Innova 3011 Codes provide crucial insights into your vehicle’s health, enabling accurate diagnostics and efficient repairs, especially when you explore resources from CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN. This comprehensive guide delves into understanding, troubleshooting, and resolving Innova 3011 diagnostic trouble codes, ensuring you stay informed and in control of your car’s maintenance. Enhance your diagnostic skills and car repair knowledge with our expert insights.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Innova 3011 Codes: A Comprehensive Overview
- 1.1. Decoding the Structure of Innova 3011 Codes
- 1.2. Generic vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes: Key Differences
- 1.3. Common Innova 3011 Codes and Their Meanings
- 1.4. The Role of Innova Scanners in Interpreting Codes
- 2. Troubleshooting Common Innova 3011 Codes: Step-by-Step Guide
- 2.1. Verifying the Code and Gathering Information
- 2.2. Inspecting Related Components: Visual and Physical Checks
- 2.3. Testing Electrical Circuits with a Multimeter
- 2.4. Replacing Faulty Parts and Clearing the Code
- 3. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Innova 3011 Codes
- 3.1. Utilizing Live Data for Real-Time Monitoring
- 3.2. Performing Pinpoint Tests: Isolate the Root Cause
- 3.3. Conducting System Scans: Identify Related Codes
- 4. Preventing Innova 3011 Codes: Maintenance Tips and Best Practices
- 4.1. Following a Regular Maintenance Schedule
- 4.2. Using High-Quality Parts: Ensure Reliability
- 4.3. Addressing Minor Issues Promptly: Prevent Escalation
1. Understanding Innova 3011 Codes: A Comprehensive Overview
What exactly are Innova 3011 codes, and why are they essential for automotive diagnostics? Innova 3011 codes are diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) generated by Innova’s diagnostic tools, like the Innova 3100, Innova 3130, and other OBD2 scanners, pinpointing specific issues within your vehicle’s systems. These codes act as a roadmap, guiding technicians and car owners to the source of problems, facilitating quicker and more accurate repairs. By understanding the structure, types, and significance of these codes, you can effectively troubleshoot and maintain your vehicle, saving time and money on potentially unnecessary repairs.
1.1. Decoding the Structure of Innova 3011 Codes
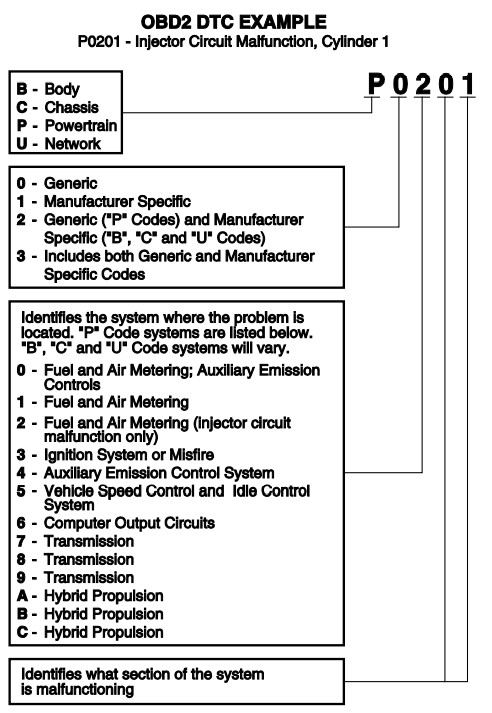
How are Innova 3011 codes structured, and what does each component signify? Innova 3011 codes, like all OBD2 DTCs, follow a standardized five-character format, each character providing specific information about the issue. The first character indicates the main system affected (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, and U for Network). The second character identifies whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1). The third character specifies the subsystem, while the fourth and fifth characters pinpoint the exact component or circuit malfunctioning. Understanding this structure enables a systematic approach to diagnosing and resolving car problems.
For instance, a code like “P0301” would break down as follows:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission, etc.)
