: What Does It Really Mean?
- 1.1 The Role of the Catalytic Converter in Reducing Emissions
- 1.2 Common Symptoms Associated with the P0420 Code
- 1.3 The Impact of a Faulty Catalytic Converter on Vehicle Performance
- 2. Diagnosing the P0420 Code: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 2.1 Performing a Visual Inspection of the Exhaust System
- 2.2 Using an OBD-II Scanner to Retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes
- 2.3 Testing the Oxygen Sensors: Upstream vs. Downstream
- 2.4 Checking for Exhaust Leaks: A Common Culprit
- 2.5 Evaluating Fuel Trim Data: Identifying Fuel Mixture Issues
- 3. Common Causes of the P0420 Code: Unveiling the Root Problem
- 3.1 Catalytic Converter Failure: The Primary Suspect
- 3.2 Oxygen Sensor Issues: Faulty Readings and Malfunctions
- 3.3 Exhaust Leaks: Disrupting the Exhaust Flow
- 3.4 Fuel System Problems: Affecting the Air-Fuel Mixture
- 3.5 Engine Misfires: Sending Unburned Fuel to the Catalytic Converter
- 4. Repairing the P0420 Code: DIY Solutions and Professional Assistance
- 4.1 Replacing the Catalytic Converter: A Major Repair
- 4.2 Replacing Oxygen Sensors: A Simpler Task
- 4.3 Repairing Exhaust Leaks: Welding or Replacing Components
- 4.4 Addressing Fuel System Problems: Cleaning or Replacing Injectors
- 4.5 Clearing the P0420 Code: Using an OBD-II Scanner
- 5. Preventing the P0420 Code: Proactive Maintenance Tips
- 5.1 Regular Vehicle Maintenance: Keeping Your Car in Top Shape
- 5.2 Using High-Quality Fuel: Avoiding Contaminants
- 5.3 Avoiding Short Trips: Allowing the Catalytic Converter to Warm Up
- 5.4 Addressing Engine Misfires Promptly: Preventing Damage
- 5.5 Inspecting the Exhaust System Regularly: Catching Leaks Early
- 6. Vehicle-Specific Considerations: P0420 Code Across Different Brands
- 6.1 Honda: Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
- 6.2 Toyota: Addressing Catalyst Monitor Misinterpretations
- 6.3 Chevy: Identifying Potential Causes and Solutions
- 6.4 Nissan: Specific Recommendations for Diagnosis and Repair
- 7. The Cost of Fixing the P0420 Code: Budgeting for Repairs
- 7.1 Catalytic Converter Replacement: A Major Expense
- 7.2 Oxygen Sensor Replacement: A More Affordable Option
- 7.3 Exhaust Leak Repairs: Variable Costs
- 7.4 DIY vs. Professional Repair: Weighing the Options
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): P0420 Code Demystified
- 8.1 What does the P0420 code specifically indicate?
- 8.2 Is it safe to drive a car with the P0420 code triggered?
- 8.3 What are the most frequent reasons for the P0420 code to appear?
- 8.4 How can I accurately diagnose the P0420 code?
- 8.5 What is the typical cost range to fix a P0420 code issue?
- 8.6 Can a malfunctioning O2 sensor cause the P0420 code to appear?
- 8.7 What actions can be taken to prevent the P0420 code from occurring?
- 8.8 Why does the P0420 code persist even after replacing the catalytic converter?
- 8.9 How long does it generally take for the P0420 code to reset after repairs?
- 8.10 Is it possible for low-quality fuel to be a cause of the P0420 code?
- 9. Conclusion: Empowering You to Resolve the P0420 Code
1. Understanding the P0420 Code: What Does It Really Mean?
The P0420 code means that your vehicle’s computer has detected that the catalytic converter isn’t working as efficiently as it should. This indicates a potential issue with the emissions system, affecting performance and potentially increasing harmful emissions. Understanding the underlying causes and symptoms associated with the P0420 code is the first step in effectively diagnosing and resolving the problem. The P0420 code signals that the catalytic converter’s efficiency has dropped below the acceptable threshold set by the vehicle’s manufacturer.
