Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans are crucial for providing targeted patient care, and CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN can help you find the resources to develop them effectively. Diagnostic nursing care plans are essential for addressing specific patient needs through focused assessments, accurate diagnoses, and customized interventions, leading to improved healthcare outcomes. This article dives into the essentials of crafting diagnostic nursing care plans, highlighting their significance in contemporary healthcare.
Contents
- 1. What Is A Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
- 1.1. Key Components of a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan
- 2. Why Are Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans Important?
- 2.1. Benefits of Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans
- 3. Who Benefits from Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans?
- 3.1. Stakeholders Benefiting from Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans
- 4. What Are the Key Steps in Creating a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
- 4.1. Steps to Develop a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan
- 5. How Do You Conduct a Patient Assessment for a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
- 5.1. Methods for Patient Assessment
- 6. What Is the Role of Nursing Diagnosis in a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
- 6.1. Importance of Nursing Diagnosis
- 7. How Do You Set Priorities in a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
- 7.1. Factors to Consider When Setting Priorities
- 8. What Are Client Goals and Desired Outcomes in a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
- 8.1. Characteristics of Effective Goals
- 9. What Are Nursing Interventions and How Do You Select Them?
- 9.1. Types of Nursing Interventions
- 10. What Is the Purpose of Providing a Rationale in a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
- 10.1. Benefits of Providing a Rationale
- 11. How Do You Evaluate a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
- 11.1. Components of Evaluation
- 12. What Are Standardized and Individualized Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans?
- 12.1. Key Differences
- 13. How Do Student Care Plans Differ from Those Used by Practicing Nurses?
- 13.1. Key Differences in Care Plans
- 14. What Are Some Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Creating Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans?
- 14.1. Common Pitfalls
- 15. How Can Technology Help in Creating and Managing Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans?
- 15.1. Technological Tools
- 16. Can You Provide Examples of Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans for Common Conditions?
- 16.1. Example Care Plans
- 17. What Are the Legal and Ethical Considerations in Diagnostic Nursing Care Planning?
- 17.1. Ethical Responsibilities
- 18. What Role Does Continuing Education Play in Enhancing Skills in Diagnostic Nursing Care Planning?
- 18.1. Benefits of Continuing Education
- 19. How Can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Help You with Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans?
- 20. Ready to Enhance Your Skills in Diagnostic Nursing Care Planning?
1. What Is A Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
A diagnostic nursing care plan is a structured approach that nurses use to address a patient’s healthcare needs. It involves a systematic process of assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. These plans are essential for providing patient-centered care and ensuring positive health outcomes. Diagnostic nursing care plans, according to a study by the National Institutes of Health, enhance patient outcomes and satisfaction by promoting individualized care.
1.1. Key Components of a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan
- Assessment: Gathering comprehensive data about the patient’s condition.
- Diagnosis: Identifying specific health problems based on the assessment.
- Planning: Setting goals and designing interventions to address the identified problems.
- Implementation: Carrying out the planned interventions.
- Evaluation: Assessing the effectiveness of the interventions and making necessary adjustments.
2. Why Are Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans Important?
Diagnostic nursing care plans ensure structured, individualized patient care, enhancing communication among healthcare providers. They document care, facilitating continuity and consistency across shifts and departments. These plans also serve as a basis for reimbursement and define the nurse’s role, ensuring accountability and high-quality patient care. Individualized plans, as highlighted by the American Nurses Association, result in greater patient satisfaction and improved health outcomes.
2.1. Benefits of Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans
- Structured Care: Ensures all aspects of patient care are addressed.
- Individualized Approach: Tailored to meet specific patient needs.
- Enhanced Communication: Facilitates better coordination among healthcare team members.
- Continuity of Care: Ensures consistent care across different shifts and departments.
- Documentation: Provides a clear record of care provided.
- Basis for Reimbursement: Supports accurate billing and reimbursement processes.