- 0: Generic (SAE-defined) code
- 3: Ignition system or misfire
- 01: Cylinder 1 misfire
This structured approach helps mechanics and DIY enthusiasts quickly narrow down the potential causes of the problem, speeding up the diagnostic process and reducing the chances of misdiagnosis. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the standardization of these codes ensures that any OBD2 scanner can read and interpret them, regardless of the vehicle’s make or model year.
1.2. Generic vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes: Key Differences
What distinguishes generic OBD2 codes from manufacturer-specific codes within the Innova 3011 system? Generic OBD2 codes are standardized codes defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and are common across all vehicle makes and models, while manufacturer-specific codes are unique to particular car brands and models. Generic codes cover basic emission-related issues, while manufacturer-specific codes address more complex problems unique to a specific vehicle. Recognizing the difference is crucial for accurate diagnosis, as manufacturer-specific codes often provide more detailed information about the issue.
| Feature | Generic OBD2 Codes | Manufacturer-Specific Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Standardization | Standardized by SAE | Defined by individual vehicle manufacturers |
| Coverage | Basic emission-related issues | Complex, model-specific issues |
| Detail Level | Less detailed, broad descriptions | More detailed, specific descriptions |
| Applicability | Applicable to all OBD2-compliant vehicles | Applicable only to specific makes and models |
| Diagnostic Assistance | Good starting point for common issues | Essential for diagnosing unique vehicle problems |
| Examples | P0300 (Random Misfire Detected), P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold) | P1450 (Ford – Unable to Bleed Fuel Tank Vacuum), B1000 (Mercedes-Benz – Control Unit Malfunction) |
Understanding these differences is crucial for proper diagnostics. For example, if an Innova 3011 scanner displays a generic code like P0300 (Random Misfire Detected), it indicates a general engine misfire issue. However, a manufacturer-specific code, like P1450 for Ford vehicles (Unable to Bleed Fuel Tank Vacuum), points to a very specific problem within the fuel system. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), technicians who understand the difference between generic and manufacturer-specific codes are more efficient in diagnosing and repairing vehicles.
1.3. Common Innova 3011 Codes and Their Meanings
What are some of the most frequently encountered Innova 3011 codes, and what do they typically indicate? Common Innova 3011 codes include P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1), P0300 (Random Misfire Detected), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold). P0171 often suggests issues with the fuel system, such as a vacuum leak or a faulty MAF sensor. P0300 indicates engine misfires, which could stem from spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors. P0420 points to problems with the catalytic converter’s efficiency. Knowing these common codes and their potential causes can significantly speed up the diagnostic process and help prioritize troubleshooting steps.
| Code | Description | Potential Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean, Bank 1 | Vacuum leak, faulty MAF sensor, fuel pump issues, clogged fuel filter |
| P0300 | Random Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold | Failing catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty oxygen sensors |
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, intake leaks, wiring issues |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected | Faulty EGR valve, clogged EGR passages, vacuum leaks |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (small leak) | Loose or damaged fuel cap, cracked hoses, faulty purge valve |
| P0507 | Idle Air Control System RPM Higher Than Expected | Vacuum leak, faulty IAC valve, throttle body issues |
According to Innova’s user manuals and diagnostic guides, understanding these common codes is essential for both professional technicians and DIY car enthusiasts. For example, the Innova 3100 and Innova 3160g scanners provide code definitions and possible causes directly on the device, making it easier for users to diagnose and address these issues. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN also offers detailed resources and guides that expand on these common codes, providing additional troubleshooting tips and repair solutions.
