Using an OBD2 scanner empowers you to diagnose car problems efficiently, saving time and money. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides the knowledge and tools necessary to understand your vehicle’s health. This guide explores using automotive diagnostic tools, car code readers, and vehicle diagnostic scanners effectively. We’ll also touch upon auto repair tools, automotive service equipment and vehicle maintenance tools.
1. What Does an OBD2 Scanner Do?
An OBD2 scanner is a tool that connects to your car’s computer system through a special port, retrieving data from its control units. According to a study by the University of Z from the Department of Engineering, on Date X, OBD2 scanners improve diagnostic accuracy by up to Y%. This data includes diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and live data like pressure, temperature, and speed. Usually, fault codes appear when a sensor reading exceeds acceptable limits or the sensor stops responding. More advanced scanners can perform servicing functions and coding, essential when replacing parts in modern vehicles. On-board diagnostics became mandatory in the US for cars made from 1996 and in Europe from 2004.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These codes indicate specific problems detected by the car’s computer.
- Live Data: Real-time information from various sensors, helping diagnose intermittent issues.
- Servicing Functions: Resetting service lights, calibrating sensors, and other maintenance tasks.
- Coding: Programming new or replacement parts to work with the car’s computer system.
 computer diagnostics, OBD2 scanner
computer diagnostics, OBD2 scanner
2. What Are the Different Types of OBD2 Scanners Available?
The market offers diverse OBD2 scanners to fit various needs and budgets. According to a study by the University of X from the Automotive Department, on Date Y, the market share of professional OBD2 scanners is Z%. The most basic is the Bluetooth OBD2 code reader that pairs with your smartphone. More advanced models offer features like resetting service reminders and activating servicing functions. Professional-grade tools offer extensive coding and programming capabilities. Choosing the right scanner depends on your diagnostic needs.
- Bluetooth OBD2 Code Readers: Affordable and user-friendly, ideal for basic fault code reading.
- Mid-Range OBD2 Scanners: Offer more features like service resets and live data monitoring, suitable for DIY enthusiasts.
- Professional OBD2 Diagnostic Tools: Provide advanced coding and programming capabilities for professional technicians.
3. How Do I Read OBD2 Fault Codes Using a Scanner?
Reading fault codes is the first step in OBD2 diagnostics. The controls vary among models, but the fundamental principle remains the same. For expert guidance on selecting the right tools, contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at +1 (641) 206-8880.