3. Who Benefits from Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans?
Diagnostic nursing care plans primarily benefit patients by providing structured and individualized care, leading to better health outcomes and higher satisfaction. Nurses benefit through clear guidelines, enhanced communication, and a defined role, which improves job satisfaction and reduces errors. Healthcare organizations also benefit from improved quality of care, better documentation, and enhanced efficiency. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality emphasizes that effective care plans improve patient safety and reduce hospital readmissions.
3.1. Stakeholders Benefiting from Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans
- Patients: Receive structured, individualized care leading to better health outcomes.
- Nurses: Benefit from clear guidelines, enhanced communication, and a defined role.
- Healthcare Organizations: Experience improved quality of care, better documentation, and enhanced efficiency.
4. What Are the Key Steps in Creating a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
Creating a diagnostic nursing care plan involves several key steps, starting with a thorough assessment of the patient. Data analysis and organization follow, leading to the formulation of nursing diagnoses. Setting priorities helps determine which issues to address first, and establishing client goals and desired outcomes provides a clear direction for interventions. Selecting appropriate nursing interventions and providing a rationale for these actions are crucial. Finally, evaluation helps assess the plan’s effectiveness and make necessary adjustments. The National League for Nursing emphasizes that mastering these steps is essential for providing competent and effective nursing care.
4.1. Steps to Develop a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan
- Assessment: Collect comprehensive data about the patient’s condition.
- Data Analysis: Analyze and organize data to identify health problems.
- Nursing Diagnosis: Formulate specific nursing diagnoses based on the analysis.
- Setting Priorities: Determine the order in which to address the diagnoses.
- Establishing Goals: Set measurable goals and desired outcomes for the patient.
- Selecting Interventions: Choose appropriate nursing interventions to achieve the goals.
- Providing Rationale: Explain the scientific reasoning behind the chosen interventions.
- Evaluation: Assess the effectiveness of the interventions and adjust as needed.
5. How Do You Conduct a Patient Assessment for a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
Patient assessment is the first and most critical step in creating a diagnostic nursing care plan. It involves collecting comprehensive data through physical examinations, health histories, interviews, medical records review, and diagnostic studies. The goal is to create a complete client database that includes all relevant health information. Critical thinking is essential in patient assessment, allowing nurses to integrate knowledge across sciences and professional guidelines to inform evaluations effectively. This process, crucial for complex clinical decision-making, aims to identify patients’ healthcare needs by leveraging a supportive environment and reliable information. The American Association of Colleges of Nursing emphasizes that thorough assessment skills are fundamental to quality nursing care.
 Patient assessment is the first and most critical step in creating a diagnostic nursing care plan
Patient assessment is the first and most critical step in creating a diagnostic nursing care plan
5.1. Methods for Patient Assessment
- Physical Examination: Conducting a thorough physical assessment to identify physical symptoms and signs.
- Health History: Gathering information about the patient’s past and present health conditions.
- Interview: Asking the patient about their symptoms, concerns, and goals.
- Medical Records Review: Examining the patient’s medical records to gather relevant data.
- Diagnostic Studies: Utilizing diagnostic tests to obtain objective data about the patient’s condition.
6. What Is the Role of Nursing Diagnosis in a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
The nursing diagnosis is a crucial component of a diagnostic nursing care plan, serving as a uniform way of identifying and addressing specific client needs and responses to actual and high-risk problems. These diagnoses focus on health problems that can be prevented or resolved through independent nursing interventions. Effective nursing diagnoses guide the planning and implementation of targeted interventions, ensuring that care is tailored to the patient’s specific needs. The North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA) provides a standardized list of nursing diagnoses, facilitating clear communication and consistency in care planning.
6.1. Importance of Nursing Diagnosis
- Uniform Identification: Provides a standardized way to identify client needs and responses.
- Focus on Client Needs: Addresses actual and high-risk problems that nurses can independently manage.
- Guides Interventions: Directs the planning and implementation of targeted nursing interventions.
- Promotes Consistency: Ensures clear communication and consistency in care planning.
