Using an OBD scanner is a game-changer for car diagnostics, offering valuable insights into your vehicle’s health. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive resources to help you master this technology, ensuring you can efficiently troubleshoot and maintain your car, ultimately saving you time and money with automotive diagnostic tools, and vehicle code readers.
Contents
- 1. What Does It Mean to Use OBD Scanner?
- 1.1 Historical Context of OBD Scanners
- 1.2 Core Functions of OBD Scanners
- 1.3 Types of OBD Scanners Available
- 1.4 Importance of Regular Vehicle Diagnostics
- 1.5 Factors Influencing the Choice of an OBD Scanner
- 1.6 Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for OBD Scanner Information
- 2. What Are The Primary OBD Scanner Applications?
- 2.1 Engine Diagnostics
- 2.2 Reading and Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 2.3 Real-Time Data Monitoring
- 2.4 Vehicle Inspections
- 2.5 Emissions Compliance
- 2.6 Transmission Diagnostics
- 2.7 ABS and Brake System Diagnostics
- 2.8 Airbag System Diagnostics
- 2.9 Electrical System Diagnostics
- 2.10 Finding Detailed Information on CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 3. What Are The Benefits of OBD Scanner Usage?
- 3.1 Quick and Accurate Diagnostics
- 3.2 Cost Savings on Repairs
- 3.3 Improved Vehicle Performance
- 3.4 Early Detection of Potential Problems
- 3.5 Enhanced Resale Value
- 3.6 DIY Repairs
- 3.7 Emissions Compliance
- 3.8 Preventative Maintenance
- 3.9 Reduced Downtime
- 3.10 Accessing Expert Resources at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 4. What Are The Key Features To Look For In an OBD Scanner?
- 4.1 Comprehensive DTC Reading and Clearing
- 4.2 Real-Time Data Monitoring
- 4.3 Bi-Directional Control
- 4.4 Compatibility with Various Vehicle Makes and Models
- 4.5 User-Friendly Interface
- 4.6 Software Update Capability
- 4.7 Data Logging and Playback
- 4.8 Wireless Connectivity
- 4.9 Built-In Code Definitions
- 4.10 Robust Design and Durability
- 4.11 CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Resources for Choosing the Right OBD Scanner
- 5. How Do I Use An OBD Scanner Step-By-Step?
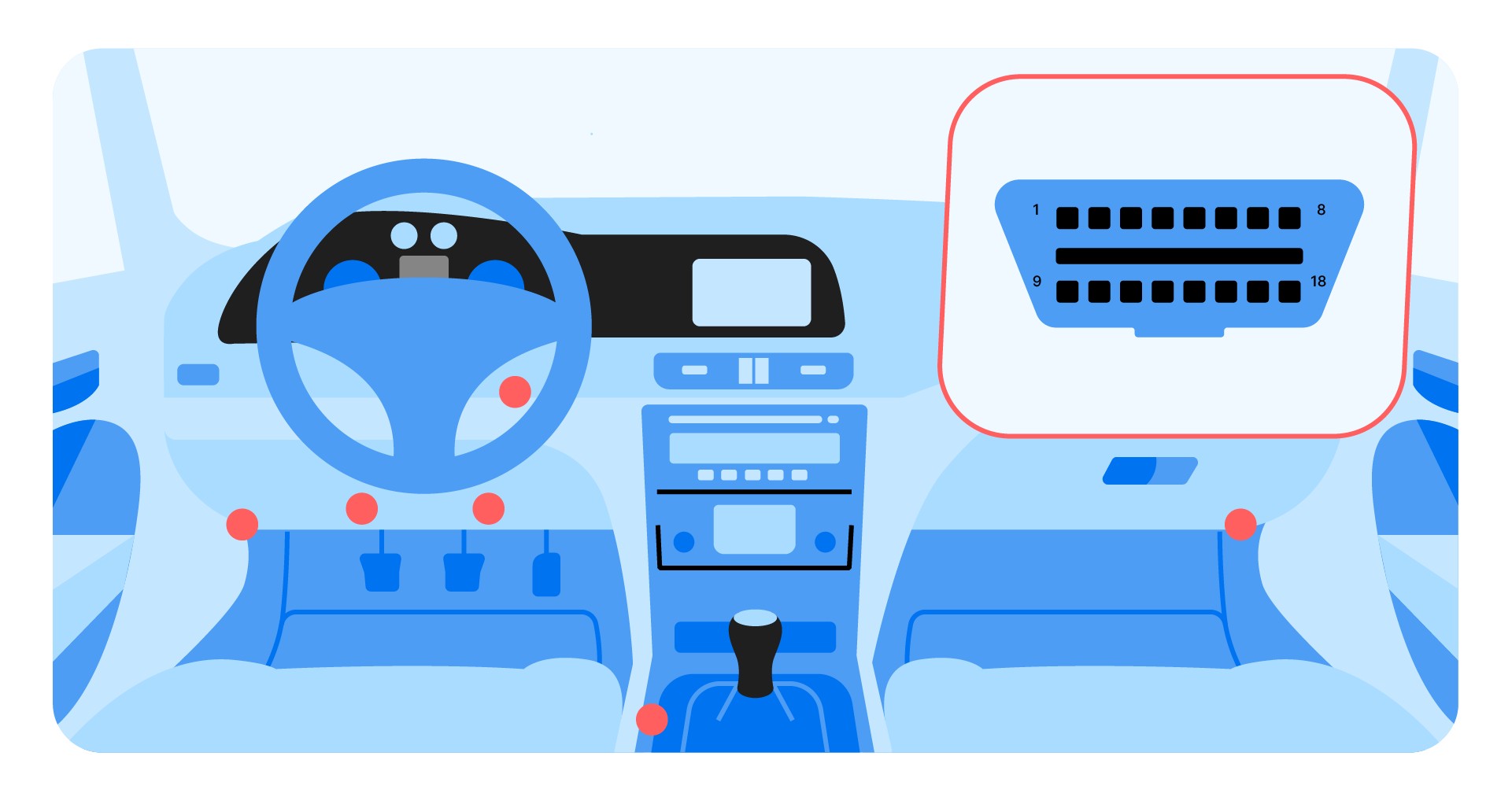
- 5.1 Step 1: Locate the OBD-II Port
- 5.2 Step 2: Connect the OBD Scanner
- 5.3 Step 3: Turn On the Ignition
- 5.4 Step 4: Navigate the Scanner’s Menu
- 5.5 Step 5: Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 5.6 Step 6: Interpret the Codes
- 5.7 Step 7: Analyze Live Data (Optional)
- 5.8 Step 8: Perform Repairs
- 5.9 Step 9: Clear the Codes
- 5.10 Step 10: Verify the Repair
- 5.11 Learn More at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 6. What Are Common Mistakes To Avoid When Using An OBD Scanner?
- 6.1 Misinterpreting DTCs
- 6.2 Failing to Verify Repairs
- 6.3 Neglecting to Update the Scanner Software
- 6.4 Ignoring Live Data
- 6.5 Not Checking for Manufacturer-Specific Codes
- 6.6 Over-Reliance on DTCs
- 6.7 Using the Wrong Scanner for the Vehicle
- 6.8 Ignoring Warning Signs
- 6.9 Not Documenting Results
- 6.10 Clearing Codes Without Repairing the Problem
