Point Of Care Diagnostics Packaging ensures the safe and effective delivery of diagnostic tests and related supplies to the location of patient care, enabling rapid and accurate results. CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive insights into the critical aspects of this field. This packaging plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of diagnostic tests, facilitating ease of use, and supporting efficient healthcare delivery.
Contents
- 1. What Exactly Is Point Of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
- 1.1. Why Is Proper Packaging Important for Point of Care Diagnostics?
- 1.2. Key Components of Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging
- 2. What Are the Main Objectives of Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
- 2.1. Maintaining Test Integrity
- 2.2. Ensuring Ease of Use
- 2.3. Supporting Efficient Healthcare Delivery
- 3. What Are the Key Materials Used in Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
- 3.1. Plastics
- 3.2. Glass
- 3.3. Aluminum
- 3.4. Specialty Materials
- 4. What Are the Design Considerations for Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
- 4.1. Usability
- 4.2. Safety
- 4.3. Regulatory Compliance
- 4.4. Sustainability
- 5. What Are the Challenges in Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
- 5.1. Maintaining Temperature Control
- 5.2. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
- 5.3. Balancing Cost-Effectiveness with Performance
- 6. What Are the Future Trends in Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
- 6.1. Smart Packaging
- 6.2. Sustainable Materials
- 6.3. Personalized Packaging Solutions
- 7. How Does Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging Improve Healthcare Outcomes?
- 7.1. Ensuring Test Accuracy
- 7.2. Improving Ease of Use
- 7.3. Supporting Efficient Healthcare Delivery
- 7.4. Faster Diagnosis
- 7.5. Better Patient Management
- 7.6. Reduced Healthcare Costs
- 8. What Are Some Innovative Examples of Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
- 8.1. Self-Contained Diagnostic Kits
- 8.2. Temperature-Controlled Packaging with Phase Change Materials
- 8.3. Smart Packaging with Connectivity Features
- 8.4. Microfluidic Devices
- 9. What Regulations Govern Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
- 9.1. FDA Regulations
- 9.2. ISO Standards
- 9.3. IATA Regulations
- 9.4. Other Regulations
- 10. What Are the Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for Information on Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
- 10.1. Comprehensive Information
- 10.2. Expert Analysis
- 10.3. Practical Guidance
- 10.4. Enhanced Decision-Making
- 10.5. Improved Quality and Safety
- 10.6. Staying Informed
- FAQ Section
- What is point of care diagnostics packaging?
- Why is proper packaging important for point of care diagnostics?
- What are the key materials used in point of care diagnostics packaging?
- What are the design considerations for point of care diagnostics packaging?
- What are the challenges in point of care diagnostics packaging?
- What are the future trends in point of care diagnostics packaging?
- How does point of care diagnostics packaging improve healthcare outcomes?
- What are some innovative examples of point of care diagnostics packaging?
- What regulations govern point of care diagnostics packaging?
- What are the benefits of using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for information on point of care diagnostics packaging?
1. What Exactly Is Point Of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
Point of care diagnostics packaging refers to the design and creation of packaging solutions for diagnostic tests performed near or at the site of patient care, ensuring test integrity and ease of use. This packaging is crucial for the storage, transport, and administration of diagnostic tools and reagents outside of traditional laboratory settings. According to a study by Grand View Research, the point-of-care diagnostics market is expected to reach $50.6 billion by 2027, highlighting the growing importance of effective packaging solutions.
1.1. Why Is Proper Packaging Important for Point of Care Diagnostics?
Proper packaging is essential for several reasons:
-
Maintaining Test Integrity: Packaging protects diagnostic kits from environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light, which can compromise test accuracy.
-
Ensuring Ease of Use: Well-designed packaging facilitates quick and easy access to test components, reducing the potential for errors during administration.
-
Supporting Regulatory Compliance: Packaging must meet stringent regulatory requirements to ensure patient safety and test reliability.
-
Facilitating Efficient Logistics: Effective packaging streamlines the storage, transportation, and distribution of diagnostic tests, particularly in remote or resource-limited settings.
1.2. Key Components of Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging
The components include:
-
Primary Packaging: Materials that directly contact the diagnostic reagents or devices, such as vials, cartridges, and pouches.
-
Secondary Packaging: Outer layers that provide additional protection and facilitate handling, such as boxes, trays, and kits.