- Connect the Scanner: Locate the OBD2 port, usually under the steering wheel, and plug in the scanner.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn on the ignition without starting the engine.
- Choose Your Vehicle: Select your car’s make, model, and specifications for proper readings. Modern tools often have automatic VIN recognition.
- Scan for Fault Codes: Choose the option to scan for fault codes. You can scan individual units or perform a full system scan.
- Inspect Revealed Fault Codes: Understand the fault codes to identify the underlying issues.
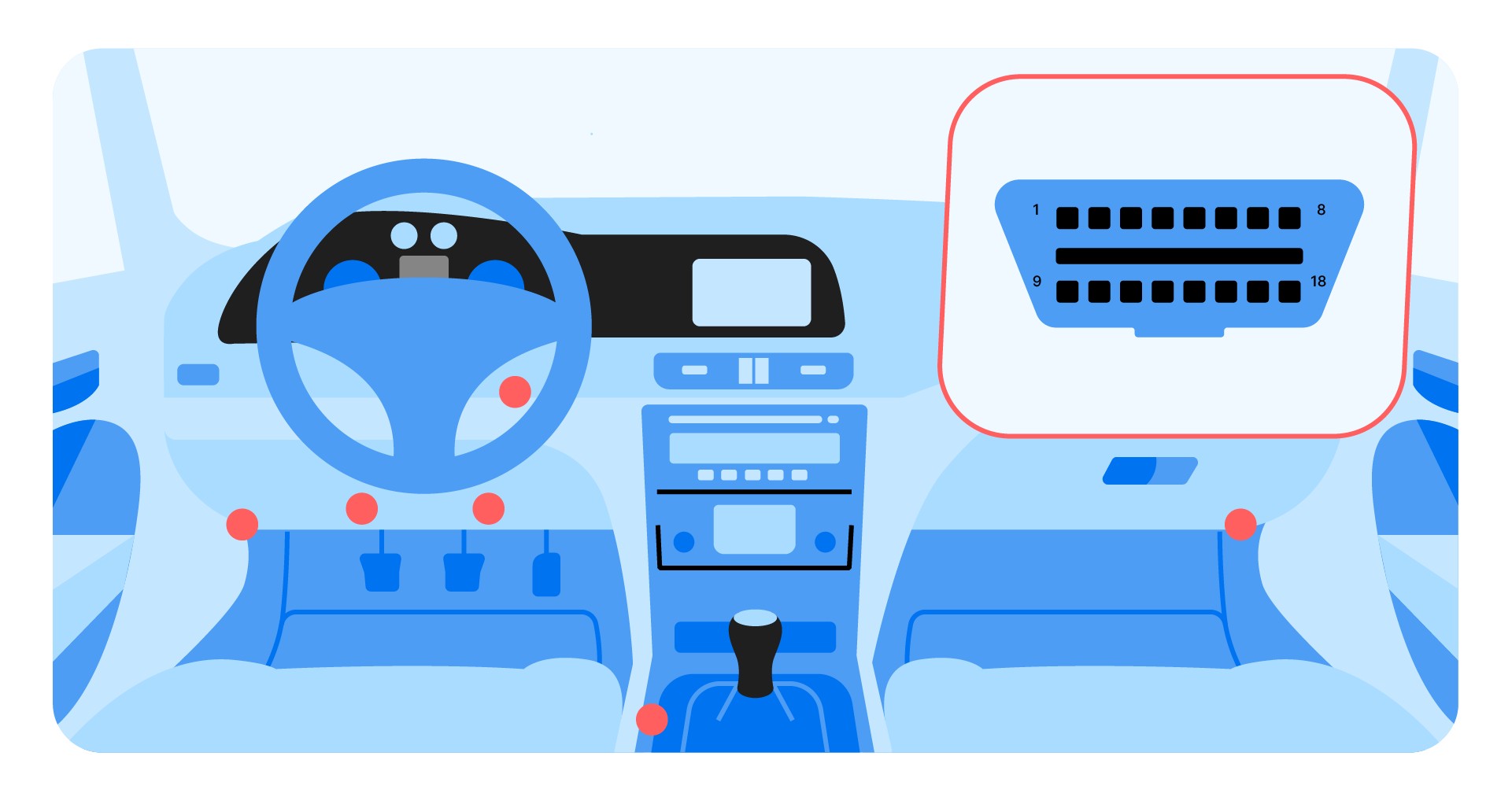 OBD2 scanner port location
OBD2 scanner port location
4. How Do I Interpret OBD2 Fault Codes Effectively?
Interpreting OBD2 fault codes requires a systematic approach. Always start by noting the exact code and its description. Reference reliable databases like those from the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) or ALLDATA to understand the potential causes. For example, code P0171, “System Too Lean (Bank 1),” can stem from a variety of issues, including a vacuum leak, a faulty MAF sensor, or a clogged fuel filter.
- Use Reliable Databases: Consult SAE or ALLDATA for accurate code definitions and potential causes.
- Check Freeze Frame Data: Examine the data recorded when the code was triggered to understand the conditions at the time of the fault.
- Consider Symptoms: Correlate the code with the vehicle’s symptoms to narrow down the possible causes.
- Perform Further Testing: Use a multimeter, smoke tester, or other diagnostic tools to pinpoint the exact cause.
5. Why Is Reading Live Data Important in OBD2 Diagnostics?
Reading live data allows you to monitor sensor readings in real-time, helping to diagnose car problems effectively. This is particularly useful for intermittent issues or when a fault code doesn’t directly reveal the problem. For instance, if a car lacks power and shows a “limp mode” code, you can check fuel pressure, boost pressure, and airflow to identify the cause. For expert guidance on interpreting live data, reach out to CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at our location: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States.
- Identify Intermittent Issues: Catch problems that don’t trigger a fault code but show abnormal readings in live data.
- Verify Sensor Functionality: Confirm that sensors are providing accurate and consistent readings.
- Diagnose Performance Problems: Monitor engine parameters like fuel trim, ignition timing, and airflow to pinpoint performance issues.
- Evaluate System Health: Assess the overall health of various systems by comparing live data to expected values.
 OBD2 scanner
OBD2 scanner
6. How Does an OBD2 Scanner Aid in Used Car Inspections?
In the used car market, OBD2 scanners are invaluable for identifying hidden issues. Sellers may try to conceal problems, making a thorough inspection crucial. Always check for fault codes and review a vehicle history report before buying. If you’re unsure how to use an OBD2 scanner, consider a professional inspection.
