An Injector Tester is an essential tool for diagnosing and maintaining fuel injectors, ensuring optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency, and CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive resources to help you choose and use the right tester. This guide explores injector testers, their usage, benefits, and how to select the best one for your needs, including leak detection and spray pattern analysis.
Contents
- 1. Understanding Injector Testers
- 1.1. What is an Injector Tester?
- 1.2. Why Do You Need an Injector Tester?
- 1.3. Types of Injector Testers
- 2. Key Features of Injector Testers
- 2.1. Pressure Range
- 2.2. Accuracy and Calibration
- 2.3. Compatibility
- 2.4. Ease of Use
- 2.5. Additional Features
- 3. How to Use an Injector Tester
- 3.1. Preparing for the Test
- 3.2. Connecting the Injector
- 3.3. Performing the Test
- 3.4. Interpreting the Results
- 4. Benefits of Using an Injector Tester
- 4.1. Improved Engine Performance
- 4.2. Enhanced Fuel Efficiency
- 4.3. Reduced Emissions
- 4.4. Cost Savings
- 4.5. Preventive Maintenance
- 5. Choosing the Right Injector Tester
- 5.1. Consider Your Needs
- 5.2. Check the Specifications
- 5.3. Read Reviews and Ratings
- 5.4. Compare Prices
- 5.5. Warranty and Support
- 6. Common Problems and Solutions
- 6.1. Inaccurate Readings
- 6.2. Leaks in the System
- 6.3. Injector Not Responding
- 6.4. Pressure Fluctuations
- 6.5. Contamination Issues
- 7. Advanced Injector Testing Techniques
- 7.1. Dynamic Flow Testing
- 7.2. Coil Resistance Testing
- 7.3. Ultrasonic Cleaning
- 7.4. Back Leakage Testing
- 7.5. Response Time Testing
- 8. Injector Tester Brands and Models
- 8.1. Bosch
- 8.2. ASNU
- 8.3. OTC
- 8.4. Launch
- 8.5. Autool
- 9. Maintenance and Calibration
- 9.1. Regular Cleaning
- 9.2. Checking for Leaks
- 9.3. Recalibration
- 9.4. Storage
- 9.5. Component Inspection
- 10. Safety Precautions
- 10.1. Personal Protective Equipment
- 10.2. Ventilation
- 10.3. Fuel Handling
- 10.4. Electrical Safety
- 10.5. Emergency Procedures
- 11. Injector Tester Applications
- 11.1. Automotive
- 11.2. Marine
- 11.3. Motorcycle
- 11.4. Industrial
- 11.5. Aviation
- 12. Future Trends in Injector Testing
- 12.1. Smart Injector Testers
- 12.2. AI-Powered Diagnostics
- 12.3. Portable Testing Solutions
- 12.4. Enhanced Data Analysis
- 12.5. Integration with Vehicle Systems
- 13. Expert Tips for Injector Testing
- 13.1. Use Clean Fuel
- 13.2. Check Electrical Connections
- 13.3. Observe Spray Patterns
- 13.4. Listen for Unusual Noises
- 13.5. Document Your Results
- 14. Cost Analysis of Injector Testing
- 14.1. Initial Investment
- 14.2. Operating Costs
- 14.3. Maintenance Costs
- 14.4. Potential Savings
- 14.5. Return on Investment
- 15. Resources for Further Learning
- 15.1. Online Courses
- 15.2. Technical Manuals
- 15.3. Forums and Communities
- 15.4. Workshops and Seminars
Table of Contents
- Understanding Injector Testers
-
- What is an Injector Tester?
-
- Why Do You Need an Injector Tester?