7. How Do You Set Priorities in a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
Setting priorities in a diagnostic nursing care plan involves establishing a preferential sequence for addressing nursing diagnoses and interventions. This step requires the nurse and the client to plan which identified problems require attention first. Diagnoses are often ranked and grouped as having high, medium, or low priority, with life-threatening problems given the highest priority. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is often used as a framework for setting priorities, ensuring that basic physiological needs are met before addressing higher-level needs such as self-esteem and self-actualization. The American Nurses Association emphasizes the importance of considering the patient’s health values, beliefs, and available resources when setting priorities.
7.1. Factors to Consider When Setting Priorities
- Severity of the Problem: Addressing life-threatening issues first.
- Patient’s Needs and Values: Considering the patient’s preferences and beliefs.
- Available Resources: Taking into account the resources available for care.
- Urgency: Addressing problems that require immediate attention.
8. What Are Client Goals and Desired Outcomes in a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
Client goals and desired outcomes are essential components of a diagnostic nursing care plan, describing what the nurse hopes to achieve by implementing nursing interventions. These goals provide direction for planning interventions, serve as criteria for evaluating patient progress, and help motivate both the client and the nurse by providing a sense of achievement. Goals should be SMART: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, and Time-oriented. They should also be client-centered, focusing on problem prevention, resolution, and rehabilitation. Short-term goals are used in acute care settings, while long-term goals are often used for clients with chronic health problems or those in extended-care facilities. The Joint Commission emphasizes the importance of measurable and client-centered goals for improving patient outcomes.
 Examples of goals and desired outcomes
Examples of goals and desired outcomes
8.1. Characteristics of Effective Goals
- Specific: Clearly defined and focused.
- Measurable: Quantifiable to track progress.
- Attainable: Realistic and achievable.
- Relevant: Aligned with the patient’s needs and values.
- Time-Oriented: With a defined timeline for achievement.
9. What Are Nursing Interventions and How Do You Select Them?
Nursing interventions are the activities or actions that a nurse performs to achieve client goals. These interventions should focus on eliminating or reducing the etiology of the priority nursing problem or diagnosis. For risk nursing problems, interventions should focus on reducing the client’s risk factors. Nursing interventions can be independent, dependent, or collaborative. They should be safe, appropriate for the client’s age, health, and condition, and in line with the client’s values, culture, and beliefs. It’s best to draw from published clinical practice guidelines or consensus statements that address the patient’s specific diagnosis. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) provides guidelines for selecting evidence-based nursing interventions.
9.1. Types of Nursing Interventions
- Independent Interventions: Actions that nurses are licensed to initiate based on their judgment and skills.
- Dependent Interventions: Actions carried out under the physician’s orders or supervision.
- Collaborative Interventions: Actions that the nurse carries out in collaboration with other health team members.