1.1 The Role of the Catalytic Converter in Reducing Emissions
The catalytic converter plays a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions from your vehicle’s exhaust. It uses catalysts like platinum, palladium, and rhodium to convert pollutants such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen. According to the EPA, a properly functioning catalytic converter can reduce emissions by up to 90%. When the catalytic converter’s efficiency drops, it cannot effectively neutralize these pollutants, leading to increased emissions and potential environmental damage.
1.2 Common Symptoms Associated with the P0420 Code
Several symptoms may indicate the presence of a P0420 code. These can include a decrease in fuel efficiency, a noticeable loss of engine power, a rattling sound coming from underneath the vehicle, and the illumination of the check engine light on the dashboard. In some cases, you may also notice a sulfur-like smell emanating from the exhaust. While these symptoms may not always be directly linked to the P0420 code, they warrant further investigation to determine the underlying cause.
- Decreased fuel efficiency: A failing catalytic converter can affect the engine’s air-fuel mixture, leading to reduced fuel economy.
- Loss of engine power: A clogged or inefficient catalytic converter can restrict exhaust flow, hindering engine performance.
- Rattling sound: Internal damage to the catalytic converter can cause loose components to rattle.
- Check engine light: The most obvious symptom, indicating a detected issue in the emissions system.
- Sulfur smell: A malfunctioning catalytic converter may not be able to convert sulfur compounds in the exhaust, resulting in a distinct odor.
1.3 The Impact of a Faulty Catalytic Converter on Vehicle Performance
A faulty catalytic converter can have a significant impact on your vehicle’s performance, leading to reduced power, poor fuel economy, and potential engine damage. When the catalytic converter is not functioning correctly, it can create back pressure in the exhaust system, hindering the engine’s ability to expel exhaust gases efficiently. This can result in decreased horsepower and torque, making it harder to accelerate and maintain speed. Additionally, a malfunctioning catalytic converter can cause the engine to run hotter, potentially leading to overheating and damage to other components.
2. Diagnosing the P0420 Code: A Step-by-Step Guide
Diagnosing the P0420 code requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause of the issue. It involves a combination of visual inspections, diagnostic tests, and careful analysis of the data obtained. By following a step-by-step guide, you can effectively pinpoint the source of the problem and take appropriate action to resolve it.
2.1 Performing a Visual Inspection of the Exhaust System
Start by performing a visual inspection of the entire exhaust system, from the exhaust manifold to the tailpipe. Look for any signs of damage, such as cracks, holes, or corrosion. Pay close attention to the catalytic converter, checking for any physical damage or discoloration. Inspect the exhaust pipes and connections for leaks, which can disrupt the flow of exhaust gases and affect the catalytic converter’s performance.
- Check the exhaust manifold for cracks or leaks.
- Inspect the exhaust pipes for rust, corrosion, or holes.
- Examine the catalytic converter for physical damage or discoloration.
- Ensure all connections are secure and free from leaks.
2.2 Using an OBD-II Scanner to Retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes
An OBD-II scanner is an invaluable tool for diagnosing the P0420 code. Connect the scanner to your vehicle’s diagnostic port and retrieve any stored trouble codes. In addition to the P0420 code, look for any other codes that may provide clues about the underlying issue. Pay attention to codes related to the oxygen sensors, fuel system, or engine misfires, as these can all contribute to catalytic converter inefficiency. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), using an OBD-II scanner can reduce diagnostic time by up to 50%.
2.3 Testing the Oxygen Sensors: Upstream vs. Downstream
The oxygen sensors play a crucial role in monitoring the catalytic converter’s performance. There are typically two oxygen sensors: an upstream sensor located before the catalytic converter and a downstream sensor located after the converter. The upstream sensor measures the oxygen content of the exhaust gases entering the converter, while the downstream sensor measures the oxygen content of the exhaust gases exiting the converter. By comparing the signals from the two sensors, the vehicle’s computer can determine the catalytic converter’s efficiency. Use an OBD-II scanner to monitor the live data from the oxygen sensors. The upstream sensor should fluctuate rapidly, while the downstream sensor should maintain a relatively steady voltage. If the downstream sensor is fluctuating similarly to the upstream sensor, it may indicate that the catalytic converter is not functioning correctly.