1.4. The Role of Innova Scanners in Interpreting Codes
How do Innova scanners assist in interpreting and utilizing Innova 3011 codes effectively? Innova scanners, such as the Innova 3100 and Innova 3160g, are designed to retrieve and interpret OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes, providing code definitions and potential causes directly on the device. These scanners often include features like ABS and SRS code reading, live data streaming, and freeze frame data, offering a comprehensive view of the vehicle’s condition. By using Innova scanners, technicians and car owners can quickly identify problems, access repair information, and verify repairs, streamlining the diagnostic process and reducing downtime.
| Feature | Innova 3100 | Innova 3160g | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Code Reading | Reads and clears OBD2 codes | Reads and clears OBD2, ABS, and SRS codes | Comprehensive coverage of vehicle systems |
| Data Streaming | Live data stream for engine parameters | Enhanced live data stream with graphing capabilities | Real-time monitoring of vehicle performance |
| Freeze Frame Data | Captures data when a code is triggered | Enhanced freeze frame data with more parameters | Detailed snapshot of conditions when a problem occurred |
| RepairSolutions2 App | Compatible with RepairSolutions2 app for vehicle-specific fixes | Compatible with RepairSolutions2 app for vehicle-specific fixes and advanced diagnostics | Access to a database of verified fixes and maintenance schedules |
| Display | Basic LCD display | Color LCD display with enhanced graphics | Easier to read and interpret data |
| Additional Features | Battery and alternator test, OBD2 hotkeys | Battery and alternator test, OBD2 hotkeys, oil reset, and TPMS reset functions | Additional diagnostic and maintenance capabilities |
| User Interface | Simple and straightforward | More advanced and intuitive | Suits both beginners and experienced users |
According to Innova’s product documentation, the use of a scanner like the Innova 3100 or 3160g can significantly reduce diagnostic time. For instance, the RepairSolutions2 app provides vehicle-specific repair information, including the most likely fix for a given code, along with the parts and tools needed. This information is compiled from a database of millions of verified fixes, ensuring that users have access to reliable and accurate repair solutions. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers tutorials and guides on how to use these scanners effectively, maximizing their diagnostic capabilities and ensuring accurate vehicle maintenance.
2. Troubleshooting Common Innova 3011 Codes: Step-by-Step Guide
What are the key steps in troubleshooting common Innova 3011 codes, ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective repairs? Troubleshooting Innova 3011 codes involves verifying the code, gathering additional information, inspecting related components, and performing necessary repairs. Start by confirming the code with a reliable scanner, then research the code’s meaning and potential causes. Next, visually inspect related components for damage or wear, and use a multimeter to test electrical circuits. Finally, replace faulty parts and clear the code to verify the repair. Following this methodical approach ensures accurate diagnosis and effective resolution of car issues.
2.1. Verifying the Code and Gathering Information
How do you properly verify an Innova 3011 code and gather all necessary information for effective troubleshooting? Verifying an Innova 3011 code involves using a reliable OBD2 scanner to confirm the presence of the code and its associated description. Once the code is verified, gather additional information by researching the code’s potential causes, symptoms, and common fixes. Consult vehicle-specific repair manuals, online forums, and databases like the RepairSolutions2 app. This comprehensive approach provides a solid foundation for accurate diagnosis and effective troubleshooting.
To effectively verify a code and gather information, consider these steps:
- Use a Reliable Scanner: Connect a trusted OBD2 scanner, such as the Innova 3100 or 3160g, to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Confirm the Code: Read the code displayed by the scanner and verify its description.
- Record Freeze Frame Data: Capture any freeze frame data associated with the code, as this provides a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions when the code was triggered.
- Research Potential Causes: Consult vehicle-specific repair manuals, online forums, and databases to understand the potential causes of the code.
- Note Symptoms: Document any symptoms the vehicle is exhibiting, such as rough idling, decreased fuel economy, or unusual noises.
- Check Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs): Review TSBs issued by the vehicle manufacturer for any known issues related to the code.
According to Innova’s diagnostic guides, gathering this information is crucial for accurate troubleshooting. For example, if the scanner displays a P0171 code (System Too Lean, Bank 1), researching the code reveals potential causes such as vacuum leaks, a faulty MAF sensor, or fuel delivery issues. Noting symptoms like rough idling and decreased fuel economy can further narrow down the possible causes. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed guides and resources that provide step-by-step instructions on how to verify codes and gather information effectively.