10. What Is the Purpose of Providing a Rationale in a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
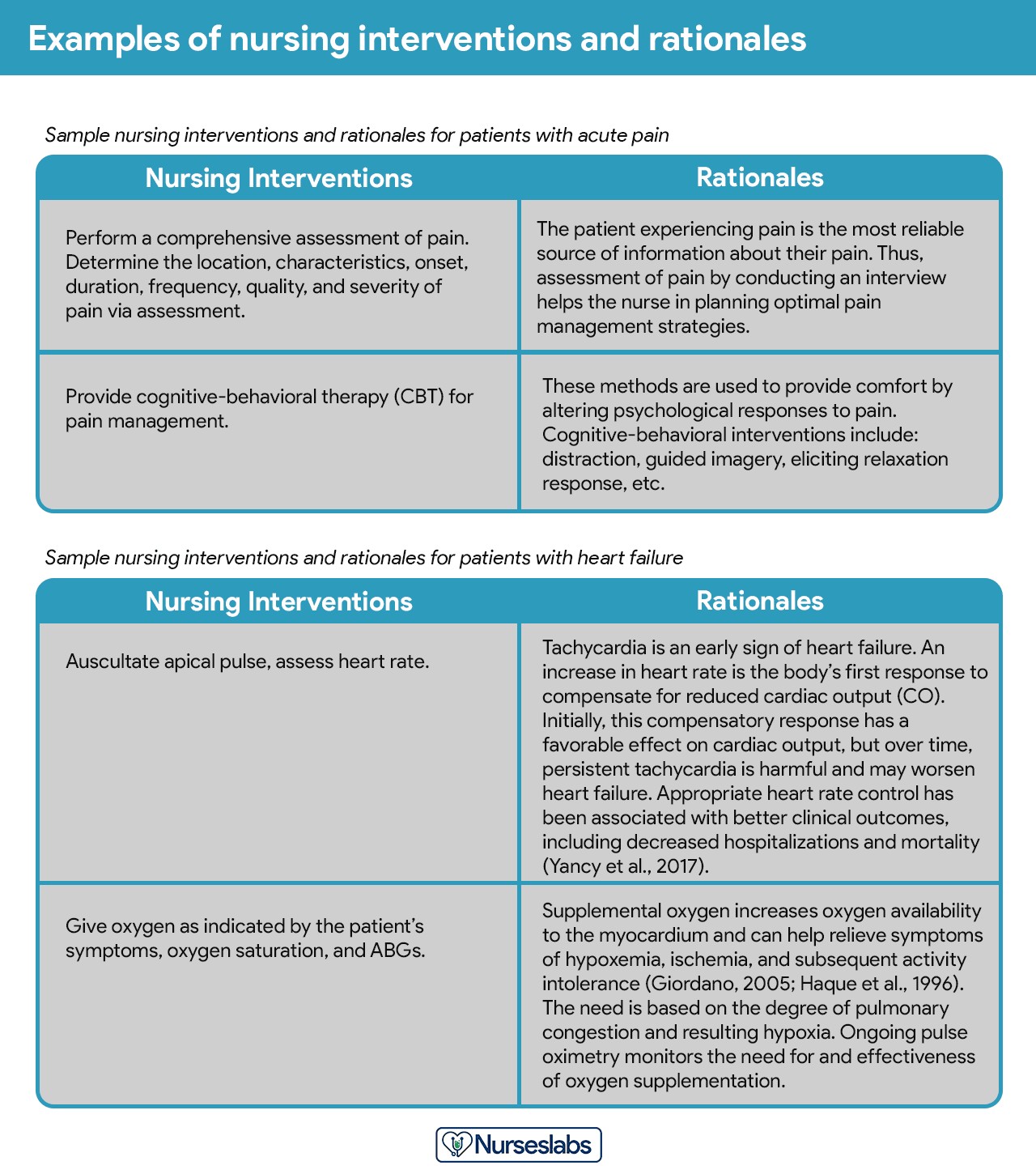
Providing a rationale, also known as a scientific explanation, explains why a particular nursing intervention was chosen for the diagnostic nursing care plan. Rationales help nursing students associate pathophysiological and psychological principles with the selected interventions. This step is crucial for developing a deeper understanding of the reasoning behind nursing actions and for promoting evidence-based practice. Rationales support the integration of nursing knowledge with clinical practice, enhancing the quality of care provided. The QSEN Institute emphasizes the importance of evidence-based practice in nursing education and clinical practice.
 Nursing Interventions and Rationale
Nursing Interventions and Rationale
10.1. Benefits of Providing a Rationale
- Enhances Understanding: Helps nurses understand the scientific basis for their actions.
- Promotes Evidence-Based Practice: Encourages the use of research and evidence in selecting interventions.
- Improves Critical Thinking: Develops critical thinking skills by requiring nurses to justify their decisions.
- Supports Integration of Knowledge: Integrates pathophysiological and psychological principles with nursing practice.