-
- Types of Injector Testers
-
- Key Features of Injector Testers
-
- Pressure Range
-
- Accuracy and Calibration
-
- Compatibility
-
- Ease of Use
-
- Additional Features
-
- How to Use an Injector Tester
-
- Preparing for the Test
-
- Connecting the Injector
-
- Performing the Test
-
- Interpreting the Results
-
- Benefits of Using an Injector Tester
-
- Improved Engine Performance
-
- Enhanced Fuel Efficiency
-
- Reduced Emissions
-
- Cost Savings
-
- Preventive Maintenance
-
- Choosing the Right Injector Tester
-
- Consider Your Needs
-
- Check the Specifications
-
- Read Reviews and Ratings
-
- Compare Prices
-
- Warranty and Support
-
- Common Problems and Solutions
-
- Inaccurate Readings
-
- Leaks in the System
-
- Injector Not Responding
-
- Pressure Fluctuations
-
- Contamination Issues
-
- Advanced Injector Testing Techniques
-
- Dynamic Flow Testing
-
- Coil Resistance Testing
-
- Ultrasonic Cleaning
-
- Back Leakage Testing
-
- Response Time Testing
-
- Injector Tester Brands and Models
-
- Bosch
-
- ASNU
-
- OTC
-
- Launch
-
- Autool
-
- Maintenance and Calibration
-
- Regular Cleaning
-
- Checking for Leaks
-
- Recalibration
-
- Storage
-
- Component Inspection
-
- Safety Precautions
-
- Personal Protective Equipment
-
- Ventilation
-
- Fuel Handling
-
- Electrical Safety
-
- Emergency Procedures
-
- Injector Tester Applications
-
- Automotive
-
- Marine
-
- Motorcycle
-
- Industrial
-
- Aviation
-
- Future Trends in Injector Testing
-
- Smart Injector Testers
-
- AI-Powered Diagnostics
-
- Portable Testing Solutions
-
- Enhanced Data Analysis
-
- Integration with Vehicle Systems
-
- Expert Tips for Injector Testing
-
- Use Clean Fuel
-
- Check Electrical Connections
-
- Observe Spray Patterns
-
- Listen for Unusual Noises
-
- Document Your Results
-
- Cost Analysis of Injector Testing
-
- Initial Investment
-
- Operating Costs
-
- Maintenance Costs
-
- Potential Savings
-
- Return on Investment
-
- Resources for Further Learning
-
- Online Courses
-
- Technical Manuals
-
- Forums and Communities
-
- Workshops and Seminars
-
- Vendor Training Programs
-
- FAQ: Answering Your Questions About Injector Testers
1. Understanding Injector Testers
1.1. What is an Injector Tester?
An injector tester, also known as a fuel injector tester, is a diagnostic device used to assess the functionality and performance of fuel injectors in internal combustion engines. These testers are crucial for evaluating spray patterns, identifying leaks, and measuring the fuel flow rate, ensuring the fuel injectors deliver the correct amount of fuel at the right pressure. Regular testing with devices such as automotive injector flow testers helps maintain engine efficiency and reduce emissions. According to a study by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), properly functioning fuel injectors can improve fuel economy by as much as 15%.
1.2. Why Do You Need an Injector Tester?
Using an injector tester is vital for several reasons. It helps diagnose engine problems such as rough idling, misfires, poor fuel economy, and reduced power, which are often caused by faulty fuel injectors. By testing fuel injectors, technicians can identify issues like blockages, leaks, or incorrect spray patterns. This proactive approach prevents further engine damage and costly repairs. According to Bosch Automotive, a leading manufacturer of fuel injection systems, regular testing and maintenance of fuel injectors can extend their lifespan and improve overall engine reliability.
1.3. Types of Injector Testers
There are several types of injector testers available, each designed for specific applications and budgets:
- On-Car Injector Testers: These portable devices allow testing of fuel injectors while they are still installed in the vehicle. They are convenient for quick diagnostics and field testing.
- Off-Car Injector Testers: These testers require the removal of fuel injectors for testing. They often include features for cleaning and back-flushing injectors, providing a more thorough analysis.
- Ultrasonic Injector Cleaners: These machines use ultrasonic waves to clean fuel injectors, removing deposits and restoring proper function. They often include testing capabilities.
- DIY Injector Testers: These are homemade testers often built using hydraulic jacks and other readily available components. While cost-effective, they may not provide the accuracy and safety of professional testers.