| Sensor | Location | Function | Expected Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upstream O2 | Before Converter | Measures oxygen content entering the catalytic converter | Fluctuates rapidly |
| Downstream O2 | After Converter | Measures oxygen content exiting the catalytic converter | Relatively steady voltage |
2.4 Checking for Exhaust Leaks: A Common Culprit
Exhaust leaks can significantly impact the catalytic converter’s performance, leading to inaccurate readings and the triggering of the P0420 code. Leaks before the catalytic converter can allow extra air into the exhaust stream, diluting the exhaust gases and reducing the converter’s efficiency. Leaks after the catalytic converter can cause the downstream oxygen sensor to misread the oxygen content, leading to false readings. To check for exhaust leaks, start by visually inspecting the exhaust system for any signs of damage or corrosion. You can also use a stethoscope or a piece of hose to listen for leaks while the engine is running. Another method is to use a smoke machine to introduce smoke into the exhaust system and identify any areas where smoke is escaping.
2.5 Evaluating Fuel Trim Data: Identifying Fuel Mixture Issues
Fuel trim refers to the adjustments the vehicle’s computer makes to the air-fuel mixture to maintain optimal engine performance. Long-term fuel trim (LTFT) values indicate the average adjustments over a longer period, while short-term fuel trim (STFT) values reflect the immediate adjustments. By analyzing the fuel trim data, you can identify potential fuel mixture issues that may be contributing to the P0420 code. High positive fuel trim values (above +10%) indicate that the engine is running lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel. High negative fuel trim values (below -10%) indicate that the engine is running rich, meaning there is too much fuel and not enough air. Lean or rich conditions can affect the catalytic converter’s efficiency and trigger the P0420 code.
3. Common Causes of the P0420 Code: Unveiling the Root Problem
The P0420 code can be triggered by various factors, ranging from a faulty catalytic converter to issues with the oxygen sensors or fuel system. Understanding the common causes of the P0420 code is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective repair.
3.1 Catalytic Converter Failure: The Primary Suspect
The most common cause of the P0420 code is a failing catalytic converter. Over time, the catalytic converter can become clogged or damaged, reducing its ability to effectively convert harmful emissions. Factors that can contribute to catalytic converter failure include:
- Age and wear: Catalytic converters have a limited lifespan and will eventually degrade over time.
- Contamination: Exposure to contaminants like oil, coolant, or fuel can damage the catalytic converter.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can cause the catalytic converter to melt or break down.
- Physical damage: Impacts from road debris or accidents can damage the catalytic converter.
3.2 Oxygen Sensor Issues: Faulty Readings and Malfunctions
Faulty oxygen sensors can also trigger the P0420 code. As mentioned earlier, the oxygen sensors monitor the oxygen content of the exhaust gases and provide feedback to the vehicle’s computer. If the oxygen sensors are not functioning correctly, they can provide inaccurate data, leading to incorrect fuel trim adjustments and reduced catalytic converter efficiency. Oxygen sensors can fail due to:
- Contamination: Exposure to oil, coolant, or fuel can contaminate the oxygen sensors.
- Wear and tear: Oxygen sensors can degrade over time due to exposure to high temperatures and harsh exhaust gases.
- Electrical issues: Faulty wiring or connectors can cause oxygen sensor malfunctions.
3.3 Exhaust Leaks: Disrupting the Exhaust Flow
Exhaust leaks can disrupt the flow of exhaust gases and affect the catalytic converter’s performance, leading to the P0420 code. Leaks before the catalytic converter can introduce extra air into the exhaust stream, diluting the exhaust gases and reducing the converter’s efficiency. Leaks after the catalytic converter can cause the downstream oxygen sensor to misread the oxygen content, leading to false readings. Common causes of exhaust leaks include:
- Corrosion: Rust and corrosion can weaken exhaust pipes and connections, leading to leaks.
- Damage: Impacts from road debris or accidents can damage the exhaust system.
- Loose connections: Loose or damaged clamps and gaskets can cause exhaust leaks.
3.4 Fuel System Problems: Affecting the Air-Fuel Mixture
Fuel system problems can affect the air-fuel mixture, leading to catalytic converter inefficiency and the P0420 code. A rich or lean fuel mixture can overload the catalytic converter, reducing its ability to effectively convert harmful emissions. Common fuel system problems include:
- Faulty fuel injectors: Leaking or clogged fuel injectors can disrupt the air-fuel mixture.