- 6.11 Get Expert Guidance at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 7. How Can I Choose the Right OBD Scanner for My Needs?
- 7.1 Assess Your Diagnostic Needs
- 7.2 Consider Vehicle Compatibility
- 7.3 Evaluate Features and Functionality
- 7.4 Set a Budget
- 7.5 Read Reviews and Comparisons
- 7.6 Consider the Interface
- 7.7 Evaluate Portability and Size
- 7.8 Check Wireless Connectivity
- 7.9 Review Customer Support
- 7.10 Ask for Recommendations
- 7.11 Find Comprehensive Reviews on CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 8. What Are The Latest Advances In OBD Scanner Technology?
- 8.1 Enhanced Wireless Connectivity
- 8.2 Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 8.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
- 8.4 Advanced Bi-Directional Control
- 8.5 Improved Data Logging Capabilities
- 8.6 Remote Diagnostics
- 8.7 Enhanced User Interface
- 8.8 Increased Vehicle Coverage
- 8.9 Integration with Mobile Apps
- 8.10 Enhanced Security Features
- 8.11 Stay Updated with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 9. What Is The Future of OBD Scanner Technology?
- 9.1 Full Integration with Vehicle Telematics
- 9.2 Predictive Maintenance Capabilities
- 9.3 Enhanced Cybersecurity Features
- 9.4 Augmented Reality (AR) Diagnostics
- 9.5 Seamless Connectivity with Smart Devices
- 9.6 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
- 9.7 Blockchain Integration
- 9.8 Advanced Sensor Integration
- 9.9 AI-Powered Diagnostic Assistants
- 9.10 Virtual Reality (VR) Training
- 9.11 Stay Informed with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 10. How Can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Help Me With OBD Scanners?
- 10.1 Detailed Product Reviews
- 10.2 Comprehensive Buying Guides
- 10.3 Step-by-Step Tutorials
- 10.4 Troubleshooting Tips
- 10.5 Community Forum
- 10.6 Comparison Tools
1. What Does It Mean to Use OBD Scanner?
Using an OBD scanner involves connecting a diagnostic tool to your vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) port to read and interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor live data, and perform various tests to identify and resolve car issues. Using an OBD scanner is a vital skill for both professional mechanics and car owners. It allows for quick and accurate diagnostics, saving time and money on repairs. The use of OBD scanners has evolved significantly, with modern devices offering advanced features such as Bluetooth connectivity, smartphone integration, and access to extensive databases of fault codes.
1.1 Historical Context of OBD Scanners
The introduction of OBD systems dates back to the late 1960s, with basic diagnostic capabilities aimed at monitoring emissions-related components. The first standardized OBD system, OBD-II, was mandated in the United States for all cars manufactured from 1996 onwards, ensuring a universal diagnostic interface. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), this standardization has significantly improved vehicle emissions monitoring and repair efficiency. In Europe, the European On-Board Diagnostics (EOBD) system became mandatory in 2001 for gasoline vehicles and 2004 for diesel vehicles.