Here’s a comparison table of different types of injector testers:
| Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| On-Car Injector Testers | Tests injectors while still installed in the vehicle. | Convenient, quick diagnostics. | Less thorough, may not detect all issues. |
| Off-Car Injector Testers | Requires removal of injectors for testing; often includes cleaning features. | More thorough analysis, includes cleaning and back-flushing. | Requires injector removal, more time-consuming. |
| Ultrasonic Injector Cleaners | Uses ultrasonic waves to clean injectors; often includes testing capabilities. | Cleans injectors effectively, restores proper function. | Can be expensive, not always necessary. |
| DIY Injector Testers | Homemade testers using readily available components. | Cost-effective. | Less accurate, may not be safe, requires technical skills. |
2. Key Features of Injector Testers
2.1. Pressure Range
The pressure range of an injector tester is a critical specification. It determines the tester’s ability to simulate the operating conditions of various fuel injection systems. Most modern fuel injection systems operate at pressures between 30 and 80 PSI (200-550 kPa), but some high-performance or direct injection systems can exceed 2000 PSI (13,800 kPa). Ensure the tester’s pressure range matches the requirements of the fuel injectors you intend to test. According to Delphi Technologies, using a tester with an inadequate pressure range can lead to inaccurate results and potential damage to the injectors.
2.2. Accuracy and Calibration
Accuracy is paramount for reliable injector testing. A high-quality tester should provide precise readings and maintain calibration over time. Calibration ensures that the tester’s measurements align with known standards. Regular calibration, typically performed annually or after a specific number of uses, is essential to maintain accuracy. Look for testers that offer easy calibration procedures or come with a calibration certificate. A study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) highlights the importance of regular calibration to ensure accurate diagnostic results.
2.3. Compatibility
Injector testers should be compatible with a wide range of fuel injector types, including gasoline, diesel, and direct injection injectors. Universal adapters and connectors can enhance compatibility, allowing the tester to be used with various makes and models of vehicles. Check the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure the tester supports the injectors you need to test. Denso, a leading supplier of automotive components, recommends verifying compatibility to avoid damaging injectors or the tester itself.
2.4. Ease of Use
A user-friendly interface is crucial for efficient and accurate testing. Look for testers with clear displays, intuitive controls, and comprehensive instructions. Features like automatic testing modes, data logging, and graphical displays can simplify the testing process and improve diagnostic accuracy. According to a survey by the Automotive Service Association (ASA), technicians prefer tools that are easy to use and require minimal training.
2.5. Additional Features
Some injector testers come with additional features that enhance their functionality and value:
- Leak Testing: Detects leaks in the injector body or nozzle.
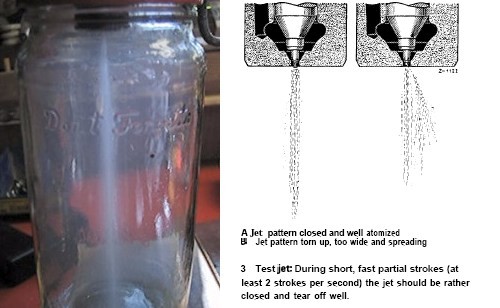
- Spray Pattern Analysis: Visualizes the fuel spray pattern to identify abnormalities.
- Flow Rate Measurement: Measures the volume of fuel delivered by the injector.
- Resistance Testing: Checks the electrical resistance of the injector coil.
- Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Control: Simulates the engine control unit (ECU) signals to control the injector.
Here’s a table summarizing the key features of injector testers:
| Feature | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Range | The range of pressure the tester can apply to the injector. | Must match the operating pressure of the injectors being tested. |
| Accuracy and Calibration | How precisely the tester measures and maintains its accuracy. | Ensures reliable and consistent test results. |
| Compatibility | The range of injector types and vehicle models the tester can support. | Allows testing of various injector types and vehicle models. |
| Ease of Use | How user-friendly the tester is in terms of interface and controls. | Simplifies the testing process and reduces the learning curve. |
| Leak Testing | Detects leaks in the injector body or nozzle. | Identifies faulty injectors that may cause fuel wastage and engine problems. |
| Spray Pattern Analysis | Visualizes the fuel spray pattern. | Helps identify abnormalities in the spray pattern that can affect engine performance. |
| Flow Rate Measurement | Measures the volume of fuel delivered by the injector. | Determines if the injector is delivering the correct amount of fuel. |
| Resistance Testing | Checks the electrical resistance of the injector coil. | Identifies electrical issues that may prevent the injector from functioning correctly. |
| PWM Control | Simulates ECU signals to control the injector during testing. | Allows for dynamic testing of the injector under various operating conditions. |
3. How to Use an Injector Tester
3.1. Preparing for the Test
Before using an injector tester, gather the necessary tools and equipment, including the tester, appropriate adapters, safety glasses, gloves, and a clean workspace. Ensure the fuel injectors are clean and free from debris. Consult the vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions and safety precautions. According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), proper preparation is essential for accurate and safe testing.