-
Labels and Instructions: Clear, concise labeling and instructions for use are critical for proper test administration and result interpretation.
-
Temperature Control Elements: Insulated containers, ice packs, or phase change materials (PCMs) to maintain temperature stability during transport and storage.
2. What Are the Main Objectives of Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
The main objectives of point of care diagnostics packaging are to maintain test integrity, ensure ease of use, and support efficient healthcare delivery. These goals are crucial for accurate and reliable diagnostic results at the point of care.
2.1. Maintaining Test Integrity
Test integrity is paramount to ensure accurate results. Effective packaging protects diagnostic kits from environmental factors such as:
-
Temperature Fluctuations: Maintaining a stable temperature is crucial for many diagnostic tests. Packaging often includes insulation and cooling elements to prevent degradation of reagents.
-
Humidity: Moisture can compromise the stability of reagents and test strips. Moisture-resistant materials and desiccants are used to control humidity levels within the packaging.
-
Light Exposure: Some reagents are light-sensitive and can degrade if exposed to ultraviolet or visible light. Opaque or amber-colored packaging materials are used to protect these components.
-
Physical Damage: Packaging must protect against physical damage during shipping and handling. Durable materials and cushioning are used to prevent breakage or leakage.
2.2. Ensuring Ease of Use
Ease of use is essential for healthcare providers, especially in time-sensitive situations. Packaging design should facilitate:
-
Quick Access: Packaging should allow healthcare workers to quickly access the test components without difficulty.
-
Clear Instructions: Instructions for use should be clear, concise, and easy to understand, reducing the risk of errors during test administration.
-
Ergonomic Design: Packaging should be designed to be easily handled and manipulated, even when wearing gloves.
-
Waste Disposal: Packaging should facilitate safe and easy disposal of used test components, minimizing the risk of contamination.
2.3. Supporting Efficient Healthcare Delivery
Efficient healthcare delivery is enhanced by packaging that supports:
-
Streamlined Logistics: Packaging should be designed to optimize storage and transportation, reducing costs and improving supply chain efficiency.
-
Inventory Management: Clear labeling and standardized packaging sizes facilitate inventory management and prevent stockouts.
-
Portability: Compact and lightweight packaging is essential for point-of-care testing in remote or mobile settings.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Packaging must comply with all relevant regulations and standards, ensuring patient safety and test reliability.
3. What Are the Key Materials Used in Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
The materials used are selected based on their ability to protect the contents, ensure ease of use, and meet regulatory requirements. These include plastics, glass, aluminum, and specialty materials like desiccants and temperature control elements.
3.1. Plastics
Plastics are widely used due to their versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Common types of plastics include:
-
Polypropylene (PP): Used for vials, containers, and device housings due to its high chemical resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures.
-
Polyethylene (PE): Used for bags, liners, and flexible packaging due to its flexibility and moisture resistance.
-
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): Used for bottles and rigid containers due to its strength and clarity.
-
Polystyrene (PS): Used for trays and packaging inserts due to its rigidity and insulation properties.
3.2. Glass
Glass is used for vials and ampoules when chemical inertness and impermeability are required. Amber glass is used to protect light-sensitive reagents.
3.3. Aluminum
Aluminum foil and laminates are used for pouches and seals to provide a barrier against moisture, light, and oxygen. Aluminum is also used for temperature-controlled packaging due to its thermal conductivity.
3.4. Specialty Materials
Specialty materials enhance the functionality of the packaging:
-
Desiccants: Silica gel or molecular sieves are used to absorb moisture and maintain low humidity levels inside the packaging.
-
Temperature Control Elements: Insulated containers, gel packs, and phase change materials (PCMs) are used to maintain temperature stability during transport.
-
Labels and Adhesives: Pressure-sensitive labels with strong adhesives are used to ensure clear identification and traceability.
-
Cushioning Materials: Foam, bubble wrap, and corrugated cardboard are used to protect fragile components from physical damage.
4. What Are the Design Considerations for Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
Design considerations for point of care diagnostics packaging include usability, safety, regulatory compliance, and sustainability. These factors ensure that the packaging is effective, safe, and environmentally responsible.
4.1. Usability
Usability is a critical factor to ensure that healthcare providers can easily and efficiently use the diagnostic tests. Considerations include:
-
Easy Opening and Access: Packaging should be easy to open, even when wearing gloves. Perforations, tear strips, and peelable seals can facilitate quick access to the contents.