11. How Do You Evaluate a Diagnostic Nursing Care Plan?
Evaluation is a planned, ongoing, purposeful activity in which the client’s progress towards achieving goals is assessed, and the effectiveness of the nursing care plan is determined. This step is essential because the conclusions drawn from the evaluation determine whether the nursing intervention should be terminated, continued, or changed. Evaluation involves measuring the client’s outcomes against the established goals and desired outcomes. If the goals have been met, the intervention may be terminated. If not, the plan may need to be revised or continued. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) emphasize the importance of regular evaluation to ensure high-quality patient care.
11.1. Components of Evaluation
- Measuring Outcomes: Assessing the client’s progress towards achieving goals.
- Comparing Outcomes: Comparing the client’s actual outcomes with the desired outcomes.
- Analyzing Effectiveness: Determining whether the nursing interventions were effective.
- Adjusting the Plan: Making necessary changes to the nursing care plan based on the evaluation results.
12. What Are Standardized and Individualized Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans?
Standardized care plans are pre-developed guides used to ensure that patients with a particular condition receive consistent care. These plans ensure that minimally acceptable criteria are met and promote the efficient use of the nurse’s time by removing the need to develop common activities that are done repeatedly. Individualized care plans, on the other hand, are tailored to meet a specific client’s unique needs or needs that are not addressed by the standardized care plan. Individualized care plans involve tailoring a standardized care plan to meet the specific needs and goals of the individual client and use approaches shown to be effective for that client. This approach allows for more personalized and holistic care better suited to the client’s unique needs, strengths, and goals. According to a study in the Journal of Nursing Administration, combining standardized and individualized care plans optimizes patient outcomes and resource utilization.
12.1. Key Differences
- Standardized Care Plans:
- Pre-developed guides for consistent care.
- Ensure minimally acceptable criteria are met.
- Promote efficient use of nurse’s time.
- Individualized Care Plans:
- Tailored to meet specific client needs.
- Address needs not covered by standardized plans.
