At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of staying informed about your vehicle’s health. Learning how to use an OBDII scanner empowers you to diagnose car problems, interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and perform basic maintenance, saving you time and money. This guide will cover everything from selecting the right scan tool to understanding live data, ensuring you can confidently tackle automotive diagnostics. We’ll also explore advanced diagnostic procedures and repair solutions, providing a complete guide to automotive troubleshooting.
Contents
- 1. What is an OBDII Scanner and Why Do You Need One?
- 2. Understanding OBDII and Its Evolution
- 2.1. A Brief History of On-Board Diagnostics
- 2.2. Key Features of OBDII
- 2.3. Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Impact
- 3. Identifying Your Vehicle’s OBDII Port
- 4. Types of OBDII Scanners Available
- 4.1. Basic OBDII Code Readers
- 4.2. Enhanced OBDII Scanners
- 4.3. Professional-Grade Diagnostic Tools
- 4.4. Smartphone-Based OBDII Adapters
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use an OBDII Scanner
- 5.1. Preparing for the Scan
- 5.2. Connecting the Scanner
- 5.3. Powering On and Navigating the Scanner
- 5.4. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 5.5. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 5.6. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 5.7. Reading Live Data
- 6. Interpreting Common OBDII Codes
- 6.1. P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 6.2. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 6.3. P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- 6.4. P0113: Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input
- 6.5. P0011: “A” Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1)
- 7. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures with an OBDII Scanner
- 7.1. Using Bidirectional Controls
- 7.2. Accessing Manufacturer-Specific Codes
- 7.3. Performing System Tests
- 8. Tips for Accurate Diagnosis and Troubleshooting
- 9. Maintaining and Updating Your OBDII Scanner
- 10. The Future of OBDII Technology
- 10.1. Enhanced Connectivity
- 10.2. Advanced Data Analytics
- 10.3. Integration with Cloud-Based Services
- 11. Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for Your Automotive Needs
- 11.1. Comprehensive Information and Resources
- 11.2. Expert Advice and Support
- 11.3. Wide Range of Products and Services
- 11.4. Community Forum and Support
- 12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 12.1. What type of OBDII scanner is best for beginners?
- 12.2. Can an OBDII scanner diagnose ABS and SRS issues?
- 12.3. How often should I scan my car for trouble codes?
- 12.4. Is it safe to clear OBDII codes without fixing the underlying problem?
- 12.5. Can I use an OBDII scanner on any car?
- 12.6. What does it mean when an OBDII scanner shows a “pending” code?
- 12.7. How accurate are OBDII scanners?
- 12.8. What is live data, and how can it help with diagnostics?
- 12.9. Do I need to update my OBDII scanner?
- 12.10. Where can I find more information about specific OBDII codes?
1. What is an OBDII Scanner and Why Do You Need One?
An OBDII scanner, or On-Board Diagnostics II scanner, is a tool that connects to your vehicle’s computer to read diagnostic information. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Transportation Sustainability Research Center in 2020, OBDII scanners can help vehicle owners identify problems early, potentially reducing repair costs by up to 40%. These scanners access data from various sensors and systems, providing insights into your car’s performance and health.
- Early Problem Detection: Identifying issues before they become major problems.
- Cost Savings: Reducing expensive trips to the mechanic for simple diagnostics.
- Informed Decisions: Understanding the nature of repairs needed before seeking professional help.
- Performance Monitoring: Keeping track of your vehicle’s overall health and efficiency.
2. Understanding OBDII and Its Evolution
OBDII (On-Board Diagnostics II) is the second generation of on-board diagnostic systems implemented in vehicles. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), OBDII became mandatory for all cars sold in the United States in 1996. This system monitors the performance of key engine components, emissions systems, and other control units, providing standardized diagnostic information.
2.1. A Brief History of On-Board Diagnostics
The evolution of on-board diagnostics can be traced through several key stages:
- OBD-I: The first generation, introduced in the 1980s, provided basic diagnostic information but lacked standardization.
- OBD-1.5: An interim step used by some manufacturers to prepare for OBDII, offering some advanced features but still not fully standardized.
- OBD-II: Mandated in 1996 in the US, it offers standardized diagnostic codes, enhanced monitoring capabilities, and improved data access.
2.2. Key Features of OBDII
OBDII offers several key features that make it an essential tool for vehicle diagnostics:
- Standardized Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): A common set of codes that allow any mechanic or vehicle owner to understand the nature of a problem.
- Enhanced Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of emissions-related components and systems.