-
Clear Labeling: Labels should be clear, concise, and easy to read. They should include essential information such as the product name, lot number, expiration date, storage conditions, and instructions for use.
-
Ergonomic Design: Packaging should be designed to be easily handled and manipulated. Features such as finger grips, rounded edges, and lightweight materials can improve ergonomics.
-
Intuitive Instructions: Instructions for use should be clear, step-by-step, and visually appealing. Diagrams and illustrations can help to clarify complex procedures.
4.2. Safety
Safety is paramount to protect healthcare providers and patients from potential hazards. Considerations include:
-
Tamper Evidence: Packaging should include tamper-evident features to ensure that the contents have not been compromised. Tamper-evident seals, labels, and closures can provide visual indication of tampering.
-
Child Resistance: If the diagnostic test is intended for home use, the packaging should be child-resistant to prevent accidental ingestion or misuse.
-
Leak Prevention: Packaging should be designed to prevent leakage of reagents or samples, which can pose a contamination risk.
-
Safe Disposal: Packaging should facilitate safe disposal of used test components. Features such as puncture-resistant containers and biohazard labels can help to minimize the risk of contamination.
4.3. Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is essential to ensure that the packaging meets all relevant standards and requirements. Considerations include:
-
FDA Regulations: In the United States, diagnostic tests are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Packaging must comply with FDA regulations for labeling, materials, and manufacturing processes.
-
ISO Standards: International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards provide guidelines for the design, development, and manufacturing of medical devices and packaging. Compliance with ISO standards can help to ensure product quality and safety.
-
Transportation Regulations: If the diagnostic test is to be transported, the packaging must comply with transportation regulations such as those issued by the International Air Transport Association (IATA) or the Department of Transportation (DOT).
-
Environmental Regulations: Packaging should comply with environmental regulations for waste disposal and recycling.
4.4. Sustainability
Sustainability is an increasingly important consideration for packaging design. Strategies to improve sustainability include:
-
Material Reduction: Minimizing the amount of material used in the packaging can reduce waste and lower costs.
-
Recyclable Materials: Using recyclable materials such as paperboard, aluminum, and certain plastics can help to reduce the environmental impact of the packaging.
-
Biodegradable Materials: Using biodegradable materials such as compostable plastics or plant-based materials can provide an alternative to traditional packaging materials.
-
Reusable Packaging: Designing packaging that can be reused can reduce waste and lower costs.
5. What Are the Challenges in Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
The challenges include maintaining temperature control, ensuring regulatory compliance, and balancing cost-effectiveness with performance. Addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions and careful consideration of material selection, design, and manufacturing processes.
5.1. Maintaining Temperature Control
Maintaining temperature control is a significant challenge, particularly for diagnostic tests that require specific storage conditions. Temperature fluctuations can compromise the accuracy and reliability of the tests. Strategies to address this challenge include:
-
Insulated Packaging: Using insulated containers with materials such as expanded polystyrene (EPS) or polyurethane (PU) can help to maintain a stable temperature inside the packaging.
-
Phase Change Materials (PCMs): PCMs are substances that absorb or release heat during phase transitions (e.g., melting or freezing). They can be used to maintain a constant temperature inside the packaging for extended periods.
-
Temperature Monitoring: Incorporating temperature monitoring devices such as data loggers or temperature indicators can provide real-time information about the temperature inside the packaging.
-
Cold Chain Logistics: Implementing a cold chain logistics system can help to ensure that the diagnostic tests are stored and transported at the correct temperature throughout the supply chain.
5.2. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring regulatory compliance can be complex and time-consuming, particularly for diagnostic tests that are sold in multiple countries. Each country may have its own regulations and standards for packaging and labeling. Strategies to address this challenge include:
-
Staying Informed: Keeping up-to-date with the latest regulations and standards can help to ensure that the packaging meets all requirements.
-
Working with Experts: Consulting with regulatory experts can provide valuable guidance and support.
-
Implementing a Quality Management System: Implementing a quality management system such as ISO 13485 can help to ensure that the packaging is consistently manufactured to a high standard.
-
Conducting Thorough Testing: Conducting thorough testing of the packaging can help to identify any potential issues before the diagnostic test is launched on the market.