- Allow for more personalized and holistic care.
13. How Do Student Care Plans Differ from Those Used by Practicing Nurses?
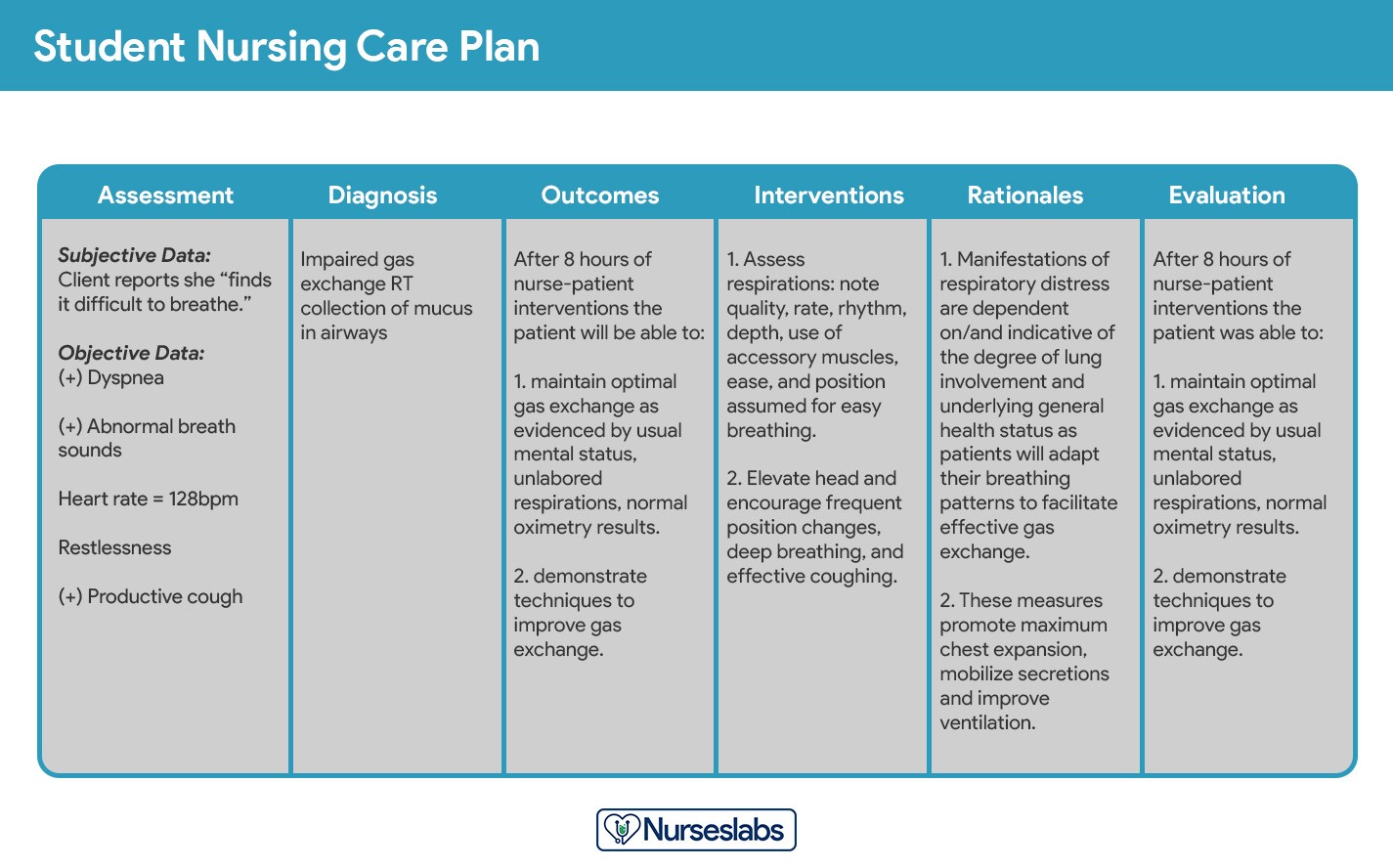
Student care plans are more lengthy and detailed than care plans used by working nurses because they serve as a learning activity for the student nurse. Care plans by student nurses are usually required to be handwritten and have an additional column for “Rationale” or “Scientific Explanation” after the nursing interventions column. Rationales are scientific principles that explain the reasons for selecting a particular nursing intervention. Practicing nurses, on the other hand, use more concise and streamlined care plans that focus on the most relevant and immediate needs of the patient. The goal of student care plans is to help students develop critical thinking skills and a thorough understanding of the nursing process. The American Association of Colleges of Nursing emphasizes that student care plans are essential for developing competent and reflective practitioners.
13.1. Key Differences in Care Plans
- Student Care Plans:
- More lengthy and detailed.
- Include a rationale for each intervention.
- Focus on developing critical thinking skills.
- Practicing Nurse Care Plans:
- More concise and streamlined.
- Focus on immediate patient needs.
- Designed for efficient use in clinical settings.
14. What Are Some Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Creating Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans?
Creating diagnostic nursing care plans can be challenging, and there are several common pitfalls to avoid. These include inadequate assessment, which results in incomplete or inaccurate data, leading to ineffective care plans. Another pitfall is formulating vague or unrealistic goals that are difficult to measure and achieve. Selecting interventions that are not evidence-based or appropriate for the patient’s condition can also lead to poor outcomes. Finally, failing to evaluate and revise the care plan regularly can result in a plan that does not meet the patient’s changing needs. The National Patient Safety Foundation emphasizes the importance of avoiding these pitfalls to ensure patient safety and quality care.
14.1. Common Pitfalls
- Inadequate Assessment: Incomplete or inaccurate data collection.
- Vague Goals: Unclear and difficult-to-measure goals.
- Non-Evidence-Based Interventions: Interventions not supported by research.
- Lack of Evaluation: Failure to regularly evaluate and revise the plan.