- Data Access: Access to a wide range of vehicle parameters, including sensor readings and system status.
- Compatibility: Universal compatibility with all OBDII-compliant vehicles, regardless of make or model.
2.3. Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Impact
OBDII compliance is crucial for meeting environmental regulations. According to the EPA, OBDII systems help ensure that vehicles meet emissions standards throughout their lifespan. By monitoring emissions-related components, OBDII systems can detect malfunctions that lead to increased pollution, prompting timely repairs and reducing environmental impact.
3. Identifying Your Vehicle’s OBDII Port
The OBDII port is a standardized 16-pin connector found in all OBDII-compliant vehicles. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the location of the port is typically within three feet of the steering wheel and does not require any tools to access.
- Common Locations: Under the dashboard, near the steering column, or in the center console.
- Port Identification: A 16-pin trapezoidal connector.
- Accessibility: Usually accessible without tools, though sometimes hidden behind a small panel.
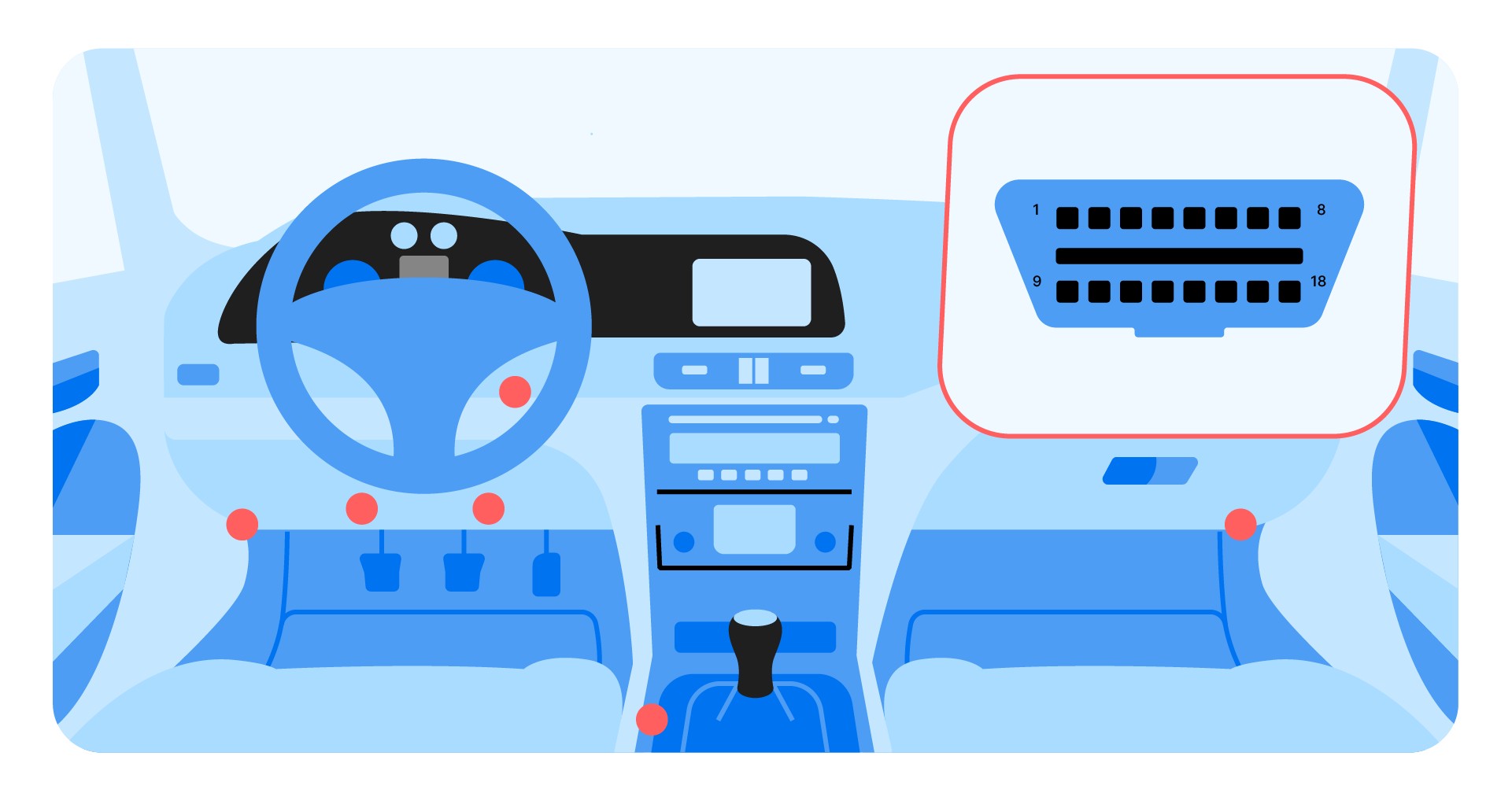 OBD2 scanner port location
OBD2 scanner port location
4. Types of OBDII Scanners Available
Choosing the right OBDII scanner depends on your needs and budget. According to a 2022 survey by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), the types of scanners range from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools.
4.1. Basic OBDII Code Readers
- Functionality: Reads and clears diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Pros: Affordable, easy to use, and suitable for basic diagnostics.
- Cons: Limited functionality, lacks advanced features like live data and bidirectional controls.
- Typical Users: Car owners who want to diagnose simple issues and clear error codes.
4.2. Enhanced OBDII Scanners
- Functionality: Reads and clears DTCs, displays live data, and offers some enhanced features like ABS and SRS diagnostics.
- Pros: More versatile than basic code readers, provides valuable real-time data, and supports additional systems.
- Cons: More expensive than basic models, may require some technical knowledge to use effectively.
- Typical Users: DIY enthusiasts and intermediate-level mechanics.
4.3. Professional-Grade Diagnostic Tools
- Functionality: Comprehensive diagnostics, including advanced functions like bidirectional controls, module programming, and access to manufacturer-specific codes.
- Pros: Extensive capabilities, allows for in-depth troubleshooting and repairs, and supports a wide range of vehicles.
- Cons: Expensive, requires significant technical expertise, and may have a steep learning curve.
- Typical Users: Professional mechanics and automotive technicians.
4.4. Smartphone-Based OBDII Adapters
- Functionality: Connects to your smartphone via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, using a dedicated app to read and clear DTCs, display live data, and perform other diagnostic functions.
- Pros: Convenient, portable, and often more affordable than dedicated scanners.
- Cons: Relies on a smartphone or tablet, may require a paid app for full functionality, and can be less reliable than dedicated scanners.
- Typical Users: Car owners who want a portable and affordable diagnostic solution.
5. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use an OBDII Scanner
Using an OBDII scanner involves a few straightforward steps. According to a technical guide by SAE International, the process ensures accurate diagnostics and data interpretation.
5.1. Preparing for the Scan
Before starting, ensure your vehicle is in a safe location and the ignition is turned off. Gather any relevant information about your vehicle, such as the make, model, and year.
- Safety First: Park in a safe area away from traffic.
- Vehicle Information: Have the make, model, and year of your car ready.
- Scanner Preparation: Ensure your scanner is charged or has fresh batteries.
5.2. Connecting the Scanner
Locate the OBDII port in your vehicle. Insert the scanner’s connector into the port, ensuring a secure fit.
- Port Location: Usually under the dashboard or in the center console.
- Secure Connection: Ensure the connector is fully inserted into the port.
- Power On: Some scanners will power on automatically; others may require a manual switch.
5.3. Powering On and Navigating the Scanner
Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine. Power on the scanner and follow the on-screen prompts to select your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Ignition Position: Turn the key to the “ON” position.
- Vehicle Selection: Choose the correct make, model, and year.
- Menu Navigation: Use the scanner’s buttons to navigate the menus.
5.4. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Select the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option from the scanner’s menu. The scanner will display any stored DTCs, along with a brief description of each code.
- Code Retrieval: Select the appropriate option to read codes.
- Code Interpretation: Note down the codes and their descriptions.
- Troubleshooting: Research the codes to understand the potential issues.
5.5. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DTCs are standardized codes that provide information about potential issues with your vehicle. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), understanding these codes is essential for effective troubleshooting.
- Code Structure: DTCs consist of five characters: a letter followed by four numbers.
- First Character: Indicates the system:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (lighting, power windows)
- C: Chassis (ABS, suspension)
- U: Network (communication systems)
- Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- Remaining Characters: Provide specific information about the fault.
5.6. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
After addressing the underlying issue, you can clear the DTCs using the scanner. Select the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option from the menu.
- Issue Resolution: Ensure the problem has been resolved before clearing codes.
- Code Clearing: Select the appropriate option to clear the codes.
- Verification: Confirm that the codes have been cleared and do not reappear.
5.7. Reading Live Data
Live data provides real-time information about your vehicle’s performance. Select the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” option to view parameters such as engine speed, temperature, and sensor readings.
- Data Selection: Choose the parameters you want to monitor.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Observe the data while the engine is running.
- Performance Analysis: Analyze the data to identify any anomalies or issues.
 OBD2 scanner
OBD2 scanner
6. Interpreting Common OBDII Codes
Understanding common OBDII codes can help you quickly identify and address common vehicle problems. According to a report by AAA, the most common DTCs relate to issues with the oxygen sensors, catalytic converter, and mass airflow sensor.
6.1. P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- Description: Indicates that the air-fuel mixture is too lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel.
- Possible Causes: Vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, clogged fuel filter, or failing fuel pump.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Check for vacuum leaks, test the oxygen sensor, replace the fuel filter, and inspect the fuel pump.
6.2. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- Description: Indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently.
- Possible Causes: Failing catalytic converter, faulty oxygen sensors, exhaust leaks, or engine issues.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Check for exhaust leaks, test the oxygen sensors, and inspect the catalytic converter.
6.3. P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- Description: Indicates that one or more cylinders are misfiring randomly.
- Possible Causes: Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, or low compression.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Check the spark plugs, test the ignition coils, inspect the fuel injectors, and check for vacuum leaks.
6.4. P0113: Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input
- Description: Indicates that the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is reporting a high temperature reading.
- Possible Causes: Faulty IAT sensor, wiring issues, or a poor connection.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Check the IAT sensor, inspect the wiring, and ensure a good connection.
6.5. P0011: “A” Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1)
- Description: Indicates that the camshaft position is over-advanced, affecting engine timing.
- Possible Causes: Faulty camshaft position sensor, oil flow issues, or timing chain problems.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Check the camshaft position sensor, inspect the oil flow, and verify the timing chain.
7. Advanced Diagnostic Procedures with an OBDII Scanner
For more complex issues, advanced diagnostic procedures may be necessary. According to a training manual by Delphi Technologies, these procedures often involve using bidirectional controls and accessing manufacturer-specific codes.
7.1. Using Bidirectional Controls
Bidirectional controls allow you to command the vehicle’s computer to perform specific actions, such as activating solenoids or running tests.
- Activating Components: Test individual components like fuel injectors or solenoids.
- Performing Tests: Run diagnostic tests on systems like the ABS or transmission.
- Verifying Repairs: Confirm that repairs have been successful by monitoring the system’s response.
7.2. Accessing Manufacturer-Specific Codes
Manufacturer-specific codes provide more detailed information about issues that are unique to a particular make or model.
- Enhanced Diagnostics: Gain access to codes not covered by the generic OBDII standard.
- Detailed Information: Obtain specific details about the fault and its potential causes.
- Targeted Repairs: Focus troubleshooting efforts on the most likely causes of the problem.
7.3. Performing System Tests
System tests allow you to evaluate the performance of specific systems, such as the ABS or SRS.
- ABS Test: Check the functionality of the anti-lock braking system.
- SRS Test: Evaluate the performance of the airbag system.
- Transmission Test: Assess the operation of the automatic transmission.
8. Tips for Accurate Diagnosis and Troubleshooting
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective troubleshooting. According to a study by the American Society for Quality (ASQ), following a systematic approach can improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce repair times.
- Verify the Code: Confirm that the DTC is valid and not a false alarm.
- Gather Information: Collect as much information as possible about the problem, including when it occurs and under what conditions.
- Consult Resources: Use online forums, repair manuals, and technical service bulletins to research the code and its potential causes.
- Follow a Process: Develop a systematic approach to troubleshooting, starting with the most likely causes and working through the possible solutions.
- Test Components: Use a multimeter or other diagnostic tools to test individual components and verify their functionality.
- Document Findings: Keep detailed records of your troubleshooting steps, including the codes, symptoms, and test results.
9. Maintaining and Updating Your OBDII Scanner
Proper maintenance and updates can ensure your OBDII scanner remains accurate and reliable. According to a guide by Fluke Corporation, regular maintenance can prolong the life of your diagnostic tools.
- Keep It Clean: Clean the scanner regularly with a soft, dry cloth.
- Store It Properly: Store the scanner in a cool, dry place away from moisture and extreme temperatures.
- Update Software: Regularly update the scanner’s software to ensure compatibility with the latest vehicles and access to the most current diagnostic information.
- Check Cables: Inspect the cables for any signs of damage and replace them if necessary.
- Calibrate Sensors: Calibrate the scanner’s sensors periodically to ensure accurate readings.