1.2 Core Functions of OBD Scanners
OBD scanners serve several critical functions:
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These codes provide specific information about detected faults in the vehicle’s systems.
- Clearing DTCs: After repairing a problem, the scanner can clear the DTCs, turning off the check engine light.
- Monitoring Live Data: Real-time data from various sensors and systems can be observed, aiding in diagnosing intermittent issues.
- Performing System Tests: Some scanners can perform tests on specific components, such as oxygen sensors or the evaporative emission control system.
1.3 Types of OBD Scanners Available
The market offers a range of OBD scanners, each with different capabilities and price points. These include:
- Basic Code Readers: These are the simplest and most affordable scanners, capable of reading and clearing DTCs.
- Mid-Range Scanners: Offering additional features such as live data monitoring and some system tests, these are suitable for DIY enthusiasts and smaller repair shops.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These advanced tools provide comprehensive diagnostics, including bi-directional control, module programming, and access to manufacturer-specific codes.
1.4 Importance of Regular Vehicle Diagnostics
Regular use of an OBD scanner can help identify minor issues before they escalate into major repairs. Early detection of problems can prevent costly breakdowns and extend the life of your vehicle. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), vehicles that undergo regular diagnostic checks have fewer unexpected repairs and lower overall maintenance costs.
1.5 Factors Influencing the Choice of an OBD Scanner
Selecting the right OBD scanner depends on several factors, including:
- Budget: Basic code readers can be found for under $50, while professional-grade scanners can cost several thousand dollars.
- Vehicle Type: Some scanners are designed to work with specific vehicle makes or models.
- Diagnostic Needs: Consider whether you need advanced features like live data monitoring or bi-directional control.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner with an intuitive interface and clear instructions.
1.6 Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for OBD Scanner Information
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wealth of information on OBD scanners, including detailed product reviews, comparison guides, and tutorials. This resource can help you make an informed decision and get the most out of your diagnostic tool.
 OBD2 scanner port location
OBD2 scanner port location
Alt: Locating the OBD2 port for connecting a car diagnostic scanner.
2. What Are The Primary OBD Scanner Applications?
The primary applications of an OBD scanner include diagnosing engine issues, reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitoring real-time data, performing vehicle inspections, and ensuring emissions compliance. OBD scanners are essential for identifying problems related to the engine, transmission, ABS, and other critical systems. These tools help mechanics and car owners pinpoint issues quickly, leading to efficient repairs and maintenance.
2.1 Engine Diagnostics
OBD scanners are crucial for diagnosing a wide range of engine-related problems. By reading DTCs, users can identify issues such as misfires, sensor failures, and fuel system problems. Live data monitoring allows for real-time assessment of engine performance, helping to diagnose intermittent issues and optimize engine tuning. A study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) found that OBD systems can accurately detect over 90% of engine-related faults, leading to faster and more effective repairs.
2.2 Reading and Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
One of the most basic yet essential functions of an OBD scanner is the ability to read and clear DTCs. These codes provide specific information about detected faults in the vehicle’s systems. Once a problem has been diagnosed and repaired, the OBD scanner can be used to clear the DTCs, turning off the check engine light. This ensures that the vehicle’s computer system is reset and ready to monitor for new issues.
2.3 Real-Time Data Monitoring
OBD scanners provide real-time data from various sensors and systems throughout the vehicle. This allows mechanics and car owners to monitor critical parameters such as engine temperature, RPM, fuel pressure, and oxygen sensor readings. By observing these data streams, it is possible to identify anomalies and diagnose issues that may not trigger a DTC. Real-time data monitoring is particularly useful for diagnosing intermittent problems and assessing overall vehicle performance.
2.4 Vehicle Inspections
OBD scanners are increasingly used for vehicle inspections, both by professional mechanics and during pre-purchase inspections. By scanning the vehicle’s computer system, inspectors can quickly identify any stored DTCs or potential issues. This provides valuable information about the vehicle’s condition and can help buyers make informed decisions. In many states, OBD scans are a required part of the vehicle inspection process to ensure emissions compliance.
2.5 Emissions Compliance
OBD systems are designed to monitor and ensure that vehicles comply with emissions standards. OBD scanners can be used to check the status of various emissions-related components and systems, such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and evaporative emission control system. If any issues are detected, the OBD system will store a DTC and illuminate the check engine light, alerting the driver to the problem. Regular use of an OBD scanner can help ensure that vehicles meet emissions requirements and avoid costly fines.
2.6 Transmission Diagnostics
In addition to engine diagnostics, OBD scanners can also be used to diagnose transmission-related issues. DTCs related to the transmission can provide information about problems such as slipping gears, incorrect gear ratios, and sensor failures. Live data monitoring can also be used to assess transmission performance, helping to identify issues such as overheating or fluid pressure problems.
2.7 ABS and Brake System Diagnostics
OBD scanners can access the vehicle’s Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and other brake-related systems. DTCs can provide information about issues such as sensor failures, hydraulic problems, and electronic control unit faults. This allows mechanics to quickly diagnose and repair brake system issues, ensuring vehicle safety.