- Fuel pressure issues: Low or high fuel pressure can affect the amount of fuel delivered to the engine.
- Vacuum leaks: Vacuum leaks can introduce extra air into the engine, leading to a lean fuel mixture.
3.5 Engine Misfires: Sending Unburned Fuel to the Catalytic Converter
Engine misfires can send unburned fuel to the catalytic converter, causing it to overheat and potentially damage it. Misfires occur when one or more of the engine’s cylinders fail to fire properly, resulting in incomplete combustion. Common causes of engine misfires include:
- Faulty spark plugs: Worn or damaged spark plugs can prevent proper ignition.
- Ignition coil problems: Faulty ignition coils can prevent the spark plugs from firing.
- Vacuum leaks: Vacuum leaks can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to misfires.
- Compression issues: Low compression can prevent proper combustion.
4. Repairing the P0420 Code: DIY Solutions and Professional Assistance
Once you have diagnosed the cause of the P0420 code, you can begin the repair process. Depending on the complexity of the issue and your mechanical skills, you may be able to perform some repairs yourself. However, in some cases, it is best to seek professional assistance from a qualified mechanic.
4.1 Replacing the Catalytic Converter: A Major Repair
If the catalytic converter is the primary cause of the P0420 code, replacement is often the only solution. Replacing a catalytic converter can be a relatively complex repair, requiring specialized tools and knowledge. Here are the general steps involved:
- Disconnect the battery: Disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent electrical shorts.
- Loosen the connections: Loosen the bolts or clamps connecting the catalytic converter to the exhaust system.
- Remove the old converter: Carefully remove the old catalytic converter.
- Install the new converter: Install the new catalytic converter, ensuring proper alignment and secure connections.
- Reconnect the battery: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
It is important to use a high-quality catalytic converter that meets or exceeds the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications. Using a cheap or substandard catalytic converter can result in poor performance and premature failure.
4.2 Replacing Oxygen Sensors: A Simpler Task
Replacing faulty oxygen sensors is a relatively straightforward repair that can often be performed by DIY mechanics. Here are the general steps involved:
- Disconnect the battery: Disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent electrical shorts.
- Locate the sensors: Locate the oxygen sensors that need to be replaced.
- Disconnect the electrical connectors: Disconnect the electrical connectors from the oxygen sensors.
- Remove the old sensors: Use an oxygen sensor socket to remove the old sensors.
- Install the new sensors: Install the new oxygen sensors, ensuring proper torque.
- Reconnect the electrical connectors: Reconnect the electrical connectors to the oxygen sensors.
- Reconnect the battery: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
When replacing oxygen sensors, it is important to use the correct type of sensor for your vehicle. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual or consult with a qualified mechanic to ensure you are using the correct sensor.
4.3 Repairing Exhaust Leaks: Welding or Replacing Components
Repairing exhaust leaks can involve welding or replacing damaged components. Small leaks can often be repaired by welding the affected area. Larger leaks or significant damage may require replacing the entire exhaust pipe or component. Here are the general steps involved in repairing exhaust leaks:
- Locate the leak: Identify the source of the exhaust leak.
- Clean the area: Clean the area around the leak with a wire brush.
- Weld the leak: If the leak is small enough, weld the area to seal it.
- Replace the component: If the leak is too large or the component is damaged, replace it.
- Secure the connections: Ensure all connections are secure and free from leaks.
Welding exhaust leaks requires specialized equipment and skills. If you are not comfortable welding, it is best to seek professional assistance.
4.4 Addressing Fuel System Problems: Cleaning or Replacing Injectors
Addressing fuel system problems may involve cleaning or replacing fuel injectors, repairing vacuum leaks, or addressing fuel pressure issues. Cleaning fuel injectors can often be done using a fuel injector cleaner additive. In some cases, it may be necessary to remove the fuel injectors and clean them manually. Replacing fuel injectors is a more complex repair that requires specialized tools and knowledge. Here are some general steps involved in addressing fuel system problems:
- Clean fuel injectors: Use a fuel injector cleaner additive or clean the injectors manually.
- Repair vacuum leaks: Locate and repair any vacuum leaks in the engine.
- Check fuel pressure: Check the fuel pressure to ensure it is within the proper range.