2.2. Inspecting Related Components: Visual and Physical Checks
What visual and physical checks should be performed on components related to Innova 3011 codes, ensuring thorough inspection? Inspecting related components involves visually examining parts for damage, wear, or leaks, and physically checking their functionality. For example, if troubleshooting a P0171 code, inspect vacuum hoses for cracks or disconnections, check the MAF sensor for contamination, and examine the fuel system for leaks. Use a multimeter to test electrical components for proper voltage and resistance. Thorough visual and physical checks can reveal obvious issues that might trigger the code.
| Component | Visual Checks | Physical Checks |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Hoses | Cracks, disconnections, brittleness | Check for vacuum leaks using a smoke machine or by spraying carburetor cleaner around connections |
| MAF Sensor | Contamination, damage to the sensor wire or film | Clean the sensor with MAF sensor cleaner; use a multimeter to test the sensor’s voltage and frequency |
| Fuel Injectors | Leaks, physical damage | Use a stethoscope to listen for proper injector clicking; check injector resistance with a multimeter |
| Spark Plugs | Wear, damage, carbon buildup | Check spark plug gap; inspect for signs of oil fouling or excessive wear |
| Ignition Coils | Cracks, damage | Test coil resistance with a multimeter; use a spark tester to check for spark |
| Catalytic Converter | Physical damage, excessive heat | Check for exhaust leaks before the converter; use an infrared thermometer to measure inlet and outlet temperatures |
| Oxygen Sensors | Physical damage, wiring issues | Test sensor voltage and response time with a multimeter |
| EGR Valve | Carbon buildup, damage | Manually actuate the valve to check for proper movement; check for vacuum at the EGR valve during operation |
According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), a thorough visual and physical inspection is crucial for accurate diagnostics. For example, a cracked vacuum hose can cause a P0171 code by allowing unmetered air into the engine, leading to a lean condition. Similarly, a contaminated MAF sensor can provide inaccurate readings, resulting in incorrect fuel delivery. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed guides and videos that demonstrate how to perform these inspections effectively, ensuring that users can identify potential issues and address them promptly.
2.3. Testing Electrical Circuits with a Multimeter
How do you effectively use a multimeter to test electrical circuits related to Innova 3011 codes, ensuring accurate readings? Testing electrical circuits with a multimeter involves checking voltage, resistance, and continuity to identify wiring issues, faulty sensors, or malfunctioning components. Start by identifying the correct terminals and test points using a wiring diagram. Set the multimeter to the appropriate setting (voltage, resistance, or continuity) and take measurements. Compare the readings to the specified values in the vehicle’s repair manual. Accurate multimeter testing can pinpoint electrical problems that are not visible through visual inspection.
| Measurement | Multimeter Setting | Procedure | What to Look For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage | DC Voltage | Connect the red lead to the positive terminal and the black lead to the negative terminal of the circuit | Compare the reading to the specified voltage in the repair manual; look for voltage drops or excessively high readings |
| Resistance | Ohms (Ω) | Disconnect the circuit and connect the multimeter leads across the component | Compare the reading to the specified resistance in the repair manual; look for open circuits (infinite resistance) or shorts (zero resistance) |
| Continuity | Continuity Mode | Disconnect the circuit and connect the multimeter leads across the wire or component | The multimeter should beep or display a low resistance value if the circuit is complete; no beep indicates an open circuit |
| Ground | Continuity Mode | Connect the black lead to a known good ground and the red lead to the component’s ground wire | The multimeter should beep or display a low resistance value if the component is properly grounded |
According to Fluke Corporation, a leading manufacturer of multimeters, proper multimeter usage is essential for accurate electrical diagnostics. For example, if troubleshooting a P0101 code (MAF Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem), a multimeter can be used to check the MAF sensor’s voltage and frequency. By comparing the readings to the specified values in the vehicle’s repair manual, technicians can determine if the sensor is functioning correctly or needs to be replaced. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers tutorials and guides on how to use a multimeter effectively, ensuring that users can accurately diagnose electrical issues and perform necessary repairs.