2.8 Airbag System Diagnostics
OBD scanners can also be used to diagnose issues with the vehicle’s airbag system. DTCs related to the airbag system can provide information about problems such as sensor failures, wiring issues, and control unit faults. Diagnosing and repairing airbag system issues is critical for ensuring passenger safety in the event of a collision.
2.9 Electrical System Diagnostics
Many electrical system issues can be diagnosed using an OBD scanner. DTCs related to the electrical system can provide information about problems such as short circuits, open circuits, and sensor failures. Live data monitoring can also be used to assess the performance of various electrical components, helping to identify issues such as voltage drops or excessive current draw.
2.10 Finding Detailed Information on CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive resource for understanding the various applications of OBD scanners. With detailed guides, product reviews, and troubleshooting tips, you can learn how to effectively use an OBD scanner to diagnose and repair a wide range of vehicle issues.
 OBD2 scanner
OBD2 scanner
Alt: A technician using an OBD2 scanner to diagnose vehicle issues.
3. What Are The Benefits of OBD Scanner Usage?
The benefits of using an OBD scanner include quick and accurate diagnostics, cost savings on repairs, improved vehicle performance, early detection of potential problems, and enhanced resale value. OBD scanners enable car owners and mechanics to identify issues early, leading to timely repairs and preventing more significant damage. The use of OBD scanners results in more efficient maintenance and better overall vehicle health.
3.1 Quick and Accurate Diagnostics
OBD scanners provide immediate access to diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and real-time data, allowing for quick and accurate identification of vehicle problems. This speed and precision reduce diagnostic time and minimize the chances of misdiagnosis. According to a study by the Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI), the use of OBD scanners can reduce diagnostic time by up to 40%.
3.2 Cost Savings on Repairs
By enabling early detection and accurate diagnosis of issues, OBD scanners help prevent minor problems from escalating into major repairs. This results in significant cost savings for car owners. Additionally, having the ability to diagnose and potentially fix issues yourself can save on labor costs at a repair shop.
3.3 Improved Vehicle Performance
Regular use of an OBD scanner allows for the monitoring of vehicle performance parameters, such as engine temperature, RPM, and fuel efficiency. This data can be used to optimize vehicle tuning and maintenance practices, leading to improved performance and fuel economy. A study by the Oak Ridge National Laboratory found that proper vehicle maintenance, guided by OBD data, can improve fuel efficiency by up to 4%.
3.4 Early Detection of Potential Problems
OBD scanners can detect potential problems before they become apparent through noticeable symptoms. This early detection allows for timely repairs and maintenance, preventing more significant damage and potential breakdowns. Regular OBD scans can help identify issues such as sensor failures, vacuum leaks, and emissions problems before they lead to more costly repairs.
3.5 Enhanced Resale Value
A well-maintained vehicle with a clean diagnostic history has a higher resale value. By using an OBD scanner to keep your vehicle in good condition, you can enhance its resale value when it comes time to sell or trade it in. Potential buyers are more likely to trust a vehicle that has been regularly monitored and maintained.
3.6 DIY Repairs
For car enthusiasts and DIYers, an OBD scanner is an invaluable tool. It allows you to diagnose and potentially fix issues yourself, saving on labor costs and giving you a better understanding of your vehicle. With the help of online resources like CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can learn how to interpret DTCs, perform basic repairs, and maintain your vehicle.
3.7 Emissions Compliance
OBD scanners can help ensure that your vehicle complies with emissions standards. By monitoring emissions-related components and systems, you can identify and address potential issues before they lead to a failed emissions test. This is particularly important in areas with strict emissions regulations.
3.8 Preventative Maintenance
Regular use of an OBD scanner can be a part of a preventative maintenance program. By monitoring vehicle health and addressing potential issues early, you can extend the life of your vehicle and minimize the risk of unexpected breakdowns. Preventative maintenance is key to keeping your vehicle running smoothly and reliably.
3.9 Reduced Downtime
Quick and accurate diagnostics, facilitated by OBD scanners, result in reduced downtime for your vehicle. This is particularly important for those who rely on their vehicles for work or daily transportation. By addressing issues promptly, you can minimize the time your vehicle spends in the repair shop.
3.10 Accessing Expert Resources at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive platform for learning about the benefits of using OBD scanners. Offering detailed guides, product comparisons, and expert advice, this resource helps you maximize the advantages of OBD technology and keep your vehicle in optimal condition.
 computer diagnostics, OBD2 scanner
computer diagnostics, OBD2 scanner
Alt: Using computer diagnostics and an OBD2 scanner for vehicle maintenance.
4. What Are The Key Features To Look For In an OBD Scanner?
Key features to look for in an OBD scanner include comprehensive DTC reading and clearing, real-time data monitoring, bi-directional control, compatibility with various vehicle makes and models, user-friendly interface, and software update capability. These features ensure that the OBD scanner is versatile, accurate, and easy to use for both professional mechanics and car owners. Choosing an OBD scanner with the right features can significantly improve diagnostic efficiency and effectiveness.