4.5 Clearing the P0420 Code: Using an OBD-II Scanner
After performing the necessary repairs, you will need to clear the P0420 code using an OBD-II scanner. Connect the scanner to your vehicle’s diagnostic port and select the option to clear the trouble codes. This will reset the vehicle’s computer and turn off the check engine light.
Important Note: Clearing the P0420 code does not guarantee that the problem is resolved. The code may reappear if the underlying issue is not properly addressed. It is important to monitor your vehicle’s performance and check for any recurring symptoms.
5. Preventing the P0420 Code: Proactive Maintenance Tips
Preventing the P0420 code is always better than dealing with the hassle and expense of repairs. By following a few proactive maintenance tips, you can significantly reduce the risk of encountering this issue.
5.1 Regular Vehicle Maintenance: Keeping Your Car in Top Shape
Regular vehicle maintenance is the foundation of preventing the P0420 code. This includes:
- Oil changes: Regular oil changes help to prevent oil contamination, which can damage the catalytic converter.
- Tune-ups: Regular tune-ups ensure that the engine is running efficiently, reducing the risk of misfires and other issues that can affect the catalytic converter.
- Air filter replacement: Replacing the air filter regularly ensures that the engine is receiving clean air, which can improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
5.2 Using High-Quality Fuel: Avoiding Contaminants
Using high-quality fuel can help to prevent contaminants from entering the fuel system, which can damage the catalytic converter and other components. Avoid using low-quality or adulterated fuel, as it may contain harmful additives that can damage your vehicle. According to a study by AAA, using top-tier gasoline can improve fuel economy and reduce engine deposits.
5.3 Avoiding Short Trips: Allowing the Catalytic Converter to Warm Up
Short trips can prevent the catalytic converter from reaching its optimal operating temperature, reducing its efficiency and potentially leading to premature failure. When the catalytic converter is cold, it cannot effectively convert harmful emissions. Try to combine short trips into longer ones whenever possible to allow the catalytic converter to warm up properly.
5.4 Addressing Engine Misfires Promptly: Preventing Damage
Addressing engine misfires promptly can prevent unburned fuel from entering the catalytic converter, which can cause it to overheat and potentially damage it. If you notice any signs of engine misfires, such as rough idling or loss of power, have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic as soon as possible.
5.5 Inspecting the Exhaust System Regularly: Catching Leaks Early
Inspecting the exhaust system regularly can help you catch exhaust leaks early, before they cause significant damage. Look for any signs of damage, such as cracks, holes, or corrosion. Listen for any unusual noises coming from the exhaust system. If you suspect an exhaust leak, have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic.
6. Vehicle-Specific Considerations: P0420 Code Across Different Brands
While the P0420 code is a generic code, certain vehicle brands and models may be more prone to this issue than others. Understanding the specific considerations for your vehicle can help you diagnose and repair the P0420 code more effectively.
6.1 Honda: Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Some Honda models are known to experience P0420 codes due to issues with the oxygen sensors or catalytic converters. Common troubleshooting tips for Hondas include:
- Checking the oxygen sensors for proper function.
- Inspecting the catalytic converter for damage or clogging.
- Ensuring that the engine is properly tuned.
6.2 Toyota: Addressing Catalyst Monitor Misinterpretations
Certain Toyota models are known to trigger P0420 when the catalyst monitor is running its tests, and the ECM misinterprets the results. This can often be resolved by:
- Updating the ECM software.
- Replacing the catalytic converter.
- Ensuring that the oxygen sensors are functioning properly.
6.3 Chevy: Identifying Potential Causes and Solutions
Chevy vehicles can experience P0420 codes due to various factors, including:
- Faulty catalytic converters.
- Oxygen sensor issues.
- Exhaust leaks.
- Fuel system problems.
6.4 Nissan: Specific Recommendations for Diagnosis and Repair
Nissan vehicles may experience P0420 codes due to issues with the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, or exhaust system. Specific recommendations for diagnosis and repair include:
- Using a Nissan-specific scan tool to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes.
- Inspecting the exhaust system for leaks or damage.
- Testing the oxygen sensors for proper function.
By understanding the vehicle-specific considerations for your brand and model, you can more effectively diagnose and repair the P0420 code.