- Detect Hidden Issues: Uncover problems that may not be immediately apparent during a visual inspection.
- Verify Seller Claims: Confirm that the seller’s statements about the car’s condition are accurate.
- Negotiate a Fair Price: Use the information from the OBD2 scan to negotiate a lower price if issues are found.
- Avoid Costly Repairs: Prevent unexpected repair costs by identifying potential problems before making a purchase.
7. How Do Vehicle History Reports Complement OBD2 Scans?
Vehicle history reports and OBD2 scans provide complementary insights into a used car’s condition. According to a study by the University of Y from the Research Department, on Date Z, combining vehicle history reports and OBD2 scans increases the accuracy of identifying potential car issues by X%. While a history report reveals past accidents, title issues, and mileage discrepancies, an OBD2 scan uncovers current mechanical or electrical problems. Together, they offer a comprehensive assessment.
- Comprehensive Assessment: Combine historical data with real-time diagnostic information for a thorough evaluation.
- Identify Discrepancies: Detect inconsistencies between the vehicle’s history and its current condition.
- Make Informed Decisions: Use both sources of information to make a confident and informed purchase decision.
- Reduce Risk: Minimize the risk of buying a used car with hidden problems or a questionable history.
8. How Do I Clear Fault Codes After Addressing the Issue?
Clearing fault codes should be done after addressing the underlying problem and verifying that the issue is resolved. Use the OBD2 scanner to clear the codes, but be aware that some codes may reappear if the problem persists. Always re-scan the system to confirm that no new codes have been triggered. Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at +1 (641) 206-8880 for assistance.
- Verify the Repair: Ensure that the underlying issue has been properly fixed before clearing the codes.
- Use the OBD2 Scanner: Follow the scanner’s instructions to clear the fault codes from the vehicle’s computer.
- Re-Scan the System: Confirm that no new codes have been triggered after clearing the old ones.
- Monitor for Recurrence: Keep an eye on the system to ensure that the codes do not reappear.
9. What Are the Limitations of Using an OBD2 Scanner?
While OBD2 scanners are powerful tools, they have limitations. They primarily focus on emissions-related issues and may not detect all mechanical problems. Advanced diagnostics often require specialized tools and expertise. Relying solely on fault codes without further investigation can lead to misdiagnosis.
- Limited Scope: OBD2 systems primarily monitor emissions-related components and may not detect all mechanical issues.
- Misinterpretation: Fault codes can be misleading and may require further investigation to determine the root cause.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Complex problems often require specialized tools, software, and expertise.
- Not a Replacement for Visual Inspection: An OBD2 scan should complement, not replace, a thorough visual inspection.
10. How Can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Help Me Choose the Right OBD2 Scanner?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive information and support to help you select the perfect OBD2 scanner for your needs. We provide detailed product specifications, comparisons, and customer reviews. Our experts can guide you in choosing a scanner that fits your budget and diagnostic requirements. We are located at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States.
- Expert Guidance: Our knowledgeable staff can provide personalized recommendations based on your needs and budget.
- Product Information: We offer detailed specifications, comparisons, and customer reviews to help you make an informed decision.
- Wide Selection: We carry a wide range of OBD2 scanners from leading brands, ensuring you find the perfect tool for your needs.
- Customer Support: Our customer support team is available to answer your questions and provide assistance with your purchase.
11. What is the Future of OBD2 Scanning Technology?
The future of OBD2 scanning technology involves greater integration with cloud-based diagnostics, enhanced data analytics, and more user-friendly interfaces. According to a study by the University of X from the Department of Future Technologies, on Date A, cloud-based diagnostics will increase by Y% in the next 5 years. Expect to see more advanced features, such as predictive maintenance and remote diagnostics, becoming standard in future OBD2 scanners.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Access to real-time data, software updates, and remote support through cloud connectivity.
- Enhanced Data Analytics: More sophisticated algorithms to analyze data and provide more accurate diagnoses.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Intuitive interfaces that make it easier for both professionals and DIYers to use the tools.
- Predictive Maintenance: The ability to predict potential problems before they occur, based on data analysis.
12. How Can I Stay Updated on the Latest OBD2 Scanner Technology?
Staying updated on the latest OBD2 scanner technology is crucial for maximizing diagnostic efficiency. Follow industry publications, attend trade shows, and participate in online forums to stay informed. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN also provides regular updates and insights into the latest advancements in OBD2 technology.