3.2. Connecting the Injector
Connect the fuel injector to the tester using the appropriate adapter. Ensure the connection is secure and leak-free. If using an off-car tester, mount the injector in the testing chamber according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For on-car testers, connect the tester to the injector while it is still installed in the vehicle, following the recommended procedure. Always double-check the connections to avoid errors and potential damage.
3.3. Performing the Test
Follow the tester’s instructions to perform the test. This typically involves setting the test parameters, such as pressure and pulse width, and initiating the test sequence. Observe the injector’s spray pattern, check for leaks, and measure the fuel flow rate. Record the results for each injector. Some testers offer automatic testing modes that simplify the process.
3.4. Interpreting the Results
Compare the test results to the manufacturer’s specifications. Look for deviations in spray pattern, flow rate, and leak rate. A healthy injector should produce a consistent, cone-shaped spray pattern with no leaks and a flow rate within the specified range. If the results indicate a problem, consider cleaning or replacing the injector. Consult with a qualified technician for further diagnosis and repair.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use an injector tester:
| Step | Action | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gather Tools and Equipment | Collect the injector tester, adapters, safety glasses, gloves, and a clean workspace. |
| 2 | Prepare the Injectors | Ensure the fuel injectors are clean and free from debris. Consult the vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions and safety precautions. |
| 3 | Connect the Injector | Connect the fuel injector to the tester using the appropriate adapter. Ensure the connection is secure and leak-free. |
| 4 | Mount the Injector (Off-Car Testers) | If using an off-car tester, mount the injector in the testing chamber according to the manufacturer’s instructions. |
| 5 | Connect the Tester (On-Car Testers) | For on-car testers, connect the tester to the injector while it is still installed in the vehicle, following the recommended procedure. |
| 6 | Set Test Parameters | Follow the tester’s instructions to set the test parameters, such as pressure and pulse width. |
| 7 | Initiate the Test Sequence | Initiate the test sequence and observe the injector’s spray pattern, check for leaks, and measure the fuel flow rate. Record the results for each injector. |
| 8 | Observe Spray Pattern | A healthy injector should produce a consistent, cone-shaped spray pattern. Look for abnormalities such as uneven spray, drips, or jets. |
| 9 | Check for Leaks | Ensure there are no leaks from the injector body or nozzle. Leaks can indicate a faulty injector that needs to be replaced. |
| 10 | Measure Fuel Flow Rate | Measure the volume of fuel delivered by the injector during the test. Compare the results to the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure the injector is delivering the correct amount of fuel. |
| 11 | Compare Results to Specifications | Compare the test results to the manufacturer’s specifications. Look for deviations in spray pattern, flow rate, and leak rate. |
| 12 | Consider Cleaning or Replacing Injector | If the results indicate a problem, consider cleaning or replacing the injector. Consult with a qualified technician for further diagnosis and repair. |
 Fuel Injector Pop Tester Jack
Fuel Injector Pop Tester Jack
Fuel Injector Tester setup showing the hydraulic jack, pressure gauge, and fuel lines connecting to the injector for testing.
4. Benefits of Using an Injector Tester
4.1. Improved Engine Performance
Testing and maintaining fuel injectors ensures they deliver the correct amount of fuel at the right pressure, resulting in optimal combustion. This leads to improved engine performance, including smoother idling, better acceleration, and increased power. According to a study by the Oak Ridge National Laboratory, properly functioning fuel injectors can significantly enhance engine responsiveness.
