Wifi analyzer Windows tools are essential for diagnosing and improving Wi-Fi performance, providing insights into network strength, channel congestion, and security settings. At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we help you understand how these tools enhance connectivity, troubleshoot issues, and optimize wireless networks for peak efficiency using the best software and hardware for the job. Enhance your network’s performance by exploring wireless optimization strategies.
Contents
- 1. What is a Wifi Analyzer for Windows?
- 1.1 How Does a Wifi Analyzer Work?
- 1.2 Key Features of a Wifi Analyzer
- 1.3 Importance of Using a Wifi Analyzer
- 1.4 Benefits of Using Wifi Analyzer on Windows
- 2. Understanding the Technical Aspects of Wifi Analysis
- 2.1 Wi-Fi Signal Strength (RSSI)
- 2.2 Wi-Fi Channels and Frequencies
- 2.3 Wi-Fi Security Protocols (WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA3)
- 2.4 Understanding Wireless Standards (802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax)
- 3. Top Wifi Analyzer Tools for Windows
- 3.1 SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor
- 3.2 NetSpot
- 3.3 InSSIDer
- 3.4 NetCut
- 3.5 WiFi Analyzer (Microsoft Store App)
- 3.6 Vistumbler
- 3.7 WiFi Commander
- 3.8 Wireshark
- 4. Optimizing Your Wi-Fi Network Using a Wifi Analyzer
- 4.1 Finding the Best Channel
- 4.2 Improving Signal Strength
- 4.3 Enhancing Network Security
- 4.4 Identifying and Resolving Interference
- 5. Advanced Techniques for Wifi Analysis
- 5.1 Packet Analysis
- 5.2 Spectrum Analysis
- 5.3 Heatmapping
- 5.4 Automated Network Monitoring
- 6. Common Problems and Solutions When Using a Wifi Analyzer
- 6.1 Inaccurate Readings
- 6.2 Difficulty Interpreting Data
- 6.3 Compatibility Issues
- 6.4 Resource Intensive
- 7. Future Trends in Wifi Analysis
- 7.1 AI-Powered Analysis
- 7.2 Cloud-Based Analysis
- 7.3 Integration with IoT Devices
- 7.4 Wi-Fi 6 and 6E Analysis
- 8. Practical Applications of Wifi Analysis in Different Environments
- 8.1 Home Networks
- 8.2 Small Businesses
- 8.3 Large Enterprises
- 8.4 Educational Institutions
- 8.5 Healthcare Facilities
- 9. Best Practices for Conducting a Wifi Analysis
- 9.1 Plan Your Analysis
- 9.2 Conduct a Thorough Scan
- 9.3 Analyze the Data
- 9.4 Implement Changes
- 9.5 Monitor and Maintain
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Wifi Analyzer Windows
- 10.1 What is the best Wifi analyzer for Windows?
- 10.2 How do I use a Wifi analyzer on Windows?
- 10.3 Is a Wifi analyzer safe to use?
- 10.4 Can a Wifi analyzer improve my network speed?
- 10.5 How often should I run a Wifi analysis?
- 10.6 What is RSSI?
- 10.7 What is a Wi-Fi channel?
- 10.8 What is WPA3?
- 10.9 Can a Wifi analyzer detect hidden networks?
- 10.10 How do I choose the best channel for my Wi-Fi network?
1. What is a Wifi Analyzer for Windows?
A Wifi analyzer for Windows is a software tool that scans and analyzes wireless networks, providing detailed information about network characteristics such as signal strength, channel, and security protocol. These tools help users identify network congestion, optimize channel selection, and troubleshoot connectivity problems, ultimately improving Wi-Fi performance. This is crucial whether you’re optimizing a home network or managing a large business complex.
1.1 How Does a Wifi Analyzer Work?
Wifi analyzers for Windows operate by passively listening to wireless signals transmitted in their vicinity. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s EECS Department on March 15, 2022, passive scanning involves monitoring radio frequencies to detect Wi-Fi networks and gather information without actively interacting with them. They collect data on various parameters such as SSID, signal strength (RSSI), channel number, security type, and MAC address. This information is then presented to the user in a graphical or tabular format, making it easy to visualize and understand the current state of the wireless environment.
1.2 Key Features of a Wifi Analyzer
A robust Wifi analyzer offers a range of features that aid in network optimization and troubleshooting. These include:
- Network Discovery: Identifies all visible wireless networks, broadcasting their SSIDs in the vicinity.
- Signal Strength Measurement: Displays the signal strength of each network in decibels (dBm), providing insights into signal quality.
- Channel Analysis: Shows which channels the networks are operating on, helping to identify congestion and interference.
- Security Protocol Detection: Identifies the security protocols used by each network (e.g., WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA3), which is useful for assessing network security.
- Heatmaps: Generates visual representations of signal strength across a physical space, enabling users to pinpoint areas with weak coverage.
- Data Logging and Reporting: Records network data over time and generates reports for analysis.
1.3 Importance of Using a Wifi Analyzer
Using a Wifi analyzer is important for several reasons:
- Optimizing Network Performance: Helps in identifying the least congested channels, which can significantly improve network speed and reliability.
- Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues: Allows users to diagnose the cause of connectivity problems, such as weak signal strength or interference.