15. How Can Technology Help in Creating and Managing Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans?
Technology plays a significant role in creating and managing diagnostic nursing care plans, with electronic health records (EHRs) providing access to comprehensive patient data and facilitating better care coordination. Nursing care plan software automates the creation and management of care plans, improving efficiency and accuracy. Mobile apps offer quick access to information and guidelines, supporting evidence-based practice at the point of care. These technologies enhance communication among healthcare team members, streamline documentation, and improve patient outcomes. A study published in the journal “Applied Clinical Informatics” found that technology improves the efficiency and effectiveness of nursing care planning.
15.1. Technological Tools
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Access to comprehensive patient data.
- Nursing Care Plan Software: Automates creation and management of care plans.
- Mobile Apps: Quick access to information and guidelines.
- Communication Platforms: Facilitate better communication among healthcare team members.
16. Can You Provide Examples of Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans for Common Conditions?
Diagnostic nursing care plans vary depending on the patient’s condition and needs. For example, a patient with heart failure may have a care plan focused on managing fluid balance, promoting cardiac function, and educating the patient on medication management. A patient with diabetes may have a care plan focused on monitoring blood glucose levels, promoting healthy eating habits, and preventing complications. These care plans include specific goals, interventions, and evaluation criteria tailored to the patient’s condition. Nursing resource websites offer numerous examples of diagnostic nursing care plans for various conditions.
16.1. Example Care Plans
- Heart Failure: Managing fluid balance, promoting cardiac function, medication education.
- Diabetes: Monitoring blood glucose, promoting healthy eating, preventing complications.
- Pneumonia: Improving respiratory function, preventing infection, providing comfort.
17. What Are the Legal and Ethical Considerations in Diagnostic Nursing Care Planning?
Legal and ethical considerations are critical in diagnostic nursing care planning. Nurses must respect patient autonomy by involving them in the care planning process and obtaining informed consent for interventions. Maintaining patient confidentiality and privacy is also essential, adhering to HIPAA regulations. Nurses must provide safe and competent care, following professional standards and guidelines. They must also advocate for their patients’ rights and needs, ensuring they receive appropriate and ethical care. The American Nurses Association’s Code of Ethics provides guidance on ethical considerations in nursing practice.
17.1. Ethical Responsibilities
- Patient Autonomy: Involving patients in care planning and obtaining informed consent.
- Confidentiality: Maintaining patient privacy and adhering to HIPAA regulations.
- Competence: Providing safe and competent care.
- Advocacy: Advocating for patients’ rights and needs.
18. What Role Does Continuing Education Play in Enhancing Skills in Diagnostic Nursing Care Planning?
Continuing education is essential for enhancing skills in diagnostic nursing care planning. It keeps nurses updated on the latest evidence-based practices, guidelines, and technologies. Continuing education helps nurses improve their assessment, diagnostic, and critical thinking skills, leading to better patient outcomes. It also supports professional development and career advancement. Nursing organizations and educational institutions offer a variety of continuing education programs focused on diagnostic nursing care planning. The American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC) provides accreditation for continuing nursing education programs.
18.1. Benefits of Continuing Education
- Staying Updated: Keeps nurses informed on the latest practices and guidelines.
- Improving Skills: Enhances assessment, diagnostic, and critical thinking skills.
- Supporting Development: Supports professional growth and career advancement.
- Improving Patient Outcomes: Leads to better patient care and outcomes.
19. How Can CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN Help You with Diagnostic Nursing Care Plans?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN can assist you in developing effective diagnostic nursing care plans by providing access to detailed information on assessment techniques, diagnostic criteria, and evidence-based interventions. Our resources help you create structured, individualized care plans that meet the specific needs of your patients. Whether you are a student nurse or an experienced practitioner, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers the tools and resources you need to enhance your skills in diagnostic nursing care planning.
20. Ready to Enhance Your Skills in Diagnostic Nursing Care Planning?
Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States, or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information and to access our comprehensive resources. Let us help you provide the best possible care for your patients. Don’t wait—reach out now and elevate your nursing practice with CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN.