Where Is The Diagnostic Port On My Car is a common question for car owners. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides a complete guide on finding and understanding your car’s OBD2 port, empowering you to maintain your vehicle efficiently. With our resources, you’ll gain insights into vehicle diagnostics, diagnostic scanners, and fault codes.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the OBD2 Port: Your Car’s Diagnostic Gateway
- 1.1 What Exactly is an OBD2 Port?
- 1.2 Why is the OBD2 Port So Important?
- 2. Locating the OBD2 Port: Where to Look
- 2.1 Common OBD2 Port Locations
- 2.2 Tips for Finding Your OBD2 Port
- 3. The OBD2 Connector and Pinout: A Technical Overview
- 3.1 The Standard 16-Pin Configuration
- 3.2 Key OBD2 Pinout Functions
- 3.3 Communication Protocols
- 4. Unlocking the Power of the OBD2 Port: What Can You Do?
- 4.1 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.2 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.3 Monitoring Real-Time Vehicle Data
- 4.4 Performing Advanced Diagnostics and Tests
- 5. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner: A Buyer’s Guide
- 5.1 Types of OBD2 Scanners
- 5.2 Features to Consider
- 5.3 Popular OBD2 Scanner Brands
- 6. Taking Vehicle Diagnostics to the Next Level with Advanced Tools
- 6.1 Introducing the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro
- 6.2 Key Features of the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro
- 6.3 Benefits of Using the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro
- 7. Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
- 7.1 Scanner Not Connecting
- 7.2 Inaccurate Readings
- 7.3 Difficulty Clearing Codes
- 8. OBD2 Port and Vehicle Security: Addressing Concerns
- 8.1 Potential Security Risks
- 8.2 Security Measures
- 9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Ports
- 9.1 What if I can’t find the OBD2 location?
- 9.2 Are all OBD2 ports the same?
- 9.3 How many OBD2 ports does a car have?
- 9.4 Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my car?
- 9.5 Is it safe to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time?
- 9.6 Can I use the OBD2 port to improve my car’s performance?
- 9.7 What is the difference between OBD1 and OBD2?
- 9.8 How do I know if my car has an OBD2 port?
- 9.9 Can I use my smartphone to read OBD2 data?
- 9.10 Where can I find reliable information about OBD2 codes?
- 10. Conclusion: Empowering You with OBD2 Knowledge
- Ready to Dive Deeper? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Today!
1. Understanding the OBD2 Port: Your Car’s Diagnostic Gateway
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) port serves as a vital interface, granting access to your vehicle’s internal computer system. Think of it as the car’s dedicated data hub, specifically designed to facilitate vehicle diagnostics. This port allows mechanics and car owners alike to connect diagnostic scanners, retrieve error codes, and evaluate the overall health and status of the vehicle. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Institute of Transportation Studies, access to OBD2 data has significantly improved vehicle maintenance and reduced emissions since its widespread adoption (University of California, Berkeley, Institute of Transportation Studies, 2020).
1.1 What Exactly is an OBD2 Port?
The OBD2 port, standardized in the mid-1990s, provides access to a wealth of information about your vehicle’s performance and health. It’s a standardized 16-pin connector (SAE J1962) typically found inside the passenger compartment. This standardization allows any compliant diagnostic tool to interface with any vehicle equipped with an OBD2 port, regardless of make or model.
1.2 Why is the OBD2 Port So Important?
The OBD2 port’s significance lies in its ability to provide valuable insights into various aspects of your vehicle. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBD2 systems are crucial for ensuring vehicles meet emission standards (EPA, 2023).
- Emission Control: It monitors components related to emissions, ensuring your car complies with environmental regulations.
- Engine Performance: It provides data on engine performance, identifying potential issues before they become major problems.
- Troubleshooting: It allows for quick and accurate diagnosis of problems through diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Preventative Maintenance: Access to real-time data allows car owners to practice preventative maintenance, addressing minor issues before they escalate.
2. Locating the OBD2 Port: Where to Look
Finding the OBD2 port is the first step to accessing your vehicle’s diagnostic information. While its location can vary slightly depending on the car’s make and model, it’s generally found in a readily accessible location within the passenger compartment.
2.1 Common OBD2 Port Locations
- Under the Dashboard: The most common location is under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Check the area beneath the steering wheel, near the pedals.
- Near the Center Console: In some vehicles, the OBD2 port might be located near the center console, often concealed by a small panel.