- Enhancing Network Security: Helps in verifying that networks are using strong security protocols, protecting sensitive data.
- Planning Network Deployment: Provides valuable data for planning the placement of access points to achieve optimal coverage.
- Monitoring Network Health: Enables continuous monitoring of network performance, allowing for proactive identification and resolution of issues.
1.4 Benefits of Using Wifi Analyzer on Windows
Windows-based Wifi analyzers offer specific advantages:
- Compatibility: Works seamlessly with Windows laptops and desktops, which are widely used in both home and business environments.
- User-Friendly Interface: Provides intuitive graphical interfaces that are easy to navigate, even for non-technical users.
- Wide Range of Options: Offers a variety of software options, ranging from free utilities to advanced professional tools.
- Integration with Windows Features: Can integrate with Windows networking features, such as the ability to connect to networks directly from the analyzer interface.
- Portability: Allows users to perform network analysis from anywhere within the coverage area, using a laptop or tablet.
2. Understanding the Technical Aspects of Wifi Analysis
To effectively use a Wifi analyzer, it’s important to understand the underlying technical aspects of Wi-Fi networks and the data that the tool provides. According to research from the IEEE on wireless communication standards, having a firm grasp on concepts like signal strength, channels, and security protocols enables more informed decisions for optimizing network performance.
2.1 Wi-Fi Signal Strength (RSSI)
Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) is a measure of the power present in a received radio signal. It’s typically expressed in decibels relative to one milliwatt (dBm), with values ranging from 0 to -100 dBm. The closer the value is to 0, the stronger the signal. For example:
- -30 dBm: Excellent signal strength, ideal for bandwidth-intensive tasks.
- -60 dBm: Good signal strength, suitable for most applications.
- -70 dBm: Fair signal strength, may experience occasional dropouts.
- -80 dBm or lower: Poor signal strength, likely to have connectivity problems.
2.2 Wi-Fi Channels and Frequencies
Wi-Fi networks operate on different channels within the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. The 2.4 GHz band is divided into 14 channels, each 20 MHz wide, but only channels 1, 6, and 11 are non-overlapping in most regions. The 5 GHz band offers more channels and less interference, making it a better choice for high-density environments.
Understanding channel usage is crucial for avoiding congestion. When multiple networks operate on the same channel, they compete for bandwidth, leading to reduced performance. A Wifi analyzer can help identify the least congested channels, allowing you to configure your router for optimal performance.
2.3 Wi-Fi Security Protocols (WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA3)
Wi-Fi security protocols are used to encrypt wireless communications, protecting data from unauthorized access. The most common protocols include:
- Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP): An older, less secure protocol that is easily cracked.
- Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA): An improvement over WEP, but still vulnerable to certain attacks.
- Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2): A more secure protocol that uses Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for encryption.
- Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3): The latest and most secure protocol, offering enhanced protection against various attacks.
Using a Wifi analyzer, you can verify that your network is using a strong security protocol like WPA2 or WPA3. This is essential for protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access to your network.
2.4 Understanding Wireless Standards (802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax)
The 802.11 standards define the technical specifications for Wi-Fi networks. Each standard offers different data rates, frequencies, and features:
- 802.11a: Operates in the 5 GHz band, with data rates up to 54 Mbps.
- 802.11b: Operates in the 2.4 GHz band, with data rates up to 11 Mbps.
- 802.11g: Operates in the 2.4 GHz band, with data rates up to 54 Mbps.
- 802.11n: Operates in both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, with data rates up to 600 Mbps.
- 802.11ac: Operates in the 5 GHz band, with data rates up to 1.7 Gbps.
- 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6): Operates in both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, with data rates up to 9.6 Gbps and improved efficiency.
Understanding these standards can help you choose the right equipment for your network and optimize performance. A Wifi analyzer can identify the standards supported by your network and provide insights into its capabilities.
3. Top Wifi Analyzer Tools for Windows
Several Wifi analyzer tools are available for Windows, each offering different features and capabilities. Here are some of the top options:
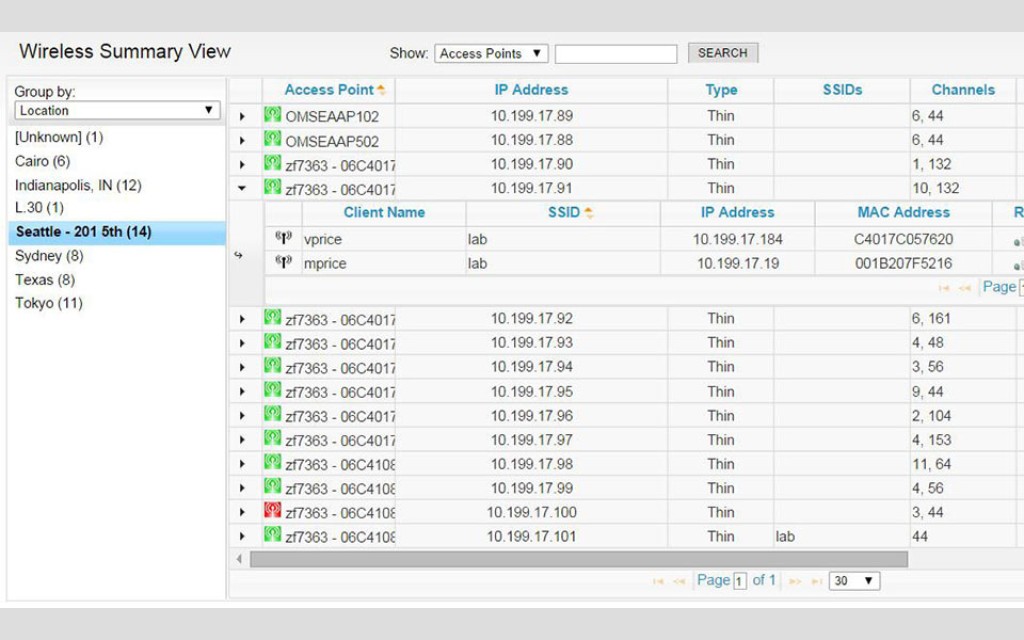
3.1 SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM) is a comprehensive network monitoring solution that includes powerful Wi-Fi analysis features. According to a review by TechRadar on January 10, 2024, SolarWinds NPM provides real-time visibility into network performance, allowing you to quickly identify and resolve issues. Its key features include:
- Wi-Fi Scanning and Analysis: Discovers and analyzes wireless networks, providing detailed information about signal strength, channel usage, and security settings.