7. The Cost of Fixing the P0420 Code: Budgeting for Repairs
The cost of fixing the P0420 code can vary widely depending on the cause of the issue and the extent of the repairs required. It is important to budget accordingly and consider the potential costs involved.
7.1 Catalytic Converter Replacement: A Major Expense
Replacing the catalytic converter is often the most expensive part of repairing the P0420 code. The cost of a new catalytic converter can range from $500 to $2000 or more, depending on the vehicle brand, model, and the type of converter required. Labor costs for replacing the catalytic converter can add an additional $100 to $500.
7.2 Oxygen Sensor Replacement: A More Affordable Option
Replacing oxygen sensors is a more affordable option than replacing the catalytic converter. The cost of a new oxygen sensor can range from $50 to $200, depending on the vehicle brand, model, and the type of sensor required. Labor costs for replacing oxygen sensors can add an additional $50 to $200.
7.3 Exhaust Leak Repairs: Variable Costs
The cost of repairing exhaust leaks can vary depending on the location and severity of the leak. Small leaks can often be repaired by welding, which can cost $50 to $200. Larger leaks or significant damage may require replacing the entire exhaust pipe or component, which can cost $100 to $500 or more.
7.4 DIY vs. Professional Repair: Weighing the Options
When considering the cost of fixing the P0420 code, it is important to weigh the options of DIY repair versus professional repair. DIY repair can save you money on labor costs, but it requires specialized tools and knowledge. Professional repair can be more expensive, but it ensures that the repairs are done correctly and come with a warranty.
According to a survey by Consumer Reports, DIY car repairs can save you an average of $300 per year. However, it is important to be honest about your mechanical skills and abilities before attempting any DIY repairs. If you are not comfortable performing the repairs yourself, it is best to seek professional assistance.
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wide range of tools and resources to help you diagnose and repair the P0420 code, whether you are a DIY mechanic or a professional technician. Visit our website today to learn more about our products and services. For personalized advice and assistance, contact us at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Our team of experts is ready to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): P0420 Code Demystified
Here are some frequently asked questions about the P0420 code:
8.1 What does the P0420 code specifically indicate?
The P0420 code specifically indicates that the catalytic converter’s efficiency is below the threshold for the specific bank of the engine it monitors. This means the converter isn’t effectively reducing harmful emissions as required. The catalyst system efficiency is below threshold (Bank 1).
8.2 Is it safe to drive a car with the P0420 code triggered?
Driving with a P0420 code is technically possible but not recommended for an extended period. It can lead to reduced fuel efficiency, higher emissions, and potential damage to the engine or catalytic converter.
8.3 What are the most frequent reasons for the P0420 code to appear?
The most frequent reasons include a malfunctioning catalytic converter, faulty oxygen sensors, exhaust leaks, fuel injector issues, or problems with the engine’s air-fuel mixture.
8.4 How can I accurately diagnose the P0420 code?
To diagnose accurately, start by checking for other codes. Inspect the exhaust system for leaks, test the oxygen sensors, and ensure the engine runs efficiently. Advanced diagnostics may require tools like an OBD-II scanner or a back-pressure tester.
8.5 What is the typical cost range to fix a P0420 code issue?
The cost varies widely, from affordable oxygen sensor replacements to expensive catalytic converter replacements. The total depends on the root cause and the extent of the repair needed.
8.6 Can a malfunctioning O2 sensor cause the P0420 code to appear?
Yes, a faulty oxygen sensor can trigger this code by providing inaccurate data about the exhaust’s oxygen levels, misleading the vehicle’s computer about the catalytic converter’s efficiency.
8.7 What actions can be taken to prevent the P0420 code from occurring?
Preventative measures include regular maintenance, timely oil changes, ensuring a clean fuel system, and keeping the engine running efficiently. Promptly address any exhaust leaks or engine performance issues.
8.8 Why does the P0420 code persist even after replacing the catalytic converter?
The code might persist due to reasons like not resetting the vehicle’s computer, a faulty installation, or another issue in the emissions system, such as a defective oxygen sensor, that wasn’t addressed.
8.9 How long does it generally take for the P0420 code to reset after repairs?
If the issue is fixed correctly, the code should clear after a few driving cycles. You can also manually clear it with an OBD-II scanner, but it will reappear if the underlying issue isn’t resolved.