10. The Future of OBDII Technology
OBDII technology continues to evolve, with new features and capabilities being introduced regularly. According to a report by MarketWatch, the future of OBDII includes enhanced connectivity, advanced data analytics, and integration with cloud-based services.
10.1. Enhanced Connectivity
Future OBDII scanners will offer enhanced connectivity options, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular connectivity.
- Remote Diagnostics: Perform diagnostics remotely using a smartphone or computer.
- Cloud Integration: Store diagnostic data in the cloud for easy access and analysis.
- Real-Time Updates: Receive real-time updates and alerts about potential issues.
10.2. Advanced Data Analytics
Advanced data analytics will allow for more sophisticated diagnostics and troubleshooting.
- Predictive Maintenance: Identify potential issues before they become major problems.
- Performance Optimization: Optimize vehicle performance based on real-time data.
- Fault Prediction: Predict potential faults based on historical data and trends.
10.3. Integration with Cloud-Based Services
Integration with cloud-based services will provide access to a wealth of diagnostic information and support.
- Remote Support: Access remote support from expert technicians.
- Data Sharing: Share diagnostic data with mechanics or other professionals.
- Software Updates: Receive automatic software updates and feature enhancements.
11. Benefits of Using CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN for Your Automotive Needs
At CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the resources and support you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Our website offers a wealth of information about automotive diagnostics, repair solutions, and maintenance tips.
11.1. Comprehensive Information and Resources
We provide detailed guides, articles, and tutorials to help you understand and address common vehicle problems.
11.2. Expert Advice and Support
Our team of experienced mechanics and automotive technicians is available to answer your questions and provide expert advice.
11.3. Wide Range of Products and Services
We offer a wide range of OBDII scanners, diagnostic tools, and repair solutions to meet your needs.
11.4. Community Forum and Support
Join our community forum to connect with other vehicle owners, share your experiences, and get help with your automotive problems.
Modern vehicles rely heavily on their onboard computer systems, making OBDII scanners an indispensable tool for diagnosing and resolving issues. Whether you are a seasoned mechanic or a vehicle owner looking to save money on repairs, understanding how to use an OBDII scanner can significantly enhance your ability to maintain your vehicle.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
12.1. What type of OBDII scanner is best for beginners?
A basic code reader or a smartphone-based adapter is ideal for beginners due to their ease of use and affordability.
12.2. Can an OBDII scanner diagnose ABS and SRS issues?
Enhanced and professional-grade scanners often include ABS and SRS diagnostic capabilities.
12.3. How often should I scan my car for trouble codes?
Scan your car whenever you notice warning lights or performance issues. Regular checks can also help catch minor problems early.
12.4. Is it safe to clear OBDII codes without fixing the underlying problem?
Clearing codes without addressing the issue is not recommended, as the problem will likely return, and you might miss critical warning signs.
12.5. Can I use an OBDII scanner on any car?
OBDII scanners are compatible with all cars and light trucks sold in the United States since 1996.
12.6. What does it mean when an OBDII scanner shows a “pending” code?
A pending code indicates that the system has detected a potential issue, but it has not yet been confirmed. Further driving may be needed to confirm the fault.
12.7. How accurate are OBDII scanners?
OBDII scanners are generally accurate, but the accuracy of the diagnosis depends on the user’s ability to interpret the data and perform further testing.
12.8. What is live data, and how can it help with diagnostics?
Live data provides real-time information about various vehicle parameters, helping to identify anomalies and pinpoint the source of a problem.
12.9. Do I need to update my OBDII scanner?
Regularly updating your scanner ensures compatibility with newer vehicles and access to the latest diagnostic information.
12.10. Where can I find more information about specific OBDII codes?
Online forums, repair manuals, and technical service bulletins are valuable resources for researching OBDII codes.
Learning how to use an OBDII scanner is a valuable skill for any car owner. It allows you to diagnose problems, monitor your vehicle’s performance, and make informed decisions about repairs. With the right tools and knowledge, you can save time and money while keeping your car running smoothly.
Are you struggling to find the right auto parts or tools for your car repairs? Do you need expert advice on selecting the best OBDII scanner for your needs? Contact us at CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN today. Our experienced team can provide detailed information, compare products, and offer recommendations to help you make the best choice for your vehicle.
Contact Information:
- Address: 456 Elm Street, Dallas, TX 75201, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN
Let CAR-TOOL.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in automotive diagnostics and repair solutions. Reach out now and let us assist you with all your automotive needs.