- Inside the Glove Compartment: Although less frequent, a few car models house the OBD2 port inside the glove compartment.
2.2 Tips for Finding Your OBD2 Port
- Consult Your Owner’s Manual: The owner’s manual is your go-to resource. It will specify the exact location of the OBD2 port for your particular car model.
- Use an Online OBD2 Port Finder: Several online tools and websites offer OBD2 port location finders. Simply enter your vehicle’s make, model, and year to find its location.
- Look for the Standard Connector: The OBD2 port is a distinct 16-pin connector. Familiarize yourself with its appearance to quickly identify it.
 Illustration of typical OBD2 port locations in a common vehicle
Illustration of typical OBD2 port locations in a common vehicle
3. The OBD2 Connector and Pinout: A Technical Overview
The OBD2 connector is a standardized interface that allows diagnostic tools to communicate with your vehicle’s computer. Understanding the pinout configuration can be helpful for advanced users and developers.
3.1 The Standard 16-Pin Configuration
The OBD2 connector features a 16-pin (2×8) configuration, adhering to the SAE J1962 standard. Each pin serves a specific purpose, facilitating communication between the diagnostic tool and the vehicle’s various systems.
3.2 Key OBD2 Pinout Functions
Here’s a quick overview of some essential OBD2 pin functions:
- Pin 4: Chassis Ground Provides a common ground reference for the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Pin 5: Signal Ground Provides a ground reference for the diagnostic signals.
- Pin 6: CAN High (J-2284) Carries the high signal for the CAN bus communication protocol.
- Pin 7: K-Line (ISO 9141-2) Used for ISO 9141-2 communication protocol (older vehicles).
- Pin 10: J1850 Bus Negative Used for SAE J1850 communication protocol.
- Pin 14: CAN Low (J-2284) Carries the low signal for the CAN bus communication protocol.
- Pin 16: Battery Voltage Provides power to the diagnostic tool.
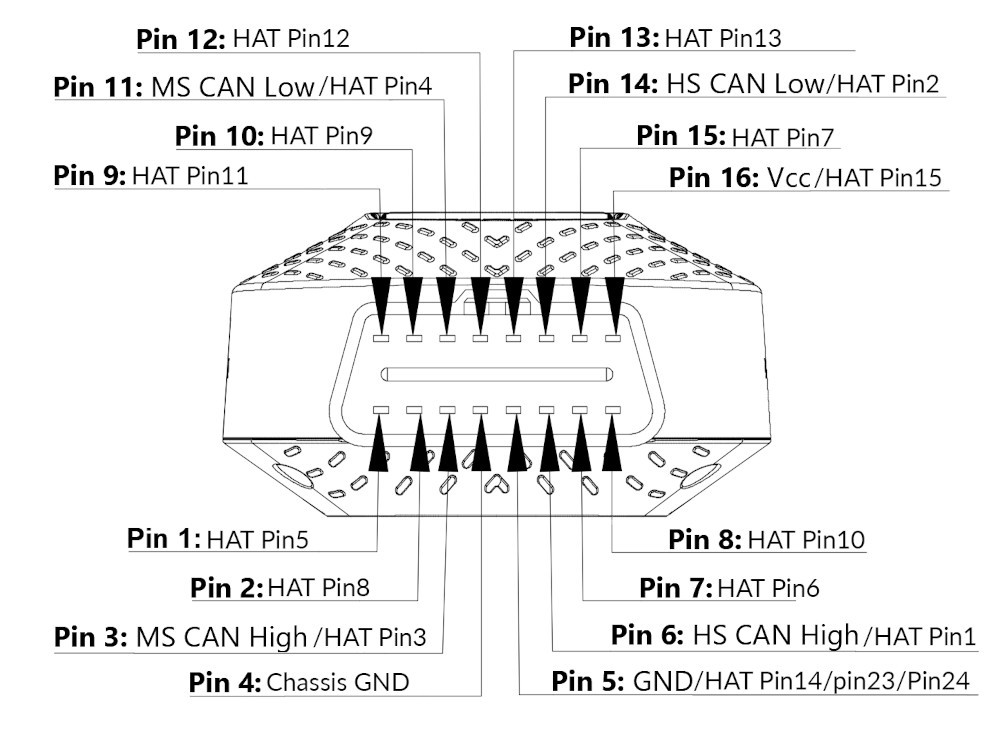 OBD2 connector pinouts from autopi device
OBD2 connector pinouts from autopi device
3.3 Communication Protocols
The OBD2 port supports several communication protocols, including:
- SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width)
- SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
- ISO 9141-2 (International Organization for Standardization)
- ISO 14230-4 KWP2000 (Keyword Protocol 2000)
- CAN (Controller Area Network) – ISO 15765-4
The CAN protocol is the most modern and widely used protocol in current vehicles.