2.4. Replacing Faulty Parts and Clearing the Code
What is the proper procedure for replacing faulty parts and clearing Innova 3011 codes, ensuring a successful repair? Replacing faulty parts involves identifying the defective component through diagnostic testing, obtaining a replacement part that meets OEM specifications, and carefully installing the new part. After replacing the part, use an OBD2 scanner to clear the trouble code and monitor the vehicle to ensure the code does not return. A test drive is recommended to verify that the repair has resolved the issue and that the vehicle is functioning correctly. This process ensures a successful repair and prevents further complications.
To properly replace a faulty part and clear the code, follow these steps:
- Identify the Faulty Part: Use diagnostic testing, such as visual inspections, multimeter tests, and scanner data, to confirm the defective component.
- Obtain a Replacement Part: Purchase a replacement part that meets or exceeds the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications. Using high-quality parts ensures reliability and proper performance.
- Disconnect the Battery: Before replacing any electrical component, disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent electrical shorts or damage.
- Install the New Part: Carefully install the new part, following the vehicle’s repair manual for proper procedures and torque specifications.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Clear the Code: Use an OBD2 scanner to clear the trouble code from the vehicle’s computer.
- Monitor the Vehicle: After clearing the code, monitor the vehicle to ensure the code does not return. Drive the vehicle under various conditions to verify that the repair has resolved the issue.
According to the National Automotive Service Task Force (NASTF), using OEM or equivalent parts is crucial for maintaining vehicle performance and reliability. For example, if replacing a faulty oxygen sensor, using a high-quality sensor from a reputable brand ensures accurate readings and proper fuel management. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed guides and resources that provide step-by-step instructions on how to replace various automotive parts, ensuring that users can perform repairs effectively and safely.
 Vacuum hose inspection for Innova 3011 codes
Vacuum hose inspection for Innova 3011 codes
3. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Innova 3011 Codes
What advanced diagnostic techniques can be employed for complex Innova 3011 codes, ensuring accurate and efficient problem-solving? Advanced diagnostic techniques for Innova 3011 codes include using live data, performing pinpoint tests, and conducting system scans. Live data analysis involves monitoring real-time sensor readings to identify anomalies. Pinpoint tests use specific procedures outlined in the vehicle’s service manual to isolate the cause of the code. System scans use advanced diagnostic tools to check all vehicle systems for related codes or issues. These techniques provide a deeper understanding of the vehicle’s condition, leading to more accurate and efficient repairs.
3.1. Utilizing Live Data for Real-Time Monitoring
How can live data be effectively utilized for real-time monitoring of vehicle parameters related to Innova 3011 codes? Utilizing live data involves connecting a diagnostic scanner to the vehicle and monitoring real-time sensor readings, such as engine temperature, O2 sensor voltage, and MAF sensor airflow. By observing these parameters, technicians can identify anomalies or inconsistencies that may be causing the trouble code. Comparing live data to known good values helps pinpoint the root cause of the issue. For example, monitoring O2 sensor voltage can reveal a lean or rich condition, while observing MAF sensor airflow can detect intake leaks or sensor malfunctions.