4.1 Comprehensive DTC Reading and Clearing
The ability to read and clear a wide range of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) is a fundamental feature of any OBD scanner. A comprehensive scanner should support generic OBD-II codes as well as manufacturer-specific codes, providing detailed information about detected faults. The scanner should also allow for easy clearing of DTCs once the issue has been resolved.
4.2 Real-Time Data Monitoring
Real-time data monitoring, also known as live data streaming, is a crucial feature for diagnosing intermittent issues and assessing overall vehicle performance. The scanner should be able to display real-time data from various sensors and systems, such as engine temperature, RPM, fuel pressure, and oxygen sensor readings. This allows for the identification of anomalies and trends that may not trigger a DTC.
4.3 Bi-Directional Control
Bi-directional control, also known as actuation testing, is an advanced feature that allows the scanner to send commands to the vehicle’s systems and components. This enables mechanics to test the functionality of various actuators, such as fuel injectors, solenoids, and relays. Bi-directional control can significantly speed up the diagnostic process and help pinpoint the root cause of a problem.
4.4 Compatibility with Various Vehicle Makes and Models
A versatile OBD scanner should be compatible with a wide range of vehicle makes and models. This ensures that the scanner can be used on multiple vehicles, making it a valuable tool for both professional mechanics and car owners with multiple vehicles. Check the scanner’s specifications to ensure compatibility with your specific vehicle makes and models.
4.5 User-Friendly Interface
A user-friendly interface is essential for ease of use and efficient diagnostics. The scanner should have a clear display, intuitive menus, and easy-to-understand instructions. Some scanners also offer features such as touchscreen displays, built-in help functions, and multilingual support.
4.6 Software Update Capability
The automotive industry is constantly evolving, with new vehicle models and technologies being introduced regularly. A scanner with software update capability ensures that it remains up-to-date with the latest vehicle information and diagnostic protocols. Regular software updates can also add new features and improve the scanner’s performance.
4.7 Data Logging and Playback
Data logging and playback is a useful feature for capturing and analyzing real-time data. The scanner should be able to log data from various sensors and systems, allowing for later playback and analysis. This can be particularly helpful for diagnosing intermittent issues that may not be present during the initial diagnostic session.
4.8 Wireless Connectivity
Wireless connectivity, such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, allows the scanner to connect to smartphones, tablets, and computers. This enables users to view diagnostic data on a larger screen, access online resources, and share diagnostic reports. Wireless connectivity can also simplify the software update process.
4.9 Built-In Code Definitions
A scanner with built-in code definitions eliminates the need to look up DTCs online or in a manual. The scanner should display the code definition directly on the screen, providing immediate information about the detected fault. This can save time and simplify the diagnostic process.
4.10 Robust Design and Durability
An OBD scanner is a tool that is likely to be used in a variety of environments, from the clean confines of a professional garage to the sometimes less-than-pristine conditions of a roadside repair. As such, a robust design and durable construction are vital. Look for scanners that are built to withstand drops, impacts, and exposure to common automotive fluids. Scanners with rubberized grips and reinforced housings are often a good choice for those who need a reliable tool that can stand up to daily use.
4.11 CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Resources for Choosing the Right OBD Scanner
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers extensive resources to help you choose an OBD scanner with the key features you need. With detailed product reviews, comparison guides, and expert advice, you can make an informed decision and select the right scanner for your diagnostic needs.
5. How Do I Use An OBD Scanner Step-By-Step?
Using an OBD scanner involves several steps: locating the OBD-II port, connecting the scanner, turning on the ignition, navigating the scanner’s menu, reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), interpreting the codes, and clearing the codes after repairs. Following these steps ensures accurate diagnostics and proper vehicle maintenance. The process is straightforward, but understanding each step is crucial for effective use.
5.1 Step 1: Locate the OBD-II Port
The first step is to locate the OBD-II port in your vehicle. The OBD-II port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Common locations include near the steering column, under the glove compartment, or in the center console. Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual if you have trouble locating the port.
5.2 Step 2: Connect the OBD Scanner
Once you have located the OBD-II port, connect the OBD scanner to the port. Ensure that the connection is secure. Some scanners may require additional adapters or cables, depending on the vehicle make and model.
5.3 Step 3: Turn On the Ignition
Turn on the vehicle’s ignition without starting the engine. This provides power to the vehicle’s computer system and allows the scanner to communicate with the system. In some cases, you may need to start the engine to read certain data or perform specific tests.
5.4 Step 4: Navigate the Scanner’s Menu
Use the scanner’s menu to navigate to the diagnostic functions. Common menu options include “Read Codes,” “Clear Codes,” “Live Data,” and “Vehicle Information.” Refer to the scanner’s user manual for specific instructions on navigating the menu.
5.5 Step 5: Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Select the “Read Codes” option to retrieve any stored DTCs from the vehicle’s computer system. The scanner will display a list of DTCs along with their descriptions. Note down the DTCs for further analysis.
5.6 Step 6: Interpret the Codes
Interpret the DTCs to understand the detected faults. Each DTC corresponds to a specific issue or problem in the vehicle. You can use online resources, repair manuals, or the scanner’s built-in code definitions to interpret the codes. Common DTCs include “P0300” (Random Misfire Detected) and “P0171” (System Too Lean).