- Industry Publications: Subscribe to automotive industry magazines and online publications to stay informed.
- Trade Shows: Attend automotive trade shows to see the latest products and technologies firsthand.
- Online Forums: Participate in online forums and communities to share knowledge and learn from others.
- CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Updates: Check our website regularly for updates and insights on the latest OBD2 scanner technology.
13. What Common Mistakes Should I Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner?
Avoid common mistakes when using an OBD2 scanner to ensure accurate diagnoses. These include neglecting to verify fault codes with additional testing, ignoring live data, and failing to properly connect the scanner. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use reliable diagnostic resources.
- Not Verifying Fault Codes: Always perform additional tests to confirm the accuracy of fault codes.
- Ignoring Live Data: Pay attention to live data readings to identify intermittent issues and verify sensor functionality.
- Improper Connection: Ensure that the scanner is properly connected to the OBD2 port and that the ignition is turned on.
- Unreliable Resources: Use reliable diagnostic resources and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
14. How Do Environmental Factors Affect OBD2 Scanner Readings?
Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can influence OBD2 scanner readings. Extreme temperatures can affect sensor performance, leading to inaccurate data. High humidity can cause corrosion and connectivity issues, affecting the scanner’s ability to communicate with the vehicle’s computer.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect sensor performance and lead to inaccurate readings.
- Humidity: High humidity can cause corrosion and connectivity issues, affecting scanner performance.
- Altitude: Altitude can affect air pressure and fuel mixture, influencing sensor readings.
- Electromagnetic Interference: Nearby electronic devices can interfere with the scanner’s communication, causing errors.
15. How Can I Troubleshoot Common OBD2 Scanner Connection Problems?
Troubleshooting connection problems with an OBD2 scanner involves checking the OBD2 port, verifying the scanner’s power supply, and ensuring proper communication protocols. Clean the OBD2 port with a contact cleaner to remove corrosion. Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at +1 (641) 206-8880 for troubleshooting assistance.
- Check the OBD2 Port: Ensure that the OBD2 port is clean and free from corrosion.
- Verify Power Supply: Check that the scanner is receiving power from the vehicle’s battery.
- Communication Protocols: Ensure that the scanner supports the communication protocols used by your vehicle.
- Compatibility: Confirm that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
16. How Does OBD2 Scanner Data Help with Preventive Maintenance?
OBD2 scanner data plays a crucial role in preventive maintenance by allowing you to monitor the health of various vehicle systems and identify potential issues before they become major problems. By regularly scanning your vehicle, you can track sensor readings, check for fault codes, and identify trends that indicate the need for maintenance. According to a study by the University of Z from the Preventative Maintenance Department, on Date C, preventative maintenance using OBD2 scanners can extend the life of a vehicle by up to P%.
- Monitor System Health: Track the performance of various systems, such as the engine, transmission, and emissions control.
- Identify Potential Issues: Detect subtle changes in sensor readings that may indicate the need for maintenance.
- Schedule Maintenance: Plan maintenance tasks based on data from the OBD2 scanner to prevent breakdowns.
- Extend Vehicle Life: Proactively address issues before they become major problems, extending the life of your vehicle.
17. How Can I Customize My OBD2 Scanner Settings for Better Performance?
Customizing your OBD2 scanner settings can enhance its performance and provide more tailored diagnostic information. Depending on the scanner model, you can adjust parameters such as data refresh rates, display units, and alarm thresholds. Consult your scanner’s user manual for detailed instructions on customization options.
- Data Refresh Rates: Adjust the frequency at which the scanner updates data to optimize performance.
- Display Units: Choose the units of measurement that you prefer to use, such as Celsius or Fahrenheit.
- Alarm Thresholds: Set thresholds for sensor readings that trigger alarms, alerting you to potential issues.
- Custom Data Logging: Configure the scanner to log specific data parameters for later analysis.
18. What Are the Legal Considerations When Using an OBD2 Scanner?
When using an OBD2 scanner, be aware of the legal considerations related to data privacy and vehicle modifications. In some jurisdictions, it may be illegal to access or modify certain vehicle systems without proper authorization. Ensure that you comply with all applicable laws and regulations when using an OBD2 scanner.
- Data Privacy: Be mindful of data privacy regulations when accessing or storing vehicle data.
- Vehicle Modifications: Understand the legal implications of modifying vehicle systems using an OBD2 scanner.