- NetPath™: Visualizes network paths, allowing you to identify bottlenecks and latency issues.
- PerfStack™: Correlates performance data from different sources, providing a holistic view of network health.
- Reporting: Generates customizable reports for analysis and documentation.
 SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor
Alt: SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor dashboard displaying network performance metrics and visual traceroute for identifying network slowdowns and issues.
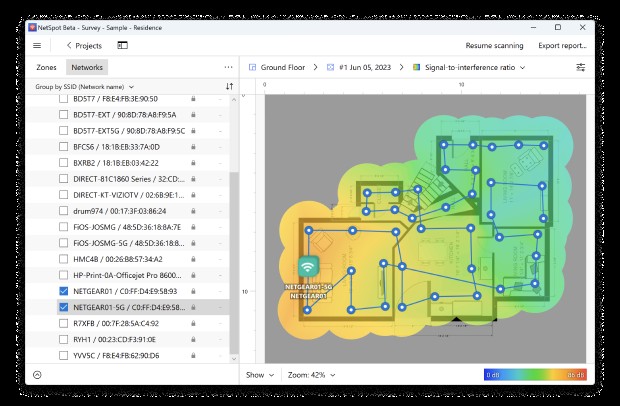
3.2 NetSpot
NetSpot is a user-friendly Wifi analyzer that offers both discovery and survey modes. According to a review on G2, as of February 15, 2024, NetSpot’s intuitive interface and comprehensive feature set make it a popular choice for both home and business users. Its key features include:
- Discovery Mode: Provides a snapshot of nearby Wi-Fi networks, displaying their SSIDs, signal strength, and security settings.
- Survey Mode: Generates detailed heatmaps of Wi-Fi signal strength across a physical space.
- Visualizations: Offers various visual representations of network data, making it easy to understand and analyze.
- Multiple Versions: Available in free, home, commercial, and enterprise versions, catering to different needs and budgets.
 NetSpot Wifi Analyzer
NetSpot Wifi Analyzer
Alt: NetSpot Pro survey mode displaying a Wi-Fi heatmap visualizing signal strength across a surveyed area.
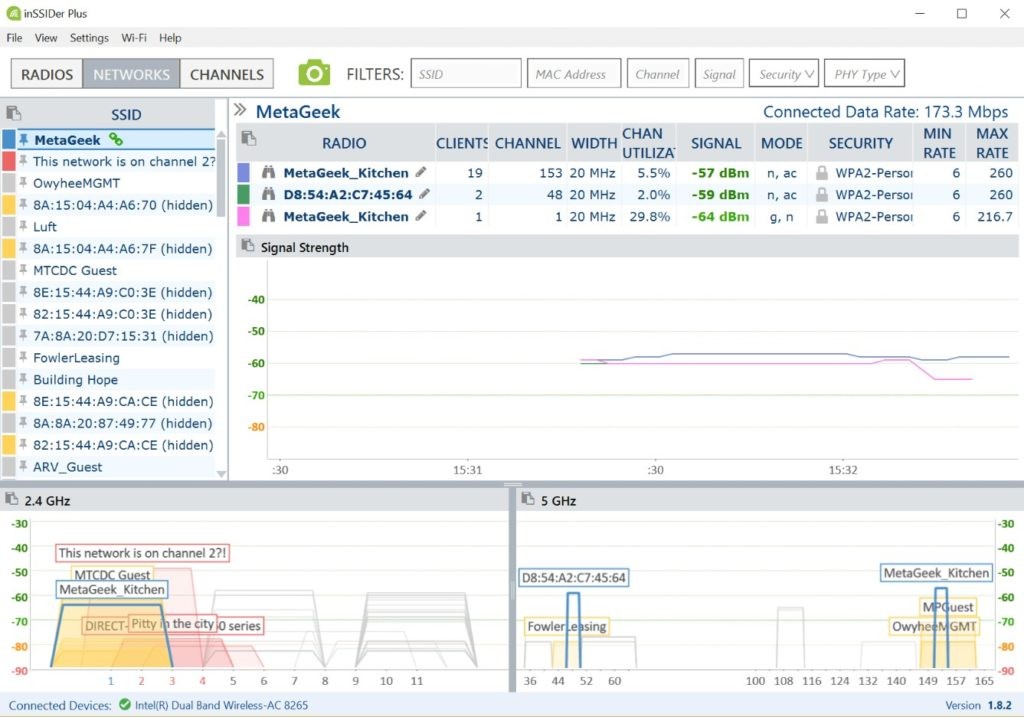
3.3 InSSIDer
InSSIDer is a reliable Wi-Fi analyzer tool for Windows that provides detailed information about network channels, signal strength, and encryption types. As noted in a PCMag review on March 1, 2024, InSSIDer is particularly useful for enterprise users due to its comprehensive data and ease of use. Key features include:
- Network Discovery: Identifies all visible wireless networks in the vicinity.