5.3. Balancing Cost-Effectiveness with Performance
Balancing cost-effectiveness with performance can be a difficult trade-off. While it is important to minimize costs, it is also essential to ensure that the packaging provides adequate protection and functionality. Strategies to address this challenge include:
-
Material Selection: Selecting the right materials can help to minimize costs without compromising performance. For example, using a thinner gauge of plastic or a less expensive cushioning material can reduce costs.
-
Design Optimization: Optimizing the design of the packaging can help to reduce material usage and improve efficiency. For example, using a smaller box or a more compact design can reduce shipping costs.
-
Manufacturing Efficiency: Improving manufacturing efficiency can help to reduce costs. For example, automating certain processes or streamlining the supply chain can lower production costs.
-
Value Engineering: Conducting a value engineering analysis can help to identify areas where costs can be reduced without compromising performance.
6. What Are the Future Trends in Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
Future trends in point of care diagnostics packaging include smart packaging, sustainable materials, and personalized packaging solutions. These innovations aim to enhance usability, safety, and environmental responsibility.
6.1. Smart Packaging
Smart packaging incorporates technology to enhance functionality and provide additional information. Trends include:
-
Temperature Monitoring: Sensors that track and record temperature data during transit, alerting users to potential issues.
-
Connectivity: Integration with smartphones or other devices to provide real-time information about test status, expiration dates, and usage instructions.
-
Authentication: Anti-counterfeiting measures such as QR codes or RFID tags to verify product authenticity.
6.2. Sustainable Materials
The demand for sustainable packaging is growing, driving the adoption of eco-friendly materials. Trends include:
-
Biodegradable Plastics: Plastics derived from renewable resources that can decompose naturally.
-
Recycled Content: Packaging made from recycled materials to reduce waste and conserve resources.
-
Plant-Based Materials: Alternatives to traditional plastics made from materials like cornstarch, sugarcane, or bamboo.
6.3. Personalized Packaging Solutions
Customized packaging solutions tailored to specific diagnostic tests and user needs. Trends include:
-
Modular Design: Packaging systems that can be easily adapted to different test formats and volumes.
-
User-Centric Design: Packaging designed with input from healthcare providers and patients to optimize usability and convenience.
-
Kitting Solutions: Pre-packaged kits that include all necessary components for a specific diagnostic test, simplifying inventory management and reducing the risk of errors.
7. How Does Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging Improve Healthcare Outcomes?
Point of care diagnostics packaging enhances healthcare outcomes by ensuring test accuracy, improving ease of use, and supporting efficient healthcare delivery. These factors contribute to faster diagnosis, better patient management, and reduced healthcare costs.
7.1. Ensuring Test Accuracy
Packaging plays a critical role in maintaining the integrity of diagnostic tests, ensuring accurate results. Effective packaging protects diagnostic kits from environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light, which can compromise test accuracy. This is particularly important for point-of-care tests, which are often used in non-laboratory settings where environmental conditions may not be as tightly controlled.
7.2. Improving Ease of Use
Well-designed packaging can improve ease of use for healthcare providers, reducing the potential for errors during test administration. Packaging that is easy to open, handle, and dispose of can save time and effort, allowing healthcare providers to focus on patient care. Clear labeling and instructions for use are also essential for proper test administration and result interpretation.
7.3. Supporting Efficient Healthcare Delivery
Packaging can support efficient healthcare delivery by streamlining the storage, transportation, and distribution of diagnostic tests. Effective packaging can reduce costs, improve supply chain efficiency, and ensure that diagnostic tests are available when and where they are needed. This is particularly important in remote or resource-limited settings where access to healthcare services may be limited.
7.4. Faster Diagnosis
By ensuring test accuracy and improving ease of use, point of care diagnostics packaging can contribute to faster diagnosis. Faster diagnosis can lead to earlier treatment, better patient outcomes, and reduced healthcare costs.
7.5. Better Patient Management
Point of care diagnostics packaging can also support better patient management by providing healthcare providers with the tools they need to make informed decisions about patient care. Accurate and reliable diagnostic tests can help healthcare providers to identify patients who are at risk for certain diseases, monitor the effectiveness of treatments, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
7.6. Reduced Healthcare Costs
By improving healthcare outcomes and reducing the need for expensive laboratory testing, point of care diagnostics packaging can help to reduce healthcare costs. This is particularly important in an era of rising healthcare costs and increasing pressure to deliver more efficient and cost-effective care.