4.2. Enhanced Fuel Efficiency
Faulty fuel injectors can cause over-fueling or under-fueling, leading to poor fuel economy. By identifying and resolving injector issues, an injector tester helps maintain optimal fuel-to-air ratios, maximizing fuel efficiency. The EPA estimates that addressing fuel injector problems can improve fuel economy by up to 15%.
4.3. Reduced Emissions
Inefficient combustion due to faulty fuel injectors can increase harmful emissions, such as hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides. Regular testing and maintenance of fuel injectors helps reduce emissions, contributing to cleaner air and compliance with environmental regulations. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) emphasizes the importance of maintaining fuel injection systems to minimize vehicle emissions.
4.4. Cost Savings
While investing in an injector tester may seem like an upfront expense, it can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. By identifying and addressing injector problems early, you can prevent further engine damage and costly repairs. Additionally, improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions contribute to lower operating costs. A report by AAA indicates that preventive maintenance, including fuel injector service, can save vehicle owners hundreds of dollars annually.
4.5. Preventive Maintenance
Regular use of an injector tester as part of a preventive maintenance program can help identify potential problems before they escalate. This proactive approach ensures that fuel injectors are functioning optimally, extending their lifespan and improving overall engine reliability. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), preventive maintenance is crucial for ensuring vehicle safety and performance.
Here’s a table summarizing the benefits of using an injector tester:
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Engine Performance | Ensures correct fuel delivery for optimal combustion. | Smoother idling, better acceleration, increased power. |
| Enhanced Fuel Efficiency | Maintains optimal fuel-to-air ratios. | Maximizes fuel efficiency, reduces fuel consumption. |
| Reduced Emissions | Minimizes harmful emissions through efficient combustion. | Contributes to cleaner air, compliance with environmental regulations. |
| Cost Savings | Prevents engine damage and costly repairs. | Lowers operating costs through improved fuel efficiency. |
| Preventive Maintenance | Identifies potential problems early. | Extends injector lifespan, improves engine reliability. |
5. Choosing the Right Injector Tester
5.1. Consider Your Needs
Before purchasing an injector tester, assess your specific needs and requirements. Consider the types of vehicles you will be working on, the frequency of testing, and your budget. If you primarily work on older vehicles with simple fuel injection systems, a basic tester may suffice. However, if you work on modern, high-performance vehicles with advanced fuel injection systems, you will need a more sophisticated tester with advanced features.
5.2. Check the Specifications
Review the tester’s specifications to ensure it meets your requirements. Pay attention to the pressure range, accuracy, compatibility, and additional features. Ensure the tester supports the types of fuel injectors you will be testing and has the necessary adapters and connectors. Read the manufacturer’s documentation carefully to understand the tester’s capabilities and limitations.
5.3. Read Reviews and Ratings
Research and read reviews and ratings from other users to get an idea of the tester’s performance and reliability. Look for testers that have consistently positive reviews and high ratings. Pay attention to comments about accuracy, ease of use, and customer support. Online forums and automotive communities can provide valuable insights and recommendations.
5.4. Compare Prices
Compare prices from different vendors to find the best deal. Keep in mind that the cheapest option is not always the best. Consider the tester’s features, quality, and warranty when evaluating price. Look for reputable vendors that offer competitive prices and reliable customer support.
5.5. Warranty and Support
Check the warranty and support offered by the manufacturer. A good warranty provides protection against defects and malfunctions. Reliable customer support can help you troubleshoot problems and get the most out of your tester. Look for manufacturers that offer technical support, online resources, and training materials.
Here’s a checklist for choosing the right injector tester:
- Assess Your Needs: Determine the types of vehicles you will be working on, the frequency of testing, and your budget.
- Check Specifications: Review the tester’s pressure range, accuracy, compatibility, and additional features.
- Read Reviews: Research and read reviews and ratings from other users.
- Compare Prices: Compare prices from different vendors.
- Check Warranty and Support: Ensure the manufacturer offers a good warranty and reliable customer support.
6. Common Problems and Solutions
6.1. Inaccurate Readings
Inaccurate readings can result from several factors, including improper calibration, worn components, or contamination. Ensure the tester is properly calibrated according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Check for worn or damaged components and replace them as needed. Clean the tester regularly to prevent contamination.