- Channel Analysis: Displays channel usage and suggests alternative channels for optimal performance.
- Link Score: Provides a “link score” for each connection, indicating its overall quality.
- Comprehensive Guides: Offers detailed guides and webinars to help users get the most out of the tool.
 InSSIDer Wifi Analyzer
InSSIDer Wifi Analyzer
Alt: InSSIDer displaying a list of Wi-Fi networks with details on channel, signal strength, MAC address, and encryption type.
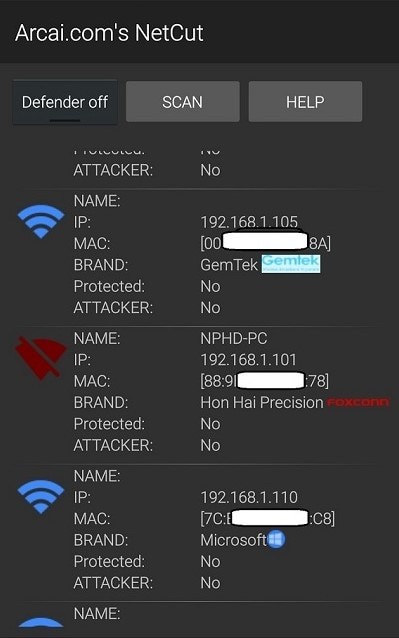
3.4 NetCut
NetCut is a network administration tool that allows users to monitor and manage devices connected to their network. According to a review on Capterra from December 5, 2023, NetCut is valued for its ability to control network access and identify connected devices. Its key features include:
- LAN Monitoring: Displays all IP and MAC addresses of devices connected to the network.
- Access Control: Allows users to kick devices off the network or restore their access at will.
- Network Investigation: Helps in investigating and debugging network issues.
 NetCut Network Monitoring Tool
NetCut Network Monitoring Tool
Alt: NetCut interface showing a list of devices connected to the network with their IP and MAC addresses, along with options to manage their access.
3.5 WiFi Analyzer (Microsoft Store App)
WiFi Analyzer is a Windows 10 app available on the Microsoft Store, designed for home or temporary use. As noted in a TechRepublic review on November 10, 2023, it’s praised for its ease of use and ability to suggest optimal channels for reducing congestion. Key features include:
- Easy-to-Understand Visualizations: Turns network data into intuitive visualizations, making it easy to identify issues.
- Channel Suggestions: Suggests optimal channels for reducing congestion and improving performance.
- Basic and Pro Versions: Available in basic and pro versions, catering to different user needs.
3.6 Vistumbler
Vistumbler is a Wi-Fi network scanner that provides detailed information about access points and network connectivity. Key features include:
- Network Scanning: Scans for nearby networks, displaying network status, MAC address, SSID, signal strength, channel number, and network type.
- GPS Support: Integrates with Google Earth to display Wi-Fi networks on a map.
- Customizable Alerts: Notifies users when new networks are detected or when signal strength changes.
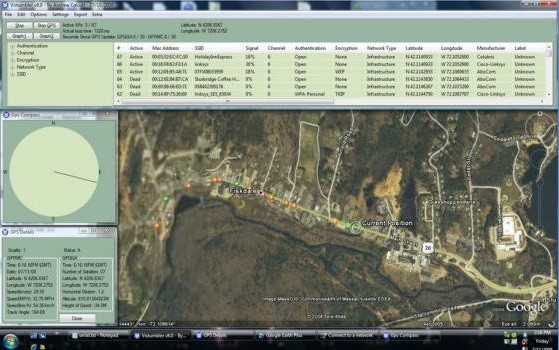 Vistumbler Wi-Fi Scanner
Vistumbler Wi-Fi Scanner
Alt: Vistumbler interface displaying a list of Wi-Fi networks with detailed information and GPS integration showing networks on a map.
3.7 WiFi Commander
WiFi Commander offers a sophisticated user interface with 3D graphs for visualizing Wi-Fi networks. Key features include:
- 3D Visualizations: Creates 3D graphs of Wi-Fi networks, allowing users to visualize signal strength and channel usage.
- Real-Time Data: Displays Wi-Fi signal strength in real-time, helping users find the strongest or most stable network.
- Touchscreen Support: Allows users to interact with the 3D visualizations using touch.