4. Unlocking the Power of the OBD2 Port: What Can You Do?
The OBD2 port opens up a world of possibilities for vehicle diagnostics, monitoring, and customization. By connecting a compatible scanner or diagnostic tool, you can access a wealth of data and perform various functions.
4.1 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
One of the primary functions of the OBD2 port is to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These codes are generated by the vehicle’s computer when it detects a problem with a specific system or component. DTCs can help pinpoint the source of the issue, allowing for targeted repairs.
4.2 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
In some cases, after addressing the underlying problem, you can use an OBD2 scanner to clear the DTCs. This will turn off the check engine light (CEL) or other warning lights on the dashboard. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the issue has been resolved before clearing the codes, as they may reappear if the problem persists.
4.3 Monitoring Real-Time Vehicle Data
The OBD2 port allows you to monitor various real-time data parameters, such as:
- Engine Speed (RPM)
- Vehicle Speed
- Engine Coolant Temperature
- Intake Air Temperature
- Mass Air Flow (MAF)
- Oxygen Sensor Readings
- Fuel Trim
This data can be invaluable for diagnosing performance issues, tracking fuel economy, and monitoring the overall health of your vehicle.
4.4 Performing Advanced Diagnostics and Tests
With specialized OBD2 scanners and software, you can perform more advanced diagnostics and tests, such as:
- Actuator Tests: Activate specific components, like fuel injectors or solenoids, to verify their functionality.
- Sensor Calibration: Calibrate sensors to ensure accurate readings.
- Module Programming: Reprogram or update control modules.
These advanced functions are typically used by experienced mechanics and technicians.
 Keywords about the OBD2 connector and why its important as a gateway
Keywords about the OBD2 connector and why its important as a gateway
5. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner: A Buyer’s Guide
With a wide variety of OBD2 scanners available on the market, selecting the right one for your needs can be challenging. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
5.1 Types of OBD2 Scanners
- Basic Code Readers: These are the most affordable options, capable of reading and clearing DTCs.
- Enhanced Scanners: These offer additional features, such as real-time data monitoring, freeze frame data, and enhanced diagnostic capabilities.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These are the most advanced and expensive scanners, offering comprehensive diagnostics, bi-directional controls, and module programming capabilities.
5.2 Features to Consider
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner with an intuitive interface and easy-to-read display.
- Functionality: Select a scanner that offers the features you need, such as real-time data, graphing, and advanced diagnostics.
- Updateability: Opt for a scanner that can be updated with the latest software and vehicle coverage.
5.3 Popular OBD2 Scanner Brands
Some of the popular OBD2 scanner brands include:
- Autel
- Launch
- Innova
- BlueDriver
6. Taking Vehicle Diagnostics to the Next Level with Advanced Tools
While basic OBD2 scanners provide essential diagnostic capabilities, advanced tools like the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro can unlock even deeper insights into your vehicle’s performance.
6.1 Introducing the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro
The AutoPi CAN-FD Pro is a powerful device that connects to your car’s OBD2 port, providing faster and more detailed insights into your vehicle’s performance. It allows you to track critical systems like the engine and emissions, offering a comprehensive view of your car’s health.
6.2 Key Features of the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro
- Advanced Diagnostics: Access a wider range of diagnostic data and perform advanced tests.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Monitor critical vehicle parameters in real-time with high precision.
- Data Logging: Record and analyze vehicle data for performance optimization and troubleshooting.
- Remote Access: Access your vehicle’s data remotely from anywhere in the world.
- Customizable Alerts: Set up alerts for specific events or conditions, such as low battery voltage or high engine temperature.
6.3 Benefits of Using the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro
- Improved Vehicle Performance: Optimize your vehicle’s performance by monitoring and analyzing key data parameters.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Identify and address potential issues early, preventing costly repairs.
- Enhanced Safety: Monitor critical safety systems and receive alerts for potential problems.
- Increased Fuel Efficiency: Track your fuel consumption and identify ways to improve fuel economy.