6.2. Leaks in the System
Leaks can occur in the tester’s connections or internal components. Check all connections for tightness and ensure they are properly sealed. Replace any damaged or worn seals and O-rings. If the leak persists, consult with a qualified technician for further diagnosis and repair.
 Diesel Fuel Injector Spray Pattern
Diesel Fuel Injector Spray Pattern
Close-up of a diesel fuel injector spray pattern during testing, highlighting the atomization quality and cone shape.
6.3. Injector Not Responding
If the injector is not responding during the test, check the electrical connections and ensure the injector is receiving power. Verify the injector’s resistance to ensure the coil is not open or shorted. If the problem persists, the injector may be faulty and require replacement.
6.4. Pressure Fluctuations
Pressure fluctuations can indicate a problem with the tester’s pump or regulator. Check the pump for proper operation and replace it if necessary. Inspect the regulator for damage or contamination and clean or replace it as needed. Ensure the tester’s pressure gauge is accurate and functioning correctly.
6.5. Contamination Issues
Contamination can cause inaccurate readings and damage the tester. Use clean fuel and filters to prevent contamination. Clean the tester regularly according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Store the tester in a clean and dry environment to prevent contamination.
Here’s a troubleshooting table for common problems with injector testers:
| Problem | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Inaccurate Readings | Improper calibration, worn components, contamination. | Calibrate tester, replace worn components, clean tester. |
| Leaks in the System | Loose connections, damaged seals. | Tighten connections, replace seals. |
| Injector Not Responding | Electrical issues, faulty injector. | Check electrical connections, verify injector resistance, replace injector. |
| Pressure Fluctuations | Pump or regulator issues. | Check pump operation, inspect regulator, ensure accurate pressure gauge. |
| Contamination Issues | Dirty fuel, lack of cleaning. | Use clean fuel and filters, clean tester regularly. |
7. Advanced Injector Testing Techniques
7.1. Dynamic Flow Testing
Dynamic flow testing involves measuring the fuel flow rate of the injector under varying conditions, such as different pulse widths and pressures. This technique provides a more comprehensive assessment of the injector’s performance and can reveal subtle issues that may not be apparent during static testing. Dynamic testing requires specialized equipment and software.
7.2. Coil Resistance Testing
Coil resistance testing measures the electrical resistance of the injector coil. This test can identify open circuits, short circuits, or excessive resistance, which can indicate a faulty injector. Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the injector coil and compare the results to the manufacturer’s specifications.
7.3. Ultrasonic Cleaning
Ultrasonic cleaning uses high-frequency sound waves to remove deposits and contaminants from the fuel injector. This technique is effective for restoring the injector’s performance and spray pattern. Ultrasonic cleaning requires specialized equipment and cleaning solutions.
7.4. Back Leakage Testing
Back leakage testing measures the amount of fuel that leaks from the injector when it is not energized. Excessive back leakage can indicate a worn or damaged injector. This test requires specialized equipment and procedures.
7.5. Response Time Testing
Response time testing measures the time it takes for the injector to open and close. Slow response times can affect fuel delivery and engine performance. This test requires specialized equipment and software.
Here’s a table summarizing advanced injector testing techniques:
| Technique | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Flow Testing | Measures fuel flow rate under varying conditions. | Comprehensive assessment of injector performance. |
| Coil Resistance Testing | Measures electrical resistance of the injector coil. | Identifies electrical issues. |
| Ultrasonic Cleaning | Uses high-frequency sound waves to remove deposits. | Restores injector performance and spray pattern. |
| Back Leakage Testing | Measures fuel leakage when the injector is not energized. | Identifies worn or damaged injectors. |
| Response Time Testing | Measures the time it takes for the injector to open and close. | Identifies slow response times that can affect fuel delivery and performance. |
8. Injector Tester Brands and Models
8.1. Bosch
Bosch is a leading manufacturer of fuel injection systems and injector testers. Their testers are known for their accuracy, reliability, and compatibility with a wide range of injectors. Popular Bosch models include the EPS 205 and EPS 708.