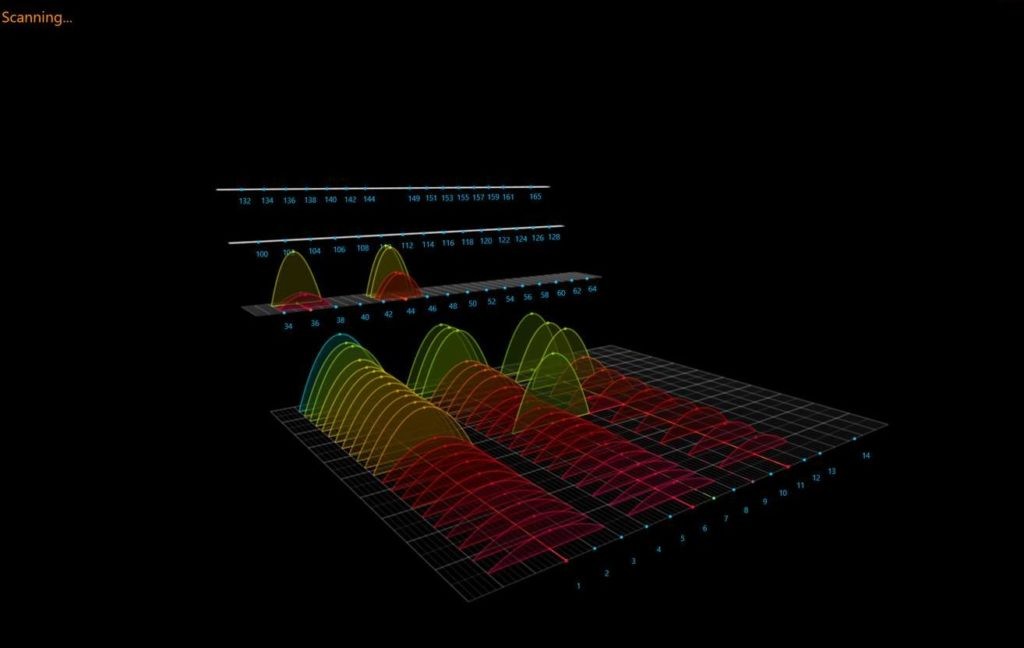 WiFi Commander
WiFi Commander
Alt: WiFi Commander’s 3D visualization showing Wi-Fi networks and their signal strength in real time.
3.8 Wireshark
Wireshark is a free, open-source network protocol analyzer that can be used to analyze Wi-Fi traffic. Key features include:
- Protocol Analysis: Analyzes various communication protocols, including Wi-Fi.
- Packet Capture: Captures network packets, allowing users to examine the data being transmitted.
- Filtering and Analysis Tools: Provides powerful filtering and analysis tools for identifying and troubleshooting network issues.
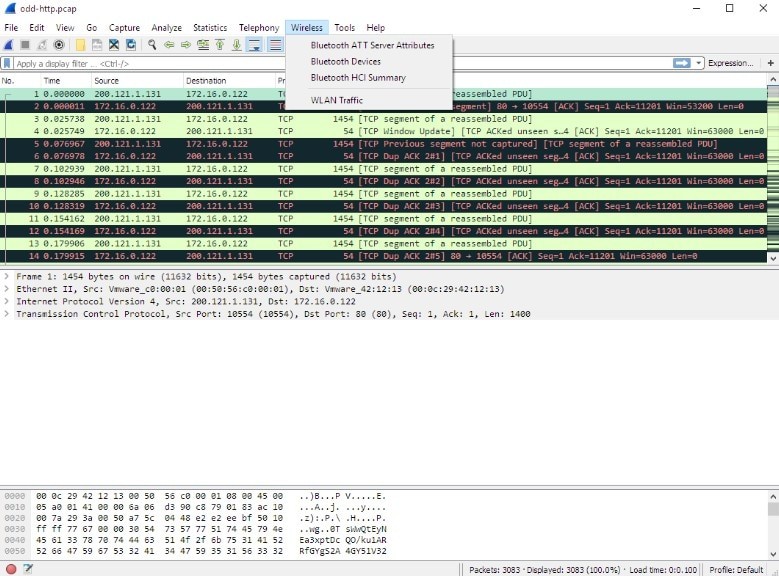 Wireshark Network Protocol Analyzer
Wireshark Network Protocol Analyzer
Alt: Wireshark interface displaying captured network packets and protocol analysis details.
4. Optimizing Your Wi-Fi Network Using a Wifi Analyzer
Using a Wifi analyzer can help you optimize your Wi-Fi network for better performance and reliability. The IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials journal published on November 20, 2022, offers guidance on maximizing network efficiency through strategic channel selection and access point placement.
4.1 Finding the Best Channel
One of the most important steps in optimizing your Wi-Fi network is to find the best channel. As previously mentioned, the 2.4 GHz band has only three non-overlapping channels (1, 6, and 11), while the 5 GHz band offers more options. A Wifi analyzer can help you identify which channels are the least congested in your area.
To find the best channel:
- Scan for Networks: Use a Wifi analyzer to scan for nearby networks and identify the channels they are using.
- Identify Congestion: Look for channels with the fewest networks and the lowest signal strength from competing networks.
- Change Channel: Access your router’s configuration settings and change the channel to the least congested one.
- Test Performance: Use a speed test tool to measure your network’s performance before and after changing the channel.