| Parameter | Description | What to Look For |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Temperature | The temperature of the engine coolant, typically measured in degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius. | Monitor for overheating or excessively low temperatures. Normal operating temperature varies by vehicle but is typically between 195°F and 220°F (90°C and 104°C). |
| O2 Sensor Voltage | The voltage output of the oxygen sensors, which indicates the air-fuel ratio in the exhaust stream. | Look for rapid fluctuations between 0.1V and 0.9V, indicating proper sensor function. A steady voltage may indicate a faulty sensor or a lean/rich condition. |
| MAF Sensor Airflow | The amount of air flowing into the engine, measured in grams per second (g/s). | Compare the reading to the engine size and RPM. A low reading may indicate a vacuum leak or a faulty MAF sensor. A high reading may indicate a dirty air filter or a restricted intake. |
| Fuel Trim (Short Term and Long Term) | Adjustments made by the engine control unit (ECU) to maintain the proper air-fuel ratio. Short-term fuel trim (STFT) is a temporary adjustment, while long-term fuel trim (LTFT) is a more permanent adjustment. | Monitor for excessive positive or negative values. Values greater than +10% or less than -10% may indicate a problem with the fuel system, such as a vacuum leak, faulty MAF sensor, or fuel injector issue. |
| Throttle Position | The position of the throttle plate, typically measured as a percentage. | Monitor for smooth and consistent changes as the throttle is opened and closed. A jerky or erratic reading may indicate a faulty throttle position sensor (TPS). |
According to Bosch Automotive, a leading supplier of automotive components and systems, live data analysis is essential for diagnosing complex engine problems. For example, if troubleshooting a P0171 code, monitoring live data can reveal a lean condition indicated by high positive fuel trim values and low O2 sensor voltages. This information helps technicians narrow down the possible causes and perform targeted repairs. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed guides and resources that provide step-by-step instructions on how to use live data effectively, ensuring that users can accurately diagnose complex issues and perform necessary repairs.
3.2. Performing Pinpoint Tests: Isolate the Root Cause
What are pinpoint tests, and how do they help isolate the root cause of Innova 3011 codes, ensuring accurate diagnosis? Pinpoint tests are specific diagnostic procedures outlined in the vehicle’s service manual that guide technicians through a series of tests to isolate the root cause of a trouble code. These tests often involve checking wiring, sensors, and components to determine if they are functioning within specified parameters. By following the pinpoint test procedure, technicians can systematically eliminate potential causes and identify the exact source of the problem. For example, a pinpoint test for a P0300 code might involve checking spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, and compression to determine the cause of the misfire.
| Component | Pinpoint Test | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Spark Plugs | Inspect spark plugs for wear, damage, or carbon buildup; check spark plug gap. | Determine if spark plugs are providing adequate spark for combustion. |
| Ignition Coils | Test coil resistance with a multimeter; use a spark tester to check for spark. | Determine if ignition coils are delivering sufficient voltage to the spark plugs. |
| Fuel Injectors | Use a stethoscope to listen for proper injector clicking; check injector resistance with a multimeter. | Determine if fuel injectors are delivering the correct amount of fuel to the cylinders. |
| Compression | Perform a compression test on each cylinder using a compression tester. | Determine if the cylinders have adequate compression for proper combustion. |
| Vacuum Leaks | Use a smoke machine to check for vacuum leaks in the intake system. | Identify any vacuum leaks that may be causing a lean condition or misfires. |
| Oxygen Sensors | Test sensor voltage and response time with a multimeter. | Determine if oxygen sensors are providing accurate readings to the engine control unit (ECU). |
| EGR Valve | Manually actuate the valve to check for proper movement; check for vacuum at the EGR valve during operation. | Determine if the EGR valve is functioning correctly and controlling exhaust gas recirculation. |
According to the National Automotive Service Task Force (NASTF), pinpoint tests are essential for accurate diagnosis, especially for complex issues. For example, a pinpoint test for a P0300 code might involve checking the spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, and compression in each cylinder to identify the cause of the misfire. By following the pinpoint test procedure, technicians can systematically eliminate potential causes and identify the exact source of the problem. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed guides and resources that provide step-by-step instructions on how to perform various pinpoint tests, ensuring that users can accurately diagnose complex issues and perform necessary repairs.