5.7 Step 7: Analyze Live Data (Optional)
If necessary, analyze live data to further diagnose the issue. Select the “Live Data” option to view real-time data from various sensors and systems. Monitor parameters such as engine temperature, RPM, and fuel pressure to identify any anomalies or trends.
5.8 Step 8: Perform Repairs
Based on the DTCs and live data analysis, perform the necessary repairs to address the detected faults. This may involve replacing faulty sensors, repairing wiring issues, or addressing mechanical problems.
5.9 Step 9: Clear the Codes
After performing the repairs, clear the DTCs from the vehicle’s computer system. Select the “Clear Codes” option and follow the on-screen instructions. Clearing the codes turns off the check engine light and resets the vehicle’s diagnostic system.
5.10 Step 10: Verify the Repair
Verify that the repair was successful by performing another scan and checking for any new DTCs. Monitor live data to ensure that the vehicle is operating within normal parameters. If no new DTCs appear and the vehicle is running smoothly, the repair was successful.
5.11 Learn More at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed guides and tutorials on how to use an OBD scanner step-by-step. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced mechanic, you can find valuable information and tips to improve your diagnostic skills.
6. What Are Common Mistakes To Avoid When Using An OBD Scanner?
Common mistakes to avoid when using an OBD scanner include misinterpreting DTCs, failing to verify repairs, neglecting to update the scanner software, ignoring live data, and not checking for manufacturer-specific codes. Avoiding these mistakes ensures accurate diagnostics and effective vehicle maintenance. Accurate usage leads to correct diagnoses and prevents unnecessary repairs.
6.1 Misinterpreting DTCs
One of the most common mistakes is misinterpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). DTCs provide valuable information about detected faults, but they do not always tell the whole story. It is important to understand the context of the DTC and perform further analysis to pinpoint the root cause of the problem. For example, a DTC indicating a faulty oxygen sensor may actually be caused by a vacuum leak or a fuel system problem.
6.2 Failing to Verify Repairs
Another common mistake is failing to verify repairs after addressing a detected fault. After performing a repair, it is important to clear the DTCs and perform another scan to ensure that the issue has been resolved. Monitor live data to verify that the vehicle is operating within normal parameters. Failing to verify repairs can lead to recurring problems and unnecessary expenses.
6.3 Neglecting to Update the Scanner Software
OBD scanner software needs to be updated regularly to ensure compatibility with the latest vehicle models and diagnostic protocols. Neglecting to update the scanner software can result in inaccurate readings and limited functionality. Check for software updates regularly and install them as soon as they are available.
6.4 Ignoring Live Data
Live data provides valuable information about the real-time performance of various sensors and systems. Ignoring live data can result in missed opportunities for diagnosing intermittent issues and assessing overall vehicle health. Monitor live data parameters such as engine temperature, RPM, and fuel pressure to identify any anomalies or trends.
6.5 Not Checking for Manufacturer-Specific Codes
Generic OBD-II codes provide basic information about detected faults, but they may not always provide enough detail for accurate diagnosis. Manufacturer-specific codes provide more detailed information and can help pinpoint the root cause of a problem. Be sure to check for manufacturer-specific codes when diagnosing vehicle issues.
6.6 Over-Reliance on DTCs
While DTCs are a valuable diagnostic tool, they should not be the only source of information. Over-reliance on DTCs can lead to misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs. Use DTCs as a starting point and perform further analysis, such as visual inspections and live data monitoring, to pinpoint the root cause of the problem.
6.7 Using the Wrong Scanner for the Vehicle
Not all OBD scanners are compatible with all vehicles. Using the wrong scanner for the vehicle can result in inaccurate readings and potential damage to the vehicle’s computer system. Check the scanner’s specifications to ensure compatibility with the vehicle make and model.
6.8 Ignoring Warning Signs
OBD scanners are designed to detect and report potential problems, but they are not a substitute for common sense. Ignoring warning signs such as unusual noises, vibrations, or odors can lead to more serious problems. Address any warning signs promptly, even if the OBD scanner does not report any DTCs.
6.9 Not Documenting Results
Failing to document diagnostic results can make it difficult to track down recurring problems and assess the effectiveness of repairs. Keep a detailed record of DTCs, live data readings, and repair procedures. This will help you diagnose and resolve vehicle issues more efficiently in the future.
6.10 Clearing Codes Without Repairing the Problem
Clearing codes without repairing the underlying problem is a common mistake that can lead to recurring issues and potential damage to the vehicle. Always diagnose and repair the problem before clearing the codes. Clearing codes without addressing the root cause only masks the problem temporarily.
6.11 Get Expert Guidance at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers expert guidance and resources to help you avoid common mistakes when using an OBD scanner. With detailed troubleshooting tips, product reviews, and expert advice, you can improve your diagnostic skills and ensure accurate and effective vehicle maintenance.