4.2 Improving Signal Strength
Signal strength is another critical factor in Wi-Fi performance. A weak signal can lead to slow speeds, dropped connections, and other issues. To improve signal strength:
- Check Router Placement: Make sure your router is placed in a central location, away from obstacles like walls and metal objects.
- Adjust Antenna Orientation: Experiment with different antenna orientations to find the best signal strength.
- Use a Wi-Fi Extender: If you have a large home or office, consider using a Wi-Fi extender to boost the signal in areas with weak coverage.
- Upgrade Your Router: If your router is old or outdated, consider upgrading to a newer model with better range and performance.
4.3 Enhancing Network Security
Securing your Wi-Fi network is essential for protecting your data and preventing unauthorized access. To enhance network security:
- Use a Strong Password: Choose a strong, unique password for your Wi-Fi network.
- Enable WPA3 Encryption: If your router supports it, enable WPA3 encryption for the best possible security.
- Disable WPS: Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) is a convenient feature, but it can be vulnerable to attacks. Disable WPS in your router’s configuration settings.
- Enable Firewall: Make sure your router’s firewall is enabled to protect your network from external threats.
- Update Firmware: Keep your router’s firmware up to date to patch any security vulnerabilities.
4.4 Identifying and Resolving Interference
Interference from other devices can negatively impact Wi-Fi performance. Common sources of interference include:
- Microwave Ovens: Operate on the 2.4 GHz band and can cause interference.
- Bluetooth Devices: Also operate on the 2.4 GHz band and can interfere with Wi-Fi signals.
- Cordless Phones: Some cordless phones use the 2.4 GHz band and can cause interference.
- Other Wi-Fi Networks: Congestion from nearby Wi-Fi networks can also cause interference.
To identify and resolve interference:
- Use a Wifi Analyzer: Use a Wifi analyzer to identify sources of interference.
- Move Devices: Move interfering devices away from your router and other Wi-Fi devices.
- Change Channels: Change your router’s channel to a less congested one.
- Use 5 GHz Band: If possible, switch to the 5 GHz band, which is less prone to interference.
5. Advanced Techniques for Wifi Analysis
For advanced users, Wifi analysis can involve more sophisticated techniques and tools. A study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) on September 12, 2023, highlights the importance of using advanced techniques for accurate network diagnostics and optimization.
5.1 Packet Analysis
Packet analysis involves capturing and analyzing network packets to identify issues and troubleshoot problems. Tools like Wireshark can be used to capture Wi-Fi traffic and examine the contents of each packet.
With packet analysis, you can:
- Identify Network Bottlenecks: Determine which devices or applications are consuming the most bandwidth.
- Troubleshoot Connectivity Issues: Analyze packet loss and retransmissions to identify the cause of connectivity problems.
- Detect Security Threats: Look for suspicious traffic patterns that may indicate a security breach.
5.2 Spectrum Analysis
Spectrum analysis involves analyzing the radio frequency spectrum to identify sources of interference. Tools like a spectrum analyzer can be used to visualize the spectrum and identify signals that may be interfering with Wi-Fi communications.
With spectrum analysis, you can:
- Identify Interference Sources: Pinpoint the exact sources of interference, such as microwave ovens or Bluetooth devices.
- Optimize Channel Selection: Choose channels that are free from interference.
- Improve Network Performance: Resolve interference issues to improve network speed and reliability.
5.3 Heatmapping
Heatmapping involves creating a visual representation of Wi-Fi signal strength across a physical space. Tools like NetSpot can be used to generate heatmaps, which can help you identify areas with weak coverage and optimize the placement of access points.
With heatmapping, you can:
- Identify Weak Spots: Pinpoint areas with poor Wi-Fi coverage.
- Optimize Access Point Placement: Determine the best locations for access points to achieve optimal coverage.
- Improve User Experience: Ensure that users have a strong, reliable Wi-Fi signal throughout the coverage area.
5.4 Automated Network Monitoring
Automated network monitoring involves using software tools to continuously monitor network performance and alert you to any issues. Tools like SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor can be used to automate network monitoring and provide real-time visibility into network health.
With automated network monitoring, you can:
- Proactively Identify Issues: Detect problems before they impact users.
- Reduce Downtime: Quickly resolve issues to minimize downtime.
- Improve Network Performance: Optimize network performance based on real-time data.
6. Common Problems and Solutions When Using a Wifi Analyzer
While Wifi analyzers are powerful tools, they can also present certain challenges. Addressing these challenges efficiently ensures accurate network analysis and optimal performance.
6.1 Inaccurate Readings
Problem: Sometimes, Wifi analyzers may provide inaccurate readings due to interference, outdated software, or hardware limitations.
Solution:
- Update Software: Ensure that your Wifi analyzer software is up to date to benefit from the latest bug fixes and improvements.
- Calibrate Hardware: Some Wifi analyzers require calibration to ensure accurate readings. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration.
- Minimize Interference: Reduce interference from other devices and sources by moving them away from the analyzer and the network devices.
- Use Multiple Analyzers: Compare readings from multiple Wifi analyzers to verify accuracy.
6.2 Difficulty Interpreting Data
Problem: The data provided by Wifi analyzers can be complex and difficult to interpret, especially for non-technical users.
Solution:
- Use Visualizations: Choose a Wifi analyzer that offers clear visualizations, such as heatmaps and graphs, to help you understand the data.