3.3. Conducting System Scans: Identify Related Codes
How do system scans help in identifying related codes that may contribute to Innova 3011 codes, ensuring a comprehensive diagnostic approach? Conducting system scans involves using an advanced diagnostic tool to scan all vehicle systems for related codes or issues. This comprehensive approach can reveal underlying problems that may be contributing to the Innova 3011 code. For example, a system scan might reveal ABS or SRS codes that are not immediately apparent but could be affecting engine performance. By addressing all related codes, technicians can ensure a more complete and effective repair.
| System | Potential Related Codes | Impact on Innova 3011 Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Control | P0XXX series codes (engine-related), P2XXX series codes (fuel and air metering) | Direct impact on engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions |
| Transmission | P07XX series codes (transmission-related) | Can affect engine load and performance, potentially triggering engine-related codes |
| ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) | C0XXX series codes (chassis-related) | Indirect impact on engine performance through traction control and stability control systems |
| SRS (Supplemental Restraint System) | B0XXX series codes (body-related) | Usually no direct impact on engine performance but can indicate electrical system issues |
| Body Control | B0XXX series codes (body-related) | Can affect electrical systems that impact engine performance, such as lighting or accessory systems |
| HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) | B1XXX series codes (body-related) | Minimal direct impact but can indicate electrical system issues |
According to Innova’s diagnostic tool manuals, system scans are essential for a comprehensive diagnostic approach. For example, a system scan might reveal ABS or SRS codes that are not immediately apparent but could be affecting engine performance. By addressing all related codes, technicians can ensure a more complete and effective repair. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed guides and resources that provide step-by-step instructions on how to perform system scans effectively, ensuring that users can accurately diagnose complex issues and perform necessary repairs.
4. Preventing Innova 3011 Codes: Maintenance Tips and Best Practices
How can Innova 3011 codes be prevented through regular maintenance and best practices, ensuring long-term vehicle health? Preventing Innova 3011 codes involves following a regular maintenance schedule, using high-quality parts, and addressing minor issues promptly. Regular maintenance includes oil changes, air filter replacements, spark plug replacements, and fluid checks. Using high-quality parts ensures reliability and proper performance. Addressing minor issues promptly prevents them from escalating into major problems. By following these maintenance tips and best practices, car owners can minimize the occurrence of Innova 3011 codes and maintain long-term vehicle health.
4.1. Following a Regular Maintenance Schedule
What are the key components of a regular maintenance schedule that can help prevent Innova 3011 codes, ensuring proactive care? Following a regular maintenance schedule involves performing routine tasks such as oil changes, filter replacements, spark plug replacements, and fluid checks at specified intervals. Regular oil changes ensure proper engine lubrication, while filter replacements maintain clean air and fuel flow. Spark plug replacements ensure efficient combustion, and fluid checks prevent system failures. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule helps prevent issues that can trigger Innova 3011 codes.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Change | Every 3,000 to 7,500 miles, depending on the vehicle and oil type | Ensures proper engine lubrication, reduces wear and tear, and prevents sludge buildup |
| Air Filter Replacement | Every 12,000 to 15,000 miles | Maintains clean air flow to the engine, improves fuel efficiency, and prevents contamination of the mass air flow (MAF) sensor |
| Spark Plug Replacement | Every 30,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the vehicle and spark plug type | Ensures efficient combustion, improves engine performance, and prevents misfires |
| Fluid Checks | Monthly | Prevents system failures by ensuring adequate fluid levels and proper fluid condition; includes checking coolant, brake fluid, power steering fluid, and transmission fluid levels |
| Tire Rotation | Every 6,000 to 8,000 miles | Promotes even tire wear, extends tire life, and improves handling |
| Brake Inspection | Every 12,000 to 15,000 miles | Ensures safe braking performance, prevents brake system failures, and identifies worn components early |
According to vehicle manufacturers like Toyota and Honda, following the recommended maintenance schedule is crucial for maintaining vehicle performance and reliability. For example, regular oil changes prevent sludge buildup and ensure proper engine lubrication, reducing the risk of engine-related codes like P0011 (Camshaft Position Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance Bank 1). CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed maintenance schedules and guides that provide step-by-step instructions on how to perform these tasks effectively, ensuring that users can proactively care for their vehicles and prevent potential issues.