8.10 Is it possible for low-quality fuel to be a cause of the P0420 code?
Low-quality fuel alone is unlikely to trigger a P0420 code directly, but it can contribute to engine performance issues over time, potentially leading to catalytic converter efficiency problems.
9. Conclusion: Empowering You to Resolve the P0420 Code
The P0420 code can be a frustrating issue, but with the right knowledge and tools, you can effectively diagnose and repair it. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and repair options, you can make informed decisions about how to address this issue and keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. Remember to perform regular maintenance, use high-quality fuel, and address any engine problems promptly to prevent the P0420 code from occurring. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is your trusted resource for all your automotive diagnostic and repair needs. Our comprehensive guides, expert advice, and high-quality tools can help you tackle any automotive challenge with confidence. Contact us today at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Our team is here to support you every step of the way. Explore our website, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, for more information and resources.
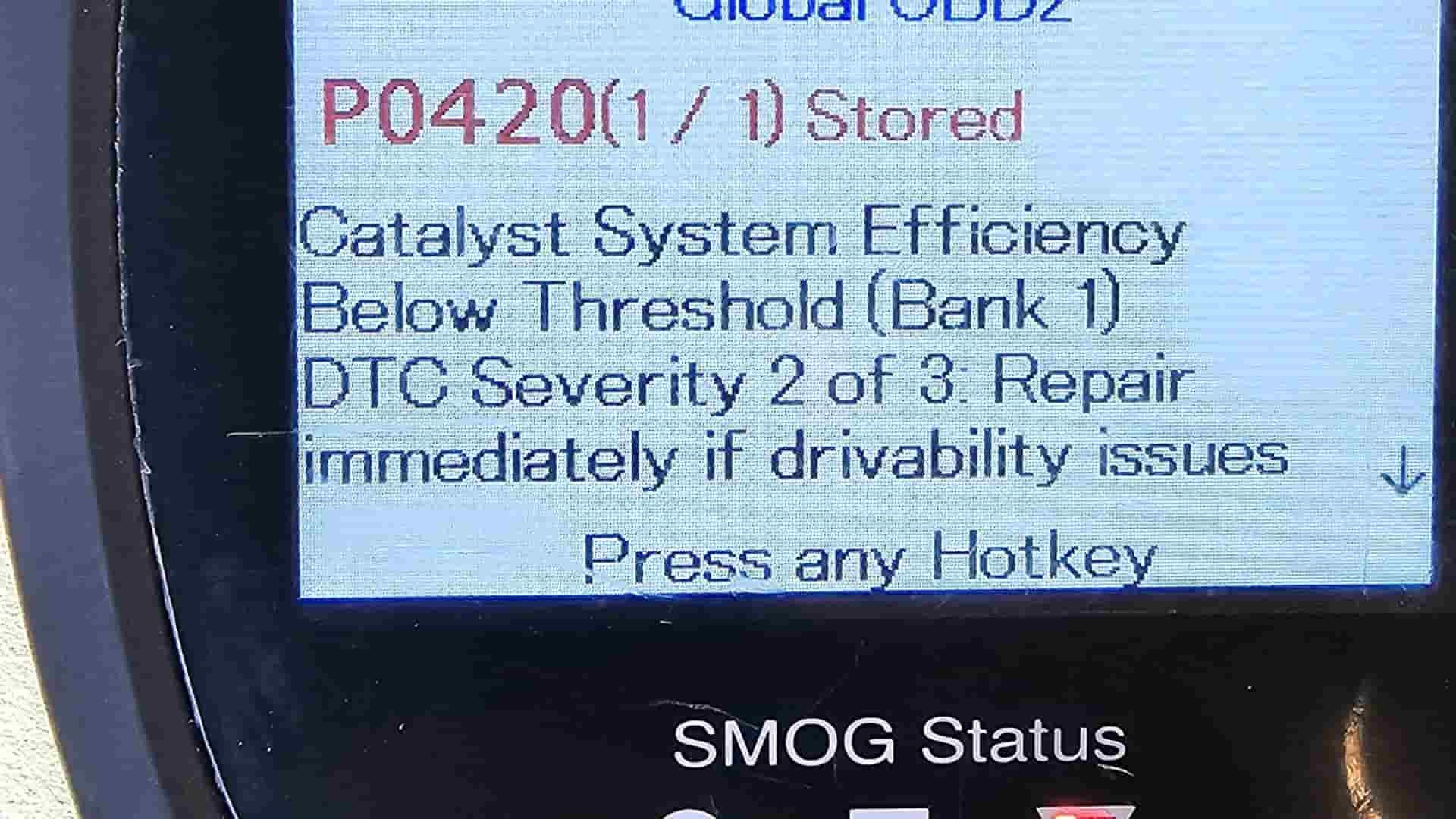 P0420 Code Indicates an Issue with Your Car's Emissions System
P0420 Code Indicates an Issue with Your Car's Emissions System
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides expert insights and solutions to help you navigate the diagnostic process.