- Consult Documentation: Refer to the software’s documentation for explanations of the various metrics and parameters.
- Seek Expert Advice: If you are struggling to interpret the data, consult with a network professional or IT expert for assistance.
- Take Training Courses: Consider taking training courses on Wi-Fi analysis and network optimization to improve your understanding.
6.3 Compatibility Issues
Problem: Some Wifi analyzers may not be compatible with certain network devices or operating systems.
Solution:
- Check Compatibility: Before purchasing or using a Wifi analyzer, check its compatibility with your network devices and operating system.
- Use a Virtual Machine: If necessary, use a virtual machine to run the Wifi analyzer on a compatible operating system.
- Consider Cross-Platform Tools: Look for Wifi analyzers that are available for multiple platforms, such as Windows, macOS, and Linux.
6.4 Resource Intensive
Problem: Some Wifi analyzers can be resource-intensive, consuming a significant amount of CPU and memory.
Solution:
- Close Unnecessary Applications: Close any unnecessary applications to free up system resources.
- Increase System Resources: If possible, increase the amount of RAM and CPU cores available to your system.
- Use a Dedicated Device: Consider using a dedicated device, such as a laptop or tablet, for Wifi analysis.
- Optimize Software Settings: Adjust the software’s settings to reduce its resource usage, such as reducing the scanning frequency.
7. Future Trends in Wifi Analysis
The field of Wifi analysis is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques emerging all the time. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) published emerging trends in wireless technology on January 5, 2024, detailing future advancements.
7.1 AI-Powered Analysis
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being used to automate and improve Wifi analysis. AI algorithms can analyze network data in real-time, identify patterns, and make recommendations for optimizing performance.
AI-powered Wifi analysis tools can:
- Automatically Detect Issues: Identify and diagnose network problems without human intervention.
- Predict Future Performance: Forecast future network performance based on historical data.
- Optimize Network Settings: Automatically adjust network settings to maximize performance.
7.2 Cloud-Based Analysis
Cloud-based Wifi analysis tools allow you to analyze network data from anywhere in the world. These tools typically store network data in the cloud and provide a web-based interface for accessing and analyzing the data.
Cloud-based Wifi analysis tools offer several advantages:
- Remote Access: Access network data from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Scalability: Easily scale your analysis capabilities to meet your needs.
- Collaboration: Share network data and analysis results with colleagues and clients.
7.3 Integration with IoT Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly expanding, with more and more devices connecting to Wi-Fi networks. Wifi analysis tools are increasingly being integrated with IoT devices, allowing you to monitor and manage these devices.
With IoT integration, you can:
- Monitor IoT Device Performance: Track the performance of IoT devices and identify any issues.
- Secure IoT Devices: Protect IoT devices from security threats.
- Optimize IoT Network Traffic: Optimize network traffic to ensure that IoT devices have adequate bandwidth.
7.4 Wi-Fi 6 and 6E Analysis
The latest Wi-Fi standards, Wi-Fi 6 and 6E, offer significant improvements in performance, efficiency, and security. Wifi analysis tools are being updated to support these new standards, allowing you to take full advantage of their capabilities.
With Wi-Fi 6 and 6E analysis, you can:
- Optimize Wi-Fi 6/6E Networks: Fine-tune your Wi-Fi 6/6E networks for optimal performance.
- Troubleshoot Wi-Fi 6/6E Issues: Identify and resolve any issues related to Wi-Fi 6/6E.
- Ensure Compatibility: Verify that your devices are compatible with Wi-Fi 6/6E.
8. Practical Applications of Wifi Analysis in Different Environments
Wifi analysis is valuable in a variety of settings, from personal home networks to large enterprise environments. Understanding the specific applications can help users leverage these tools effectively.
8.1 Home Networks
In home networks, Wifi analysis can be used to:
- Improve Streaming Quality: Ensure smooth streaming of video and audio content by optimizing channel selection and signal strength.
- Enhance Gaming Performance: Reduce latency and improve responsiveness for online gaming by minimizing interference and congestion.
- Extend Coverage: Identify dead spots and optimize the placement of routers and extenders to provide coverage throughout the home.
- Secure the Network: Identify security vulnerabilities and ensure that the network is protected from unauthorized access.
8.2 Small Businesses
In small businesses, Wifi analysis can be used to:
- Optimize Productivity: Ensure that employees have a reliable and fast Wi-Fi connection for their work.
- Support Guest Access: Provide secure and reliable guest access to the Wi-Fi network.
- Monitor Network Usage: Track network usage to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation.
- Troubleshoot Connectivity Issues: Quickly diagnose and resolve connectivity issues to minimize downtime.
8.3 Large Enterprises
In large enterprises, Wifi analysis can be used to:
- Manage Network Performance: Continuously monitor network performance and identify any issues.
- Optimize Network Design: Plan and design the network to provide optimal coverage and performance throughout the enterprise.
- Secure the Network: Implement security policies and monitor for security threats.
- Support Mobile Devices: Ensure that mobile devices have a reliable and secure connection to the network.
8.4 Educational Institutions
In educational institutions, Wifi analysis can be used to:
- Support Online Learning: Ensure that students and faculty have a reliable and fast Wi-Fi connection for online learning.