4.2. Using High-Quality Parts: Ensure Reliability
Why is using high-quality parts important in preventing Innova 3011 codes, ensuring long-term performance? Using high-quality parts ensures reliability and proper performance, reducing the risk of premature failure and related trouble codes. OEM or equivalent parts are designed to meet the vehicle’s specific requirements, ensuring optimal function and longevity. Lower-quality parts may fail prematurely, leading to performance issues and the triggering of Innova 3011 codes. Investing in high-quality parts is a cost-effective way to maintain vehicle health and prevent future problems.
| Part Type | Benefits of High-Quality Parts | Risks of Low-Quality Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Spark Plugs | Ensures efficient combustion, improves engine performance, and provides longer service life | Can cause misfires, reduce fuel efficiency, and lead to engine damage |
| Ignition Coils | Delivers consistent voltage to the spark plugs, improves engine performance, and provides longer service life | Can cause misfires, reduce engine power, and lead to ignition system failures |
| Oxygen Sensors | Provides accurate readings to the engine control unit (ECU), optimizes fuel efficiency, and reduces emissions | Can cause inaccurate air-fuel ratio, reduce fuel efficiency, and lead to catalytic converter damage |
| MAF Sensors | Accurately measures air flow into the engine, optimizes fuel delivery, and improves engine performance | Can cause inaccurate air-fuel ratio, reduce engine power, and lead to poor fuel economy |
| Fuel Injectors | Delivers the correct amount of fuel to the cylinders, improves engine performance, and provides longer service life | Can cause poor fuel economy, rough idling, and lead to engine damage |
| Catalytic Converter | Effectively reduces harmful emissions, complies with environmental regulations, and provides longer service life | Can fail prematurely, increase emissions, and lead to engine damage |
According to the National Automotive Service Task Force (NASTF), using OEM or equivalent parts is crucial for maintaining vehicle performance and reliability. For example, using a high-quality MAF sensor ensures accurate air flow measurement, preventing lean or rich conditions that can trigger codes like P0171 or P0172. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed guides and resources that provide information on selecting high-quality parts, ensuring that users can make informed decisions and maintain their vehicles effectively.
4.3. Addressing Minor Issues Promptly: Prevent Escalation
Why is addressing minor issues promptly important in preventing Innova 3011 codes, ensuring proactive maintenance? Addressing minor issues promptly prevents them from escalating into major problems that can trigger Innova 3011 codes. For example, a small vacuum leak can be easily fixed by replacing a cracked hose, preventing a lean condition that could damage the engine. Similarly, a loose gas cap can be tightened to prevent evaporative emissions codes. By addressing these minor issues early, car owners can prevent more serious problems and maintain their vehicle’s health.
| Minor Issue | Potential Escalation | Preventative Action |
|---|---|---|
| Small Vacuum Leak | Lean condition, engine misfires, catalytic converter damage | Replace cracked or damaged vacuum hoses |
| Loose Gas Cap | Evaporative emissions codes, fuel запах, reduced fuel efficiency | Tighten or replace the gas cap |
| Rough Idling | Engine misfires, spark plug fouling, fuel injector clogging | Inspect and replace spark plugs, clean fuel injectors |
| Unusual Noises | Component failure, engine damage | Investigate and repair the source of the noise |
| Decreased Fuel Economy | Clogged air filter, faulty oxygen sensors, engine misfires | Replace air filter, inspect and replace oxygen sensors, address engine misfires |
| Fluid Leaks | System failure, component damage | Identify and repair the source of the leak |
According to AAA (American Automobile Association), addressing minor issues promptly can save car