 The new CAN-FD AutoPi TMU Device
The new CAN-FD AutoPi TMU Device
7. Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
While the OBD2 port is a valuable tool, you may encounter some issues when using it. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting tips:
7.1 Scanner Not Connecting
- Check the Connection: Ensure the scanner is securely plugged into the OBD2 port.
- Verify Power: Make sure the scanner is receiving power.
- Check Compatibility: Verify that the scanner is compatible with your vehicle.
- Inspect the OBD2 Port: Check for any damage or corrosion on the OBD2 port.
7.2 Inaccurate Readings
- Use a Quality Scanner: Low-quality scanners may provide inaccurate readings.
- Check Sensor Calibration: Ensure the sensors are properly calibrated.
- Inspect Wiring: Check for any damaged or loose wiring connections.
7.3 Difficulty Clearing Codes
- Address the Underlying Issue: Ensure the underlying problem has been resolved before clearing the codes.
- Use the Correct Procedure: Follow the scanner’s instructions for clearing codes.
- Check for Permanent Codes: Some codes cannot be cleared until the vehicle passes certain tests.
8. OBD2 Port and Vehicle Security: Addressing Concerns
With the increasing connectivity of modern vehicles, security concerns surrounding the OBD2 port have emerged. It’s essential to be aware of these concerns and take steps to protect your vehicle.
8.1 Potential Security Risks
- Unauthorized Access: Malicious actors could potentially gain access to your vehicle’s systems through the OBD2 port.
- Malware Injection: Hackers could inject malware into your vehicle’s control modules.
- Data Theft: Sensitive vehicle data could be stolen through the OBD2 port.
8.2 Security Measures
- Use Reputable Scanners: Only use OBD2 scanners from reputable manufacturers.
- Keep Software Updated: Ensure your scanner’s software is up to date with the latest security patches.
- Be Cautious with Third-Party Apps: Exercise caution when using third-party apps that access your vehicle’s data through the OBD2 port.
- Consider a Security Device: Install a security device that monitors and protects your OBD2 port.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBD2 Ports
9.1 What if I can’t find the OBD2 location?
Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual or search online for your specific vehicle’s diagnostic connector location. You can also consult CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN’s documentation for assistance.
9.2 Are all OBD2 ports the same?
Yes, all OBD2 ports and connectors follow the same standardization (SAE J1962).
9.3 How many OBD2 ports does a car have?
Typically, a standard passenger car has one OBD2 port.
9.4 Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my car?
Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with all vehicles manufactured after 1996. However, it’s always best to check the scanner’s compatibility list before purchasing.
9.5 Is it safe to leave an OBD2 scanner plugged in all the time?
Leaving an OBD2 scanner plugged in can drain your battery, especially if the scanner draws power continuously. It’s generally recommended to unplug the scanner when not in use.
9.6 Can I use the OBD2 port to improve my car’s performance?
While the OBD2 port itself cannot directly improve performance, it allows you to monitor key performance parameters and identify areas for improvement.
9.7 What is the difference between OBD1 and OBD2?
OBD1 was a non-standardized system used in vehicles before 1996. OBD2 is a standardized system that provides more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
9.8 How do I know if my car has an OBD2 port?
All cars manufactured after 1996 are required to have an OBD2 port.
9.9 Can I use my smartphone to read OBD2 data?
Yes, you can use a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi OBD2 adapter to connect your smartphone to your car’s OBD2 port and read data using a compatible app.
9.10 Where can I find reliable information about OBD2 codes?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive database of OBD2 codes and their meanings. You can also consult other reputable online resources and repair manuals.
 different OBD2 port locations in a car
different OBD2 port locations in a car
10. Conclusion: Empowering You with OBD2 Knowledge
The OBD2 diagnostic port is a powerful tool that provides valuable insights into your vehicle’s health and performance. By understanding its location, functionality, and potential, you can take proactive steps to maintain your car, troubleshoot issues, and optimize its performance.
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is your trusted resource for all things OBD2. We provide comprehensive information, tools, and resources to help you unlock the full potential of your vehicle’s diagnostic capabilities.
Ready to Dive Deeper? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Today!
Are you looking for specific parts or tools? Do you have questions about vehicle diagnostics? CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to help!
Contact us today for expert advice and assistance:
- Address: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
Let CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN be your partner in keeping your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. We offer detailed information on auto parts, repair tools (specifications, brands, and durability), user reviews, and reputable suppliers.
Don’t let vehicle maintenance be a challenge. Contact us today and experience the CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN difference!
Let us help you find the perfect tools and parts for your needs. Contact us now!