8.2. ASNU
ASNU is a well-known brand specializing in fuel injector testing and cleaning equipment. Their testers are used by professional technicians and automotive enthusiasts worldwide. ASNU models are known for their advanced features and user-friendly interface.
8.3. OTC
OTC (Owatonna Tool Company) offers a range of injector testers designed for automotive diagnostics and repair. Their testers are known for their durability and ease of use. Popular OTC models include the 7000A and 7005.
8.4. Launch
Launch Tech Co. Ltd. is a global leader in automotive diagnostic equipment, including injector testers. Their testers are known for their innovative features and compatibility with a wide range of vehicles. Launch models are popular among professional technicians.
8.5. Autool
Autool offers a variety of injector testers at affordable prices. Their testers are suitable for both professional and DIY use. Autool models are known for their ease of use and value for money.
Here’s a comparison table of injector tester brands and models:
| Brand | Model | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Bosch | EPS 205 | Accurate, reliable, compatible with a wide range of injectors. |
| ASNU | Various | Advanced features, user-friendly interface. |
| OTC | 7000A | Durable, easy to use. |
| Launch | Various | Innovative features, compatible with a wide range of vehicles. |
| Autool | Various | Affordable, suitable for professional and DIY use, easy to use. |
9. Maintenance and Calibration
9.1. Regular Cleaning
Regular cleaning is essential to maintain the accuracy and reliability of your injector tester. Clean the tester after each use to remove fuel residue and contaminants. Use a mild solvent or cleaner recommended by the manufacturer.
9.2. Checking for Leaks
Check the tester for leaks regularly. Inspect all connections and seals for damage or wear. Replace any damaged or worn components.
9.3. Recalibration
Recalibrate the tester periodically to ensure accuracy. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration. If you are unsure how to calibrate the tester, consult with a qualified technician.
9.4. Storage
Store the tester in a clean and dry environment to protect it from damage. Cover the tester to prevent dust and contaminants from entering the system.
9.5. Component Inspection
Inspect all components of the tester regularly, including hoses, connectors, and gauges. Replace any worn or damaged components.
Here’s a maintenance checklist for injector testers:
- Clean After Each Use: Remove fuel residue and contaminants.
- Check for Leaks Regularly: Inspect connections and seals for damage.
- Recalibrate Periodically: Ensure accuracy according to manufacturer’s instructions.
- Store Properly: Keep in a clean, dry environment.
- Inspect Components: Check hoses, connectors, and gauges for wear.
10. Safety Precautions
10.1. Personal Protective Equipment
Always wear personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with fuel injectors and injector testers. This includes safety glasses, gloves, and a lab coat or apron.
10.2. Ventilation
Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fuel vapors. If ventilation is limited, use a respirator or mask.
10.3. Fuel Handling
Handle fuel with care to avoid spills and fire hazards. Use approved containers for storing fuel. Clean up any spills immediately.
10.4. Electrical Safety
Ensure the tester is properly grounded to prevent electrical shock. Use caution when working with electrical components.
10.5. Emergency Procedures
Know the emergency procedures in case of a fire or fuel spill. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
Here’s a summary of safety precautions for using injector testers:
- Wear PPE: Use safety glasses, gloves, and a lab coat.
- Ensure Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Handle Fuel Carefully: Avoid spills and fire hazards.
- Maintain Electrical Safety: Ensure proper grounding.
- Know Emergency Procedures: Be prepared for fires and spills.
 Building a Diesel Injector Pop Tester
Building a Diesel Injector Pop Tester
Illustration of a DIY diesel injector pop tester setup, showing the connection of fuel lines, pressure gauge, and injector nozzle.
11. Injector Tester Applications
11.1. Automotive
Injector testers are widely used in the automotive industry for diagnosing and maintaining fuel injectors in gasoline and diesel engines. They are essential tools for automotive technicians and mechanics.
11.2. Marine
Injector testers are used in the marine industry for testing fuel injectors in boat engines. They help ensure optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
11.3. Motorcycle
Injector testers are used for testing fuel injectors in motorcycles. They help improve engine performance and fuel economy.
11.4. Industrial
Injector testers are used in industrial applications for testing fuel injectors in generators, pumps, and other equipment. They help ensure reliable operation and reduce downtime.