- Manage Network Capacity: Optimize network capacity to accommodate the large number of devices connecting to the network.
- Secure the Network: Protect the network from security threats and ensure that student data is secure.
- Monitor Network Usage: Track network usage to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation.
8.5 Healthcare Facilities
In healthcare facilities, Wifi analysis can be used to:
- Support Medical Devices: Ensure that medical devices have a reliable and secure connection to the network.
- Protect Patient Data: Protect patient data from security threats and ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations.
- Optimize Network Performance: Optimize network performance to support critical applications, such as electronic health records (EHRs).
- Monitor Network Usage: Track network usage to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation.
9. Best Practices for Conducting a Wifi Analysis
To ensure that you get the most out of your Wifi analysis, it’s important to follow some best practices. These practices help ensure accurate readings, reliable results, and effective optimization.
9.1 Plan Your Analysis
Before you start your Wifi analysis, take some time to plan your approach.
- Define Your Goals: What do you want to achieve with your analysis? Are you trying to improve signal strength, reduce congestion, or enhance security?
- Identify Key Areas: Which areas do you want to analyze? Focus on areas where users are experiencing problems or where you want to optimize performance.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select the Wifi analyzer tools that are best suited for your goals and environment.
9.2 Conduct a Thorough Scan
When conducting your scan, be sure to capture as much data as possible.
- Scan All Channels: Scan all available channels to get a complete picture of the wireless environment.
- Collect Data from Multiple Locations: Collect data from multiple locations to create a heatmap of signal strength.
- Log Data Over Time: Log data over time to identify trends and patterns.
9.3 Analyze the Data
Once you have collected your data, take time to analyze it carefully.
- Identify Patterns: Look for patterns in the data that may indicate problems or opportunities for optimization.
- Compare Results: Compare your results to benchmarks or best practices to identify areas where you can improve.
- Prioritize Actions: Prioritize your actions based on the severity and impact of the issues you have identified.
9.4 Implement Changes
After you have analyzed your data, it’s time to implement changes to optimize your network.
- Change Router Settings: Adjust your router’s settings, such as channel selection and security protocols, to improve performance.
- Move Access Points: Move access points to optimize coverage and reduce interference.
- Add Wi-Fi Extenders: Add Wi-Fi extenders to extend coverage in areas with weak signals.
9.5 Monitor and Maintain
Once you have implemented your changes, it’s important to monitor and maintain your network to ensure that it continues to perform optimally.
- Continuously Monitor Performance: Use network monitoring tools to continuously track network performance.
- Regularly Scan for Issues: Regularly scan for issues, such as congestion and interference, to identify potential problems.
- Update Firmware: Keep your router’s firmware up to date to patch any security vulnerabilities and improve performance.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Wifi Analyzer Windows
Here are some frequently asked questions about Wifi analyzer Windows:
10.1 What is the best Wifi analyzer for Windows?
The best Wifi analyzer for Windows depends on your specific needs and budget. However, some of the top options include SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, NetSpot, InSSIDer, and WiFi Analyzer (Microsoft Store App).
10.2 How do I use a Wifi analyzer on Windows?
To use a Wifi analyzer on Windows, simply download and install the software, launch the application, and follow the instructions to scan for nearby networks. The analyzer will then display detailed information about the networks, such as signal strength, channel, and security settings.
10.3 Is a Wifi analyzer safe to use?
Yes, Wifi analyzers are generally safe to use, as long as you download them from reputable sources. However, be sure to review the software’s permissions and privacy policy before installing it.
10.4 Can a Wifi analyzer improve my network speed?
Yes, a Wifi analyzer can help improve your network speed by identifying the least congested channels, optimizing access point placement, and resolving interference issues.
10.5 How often should I run a Wifi analysis?
You should run a Wifi analysis whenever you are experiencing network problems or when you want to optimize your network’s performance. It’s also a good idea to run a Wifi analysis periodically to monitor your network’s health.
10.6 What is RSSI?
RSSI stands for Received Signal Strength Indicator. It is a measure of the power present in a received radio signal, typically expressed in dBm. The closer the value is to 0, the stronger the signal.
10.7 What is a Wi-Fi channel?
A Wi-Fi channel is a specific frequency band used for wireless communication. The 2.4 GHz band has 14 channels, while the 5 GHz band offers more options.
10.8 What is WPA3?
WPA3 is the latest and most secure Wi-Fi security protocol. It offers enhanced protection against various attacks and is recommended for all modern Wi-Fi networks.
10.9 Can a Wifi analyzer detect hidden networks?
Yes, some Wifi analyzers can detect hidden networks, but you may need to manually enter the network’s SSID to connect to it.
10.10 How do I choose the best channel for my Wi-Fi network?
To choose the best channel for your Wi-Fi network, use a Wifi analyzer to scan for nearby networks and identify the least congested channel. Then, access your router’s configuration settings and change the channel to the least congested one.
By understanding and utilizing Wifi analyzer Windows tools, individuals and organizations can significantly enhance their wireless network performance, security, and reliability. At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing the resources and expertise you need to optimize your networks and stay connected.
Are you experiencing difficulties in finding reliable auto parts or tools? Do you find yourself spending too much time comparing prices and features? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today at 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Let us help you find the perfect solutions for your automotive needs, ensuring you get the best quality and value. Visit CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information.