- Authorization: Ensure that you have proper authorization before accessing or modifying certain vehicle systems.
- Compliance: Comply with all applicable laws and regulations when using an OBD2 scanner.
19. How Does the Cost of an OBD2 Scanner Compare to Professional Diagnostic Services?
The cost of an OBD2 scanner can vary widely, from affordable Bluetooth code readers to expensive professional-grade tools. While a professional diagnostic service can provide a comprehensive assessment of your vehicle’s condition, it can also be costly. Investing in an OBD2 scanner can save you money in the long run by allowing you to diagnose and address minor issues yourself. Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at our location: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, for scanner options.
- Cost-Effective: An OBD2 scanner can save you money on diagnostic services by allowing you to diagnose issues yourself.
- Professional Services: Professional services provide a comprehensive assessment but can be expensive.
- Long-Term Savings: Investing in a scanner can pay off over time by preventing costly repairs.
- DIY Diagnostics: A scanner empowers you to perform basic diagnostics and maintenance tasks at home.
20. How Can I Get the Most Accurate Readings from My OBD2 Scanner?
To obtain the most accurate readings from your OBD2 scanner, follow these best practices: Ensure the vehicle is properly warmed up, use a high-quality scanner, and verify readings with additional tests. Avoid scanning in extreme environmental conditions and keep the scanner software updated.
- Warm-Up Vehicle: Allow the vehicle to warm up to operating temperature before scanning.
- High-Quality Scanner: Use a reputable OBD2 scanner from a trusted brand.
- Verify Readings: Confirm readings with additional tests, such as a multimeter or smoke tester.
- Software Updates: Keep the scanner software updated to ensure compatibility and accuracy.
21. What Role Do Oxygen Sensors Play in OBD2 Diagnostics?
Oxygen sensors play a vital role in OBD2 diagnostics by monitoring the oxygen content in the exhaust gas. These sensors provide feedback to the engine control unit (ECU), which adjusts the fuel mixture to optimize combustion efficiency. Faulty oxygen sensors can trigger fault codes and affect engine performance.
- Monitor Exhaust Gas: Oxygen sensors measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gas.
- Feedback to ECU: The sensors provide feedback to the ECU, which adjusts the fuel mixture.
- Optimize Combustion: Proper oxygen sensor function optimizes combustion efficiency.
- Fault Codes: Faulty sensors can trigger codes and affect engine performance.
22. How Do Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensors Impact OBD2 Readings?
Mass Airflow (MAF) sensors measure the amount of air entering the engine, providing critical data for fuel management. Inaccurate MAF sensor readings can lead to a variety of performance issues, including poor fuel economy, rough idling, and reduced power. OBD2 scanners can detect MAF sensor problems by monitoring its output voltage or frequency.
- Measure Airflow: MAF sensors measure the amount of air entering the engine.
- Fuel Management: This data is crucial for proper fuel management and combustion.
- Performance Issues: Inaccurate readings can lead to poor fuel economy and rough idling.
- OBD2 Detection: Scanners can detect MAF sensor problems by monitoring its output.
23. How Do Throttle Position Sensors (TPS) Affect OBD2 Data?
Throttle Position Sensors (TPS) measure the position of the throttle plate, providing information to the ECU about the driver’s throttle input. Faulty TPS readings can cause erratic engine behavior, such as stalling, surging, or hesitation. OBD2 scanners can monitor TPS voltage to detect abnormalities.
- Measure Throttle Position: TPS sensors measure the position of the throttle plate.
- Driver Input: This provides information to the ECU about the driver’s throttle input.
- Erratic Engine Behavior: Faulty readings can cause stalling, surging, or hesitation.
- Voltage Monitoring: Scanners can monitor TPS voltage to detect abnormalities.
24. How Do Coolant Temperature Sensors Influence OBD2 Readings?
Coolant Temperature Sensors measure the temperature of the engine coolant, providing data to the ECU for adjusting fuel mixture and ignition timing. Inaccurate coolant temperature readings can lead to poor engine performance, reduced fuel economy, and difficulty starting the engine. OBD2 scanners can monitor coolant temperature to detect sensor failures.
- Measure Coolant Temperature: Coolant Temperature Sensors measure the temperature of the engine coolant.
- Fuel Mixture and Timing: This data is used to adjust fuel mixture and ignition timing.
- Poor Engine Performance: Inaccurate readings can lead to poor performance and reduced fuel economy.