8. What Are Some Innovative Examples of Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
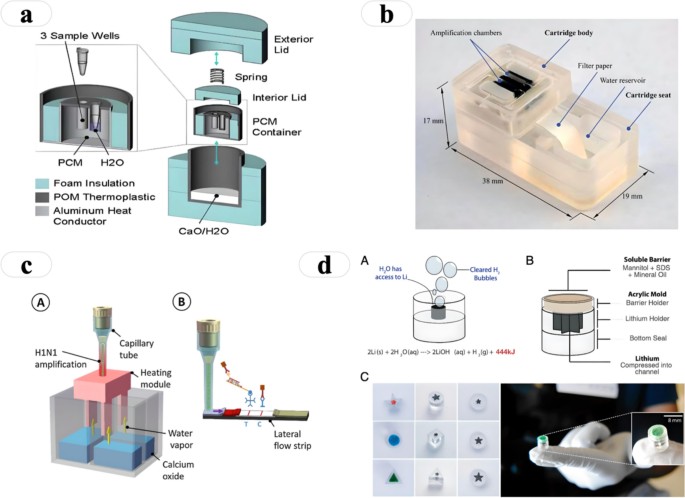
Innovative examples of point of care diagnostics packaging include self-contained diagnostic kits, temperature-controlled packaging with phase change materials, and smart packaging with connectivity features. These solutions demonstrate the potential of packaging to enhance the performance and usability of point-of-care tests.
8.1. Self-Contained Diagnostic Kits
Self-contained diagnostic kits include all necessary components for a specific diagnostic test in a single, easy-to-use package. These kits often include pre-measured reagents, disposable sampling devices, and integrated waste disposal features. Examples include:
-
Rapid Strep Test Kits: These kits contain all the materials needed to perform a rapid strep test, including a throat swab, reagent solutions, and a test strip.
-
HIV Self-Test Kits: These kits allow individuals to test themselves for HIV in the privacy of their own homes. They include a finger-prick device, a test strip, and instructions for use.
8.2. Temperature-Controlled Packaging with Phase Change Materials
Temperature-controlled packaging with phase change materials (PCMs) is used to maintain a stable temperature inside the packaging for extended periods. PCMs are substances that absorb or release heat during phase transitions (e.g., melting or freezing). Examples include:
-
Vaccine Transport Containers: These containers use PCMs to maintain the temperature of vaccines during transport, ensuring that they remain effective.
-
Diagnostic Test Kits: These kits use PCMs to maintain the temperature of reagents during storage and transport, ensuring that they remain stable.
8.3. Smart Packaging with Connectivity Features
Smart packaging with connectivity features incorporates technology to enhance functionality and provide additional information. Examples include:
-
Temperature Monitoring Sensors: These sensors track and record temperature data during transit, alerting users to potential issues.
-
Connectivity to Smartphones: Some packaging can connect to smartphones via Bluetooth or NFC, allowing users to access information about the product, such as expiration dates, usage instructions, and lot numbers.
8.4. Microfluidic Devices
Microfluidic devices integrate diagnostic tests into small, self-contained packages. These devices can perform complex assays with minimal sample volumes and provide rapid results. Examples include:
-
Lab-on-a-Chip Devices: These devices integrate multiple laboratory functions onto a single chip, allowing for rapid and automated diagnostic testing.
-
Point-of-Care Analyzers: These devices can perform a variety of diagnostic tests at the point of care, providing healthcare providers with rapid results.
9. What Regulations Govern Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
Regulations governing point of care diagnostics packaging include those from the FDA, ISO, and IATA. Compliance with these regulations is essential to ensure patient safety, product integrity, and regulatory approval.
9.1. FDA Regulations
In the United States, diagnostic tests are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The FDA has regulations for labeling, materials, and manufacturing processes. Key FDA regulations include:
-
21 CFR Part 820: This regulation outlines the requirements for quality system regulation, which includes requirements for packaging and labeling.
-
21 CFR Part 606: This regulation outlines the requirements for current good manufacturing practice for blood and blood components, which includes requirements for packaging and labeling.