7. How Can I Choose the Right OBD Scanner for My Needs?
Choosing the right OBD scanner involves assessing your diagnostic needs, considering vehicle compatibility, evaluating features and functionality, setting a budget, and reading reviews and comparisons. A well-informed decision ensures that the scanner meets your requirements and provides accurate and reliable diagnostic information. Evaluate available options based on your specific needs.
7.1 Assess Your Diagnostic Needs
The first step in choosing the right OBD scanner is to assess your diagnostic needs. Consider the types of vehicles you will be working on, the types of issues you will be diagnosing, and the level of functionality you require. Are you a DIY enthusiast looking to perform basic maintenance and repairs, or a professional mechanic in need of advanced diagnostic capabilities?
7.2 Consider Vehicle Compatibility
Ensure that the OBD scanner is compatible with the vehicles you will be working on. Check the scanner’s specifications to verify compatibility with the vehicle makes, models, and years. Some scanners are designed to work with specific vehicle brands, while others offer broader compatibility.
7.3 Evaluate Features and Functionality
Evaluate the features and functionality offered by the OBD scanner. Consider the following features:
- DTC Reading and Clearing: The ability to read and clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Live Data Monitoring: The ability to monitor real-time data from various sensors and systems.
- Bi-Directional Control: The ability to send commands to the vehicle’s systems and components.
- Software Update Capability: The ability to update the scanner software with the latest vehicle information.
- User-Friendly Interface: A clear display, intuitive menus, and easy-to-understand instructions.
7.4 Set a Budget
OBD scanners range in price from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools. Set a budget based on your needs and the features you require. Keep in mind that more expensive scanners often offer more advanced functionality and broader compatibility.
7.5 Read Reviews and Comparisons
Read reviews and comparisons of different OBD scanners to get an idea of their performance, reliability, and user satisfaction. Look for reviews from reputable sources and consider the experiences of other users.
7.6 Consider the Interface
The interface of the OBD scanner is crucial for its ease of use. Look for a scanner with a clear and easy-to-read display, as well as intuitive menus and controls. Some scanners also offer touchscreen interfaces for added convenience.
7.7 Evaluate Portability and Size
Depending on your needs, you may want to consider the portability and size of the OBD scanner. Compact scanners are easy to carry around and store, while larger scanners may offer more features and a larger display.
7.8 Check Wireless Connectivity
Some OBD scanners offer wireless connectivity via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. This allows you to connect the scanner to your smartphone, tablet, or computer for added functionality. Check if wireless connectivity is important to you and choose a scanner accordingly.
7.9 Review Customer Support
Consider the level of customer support offered by the manufacturer. Look for a scanner with readily available customer support, including online resources, phone support, and email support.
7.10 Ask for Recommendations
Ask for recommendations from friends, colleagues, or online forums. Getting input from others who have used OBD scanners can help you make a more informed decision.
7.11 Find Comprehensive Reviews on CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive reviews and comparisons of OBD scanners to help you choose the right tool for your needs. With expert advice and detailed product information, you can make an informed decision and select a scanner that meets your requirements.
8. What Are The Latest Advances In OBD Scanner Technology?
The latest advances in OBD scanner technology include enhanced wireless connectivity, cloud-based diagnostics, artificial intelligence (AI) integration, advanced bi-directional control, and improved data logging capabilities. These advances offer more efficient, accurate, and user-friendly diagnostics for both mechanics and car owners. The continuous evolution of OBD technology ensures better vehicle maintenance.
8.1 Enhanced Wireless Connectivity
Enhanced wireless connectivity, such as Bluetooth 5.0 and Wi-Fi 6, provides faster and more reliable connections between OBD scanners and smartphones, tablets, and computers. This enables users to view diagnostic data on larger screens, access online resources, and share diagnostic reports more efficiently.
8.2 Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Cloud-based diagnostics allows OBD scanners to access and store diagnostic data in the cloud. This enables users to access their diagnostic data from anywhere, collaborate with other mechanics, and receive remote support from experts. Cloud-based diagnostics also facilitates software updates and data backups.
8.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being integrated into OBD scanners to provide more intelligent and automated diagnostics. AI algorithms can analyze diagnostic data, identify potential problems, and suggest repair procedures. This can help mechanics diagnose and repair vehicle issues more quickly and accurately.
8.4 Advanced Bi-Directional Control
Advanced bi-directional control enables OBD scanners to perform more comprehensive testing and actuation of vehicle systems and components. This allows mechanics to test the functionality of various actuators, such as fuel injectors, solenoids, and relays, and to diagnose issues more effectively.
8.5 Improved Data Logging Capabilities
Improved data logging capabilities allow OBD scanners to capture and store more data over longer periods of time. This enables mechanics to diagnose intermittent issues and track vehicle performance more effectively. Advanced data logging features include customizable data logging parameters, high-speed data logging, and data visualization tools.
8.6 Remote Diagnostics
Remote diagnostics allows mechanics to diagnose and repair vehicles remotely, using OBD scanners connected to the cloud. This can be particularly useful for diagnosing vehicles in remote locations or for providing support to customers who are unable to bring their vehicles to the shop.