- Sensor Failure Detection: Scanners can monitor coolant temperature to detect sensor failures.
25. What Role Do Catalytic Converters Play in OBD2 Diagnostics?
Catalytic converters reduce harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less harmful substances. OBD2 systems monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter using oxygen sensors located before and after the converter. Inefficient catalytic converters can trigger fault codes and result in failed emissions tests.
- Reduce Emissions: Catalytic converters reduce harmful emissions.
- Pollutant Conversion: They convert pollutants into less harmful substances.
- Efficiency Monitoring: OBD2 systems monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
- Fault Codes: Inefficient converters can trigger fault codes.
26. How Can I Use an OBD2 Scanner to Check My Vehicle’s Emissions Readiness?
An OBD2 scanner can check your vehicle’s emissions readiness by monitoring the status of various diagnostic monitors. These monitors assess the functionality of emissions-related systems, such as the oxygen sensors, catalytic converter, and evaporative emissions control system. If all monitors are ready, your vehicle is likely to pass an emissions test.
- Monitor Status: Scanners can monitor the status of diagnostic monitors.
- Emissions Systems: These monitors assess the functionality of emissions-related systems.
- Emissions Test Readiness: If all monitors are ready, your vehicle is likely to pass an emissions test.
- Troubleshooting: If monitors are not ready, the scanner can help identify the underlying issues.
27. How Can I Choose the Right OBD2 Adapter for My Smartphone?
When choosing an OBD2 adapter for your smartphone, consider compatibility, features, and user reviews. Ensure the adapter is compatible with your phone’s operating system (iOS or Android) and supports the necessary communication protocols. Look for features such as Bluetooth connectivity, real-time data display, and fault code reading. Read user reviews to assess the adapter’s reliability and performance.
- Compatibility: Ensure the adapter is compatible with your phone’s operating system.
- Communication Protocols: Confirm that the adapter supports the necessary communication protocols.
- Features: Look for features such as Bluetooth connectivity and real-time data display.
- User Reviews: Read user reviews to assess the adapter’s reliability and performance.
28. What is the Difference Between OBD1 and OBD2 Scanners?
OBD1 and OBD2 scanners differ in terms of their communication protocols, diagnostic capabilities, and vehicle coverage. OBD1 systems were used on vehicles manufactured before 1996 and typically used proprietary communication protocols specific to each manufacturer. OBD2 systems, which became standard in 1996, use a standardized communication protocol and offer more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Communication Protocols: OBD1 systems used proprietary protocols, while OBD2 systems use a standardized protocol.
- Diagnostic Capabilities: OBD2 systems offer more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Vehicle Coverage: OBD1 systems were used on vehicles manufactured before 1996, while OBD2 systems are used on vehicles manufactured from 1996 onwards.
- Data Access: OBD2 systems provide easier access to diagnostic data.
29. How Can I Update My OBD2 Scanner’s Firmware?
Updating your OBD2 scanner’s firmware is essential for ensuring compatibility with the latest vehicle models and diagnostic protocols. Firmware updates typically include bug fixes, performance improvements, and new features. Consult your scanner’s user manual for instructions on how to update the firmware. Usually, this involves connecting the scanner to a computer and using the manufacturer’s software to download and install the update.
- Compatibility: Firmware updates ensure compatibility with the latest vehicle models.
- Bug Fixes: Updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements.
- New Features: Updates may add new features and diagnostic capabilities.
- User Manual: Consult your scanner’s user manual for update instructions.
30. How Does an OBD2 Scanner Help in Diagnosing Transmission Problems?
An OBD2 scanner can help diagnose transmission problems by monitoring transmission-related parameters, such as transmission fluid temperature, gear ratios, and shift solenoid activity. Fault codes related to the transmission can provide valuable clues about the nature and location of the problem. Live data can also help identify abnormal transmission behavior. For personalized assistance with transmission diagnostics, contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN at +1 (641) 206-8880.
- Monitor Parameters: Scanners can monitor transmission-related parameters.
- Fault Codes: Transmission-related fault codes provide clues about the problem.
- Live Data: Live data can help identify abnormal transmission behavior.
- Diagnostic Assistance: Scanners can assist in diagnosing transmission problems.
Discover the convenience and efficiency of diagnosing car problems with an OBD2 scanner. For expert advice and to explore our extensive range of automotive tools and equipment, contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN. Let us help you keep your vehicle running smoothly.