11.5. Aviation
Injector testers are used in the aviation industry for testing fuel injectors in aircraft engines. They are essential for ensuring flight safety and performance.
Here’s a table of injector tester applications:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Testing fuel injectors in gasoline and diesel engines. |
| Marine | Testing fuel injectors in boat engines. |
| Motorcycle | Testing fuel injectors in motorcycles. |
| Industrial | Testing fuel injectors in generators, pumps, and other equipment. |
| Aviation | Testing fuel injectors in aircraft engines. |
12. Future Trends in Injector Testing
12.1. Smart Injector Testers
Smart injector testers are equipped with advanced sensors and microprocessors that provide more accurate and detailed test results. They can also communicate with other diagnostic tools and vehicle systems.
12.2. AI-Powered Diagnostics
AI-powered diagnostics use artificial intelligence to analyze test results and identify potential problems with fuel injectors. This technology can help technicians diagnose issues more quickly and accurately.
12.3. Portable Testing Solutions
Portable testing solutions are designed for on-the-go testing and diagnostics. They are lightweight, compact, and easy to use.
12.4. Enhanced Data Analysis
Enhanced data analysis tools provide more detailed information about fuel injector performance. They can help technicians identify subtle issues and optimize fuel delivery.
12.5. Integration with Vehicle Systems
Integration with vehicle systems allows injector testers to communicate directly with the vehicle’s ECU and other systems. This can provide valuable information about fuel injector performance and engine operation.
Here’s a summary of future trends in injector testing:
- Smart Injector Testers: Advanced sensors and microprocessors for accurate results.
- AI-Powered Diagnostics: AI analysis for quick and accurate issue identification.
- Portable Testing Solutions: Lightweight and compact for on-the-go testing.
- Enhanced Data Analysis: Detailed information about fuel injector performance.
- Integration with Vehicle Systems: Direct communication with vehicle ECU.
13. Expert Tips for Injector Testing
13.1. Use Clean Fuel
Always use clean fuel when testing fuel injectors to prevent contamination.
13.2. Check Electrical Connections
Check all electrical connections to ensure they are secure and functioning properly.
13.3. Observe Spray Patterns
Observe the spray patterns carefully to identify any abnormalities.
13.4. Listen for Unusual Noises
Listen for any unusual noises during testing, such as clicking or hissing sounds.
13.5. Document Your Results
Document your test results for future reference.
Here’s a list of expert tips for injector testing:
- Use Clean Fuel: Prevent contamination.
- Check Electrical Connections: Ensure secure connections.
- Observe Spray Patterns: Identify abnormalities.
- Listen for Unusual Noises: Detect potential issues.
- Document Results: Keep records for future reference.
14. Cost Analysis of Injector Testing
14.1. Initial Investment
The initial investment for an injector tester can range from a few hundred dollars for a basic model to several thousand dollars for an advanced model.
14.2. Operating Costs
Operating costs include the cost of fuel, cleaning solutions, and replacement parts.
14.3. Maintenance Costs
Maintenance costs include the cost of calibration and repairs.
14.4. Potential Savings
Potential savings include improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and prevention of costly repairs.
14.5. Return on Investment
The return on investment (ROI) for an injector tester can be significant, especially for professional technicians and mechanics.
Here’s a breakdown of the cost analysis of injector testing:
| Cost Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Cost of purchasing the injector tester. |
| Operating Costs | Fuel, cleaning solutions, replacement parts. |
| Maintenance Costs | Calibration and repairs. |
| Potential Savings | Improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, prevention of costly repairs. |
| Return on Investment | Significant, especially for professional technicians and mechanics. |
15. Resources for Further Learning
15.1. Online Courses
Online courses offer comprehensive training on fuel injection systems and injector testing.
15.2. Technical Manuals
Technical manuals provide detailed information about fuel injection systems and injector testing procedures.
15.3. Forums and Communities
Forums and communities offer a platform for sharing knowledge and experience with other technicians and enthusiasts.
15.4. Workshops and Seminars
Workshops and seminars provide hands-on training on fuel injection systems and injector testing.