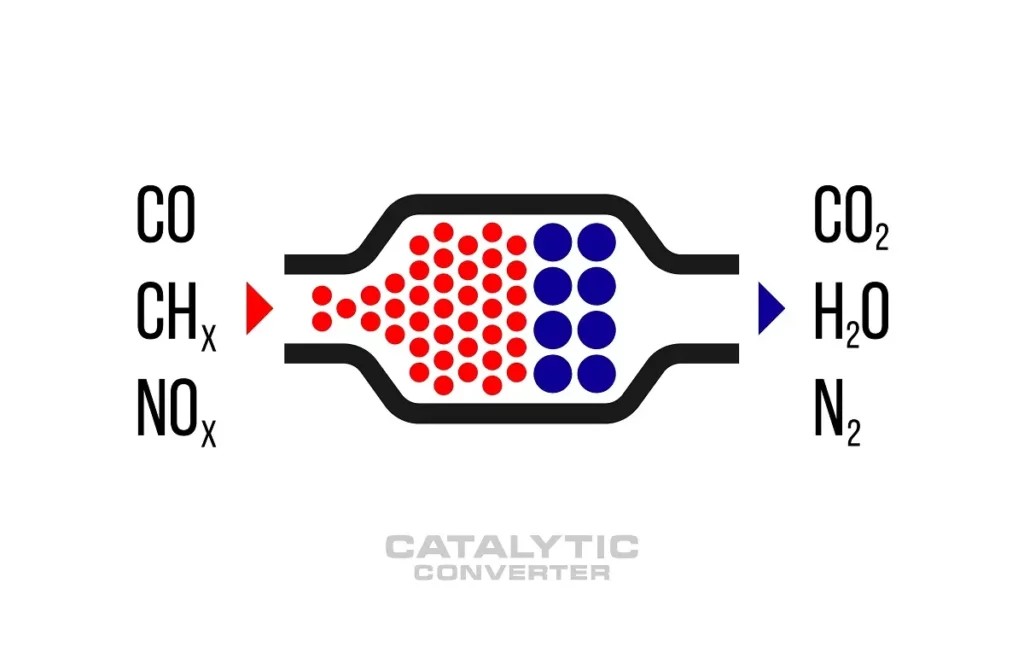 Diagnosing the P0420 Code Requires a Systematic Approach
Diagnosing the P0420 Code Requires a Systematic Approach
Understanding the underlying causes and symptoms associated with the P0420 code is the first step in effectively diagnosing and resolving the problem.
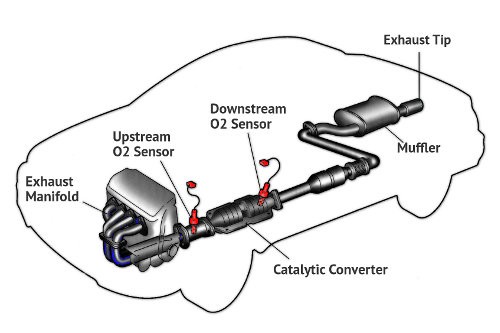 Exhaust System Schematic for P0420 Diagnostic Code
Exhaust System Schematic for P0420 Diagnostic Code
Diagnosing the P0420 code requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause of the issue.
 Catalytic Converters and O2 Sensors Play a Role in Preventing the P0420 Code
Catalytic Converters and O2 Sensors Play a Role in Preventing the P0420 Code
Regular maintenance is the first line of defense against P0420.