9.2. ISO Standards
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards provide guidelines for the design, development, and manufacturing of medical devices and packaging. Key ISO standards include:
-
ISO 13485: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system for medical devices, which includes requirements for packaging and labeling.
-
ISO 11607: This standard outlines the requirements for packaging for terminally sterilized medical devices, which includes requirements for materials, design, and testing.
9.3. IATA Regulations
If the diagnostic test is to be transported, the packaging must comply with transportation regulations such as those issued by the International Air Transport Association (IATA). Key IATA regulations include:
- IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations: These regulations outline the requirements for the transport of dangerous goods, which includes diagnostic tests that contain hazardous materials.
9.4. Other Regulations
Other regulations that may apply to point of care diagnostics packaging include:
-
REACH Regulation: This regulation applies to the registration, evaluation, authorization, and restriction of chemicals in the European Union.
-
RoHS Directive: This directive restricts the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment in the European Union.
10. What Are the Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for Information on Point of Care Diagnostics Packaging?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides detailed information, expert analysis, and practical guidance on point of care diagnostics packaging. Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN helps professionals stay informed, make better decisions, and improve the quality and safety of diagnostic tests.
10.1. Comprehensive Information
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wide range of resources, including articles, guides, and case studies, covering all aspects of point of care diagnostics packaging. This comprehensive information helps professionals stay informed about the latest trends, technologies, and best practices.
10.2. Expert Analysis
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides expert analysis and insights from industry leaders, regulatory experts, and packaging professionals. This analysis helps professionals understand the complex challenges and opportunities in point of care diagnostics packaging and make informed decisions.
10.3. Practical Guidance
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN offers practical guidance and tools for designing, developing, and manufacturing point of care diagnostics packaging. This guidance helps professionals improve the quality, safety, and cost-effectiveness of their packaging solutions.
10.4. Enhanced Decision-Making
By providing comprehensive information, expert analysis, and practical guidance, CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN empowers professionals to make better decisions about point of care diagnostics packaging. This can lead to improved product quality, reduced costs, and enhanced patient safety.
10.5. Improved Quality and Safety
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN helps professionals improve the quality and safety of diagnostic tests by providing information and guidance on packaging materials, design, and manufacturing processes. This can lead to more accurate and reliable diagnostic results and better patient outcomes.
10.6. Staying Informed
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN keeps professionals up-to-date with the latest trends, technologies, and regulations in point of care diagnostics packaging. This helps professionals stay ahead of the curve and maintain a competitive advantage.
Are you looking for detailed information about point of care diagnostics packaging? Do you need help comparing different packaging options or finding a reliable supplier? Contact CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today! Our experts can provide you with the information and support you need to make informed decisions.
Contact us:
- Address: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
We are here to help you find the best point of care diagnostics packaging solutions for your needs.
FAQ Section
What is point of care diagnostics packaging?
Point of care diagnostics packaging involves designing and creating packaging solutions for diagnostic tests performed near or at the site of patient care, ensuring test integrity and ease of use.
Why is proper packaging important for point of care diagnostics?
Proper packaging is essential for maintaining test integrity, ensuring ease of use, supporting regulatory compliance, and facilitating efficient logistics.
What are the key materials used in point of care diagnostics packaging?
Key materials include plastics (PP, PE, PET, PS), glass, aluminum, and specialty materials like desiccants and temperature control elements.
What are the design considerations for point of care diagnostics packaging?
Design considerations include usability, safety, regulatory compliance, and sustainability.
What are the challenges in point of care diagnostics packaging?
Challenges include maintaining temperature control, ensuring regulatory compliance, and balancing cost-effectiveness with performance.
What are the future trends in point of care diagnostics packaging?
Future trends include smart packaging, sustainable materials, and personalized packaging solutions.
How does point of care diagnostics packaging improve healthcare outcomes?
It enhances healthcare outcomes by ensuring test accuracy, improving ease of use, and supporting efficient healthcare delivery.
What are some innovative examples of point of care diagnostics packaging?
Innovative examples include self-contained diagnostic kits, temperature-controlled packaging with phase change materials, and smart packaging with connectivity features.
What regulations govern point of care diagnostics packaging?
Regulations include those from the FDA, ISO, and IATA.
What are the benefits of using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for information on point of care diagnostics packaging?
CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive information, expert analysis, and practical guidance on point of care diagnostics packaging, helping professionals stay informed and make better decisions.