8.7 Enhanced User Interface
Modern OBD scanners feature enhanced user interfaces with larger displays, intuitive menus, and touchscreen controls. This makes it easier for mechanics and car owners to navigate the scanner and access the diagnostic functions they need.
8.8 Increased Vehicle Coverage
OBD scanner manufacturers are constantly expanding the vehicle coverage of their products. This ensures that the scanners are compatible with the latest vehicle models and diagnostic protocols.
8.9 Integration with Mobile Apps
Many OBD scanners now offer integration with mobile apps. This allows users to access diagnostic data and perform diagnostic functions using their smartphones or tablets. Mobile apps can also provide access to online resources, repair manuals, and diagnostic support.
8.10 Enhanced Security Features
With the increasing connectivity of OBD scanners, security is becoming more important than ever. Modern OBD scanners feature enhanced security features to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
8.11 Stay Updated with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides the latest information on advances in OBD scanner technology. With detailed articles, product reviews, and expert insights, you can stay up-to-date on the latest developments and choose the best OBD scanner for your needs.
9. What Is The Future of OBD Scanner Technology?
The future of OBD scanner technology includes full integration with vehicle telematics, predictive maintenance capabilities, enhanced cybersecurity features, augmented reality (AR) diagnostics, and seamless connectivity with smart devices. These advancements will transform vehicle diagnostics, making it more efficient, proactive, and user-friendly. The evolution of OBD scanners will drive innovation in vehicle maintenance.
9.1 Full Integration with Vehicle Telematics
Full integration with vehicle telematics will allow OBD scanners to access and utilize real-time data from the vehicle’s onboard systems. This will enable more comprehensive and accurate diagnostics, as well as proactive monitoring of vehicle health.
9.2 Predictive Maintenance Capabilities
Predictive maintenance capabilities will allow OBD scanners to analyze vehicle data and predict potential failures before they occur. This will enable mechanics and car owners to perform preventative maintenance and avoid costly repairs.
9.3 Enhanced Cybersecurity Features
With the increasing connectivity of vehicles, cybersecurity is becoming more important than ever. Future OBD scanners will feature enhanced cybersecurity features to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
9.4 Augmented Reality (AR) Diagnostics
Augmented reality (AR) diagnostics will allow mechanics to visualize diagnostic data and repair procedures in real-time, using AR headsets or smartphones. This will make it easier to diagnose and repair complex vehicle issues.
9.5 Seamless Connectivity with Smart Devices
Future OBD scanners will offer seamless connectivity with smart devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches. This will allow users to access diagnostic data and perform diagnostic functions from anywhere.
9.6 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Over-the-air (OTA) updates will allow OBD scanners to receive software updates and new features automatically, without the need for manual installation. This will ensure that the scanners are always up-to-date with the latest vehicle information and diagnostic protocols.
9.7 Blockchain Integration
Blockchain integration will allow for secure and transparent sharing of diagnostic data between mechanics, car owners, and vehicle manufacturers. This will improve trust and collaboration in the automotive industry.
9.8 Advanced Sensor Integration
Future OBD scanners will integrate with advanced sensors to provide more comprehensive diagnostic data. These sensors may include vibration sensors, acoustic sensors, and thermal sensors.
9.9 AI-Powered Diagnostic Assistants
AI-powered diagnostic assistants will provide mechanics with real-time guidance and support, using natural language processing and machine learning. This will make it easier to diagnose and repair complex vehicle issues.
9.10 Virtual Reality (VR) Training
Virtual reality (VR) training will allow mechanics to practice diagnostic and repair procedures in a safe and realistic virtual environment. This will improve their skills and confidence.
9.11 Stay Informed with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides the latest insights into the future of OBD scanner technology. With expert analysis, industry news, and detailed articles, you can stay informed about the latest trends and developments in vehicle diagnostics.
10. How Can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Help Me With OBD Scanners?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN can help you with OBD scanners by providing detailed product reviews, comprehensive buying guides, step-by-step tutorials, troubleshooting tips, and a community forum for support and advice. This comprehensive resource ensures that you have the knowledge and tools to effectively Use Obd Scanners for vehicle maintenance and diagnostics. Rely on CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert guidance on automotive tools and technology.
10.1 Detailed Product Reviews
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed product reviews of various OBD scanners, providing unbiased assessments of their features, performance, and value. These reviews can help you make an informed decision when choosing an OBD scanner.
10.2 Comprehensive Buying Guides
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive buying guides that help you understand the key features and considerations when purchasing an OBD scanner. These guides can help you narrow down your options and choose the right scanner for your needs.
10.3 Step-by-Step Tutorials
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers step-by-step tutorials on how to use OBD scanners for various diagnostic and maintenance tasks. These tutorials can help you learn how to read and clear DTCs, monitor live data, and perform system tests.
10.4 Troubleshooting Tips
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides troubleshooting tips for common OBD scanner issues, helping you resolve problems and get the most out of your scanner. These tips can help you diagnose and fix issues such as connection problems, software errors, and inaccurate readings.
10.5 Community Forum
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN hosts a community forum where you can ask questions, share experiences, and get advice from other OBD scanner users. This forum can provide valuable support and insights from fellow mechanics and car owners.